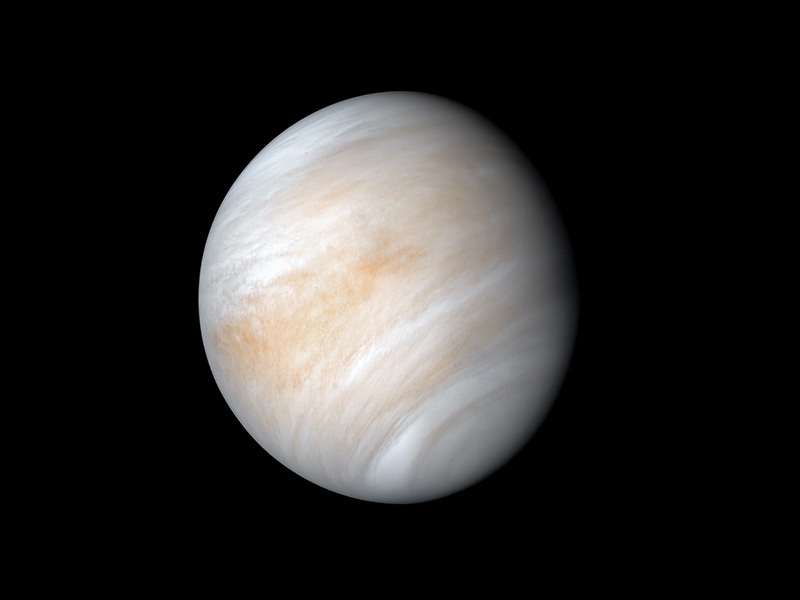
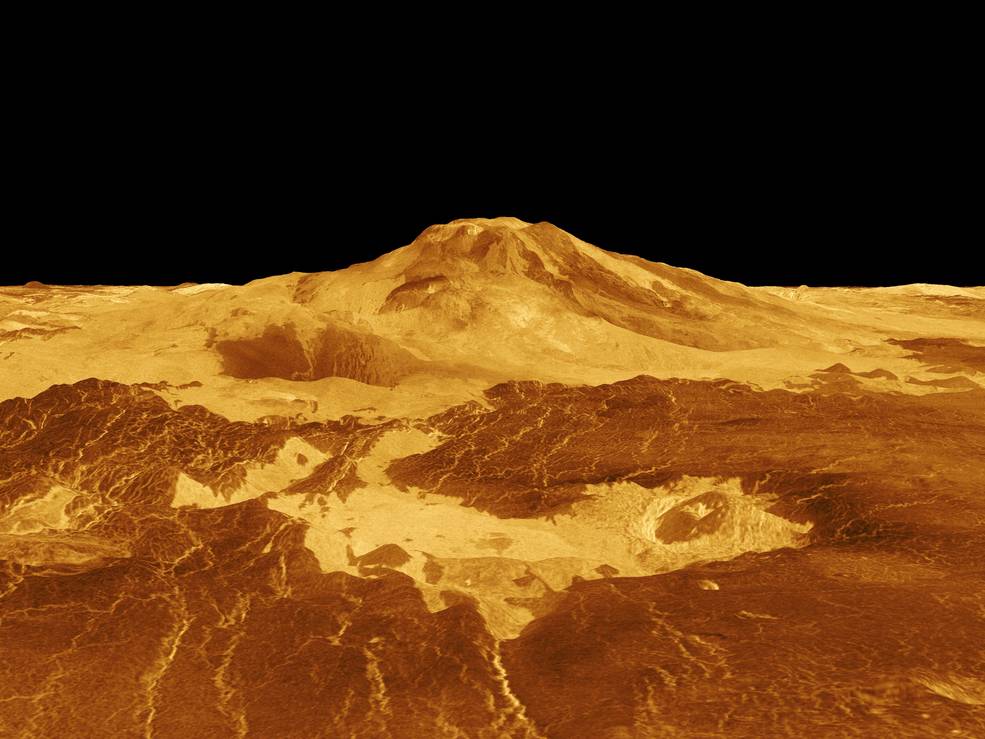
Sending a lander to Venus presents several huge engineering problems. Granted, we’d get a break from the nail-biting entry, descent and landing, since Venus’ atmosphere is so thick, a lander would settle gently to the surface like a stone settles in water — no sky cranes or retrorockets required.
But the rest of the endeavor is fraught with challenges. The average temperature at the surface is 455 degrees C (850 F), hot enough to melt lead. The mix of chemicals that make up the atmosphere, such as sulfuric acid, is corrosive to most metals. And the crushing atmospheric pressure is roughly equivalent to being 1,500 meters (5,000 ft) under water. These extreme environmental conditions are where metals and electronics go to die; therefore, the few Venus lander missions that have made it to the surface — like the Soviet Venera missions — only lasted two hours or less. Any future landers or rovers will need to have nearly super-hero-type characteristics to endure on the surface of Earth’s evil twin.
But there’s one additional challenge that might be close to being solved: creating batteries that can operate long enough in Venus’ hellish conditions to make a lander mission worth the effort.
Continue reading “Can a Venus Lander Survive Longer Than a Few Minutes?”