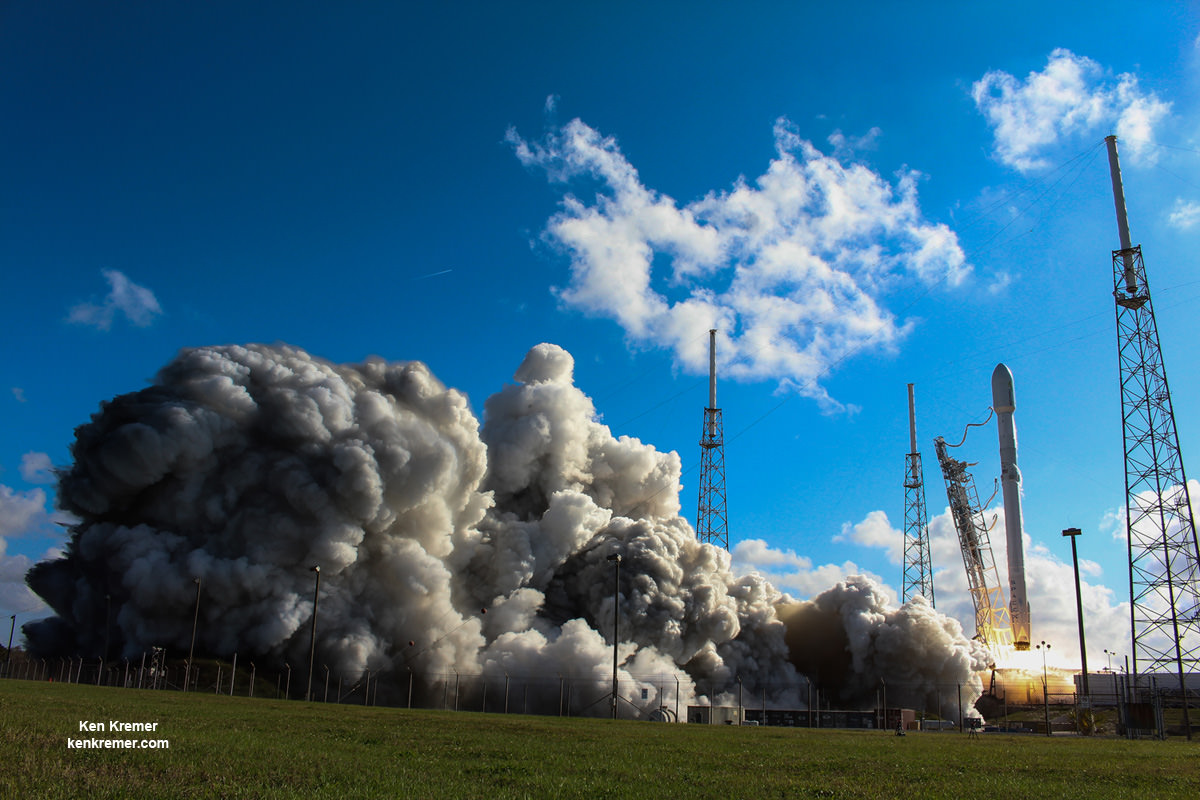
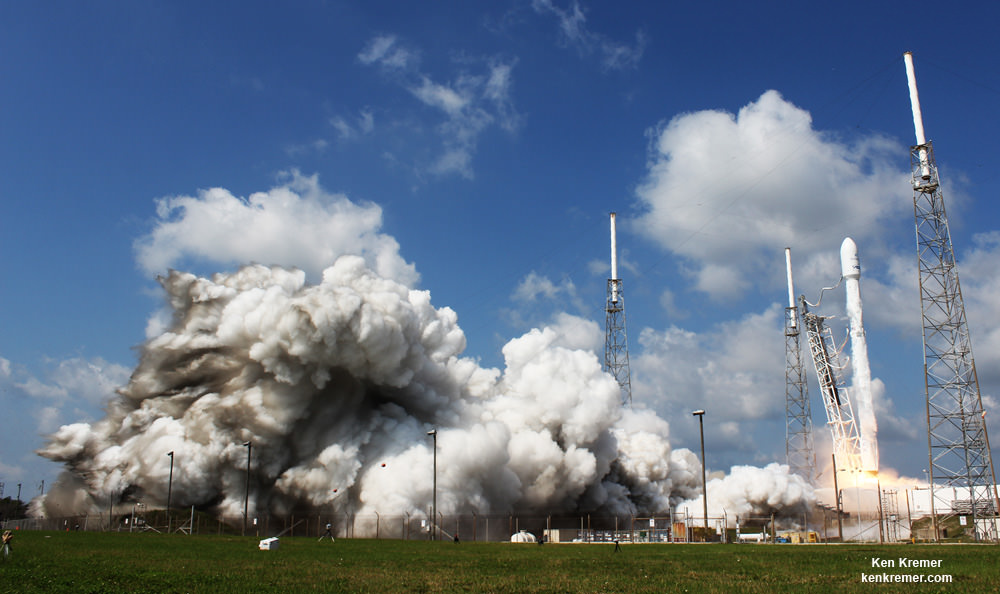
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – The fierce competition for lucrative launch contracts from the U.S. Air Force just got more even intense with the announcement that SpaceX outbid arch rival United Launch Alliance (ULA) to launch an advanced military Global Positioning System (GPS III) navigation satellite to orbit in approx. 2 years.
The U.S. Air Force has announced that SpaceX has won the national security contract to launch a single next generation GPS III satellite to Earth orbit in the first half of 2019. The contract award is valued at $96.5 million.
“SpaceX is proud to have been selected to support this important National Security Space Mission,” Gwynne Shotwell, President & COO, told Universe Today in a statement in response to the GPS III award.
The GPS constellation of navigation satellites is vital to both military and civilian users on a 24/7 basis.
“Space Exploration Technologies Corp., Hawthorne, California, has been awarded a $96,500,490 firm-fixed-price contract for launch services to deliver a GPS III satellite to its intended orbit,” the Air Force announced in a statement.
There could be as many as 15 Air Force launch contracts awarded this year in competitive bidding between ULA and SpaceX.
The upshot is that ULA’s decade long near monopoly on national security launches has now been broken several times in the past year with SpaceX outbidding ULA based on the price of their newer Falcon family of rockets compared to ULA’s long established Atlas and Delta rocket families.
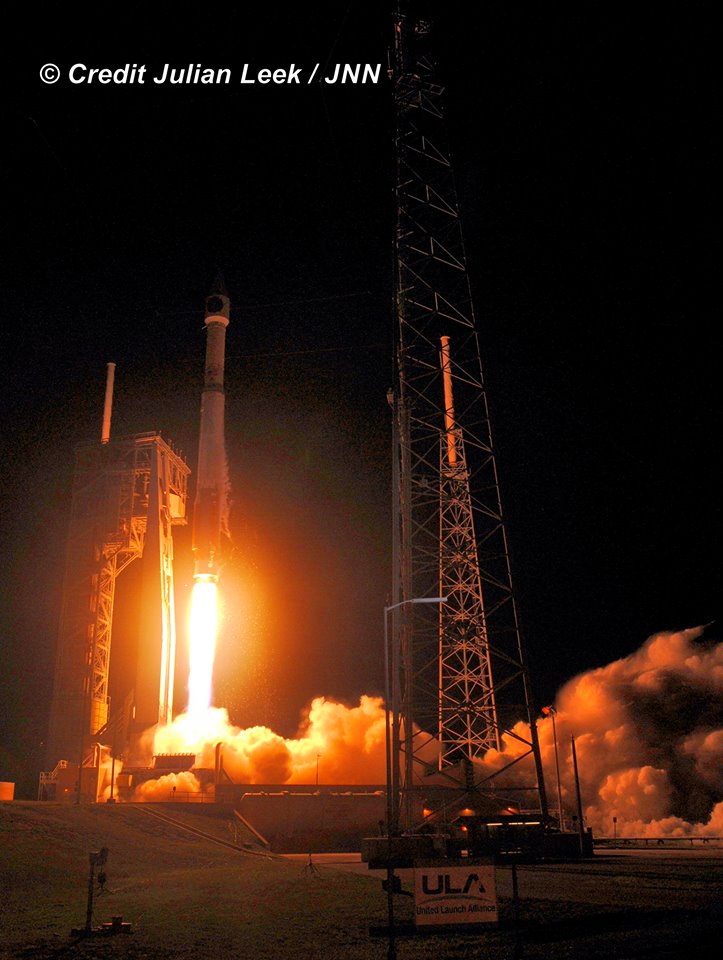
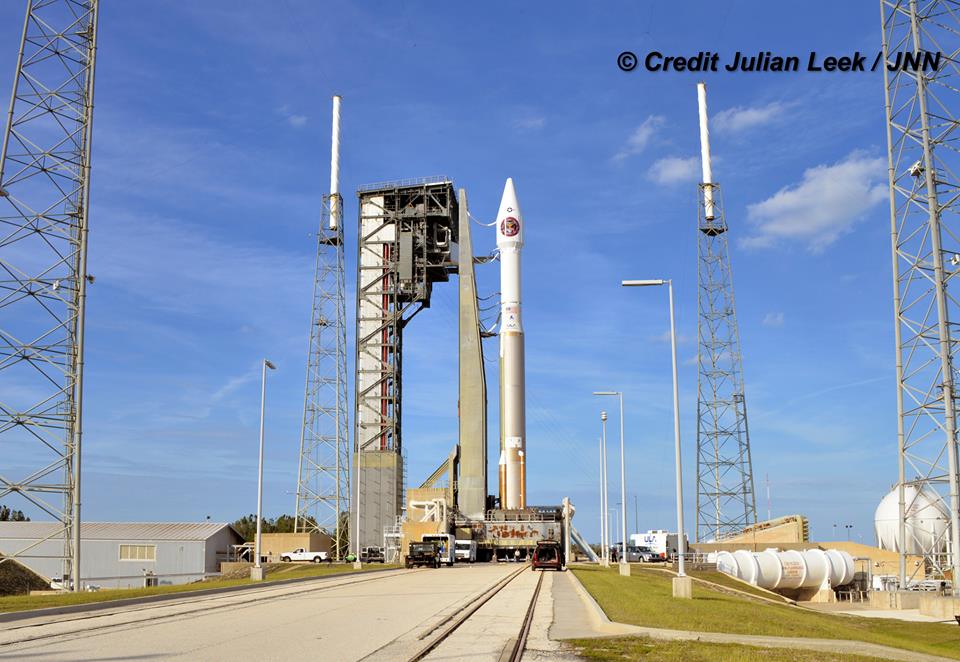
Last year SpaceX won the competition to launch the first GPS-III satellite on a Falcon 9 rocket in 2018 with a bid of $82.7 million after ULA decided not to enter a bid.
“We appreciate the confidence that the U.S. Air Force has placed in our company and we look forward to working together towards the successful launch of another GPS-III mission,” Shotwell elaborated to Universe Today.

ULA did not bid on the first GPS III contract citing the lack of availability of “any Atlas engines available to bid” and other contract factors as the reason for not submitting a bid for the 2018 launch based on the request for proposals (RFP) for the global positioning satellite.
The Atlas V is powered by Russian made RD-180 engines, who’s import for military uses had been temporarily restricted by Congress following the Russian invasion of the Crimea.
The launch price was a deciding factor in the winning bid.
“Each contractor had to prove through their proposal that they could meet the technical, the schedule and the risk criteria,” said Claire Leon, director of the launch enterprise directorate at the Air Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center, during a media briefing.
“SpaceX was able to do that. I wouldn’t say that they were necessarily better. They adequately met our criteria.”
SpaceX has been snatching away numerous launch contracts from ULA other launch providers across the globe with their substantially lower rocket prices. SpaceX has been hiring while other firms including ULA have suffered layoffs.
So in response to competitive pressures from SpaceX, ULA took concrete steps to dramatically cut launch costs and end dependency on the RD-180s when CEO Tory Bruno announced in April 2015 that the company would develop the new all-American made Vulcan rocket.
Vulcan is slated for an inaugural liftoff in 2019.
The Air Force expects SpaceX to achieve a rapid turnaround from winning the bid to actually launching the GPS satellite by April 2019.
“Contractor will provide launch vehicle production, mission integration, launch operations, spaceflight worthiness and mission unique activities for a GPS III mission. Work will be performed at Hawthorne, California; Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida; and McGregor, Texas, and is expected to be complete by April 30, 2019,” said the Air Force.
Only SpaceX and ULA bid on the GPS III satellite launch contract.
“This award is the result of a competitive acquisition with two offers received. Fiscal 2016 space procurement funds in the amount of $96,500,490 are being obligated at the time of award.”
The Air Force opened up military launch contracts to competitive bidding in 2015 after certifying SpaceX as a qualified bidder to launch the nation’s most critical and highly valuable national security satellites on their Falcon 9 booster.
Until 2015, ULA had a near sole source contract with the USAF as the only company certified to bid on and launch those most critical national security satellites. New space upstart SpaceX, founded by billionaire CEO Elon Musk, then forced the bidding issue by filing a lawsuit suing the Air Force.
In response to the lost GPS-III bid, ULA touted their demonstrated record of 100 percent success launching more than 115 satellites.
“United Launch Alliance continues to believe a best value launch service competition with evaluation of mission success and assurance, and past performance including demonstrated schedule reliability, is appropriate and needed for the Phase 1A missions given the technical complexities of rocket launch services and their critical significance to the war fighter and U.S. national security,” ULA spokeswoman Jessica Rye told Universe Today.
“Over the past decade, ULA has provided unmatched reliability with 100 percent mission success and ensured more than 115 satellites were delivered safely to their orbits each and every time. We look forward to continuing to provide the best value launch services to enable our customers’ critical missions.”

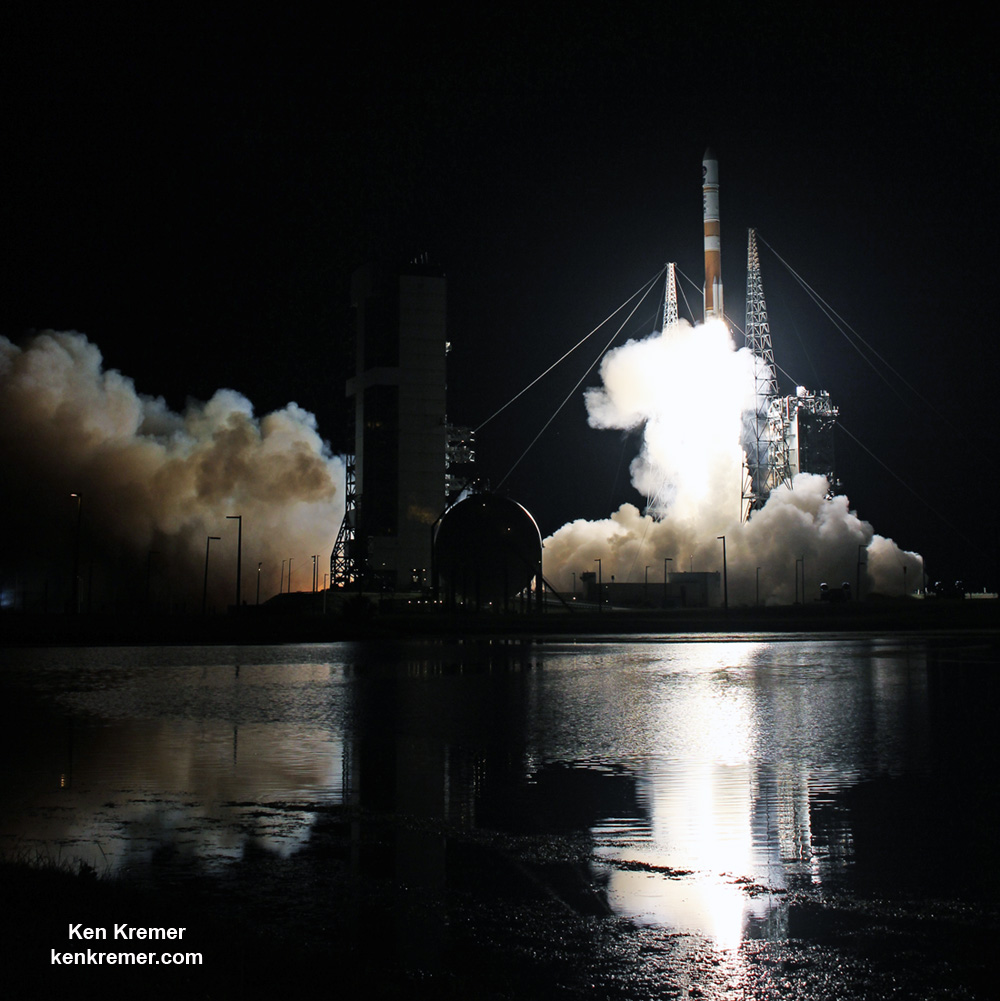
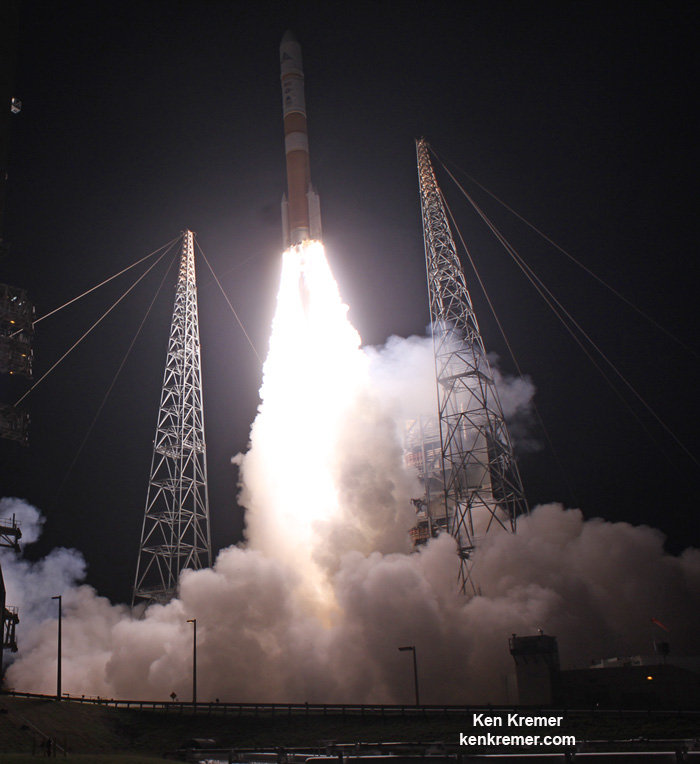
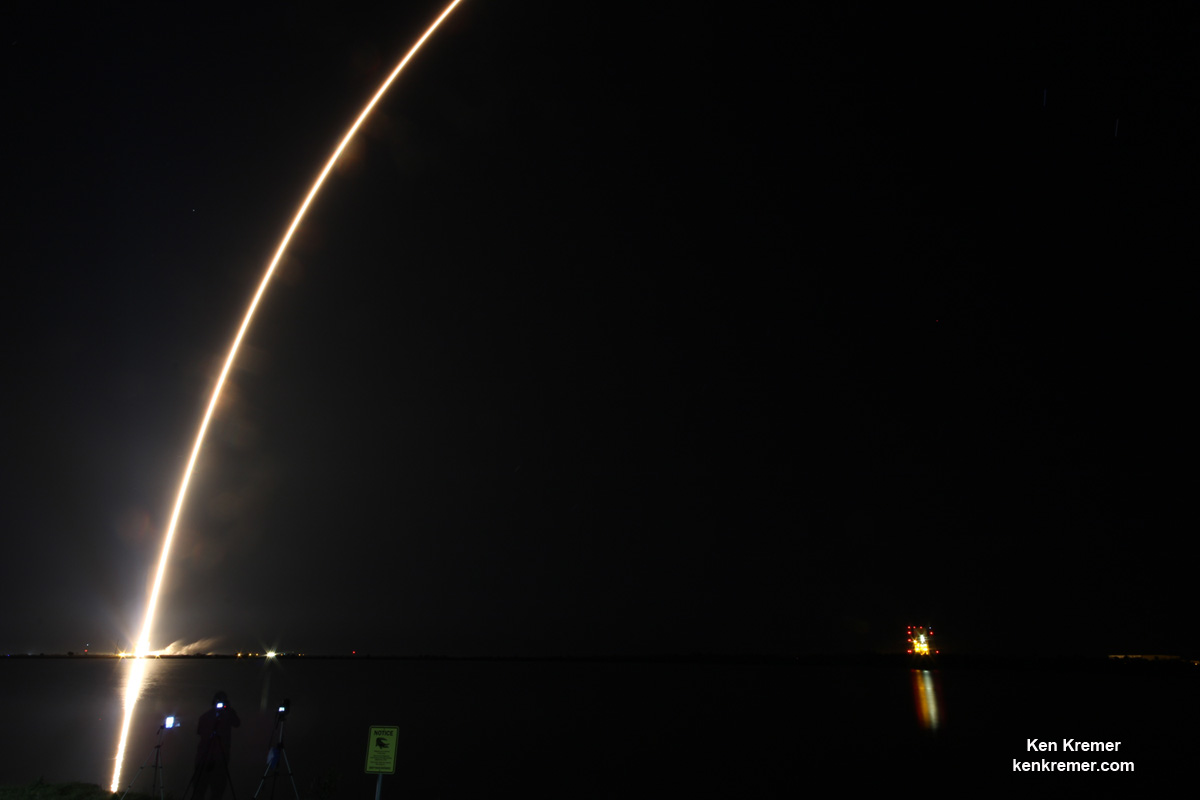
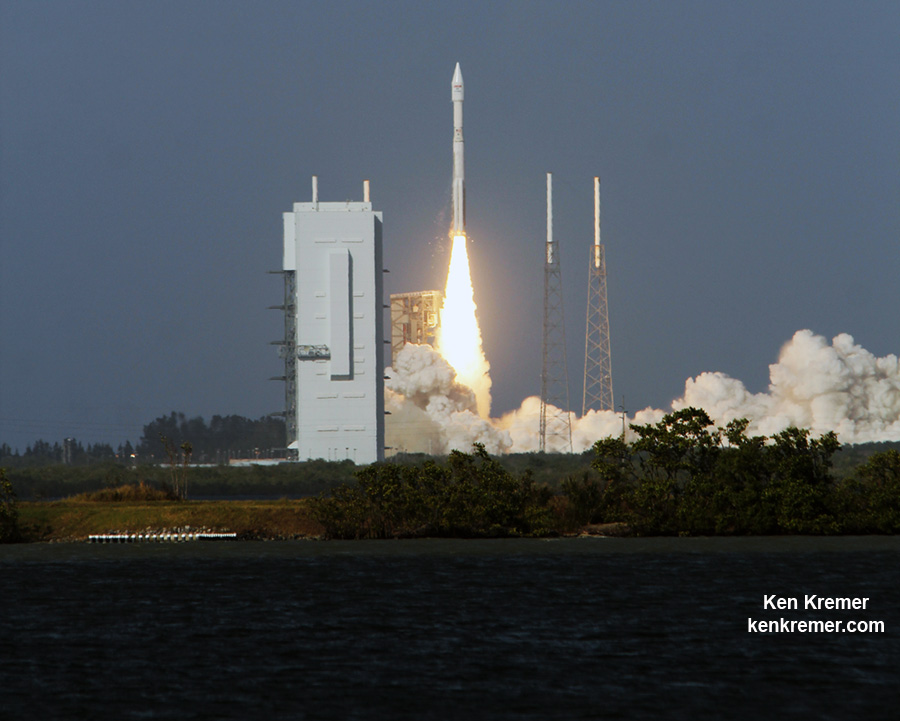
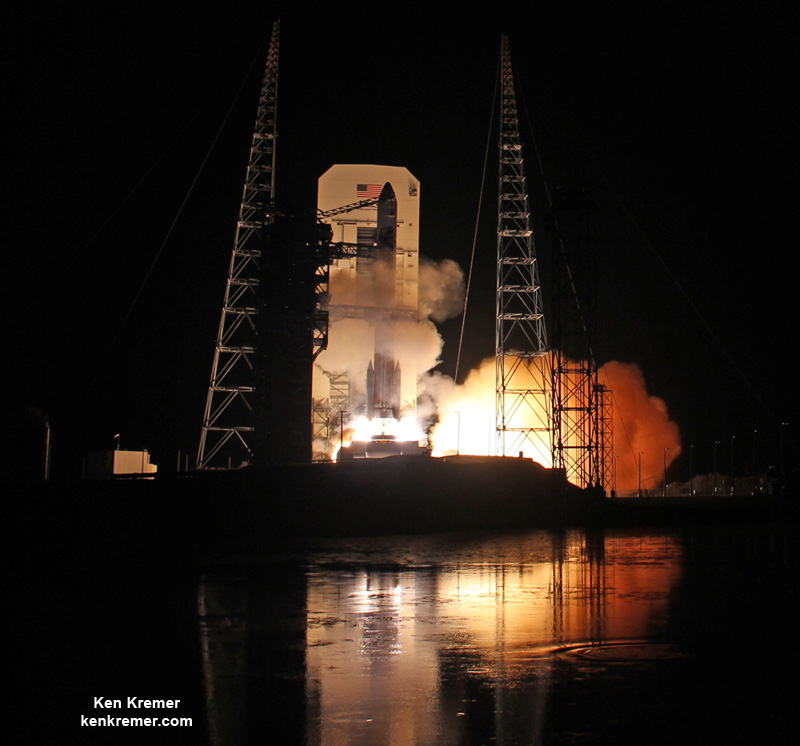
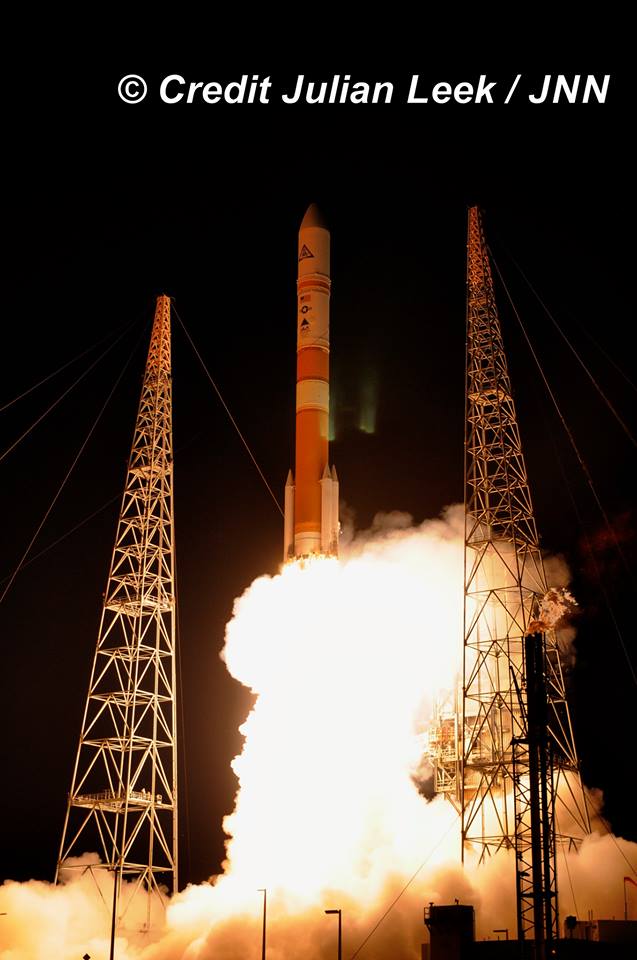
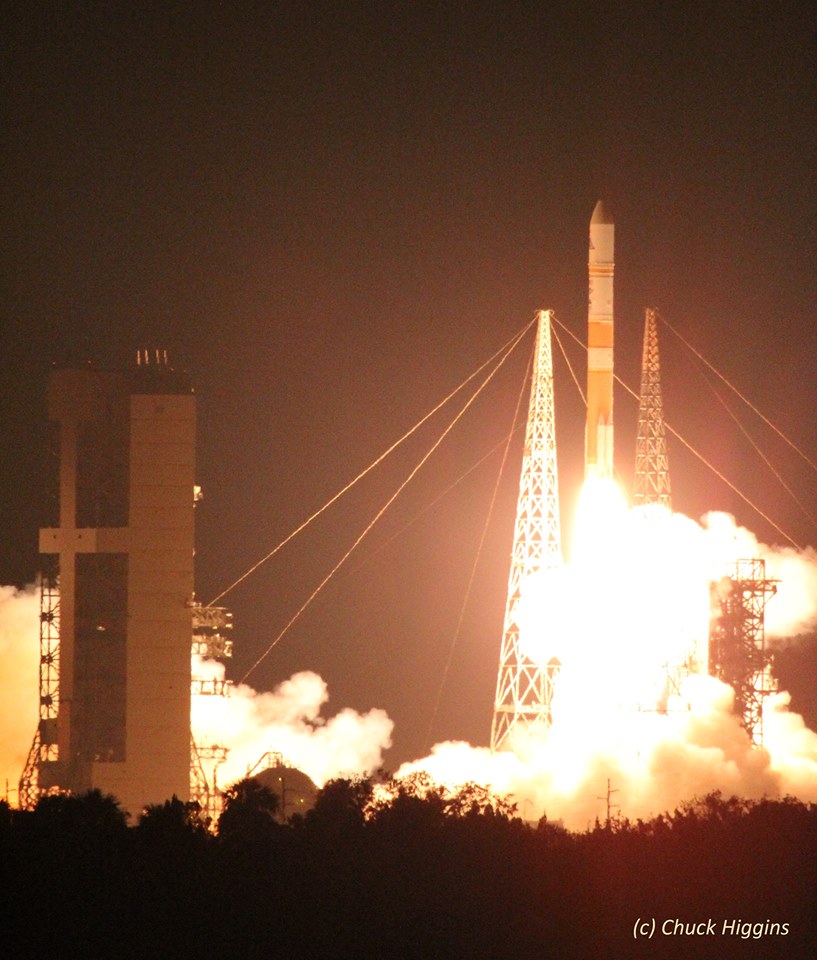
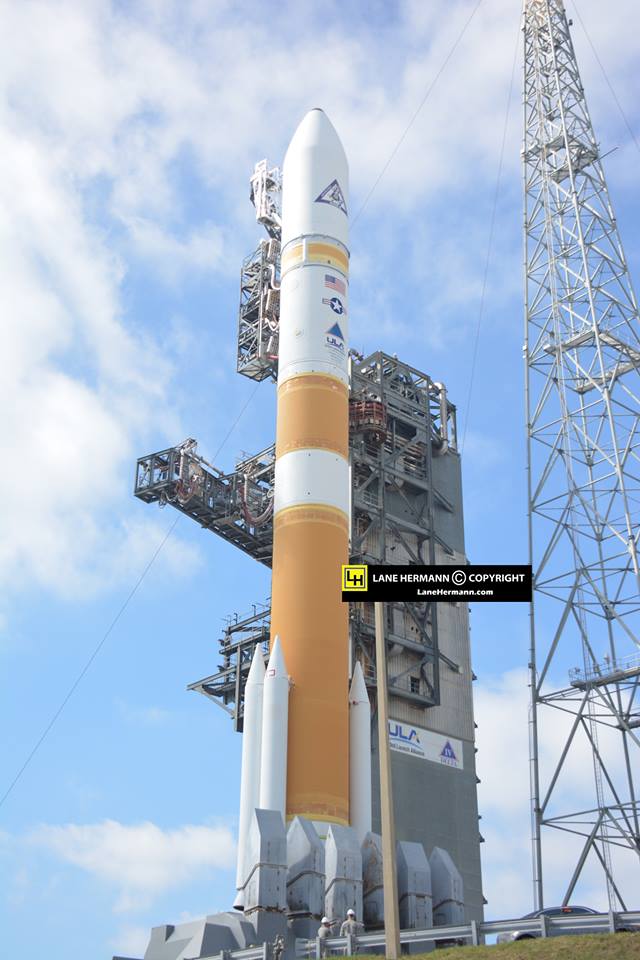
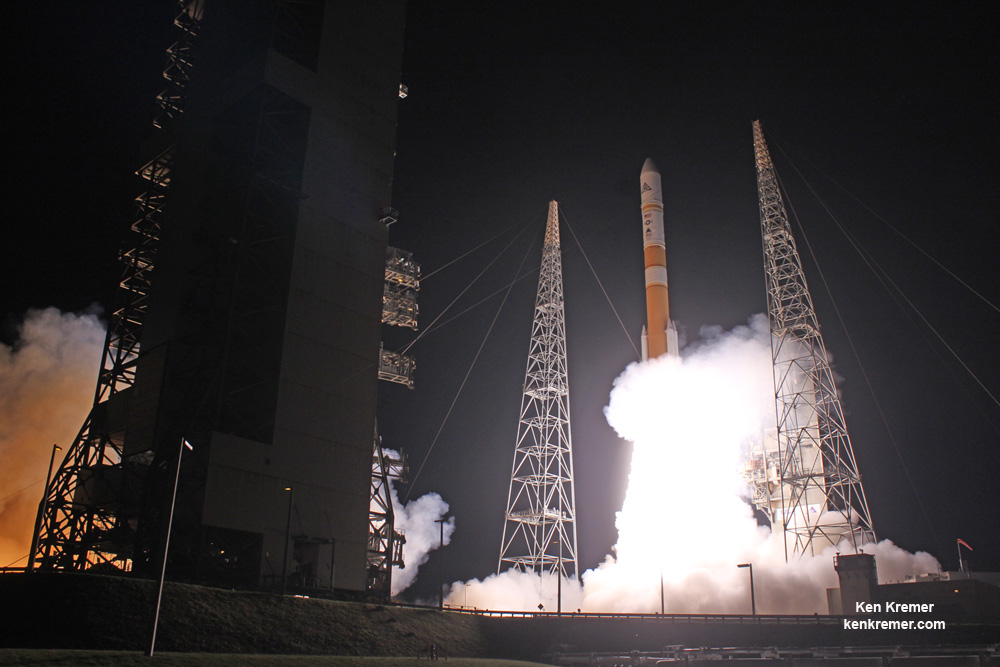
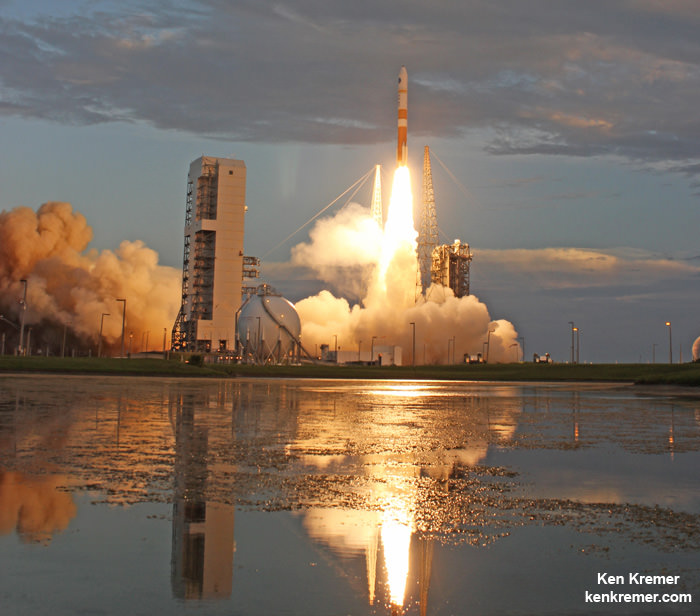
The most recent ULA launch for the Air Force took place days ago involving the stunning Delta blastoff of the WGS-9 high speed communications satellite on March 18, 2017.
SpaceX has suffered a pair of calamitous Falcon 9 rocket failures in June 2015 and Sept. 2016, destroying both the rocket and payloads for NASA and the AMOS-6 communications satellite respectively.
So the U.S. Air Force should definitely be balancing risk vs. reward with regard to lower pricing and factoring in rocket robustness and reliability, regarding launches of national security satellites which could cost into the multi-billions of dollars, take years to manufacture and are not swiftly replaceable in case of catastrophic launch failures.
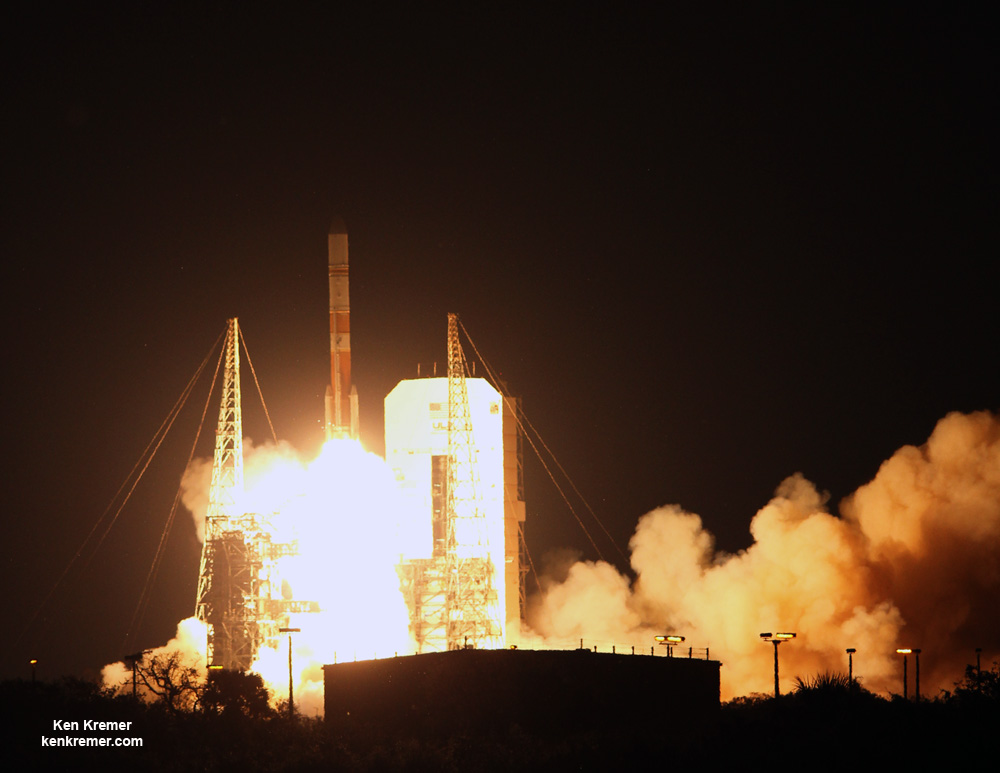
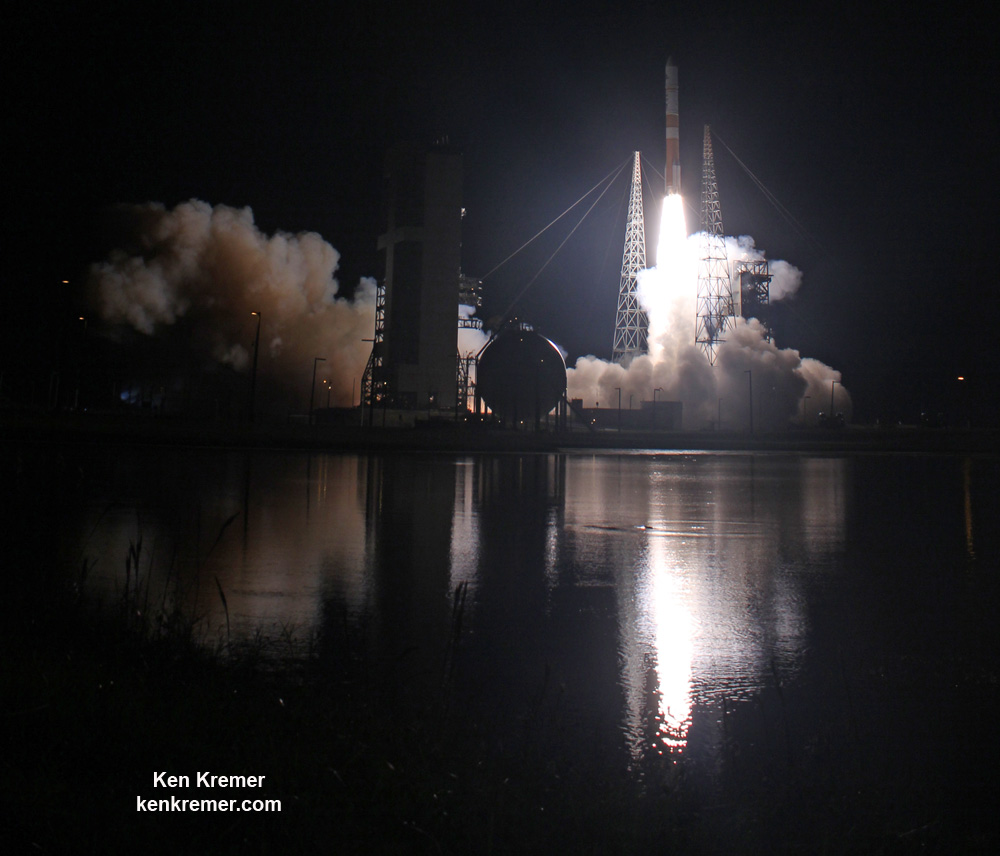
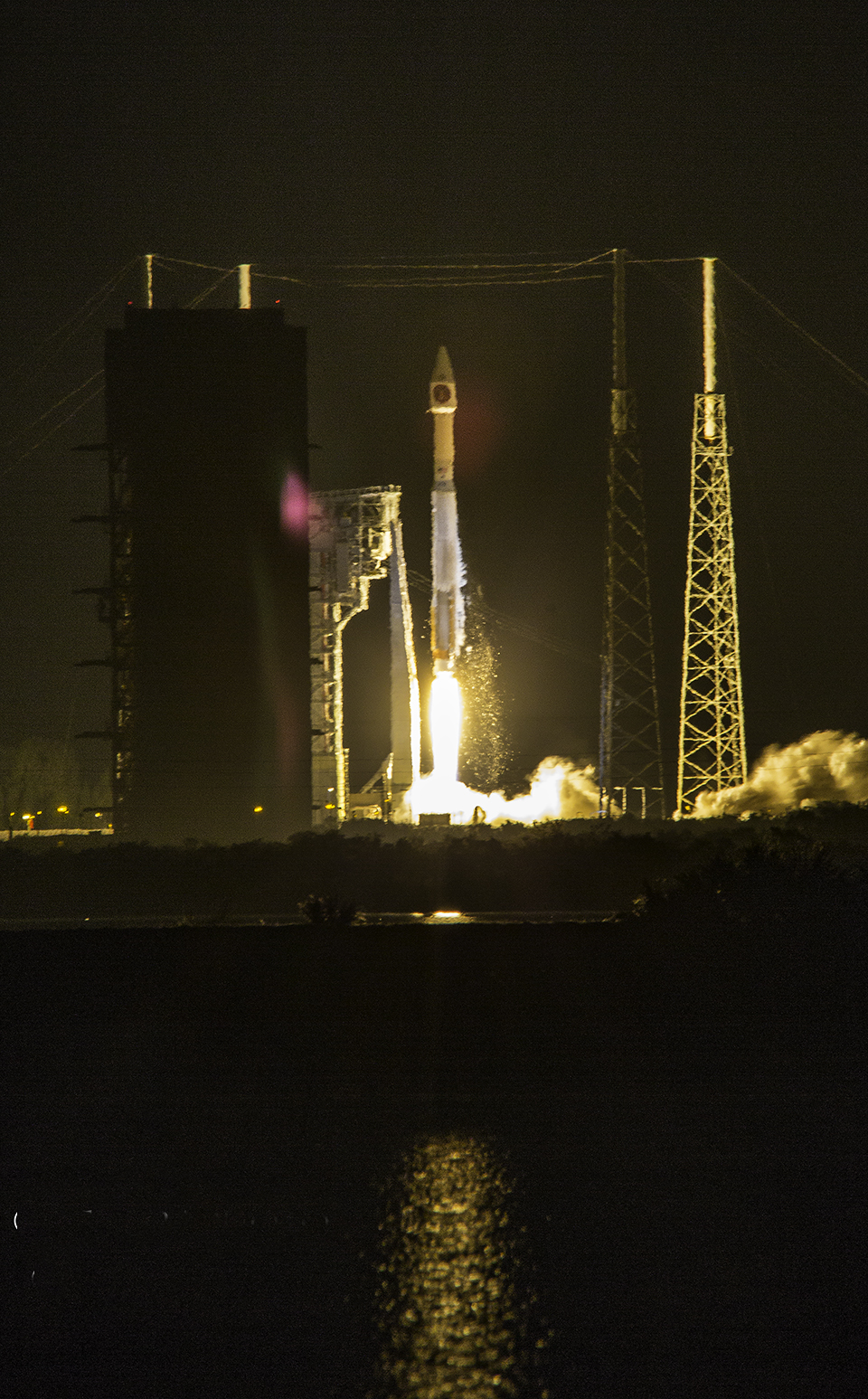
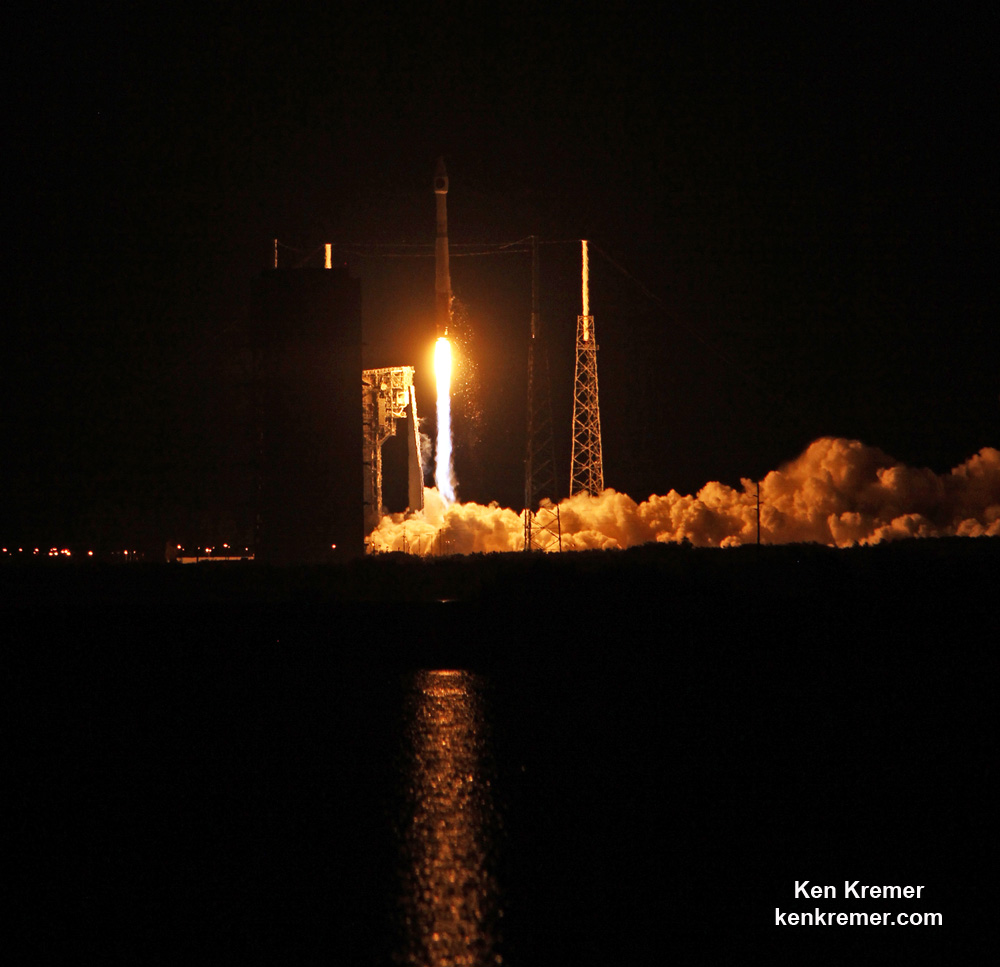
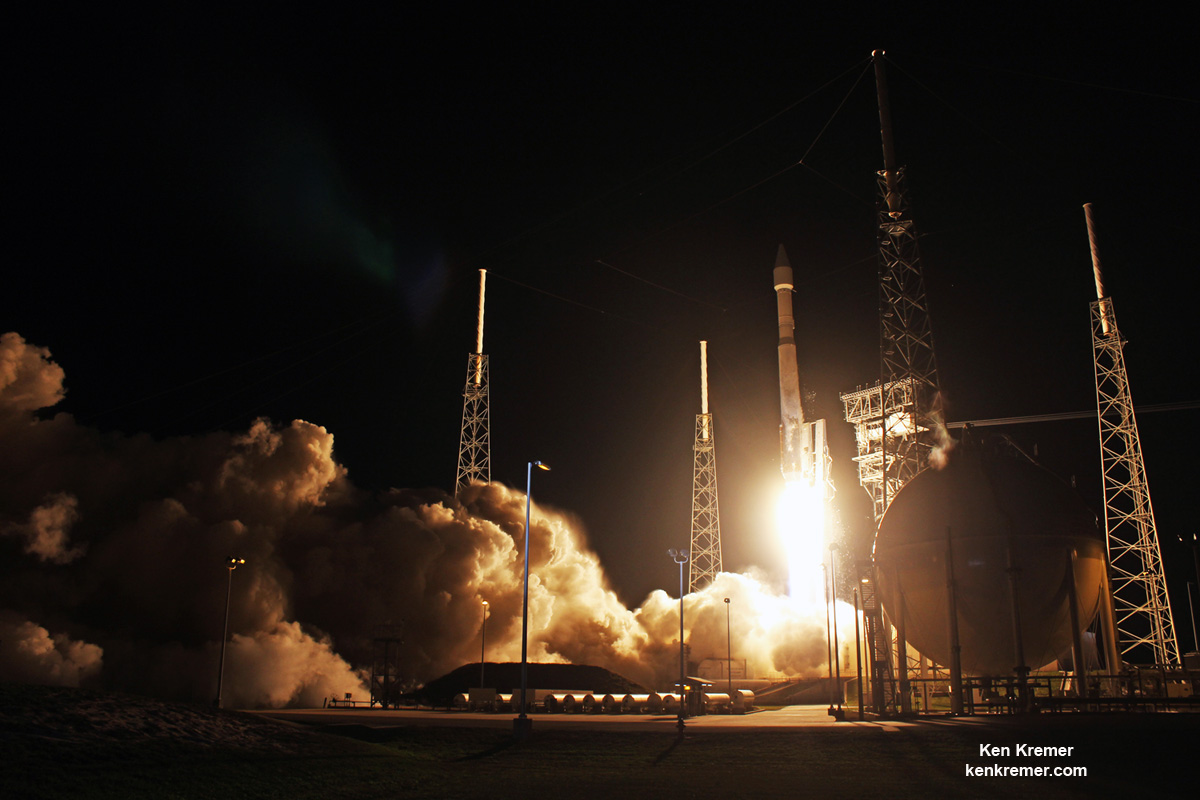
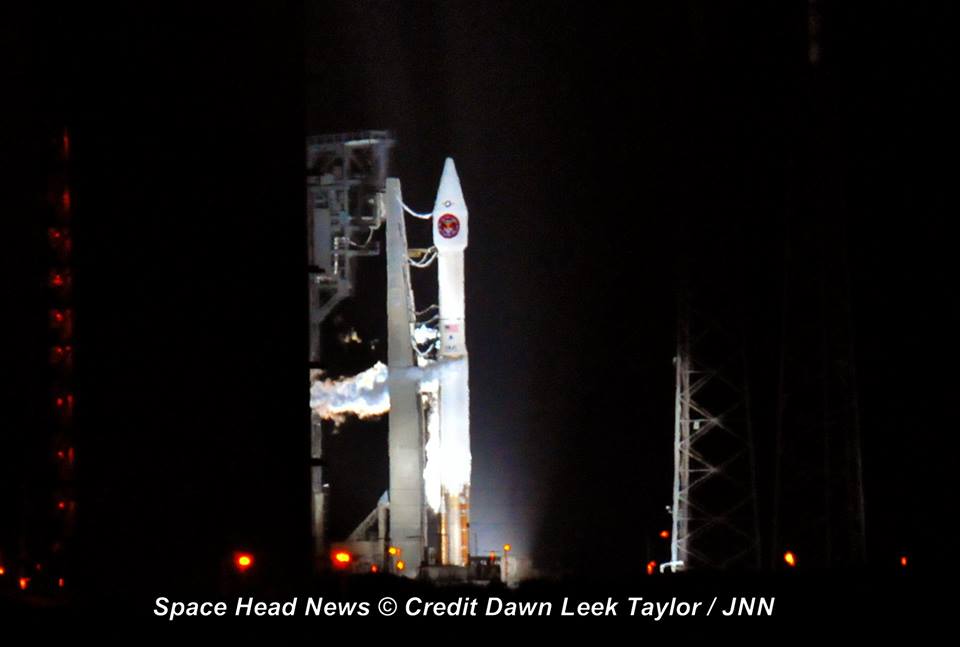
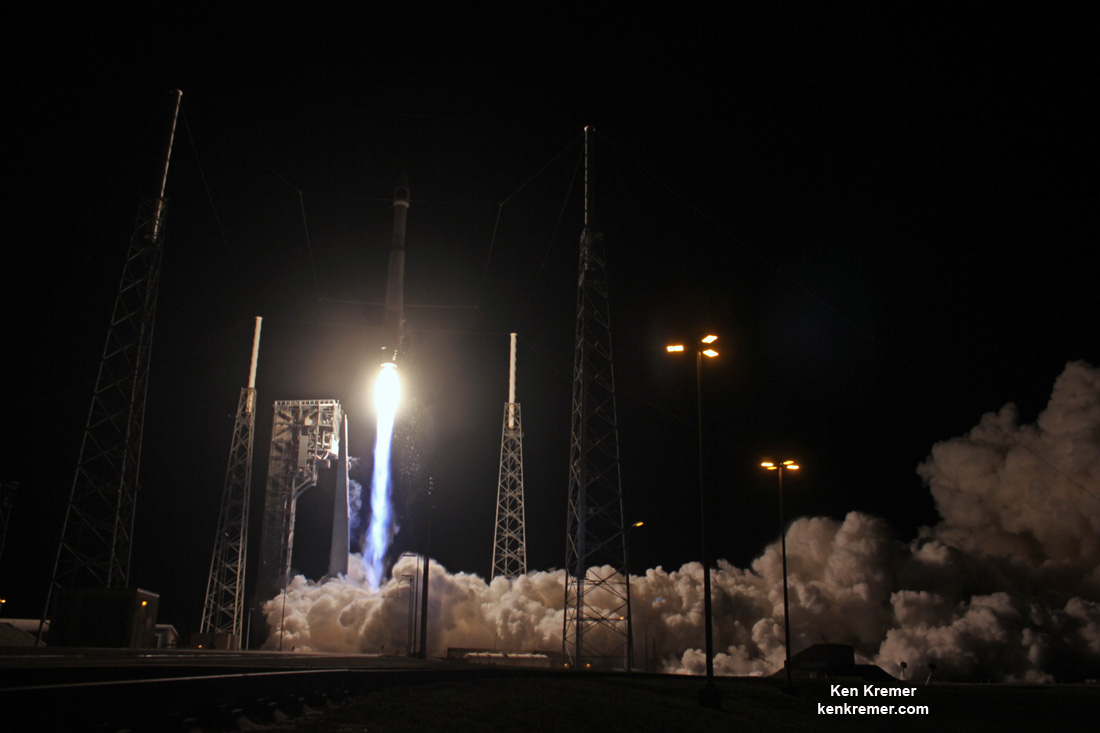
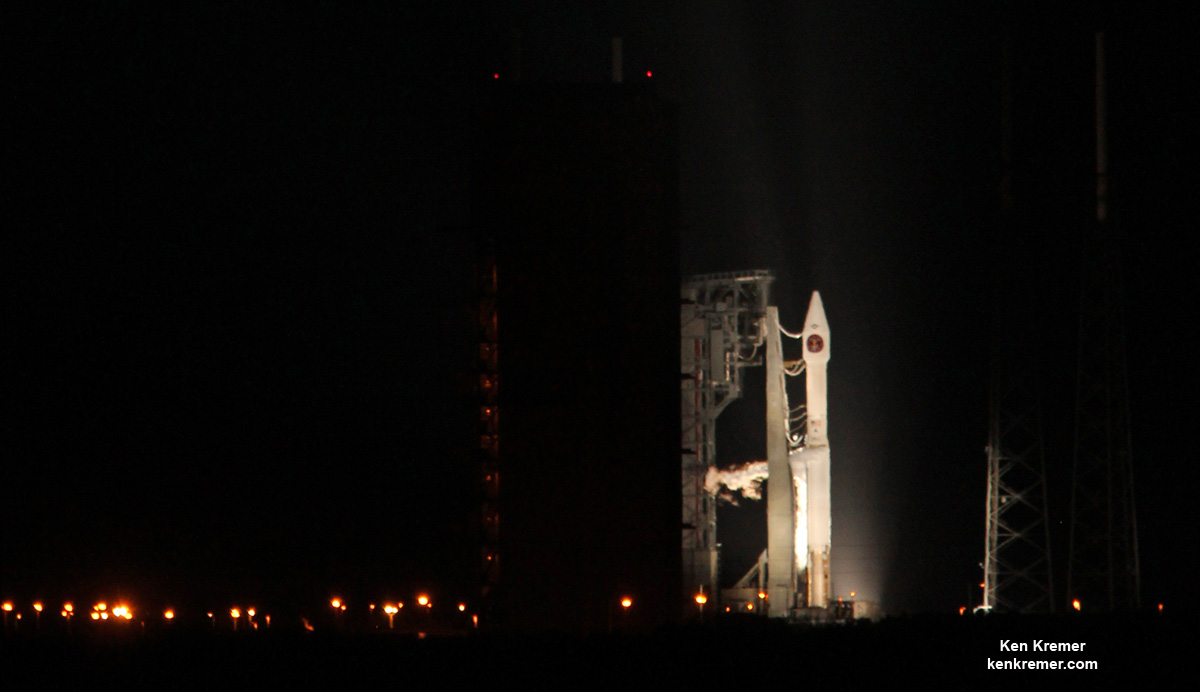
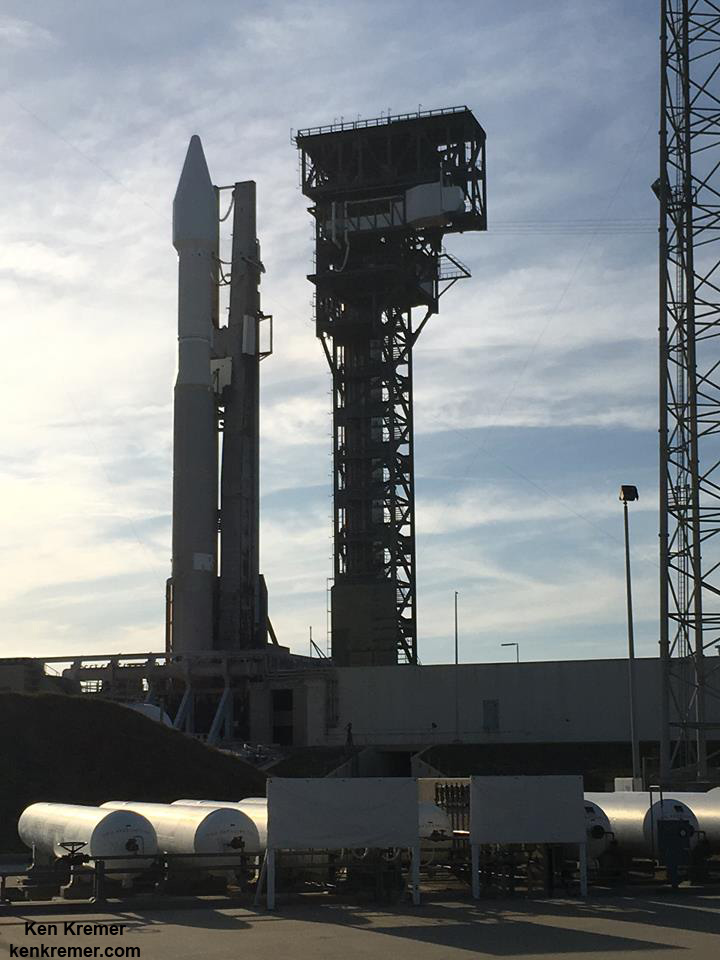
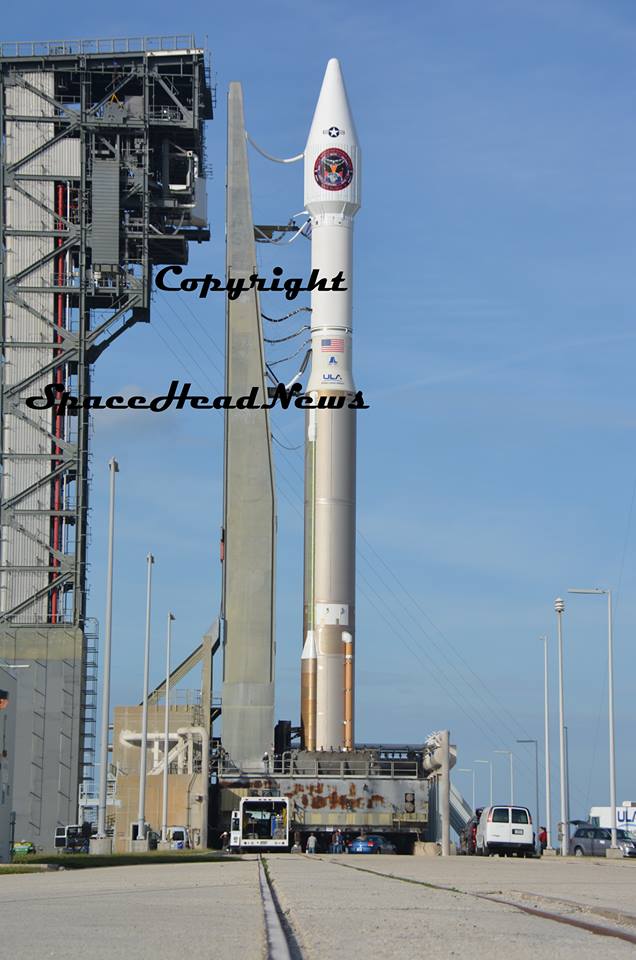
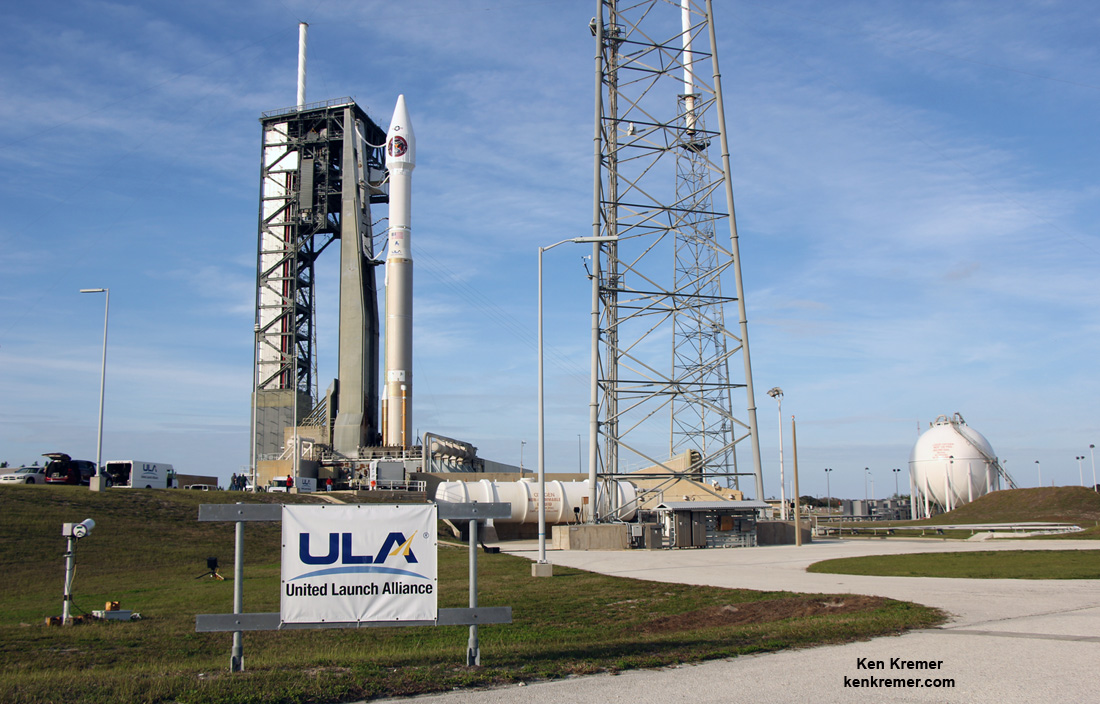
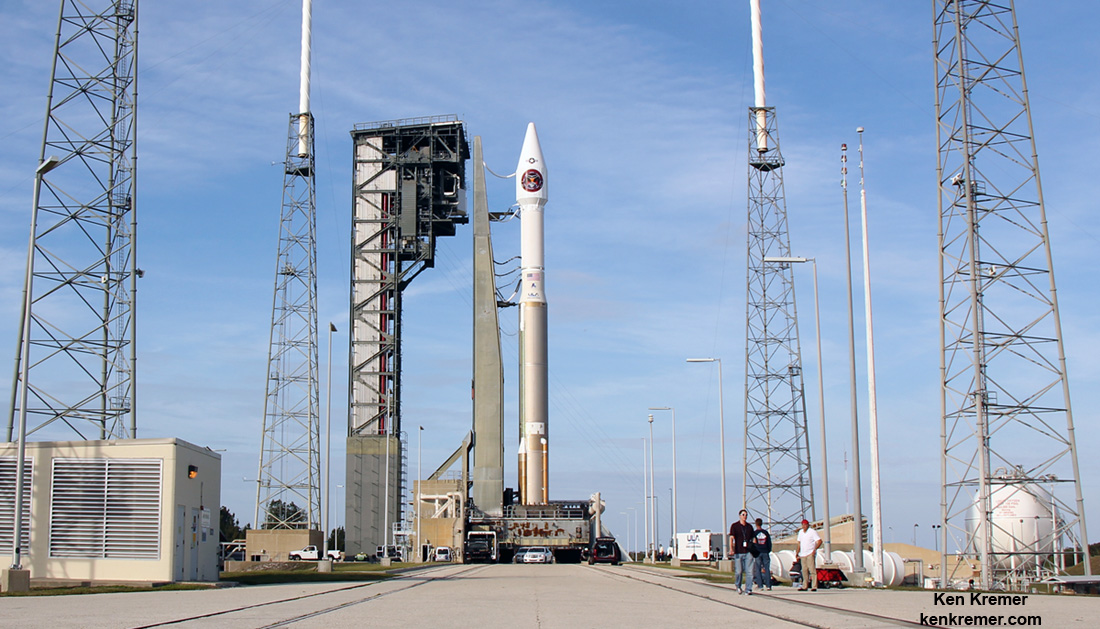
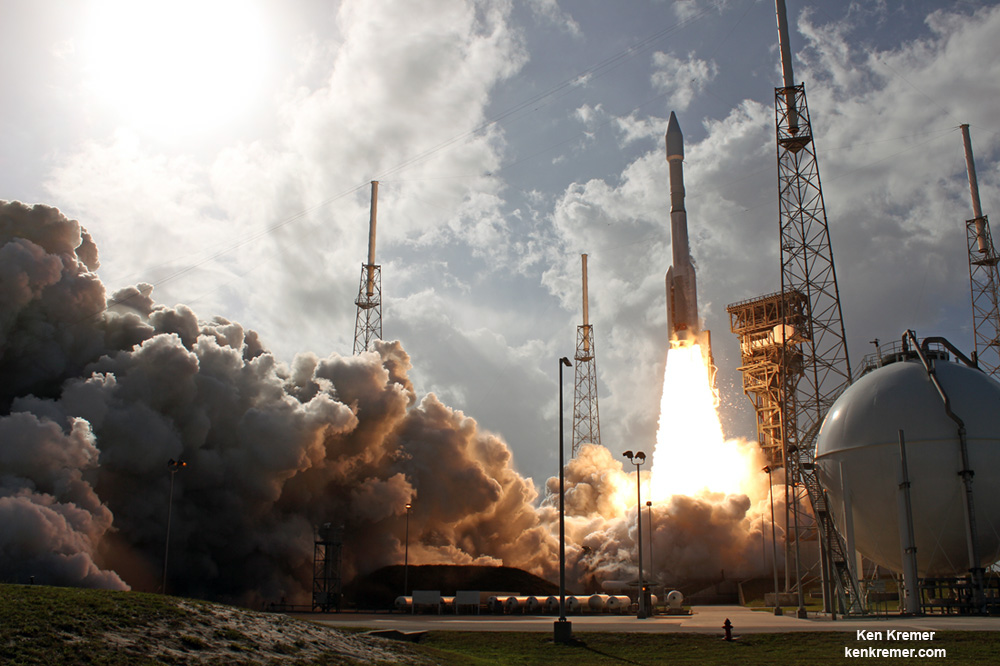
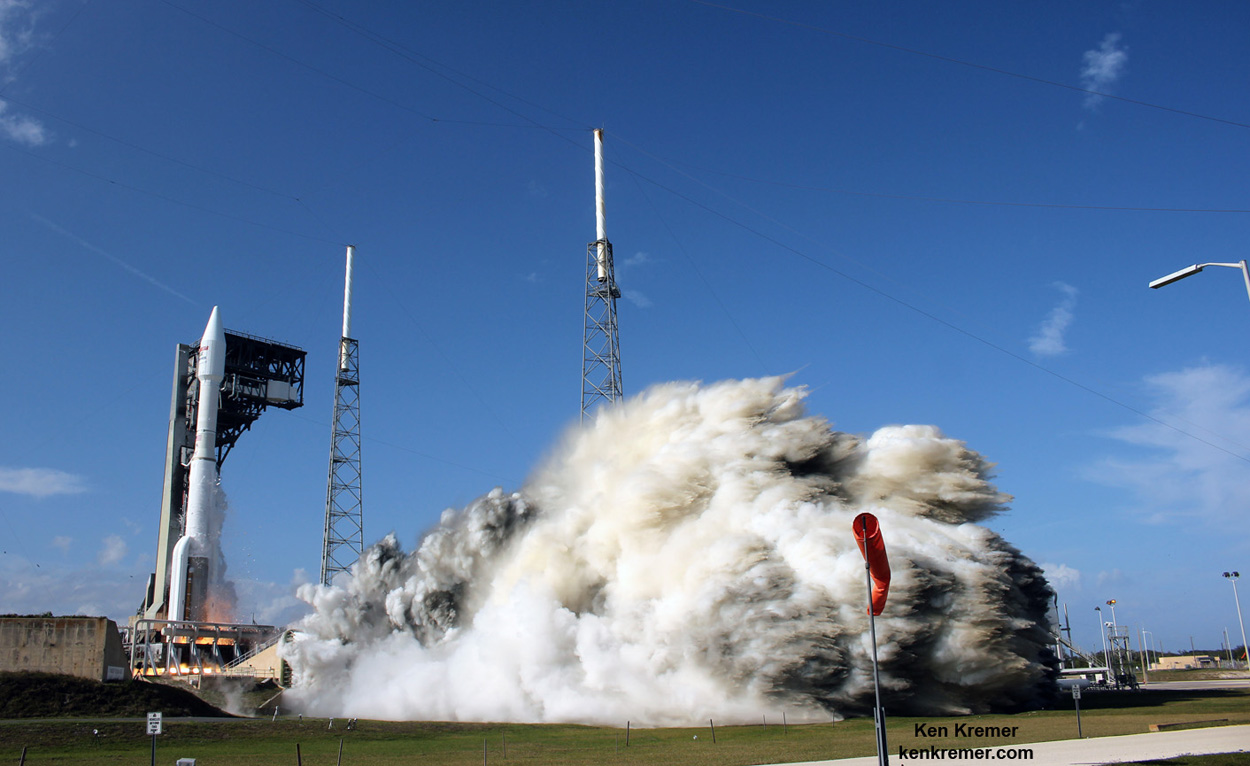
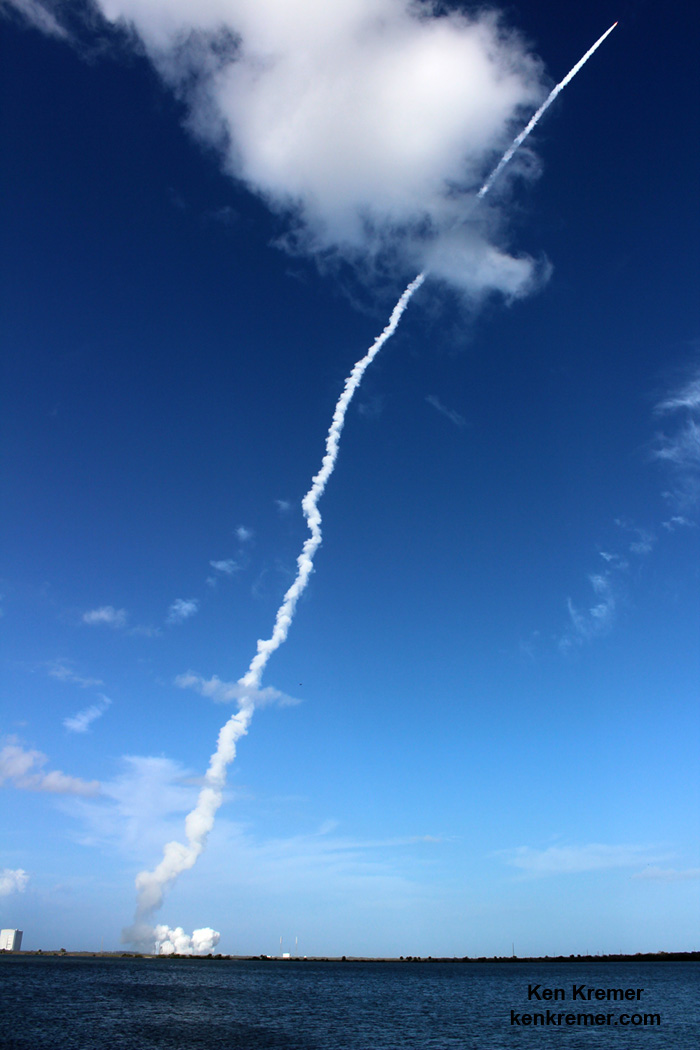
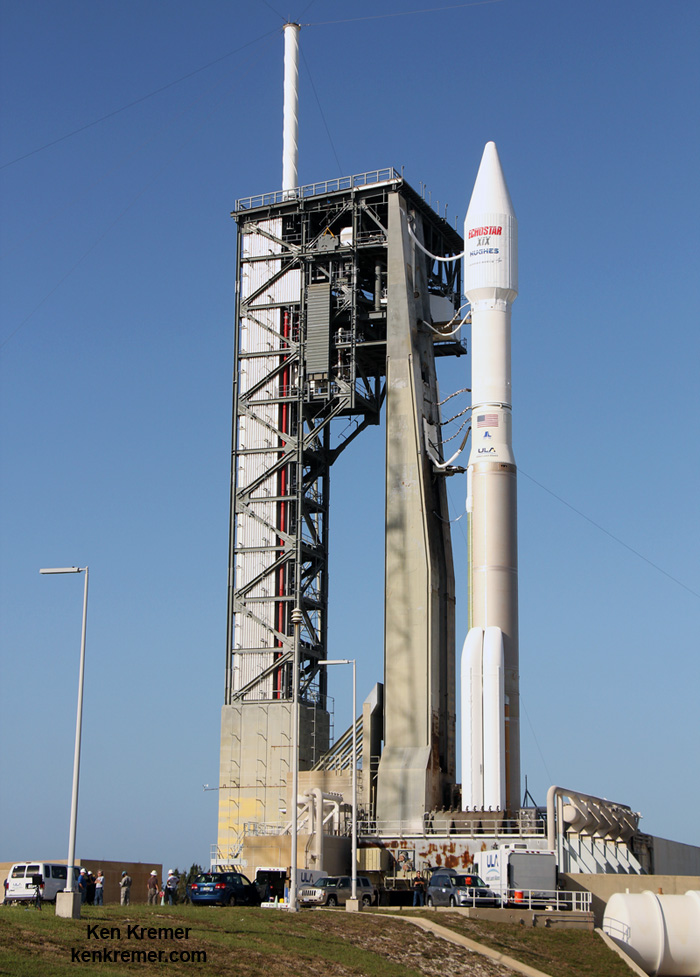
ULA’s workhorse Atlas V rocket successfully delivered the final GPS satellite in the IIF series to orbit for the US Air Force on Feb 5, 2016.
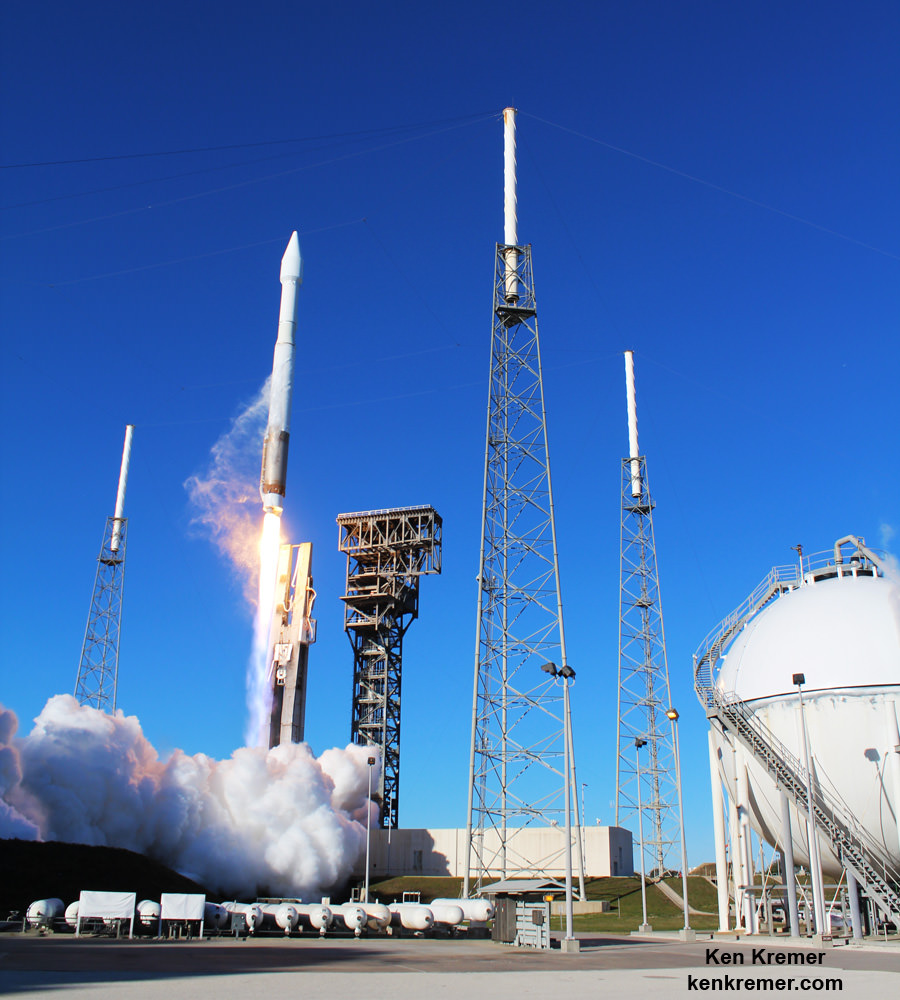

At that time the Global Positioning System (GPS) IIF-12 navigation satellite completed the constellation of GPS IIF satellites that are critical to both military and civilian users on a 24/7 basis.
The Atlas V rocket delivered the GPS IIF-12 satellite to a semi-synchronous circular orbit at an altitude of approximately 11,000 nautical miles above Earth.
“GPS III is the next generation of GPS satellites that will introduce new capabilities to meet the higher demands of both military and civilian users,” according to the USAF.
“GPS III is expected to provide improved anti-jamming capabilities as well as improved accuracy for precision navigation and timing. It will incorporate the common L1C signal which is compatible with the European Space Agency’s Galileo global navigation satellite system and compliment current services with the addition of new civil and military signals.”
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.