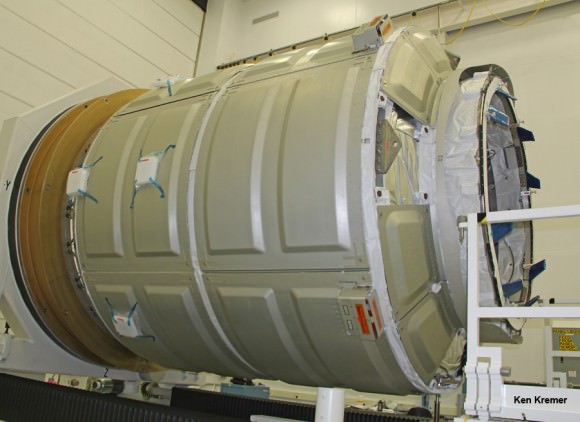
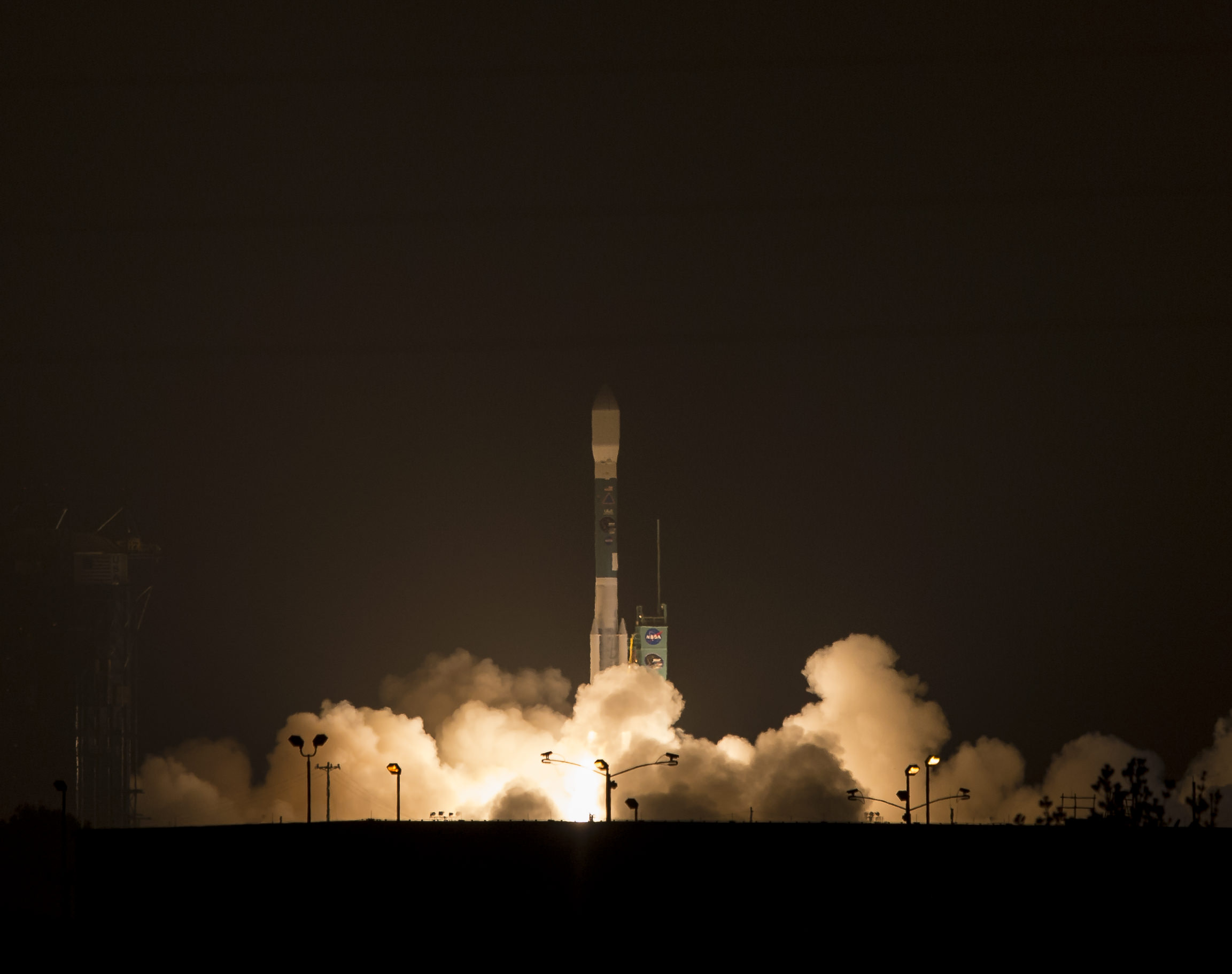
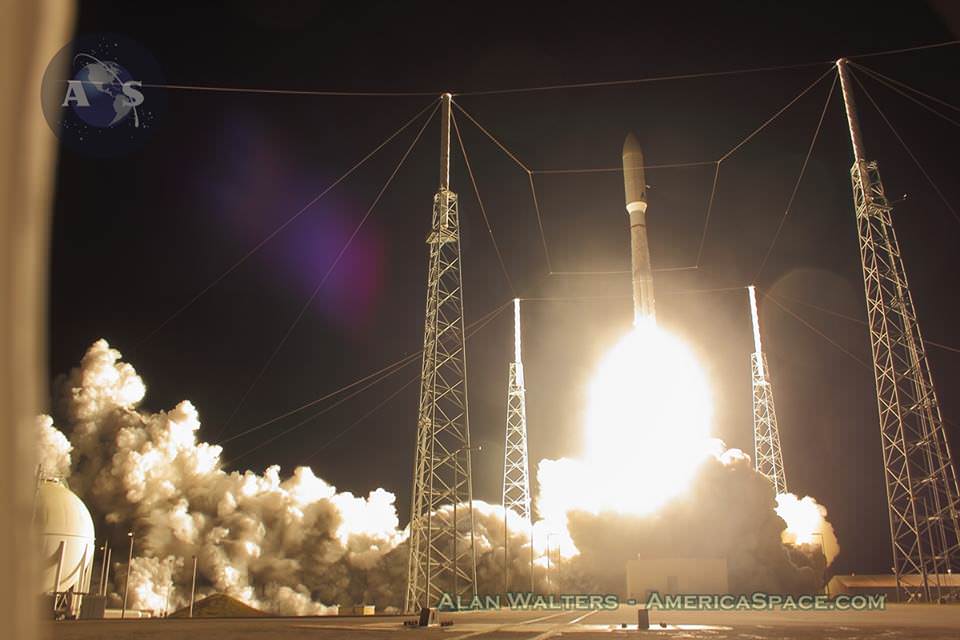
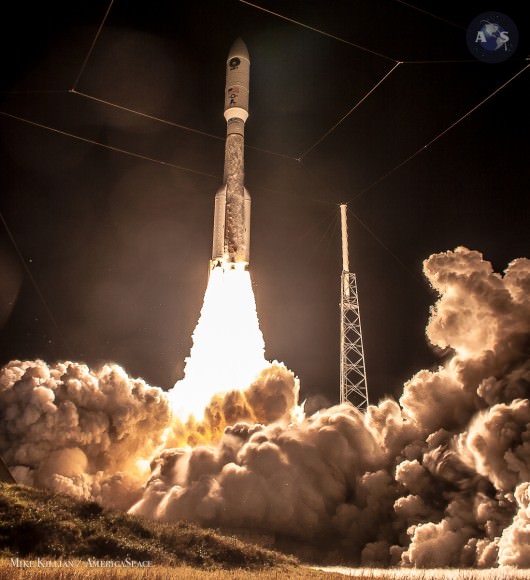
Help ULA name America’s next rocket to space. Credit: ULA
Voting Details below
Watch ULA’s March 25 Delta Launch Live – details below
Update 3/26: 2 new names have been added to the voting list – Zeus and Vulcan ![/caption]
United Launch Alliance (ULA) is asking the public for your help in naming their new American made rocket, now under development that “represents the future of space”- and will replace the firms current historic lines of Atlas and Delta rocket families that began launching back near the dawn of the space age.
Eagle, Freedom or GalaxyOne – those are the names to choose from for the next two weeks, from now until April 6.
UPDATE 3/26: 2 new names have been added to the voting list – Zeus and Vulcan !
ULA says the names were selected from a list of over 400 names submitted earlier this year by ULA’s 3400 employees and many space enthusiasts.
ULA has set up a simple voting system whereby you can vote for your favorite name via text or an online webpage.
Currently dubbed the “Next Generation Launch System,” or NGLS, ULA’s new president and CEO Tory Bruno is set to unveil the next generation rockets design and name at the National Space Symposium on April 13 in Colorado Springs, Colorado.
“ULA’s new rocket represents the future of space – innovative, affordable and reliable,” said Bruno, in a statement.
“More possibilities in space means more possibilities here on earth. This is such a critical time for space travel and exploration and we’re excited to bring all of America with us on this journey into the future.”
The NGLS is ULA’s response to what’s shaping up as a no holds barred competition with SpaceX for future launch contracts where only the innovative and those who dramatically cut the cost of access to space will survive.
The first flight of the NGLS is slated for 2019.
Here’s how you can cast your vote for America’s next rocket to April 6, 2015:
Visit the website: http://bit.ly/rocketvote
OR
Voters can text 22333 to submit a vote for their favorite name. The following key can be used to text a vote:
• ULA1 for “Eagle”
• ULA2 for “Freedom”
• ULA3 for “GalaxyOne”
3/26 Update: Zeus and Vulcan have been added to the voting list

“Name America’s next ride to space. Vote early, vote often … ” says Bruno.
I have already voted – early and often.
Over 11,000 votes were tallied in just the first day.
Currently ULA is the nation’s premier launch provider, launching at a rate of about once per month. 13 launches are planned for 2015- as outlined in my earlier article here.
But ULA faces stiff and relentless pricing and innovative competition from NewSpace upstart SpaceX, founded by billionaire Elon Musk.
NGLS is ULA’s answer to SpaceX – they must compete in order to survive.
To date ULA has accomplished a 100 percent mission success for 94 launches since the firms founding in 2006 as a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin. They have successfully launched numerous NASA, national security and commercial payloads into orbit and beyond.
Planetary missions launched for NASA include the Mars rovers and landers Phoenix and Curiosity, Pluto/New Horizons, Juno, GRAIL, LRO and LCROSS.
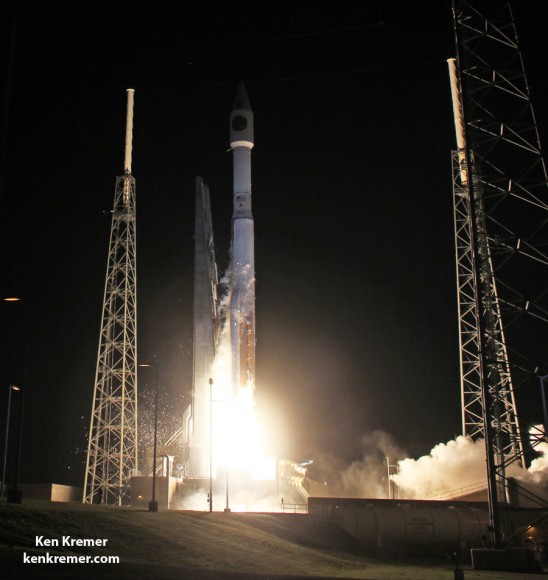

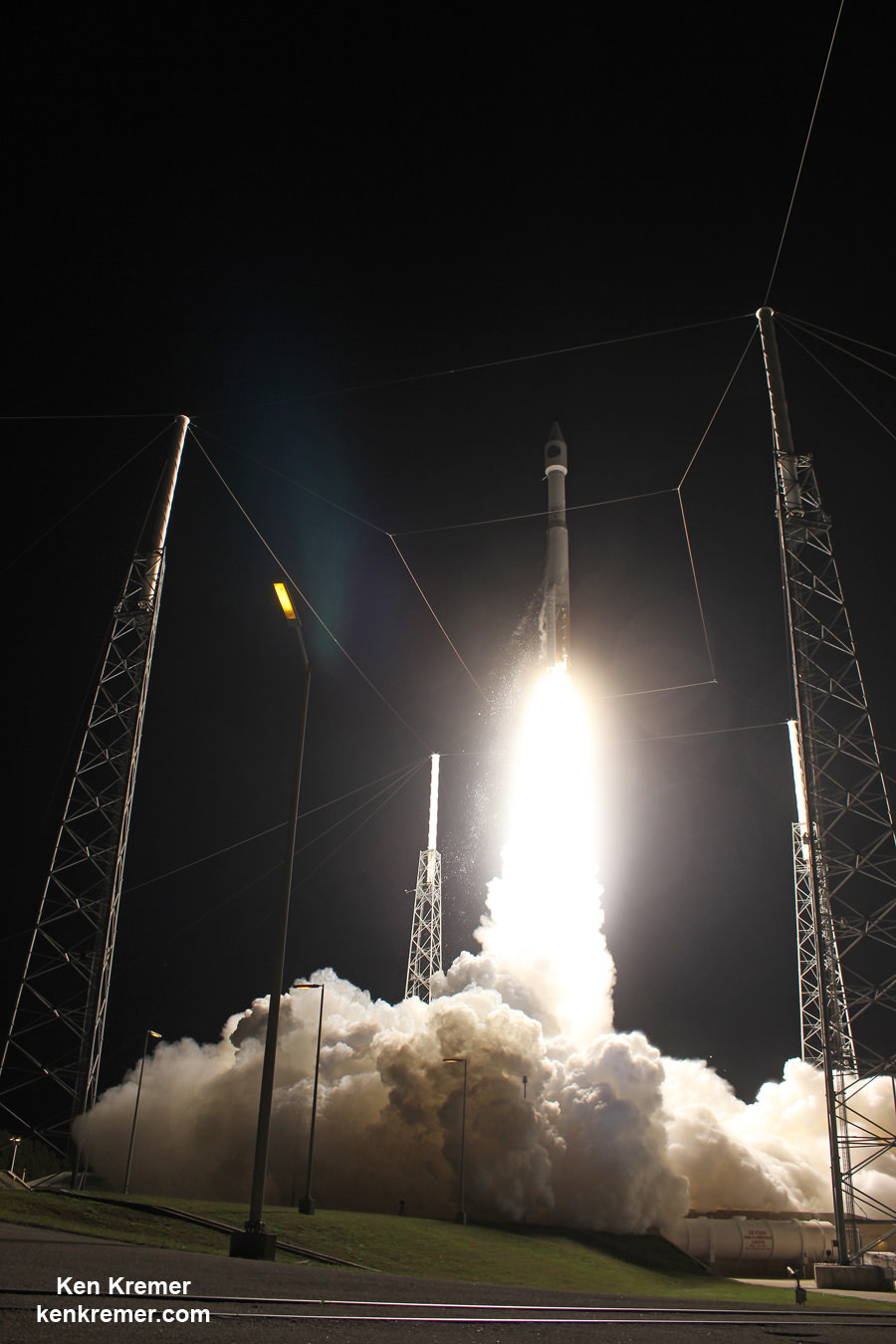
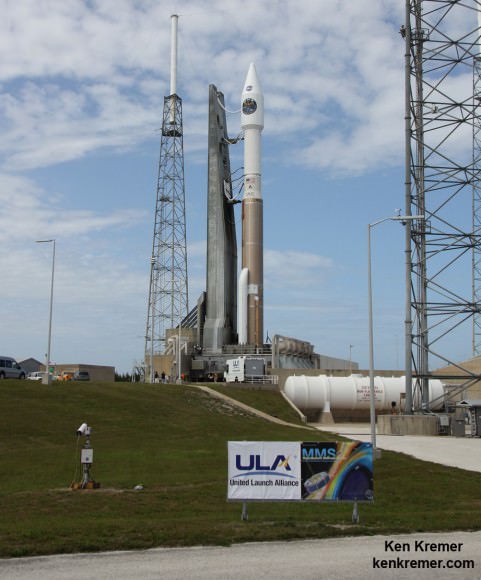
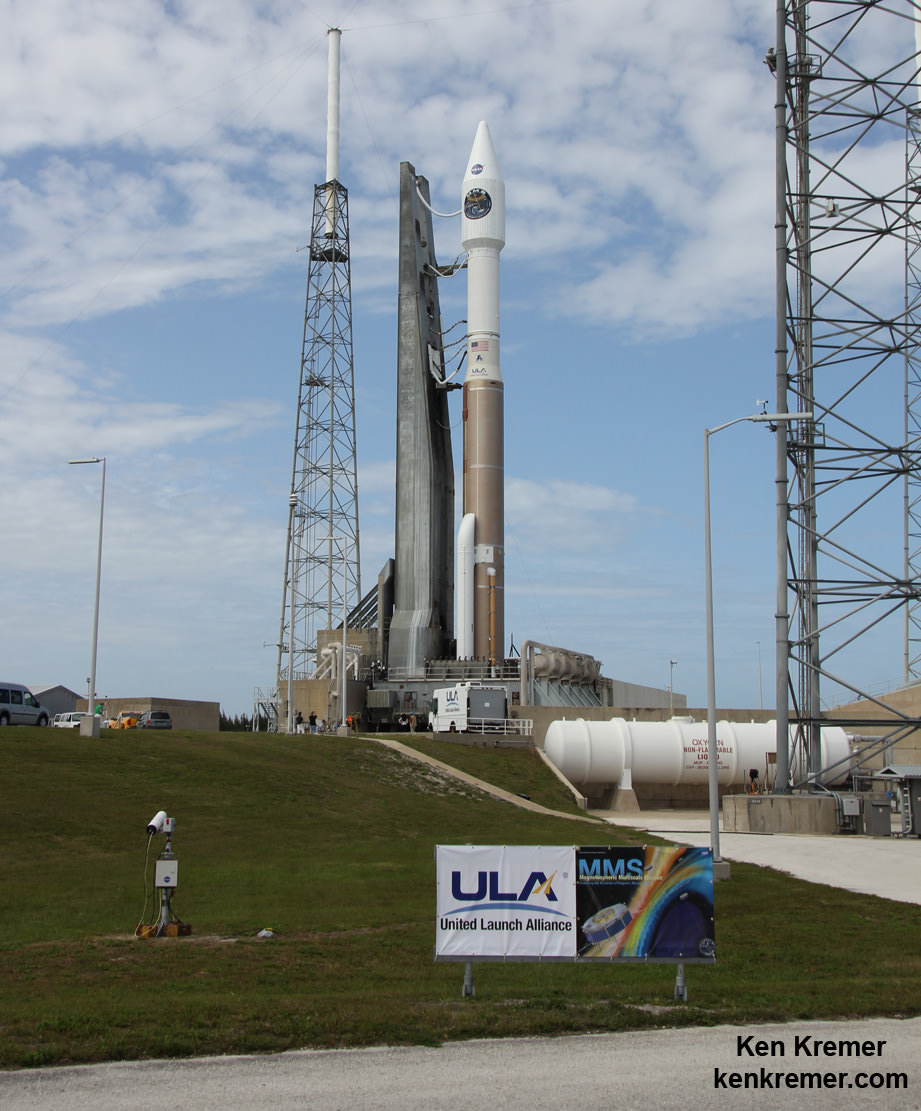
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) spacecraft onboard launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, March 12, 2015, Florida. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com
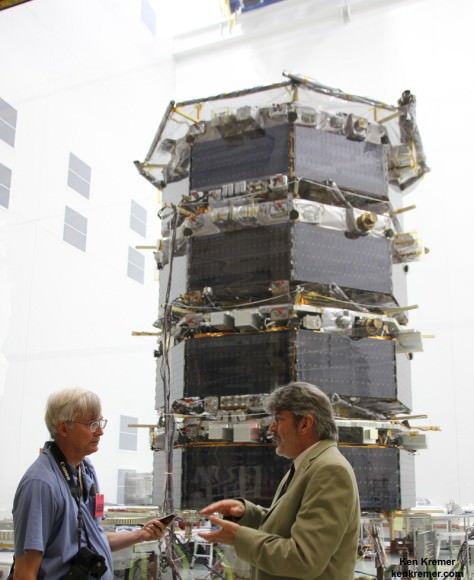
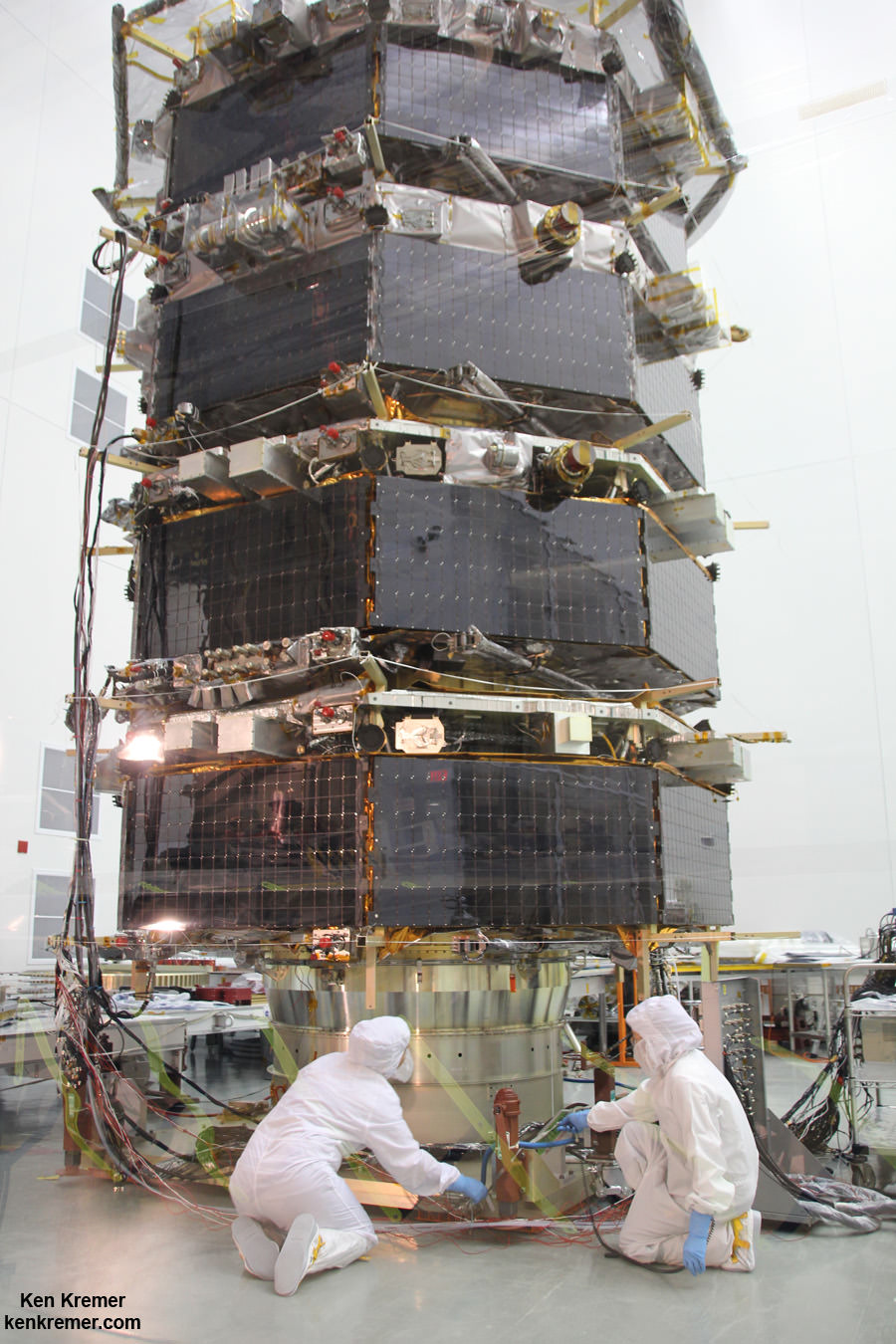
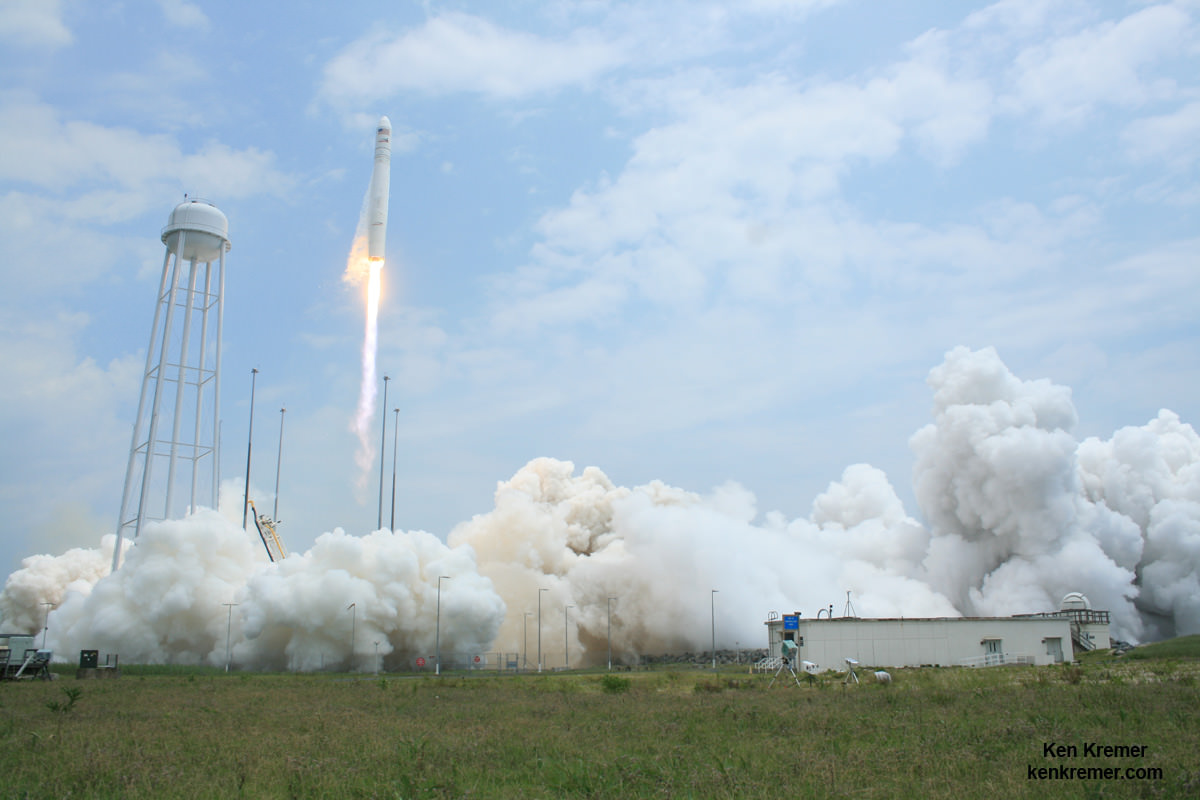
ULA’s most recent launch for NASA involved the $1.1 Billion Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission comprised of four formation flying satellites which blasted to Earth orbit atop an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, during a spectacular nighttime blastoff on March 12, 2015. Read my onsite reports – here and here.
“Space launch affects everyone, every day, and our goal in letting America name its next rocket is to help all Americans imagine the future of endless possibilities created by affordable space launch,” Bruno added.
NGLS will include some heritage design from the Atlas V and Delta IV rockets, but will feature many new systems and potentially some reusable systems – to be outlined by Bruno on April 13.
ULA plans to phase out the Delta IV around 2019 when the current contracts are concluded. The Atlas V will continue for a transitional period.
The Atlas V is also the launcher for Boeing’s CST-100 manned space taxi due to first launch in 2017.
NGLS will launch from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, the same pad as for the Atlas V, as well as from Vandenberg AFB, Calif.
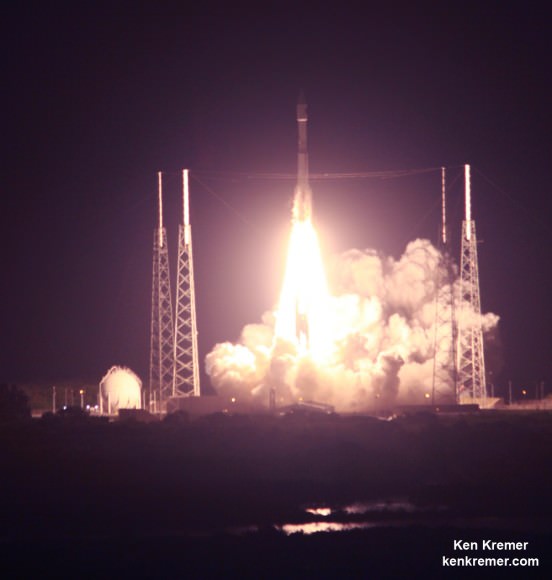
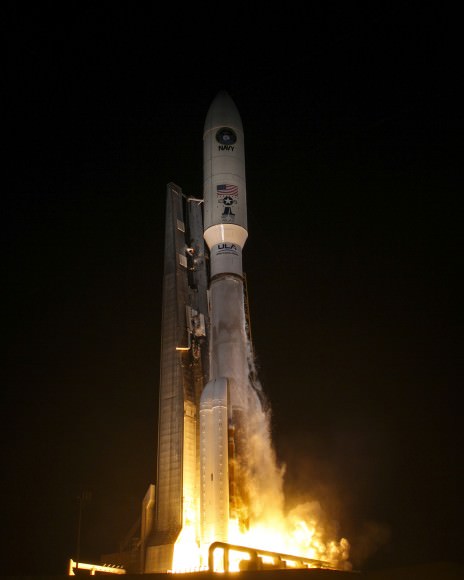
ULA’s next Delta IV launch with GPS IIF-9 is scheduled shortly for Wednesday, March 25, with liftoff at 2:36 p.m. EDT from Cape Canaveral.
Live webcast begins at 2:06 p.m. Live link here – http://www.ulalaunch.com/webcast.aspx
Vote now!
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.