When you’re walking around on soft ground, do you notice how your feet leave impressions? Perhaps you’ve tracked some of the looser earth in your yard into the house on occasion? If you were to pick up some of these traces – what we refer to as dirt or soil – and examine them beneath a microscope, what would you see?
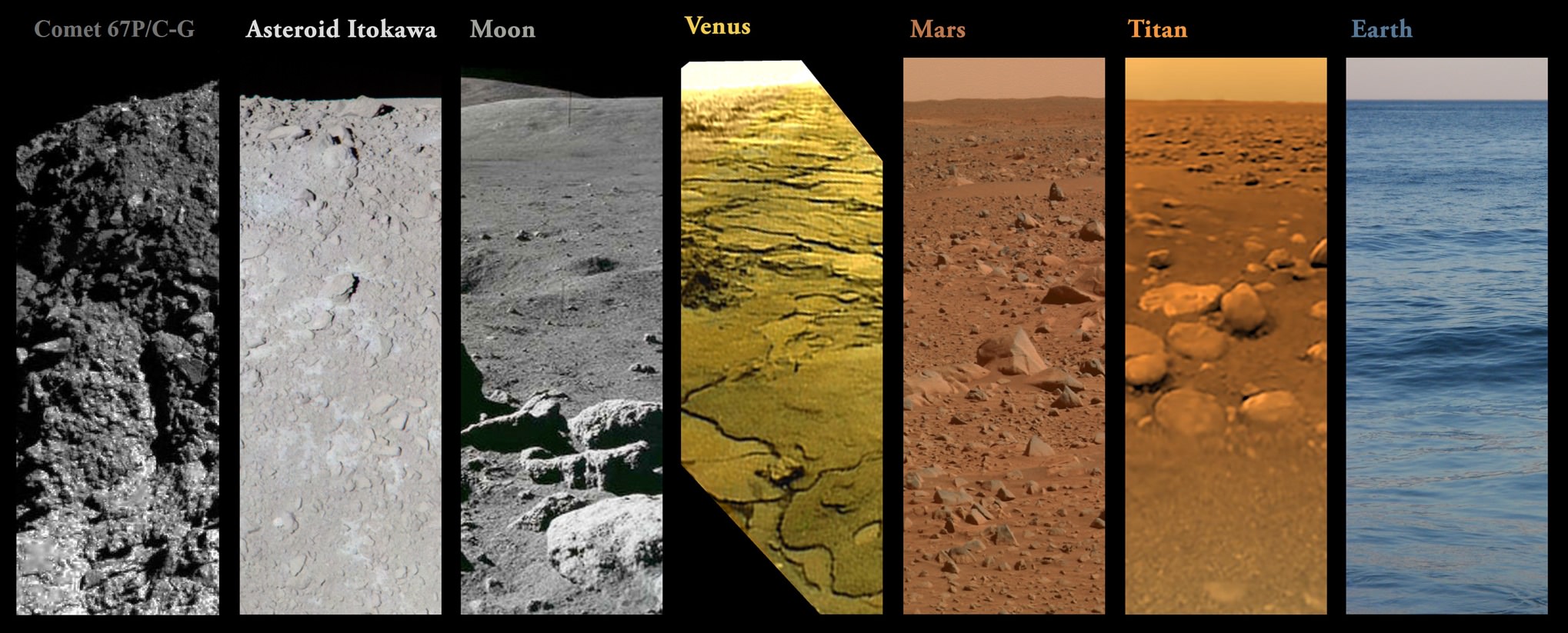
Essentially, you would be seeing the components of what is known as regolith, which is a collection of particles of dust, soil, broken rock, and other materials found here on Earth. But interestingly enough, this same basic material can be found in other terrestrial environments as well – including the Moon, Mars, other planets, and even asteroids.
Definition:
The term regolith refers to any layer of material covering solid rock, which can come in the form of dust, soil or broken rock. The word is derived from the combination of two Greek words – rhegos (which means “blanket”) and lithos (which means “rock).
Earth:
On Earth, regolith takes the form of dirt, soil, sand, and other components that are formed as a result of natural weathering and biological processes. Due to a combination of erosion, alluvial deposits (i.e. moving water deposing sand), volcanic eruptions, or tectonic activity, the material is slowly ground down and laid out over solid bedrock.

It can be made up of clays, silicates, various minerals, groundwater, and organic molecules. Regolith on Earth can vary from being essentially absent to being hundreds of meters thick. Its can also be very young (in the form of ash, alluvium, or lava rock that was just deposited) to hundreds of millions of years old (regolith dating to the Precambrian age occurs in parts of Australia).
On Earth, the presence of regolith is one of the important factors for most life, since few plants can grow on or within solid rock and animals would be unable to burrow or build shelter without loose material. Regolith is also important for human beings since it has been used since the dawn of civilization (in the form of mud bricks, concrete and ceramics) to build houses, roads, and other civil works.
The difference in terminology between “soil” (aka. dirt, mud, etc.) and “sand” is the presence of organic materials. In the former, it exists in abundance, and is what separates regolith on Earth from most other terrestrial environments in our Solar System.
The Moon:
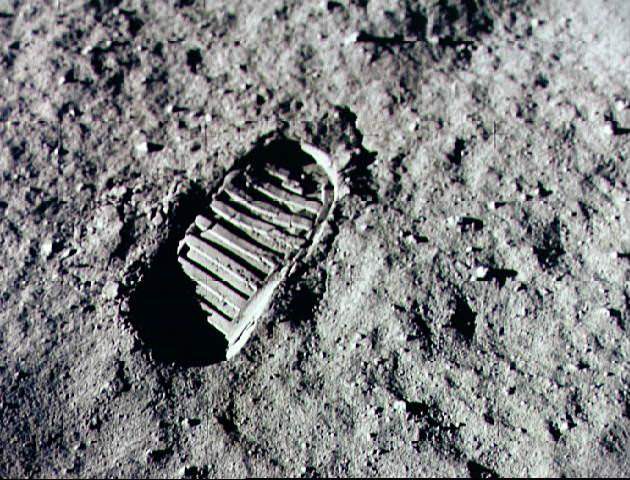
The surface of the Moon is covered with a fine powdery material that scientists refer to it as “lunar regolith”. Nearly the entire lunar surface is covered with regolith, and bedrock is only visible on the walls of very steep craters.

The Moon regolith was formed over billions of years by constant meteorite impacts on the surface of the Moon. Scientists estimate that the lunar regolith extends down 4-5 meters in some places, and even as deep as 15 meters in the older highland areas.
When the plans were put together for the Apollo missions, some scientists were concerned that the lunar regolith would be too light and powdery to support the weight of the lunar lander. Instead of landing on the surface, they were worried that the lander would just sink down into it like a snowbank.
However, landings performed by robotic Surveyor spacecraft showed that the lunar soil was firm enough to support a spacecraft, and astronauts later explained that the surface of the Moon felt very firm beneath their feet. During the Apollo landings, the astronauts often found it necessary to use a hammer to drive a core sampling tool into it.
Once astronauts reached the surface, they reported that the fine moon dust stuck to their spacesuits and then dusted the inside of the lunar lander. The astronauts also claimed that it got into their eyes, making them red; and worse, even got into their lungs, giving them coughs. Lunar dust is very abrasive, and has been noted for its ability to wear down spacesuits and electronics.

The reason for this is because lunar regolith is sharp and jagged. This is due to the fact that the Moon has no atmosphere or flowing water on it, and hence no natural weathering process. When the micro-meteoroids slammed into the surface and created all the particles, there was no process for wearing down its sharp edges.
The term lunar soil is often used interchangeably with “lunar regolith”, but some have argued that the term “soil” is not correct because it is defined as having organic content. However, standard usage among lunar scientists tends to ignore that distinction. “Lunar dust” is also used, but mainly to refer to even finer materials than lunar soil.
As NASA is working on plans to send humans back to the Moon in the coming years, researchers are working to learn the best ways to work with the lunar regolith. Future colonists could mine minerals, water, and even oxygen out of the lunar soil, and use it to manufacture bases with as well.
Mars:
Landers and rovers that have been sent to Mars by NASA, the Russians and the ESA have returned many interesting photographs, showing a landscape that is covered with vast expanses of sand and dust, as well as rocks and boulders.

Compared to lunar regolith, Mars dust is very fine and enough remains suspended in the atmosphere to give the sky a reddish hue. The dust is occasionally picked up in vast planet-wide dust storms, which are quite slow due to the very low density of the atmosphere.
The reason why Martian regolith is so much finer than that found on the Moon is attributed to the flowing water and river valleys that once covered its surface. Mars researchers are currently studying whether or not martian regolith is still being shaped in the present epoch as well.
It is believed that large quantities of water and carbon dioxide ices remain frozen within the regolith, which would be of use if and when manned missions (and even colonization efforts) take place in the coming decades.
Mars moon of Deimos is also covered by a layer of regolith that is estimated to be 50 meters (160 feet) thick. Images provided by the Viking 2 orbiter confirmed its presence from a height of 30 km (19 miles) above the moon’s surface.
Asteroids and Outer Solar System:
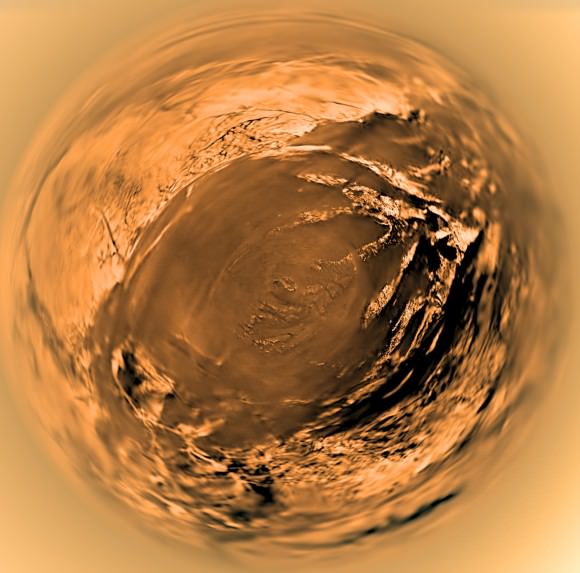
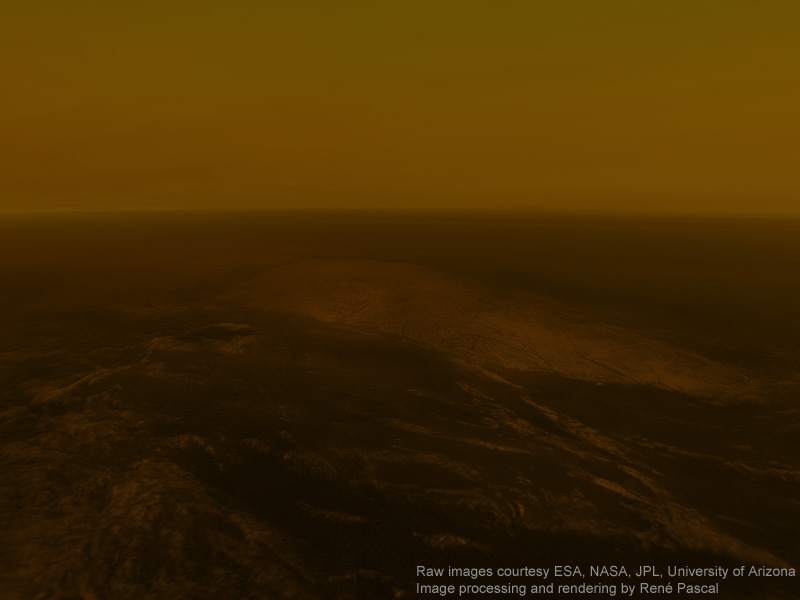
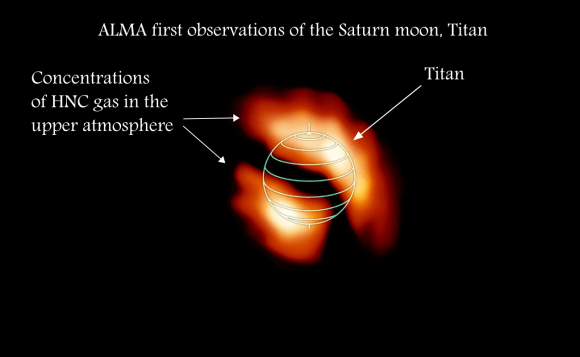
The only other planet in our Solar System that is known to have regolith is Titan, Saturn’s largest moon. The surface is known for its extensive fields of dunes, though the precise origin of them are not known. Some scientists have suggested that they may be small fragments of water ice eroded by Titan’s liquid methane, or possibly particulate organic matter that formed in Titan’s atmosphere and rained down on the surface.
Another possibility is that a series of powerful wind reversals, which occur twice during a single Saturn year (30 Earth years), are responsible for forming these dunes, which measure several hundred meters high and stretch across hundreds of kilometers. Currently, Earth scientists are still not certain what Titan’s regolith is composed of.
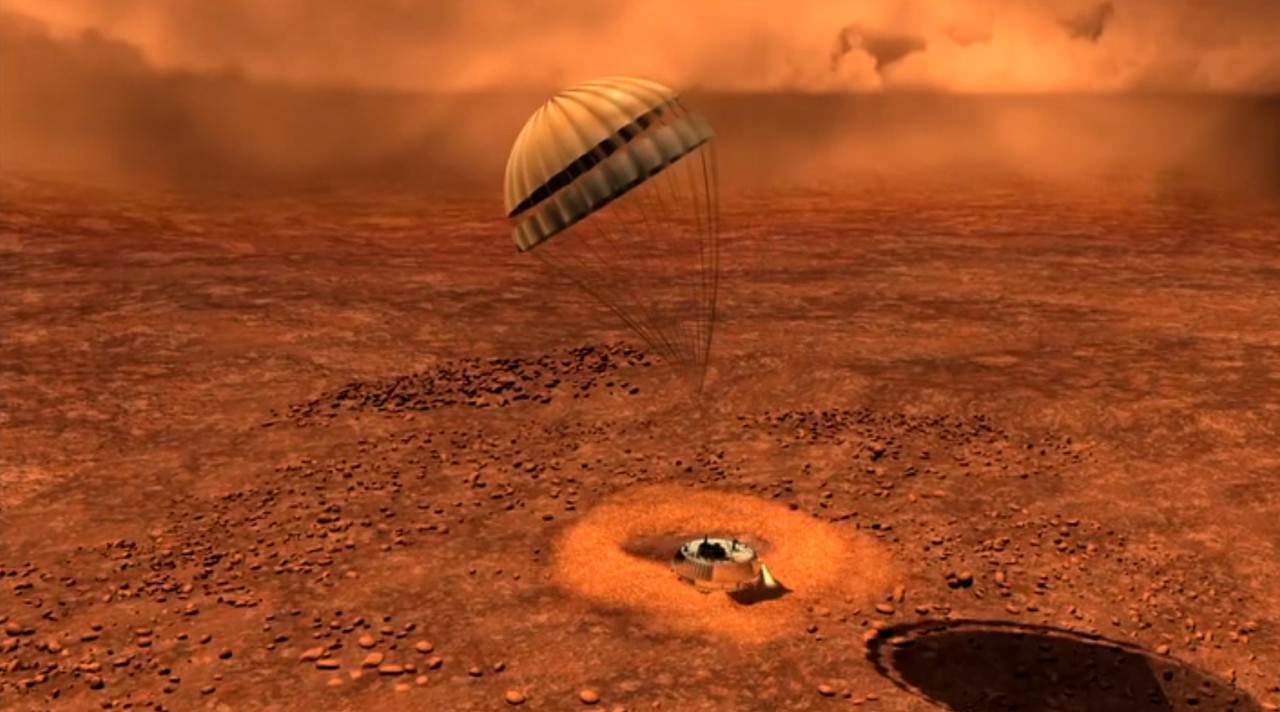
Data returned by the Huygens Probe’s penetrometer indicated that the surface may be clay-like, but long-term analysis of the data has suggested that it may be composed of sand-like ice grains. The images taken by the probe upon landing on the moon’s surface show a flat plain covered in rounded pebbles, which may be made of water ice, and suggest the action of moving fluids on them.
Asteroids have been observed to have regolith on their surfaces as well. These are the result of meteoriod impacts that have taken place over the course of millions of years, pulverizing their surfaces and creating dust and tiny particles that are carried within the craters.

NASA’s NEAR Shoemaker spacecraft produced evidence of regolith on the surface of the asteroid 433 Eros, which remains the best images of asteroid regolith to date. Additional evidence has been provided by JAXA’s Hayabusa mission, which returned clear images of regolith on an asteroid that was thought to be too small to hold onto it.
Images provided by the Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared Remote Imaging System (OSIRIS) cameras on board the Rosetta Spacecraft confirmed that the asteroid 21 Lutetia has a layer of regolith near its north pole, which was seen to flow in major landslides associated with variations in the asteriod’s albedo.
To break it down succinctly, wherever there is rock, there is likely to be regolith. Whether it is the product of wind or flowing water, or the presence of meteors impacting the surface, good old fashioned “dirt” can be found just about anywhere in our Solar System; and most likely, in the universe beyond…
We’ve done several articles about the Moon’s regolith here on Universe Today. Here’s a way astronauts might be able to extract water from lunar regolith with simple kitchen appliances, and an article about NASA’s search for a lunar digger.
Want to buy some lunar regolith simulant? Here’s a site that lets you buy it. Do you want to be a Moon miner? There’s lots of good metal in that lunar regolith.
You can listen to a very interesting podcast about the formation of the Moon from Astronomy Cast, Episode 17: Where Did the Moon Come From?
Reference:
NASA