In a significant step towards restoring America’s indigenous human spaceflight capability and fostering the new era of commercial space fight, NASA has awarded a slew of additional astronaut taxi flights from Boeing and SpaceX to carry crews to the International Space Station (ISS).
NASA’s new announcement entails awarding an additional four crew rotation missions each to commercial partners, Boeing and SpaceX, on top of the two demonstration fights previously awarded to each company under the agency’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) initiative, in a Jan. 3 statement.
However, the newly awarded crew rotation missions will only take place after NASA has certified that each provider is fully and satisfactorily meeting NASA’s long list of stringent safety and reliability requirements to ensure the private missions will be safe to fly with humans aboard from NASA and its partner entities.
And NASA officials were careful to point out that these orders “do not include payments at this time.”
In other words, NASA will pay for performance, not mere promises of performance – because human lives are on the line.
“They fall under the current Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contracts, and bring the total number of missions awarded to each provider to six,” NASA officials announced.

The goal of the CCP program is to ensure robust and reliable crew transportation to the International Space Station in this decade and beyond – using American rockets and capsules launching from American soil.
A further goal is to end America’s sole reliance on Russia for transporting American astronauts to and from the space station using Russia’s Soyuz crew capsules.
Since the forced retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle’s in July 2011, NASA astronauts and its partners have been 100% dependent on Russia for rides to space – currently to the tune of over $80 million per seat.
By awarding these new contracts, Boeing and SpaceX should be able to plan further ahead in the future, order long lead time hardware and software, and ultimately cut costs through economy of scale.
“Awarding these missions now will provide greater stability for the future space station crew rotation schedule, as well as reduce schedule and financial uncertainty for our providers,” said Phil McAlister, director, NASA’s Commercial Spaceflight Development Division, in a statement.
“The ability to turn on missions as needed to meet the needs of the space station program is an important aspect of the Commercial Crew Program.”
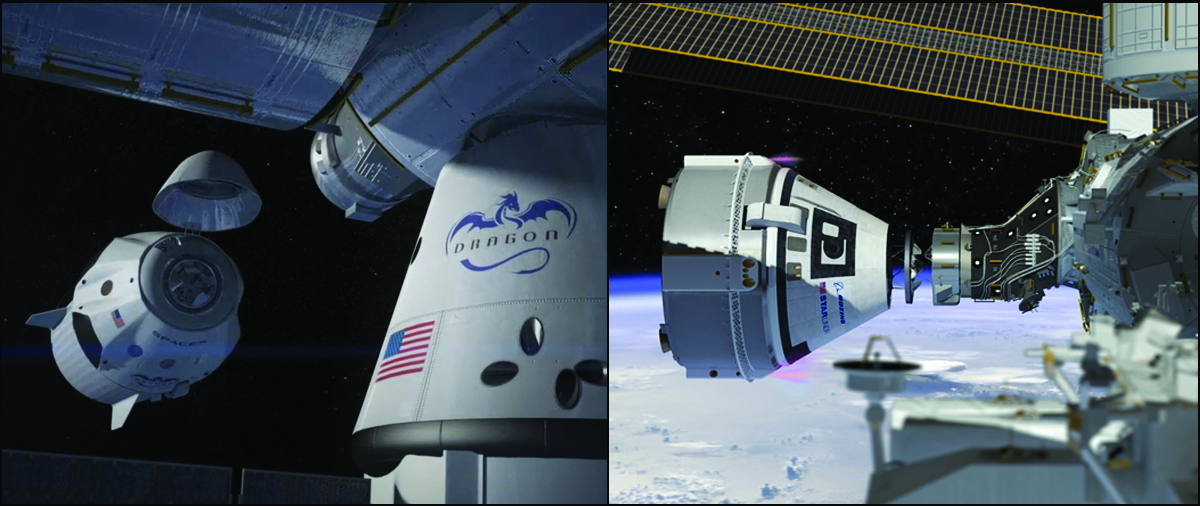
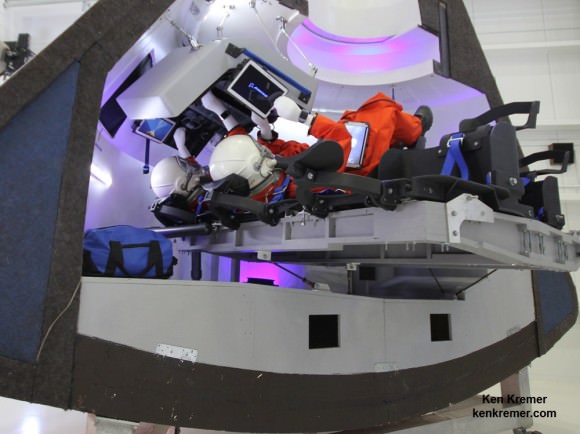
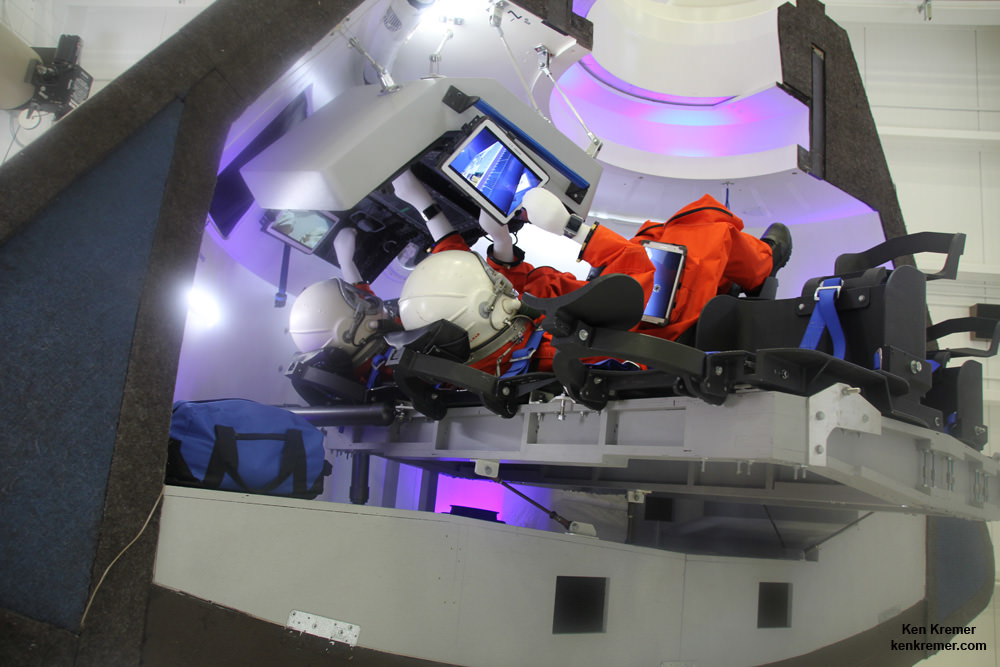
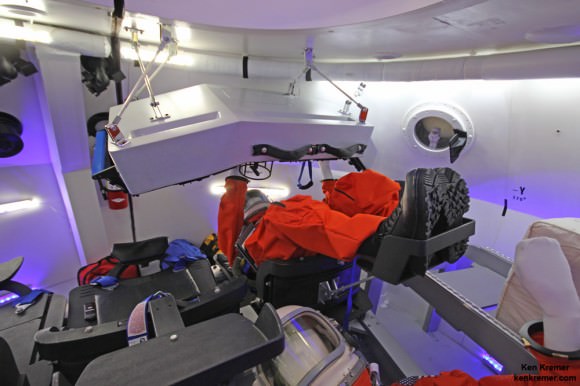
Each spaceship can deliver a crew of four and 220 pounds of cargo, experiments and gear to the million pound science laboratory orbiting Earth at an altitude of appox. 250 miles (400 km). They also serve as a lifeboat in case the occupants need to evacuate the station for any reason.

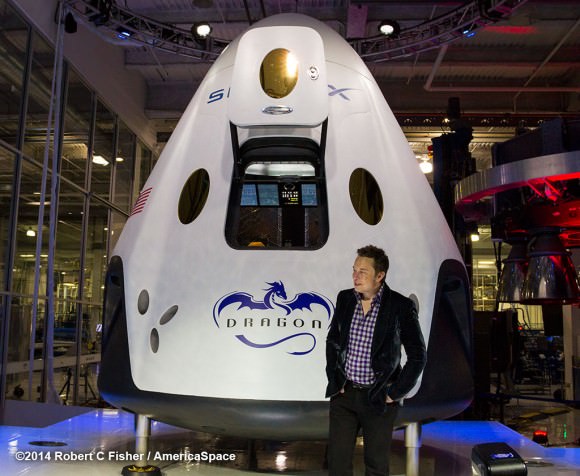
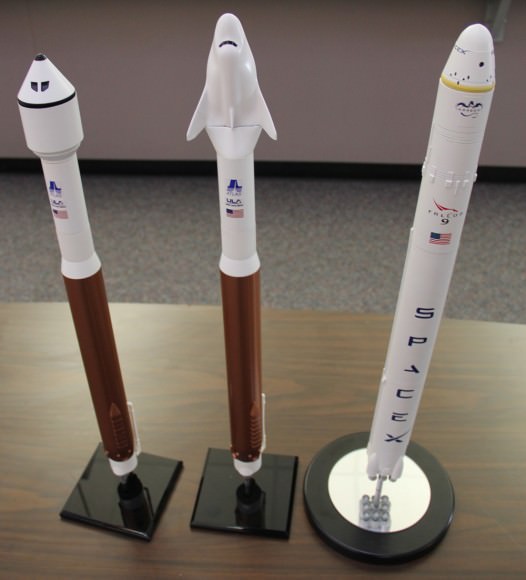
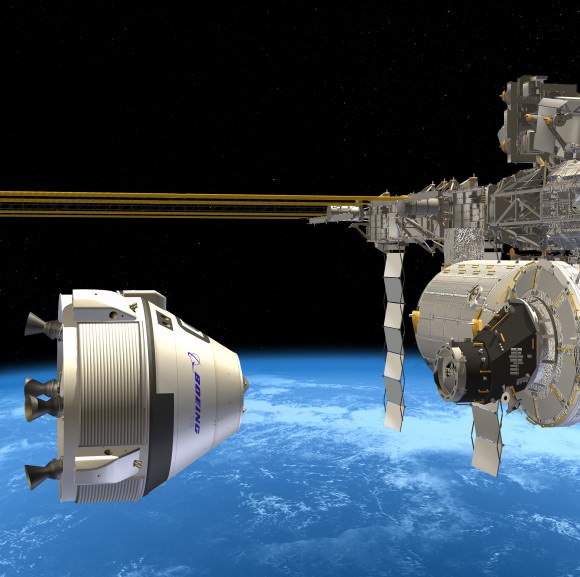
Boeing and SpaceX were awarded contracts by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden in September 2014 worth $6.8 Billion to complete the development and manufacture of the privately developed Starliner CST-100 and Crew Dragon astronaut transporters, respectively, under the agency’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) program and NASA’s Launch America initiative.
The CCP initiative was started back in 2010 under the Obama Administration to replace NASA’s outgoing space shuttle orbiters.
However, launch targets for first fight by the Boeing Starliner and SpaceX Crew Dragon have been repeatedly postponed from 2015 to 2018 – in the latest iteration – due to severe and extremely shortsighted funding cutbacks by Congress year after year.
Thus NASA has been forced to order several years more additional Soyuz taxi seat flights and send hundreds and hundreds of millions of more US dollars to Putin’s Russia – thanks to the US Congress.
Congress enjoys whining about Russia on one hand, while at the same time they put America’s aerospace workers on the unemployment line by curtailing NASA’s ability to move forward and put Americans back to work. There is ample bipartisan blame for this sad state of affairs.
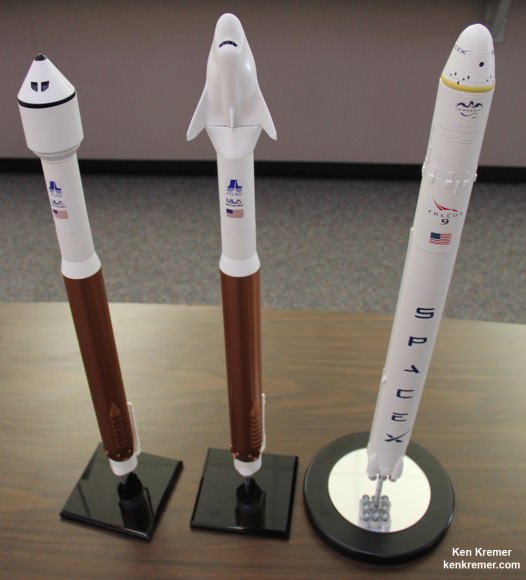
The Boeing Starliner and SpaceX Crew Dragon are both Made in America.
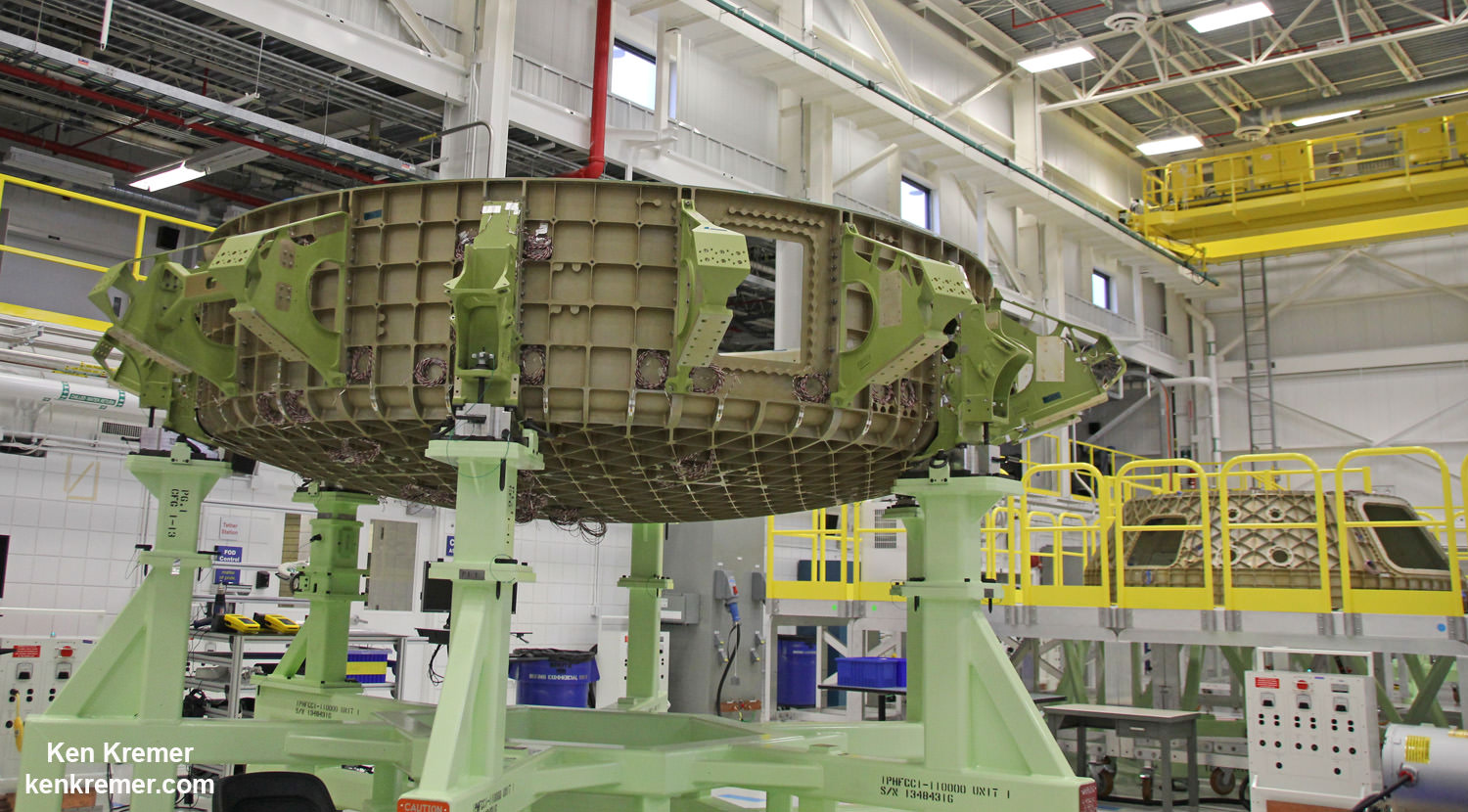
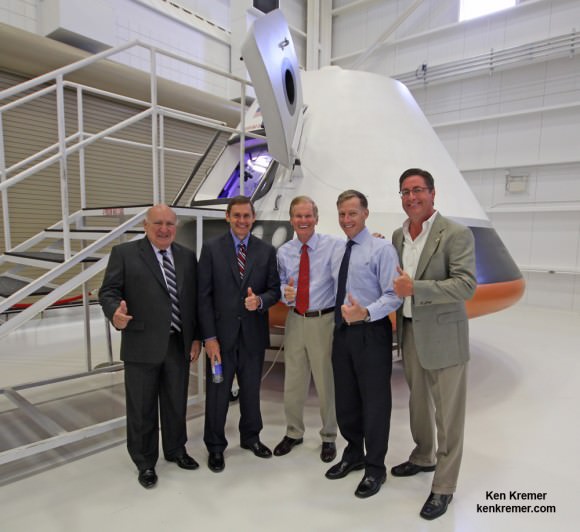
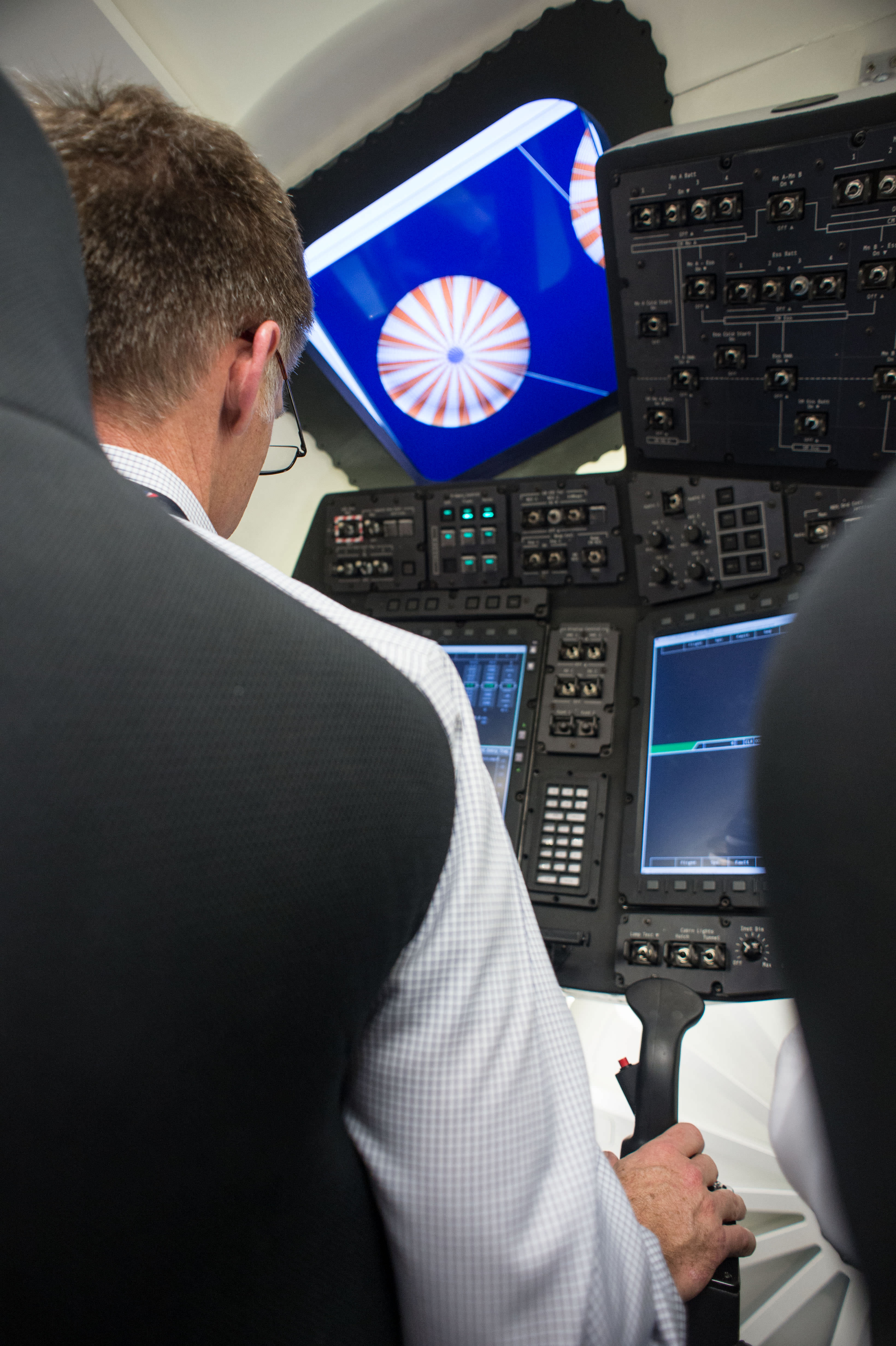
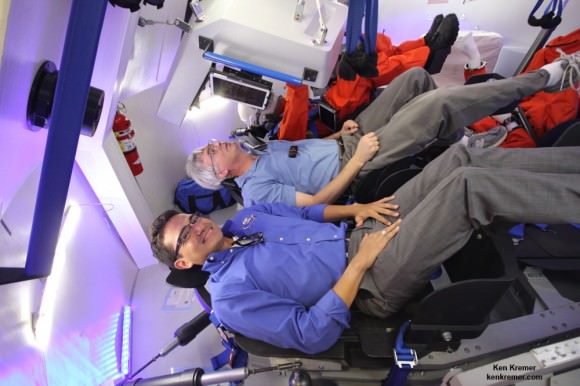
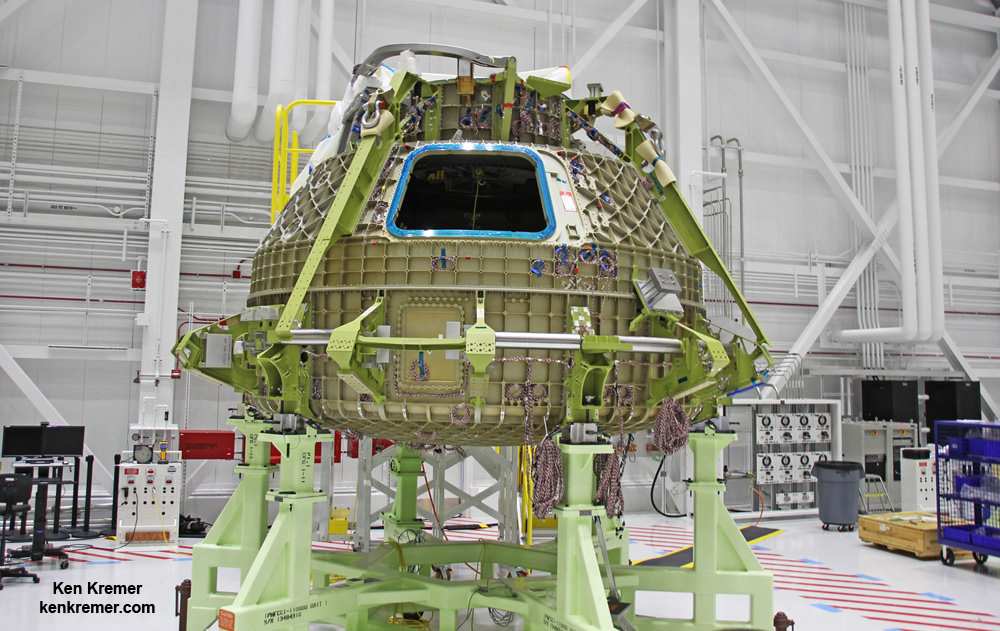
The Boeing Starliner is being manufactured at the Kennedy Space Center inside a repurposed and renovated former Space Shuttle Orbiter Processing hangar. This author has visited the C3PF facility periodically to observe and assess Boeing’s progress.
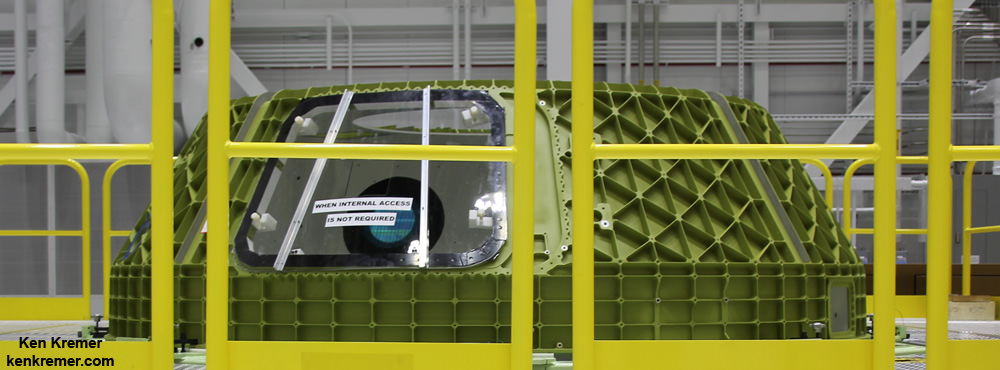
Indeed, Boeing has already started construction of the first flight worthy Starliner – currently dubbed Spacecraft 1- at KSC this past summer 2016.
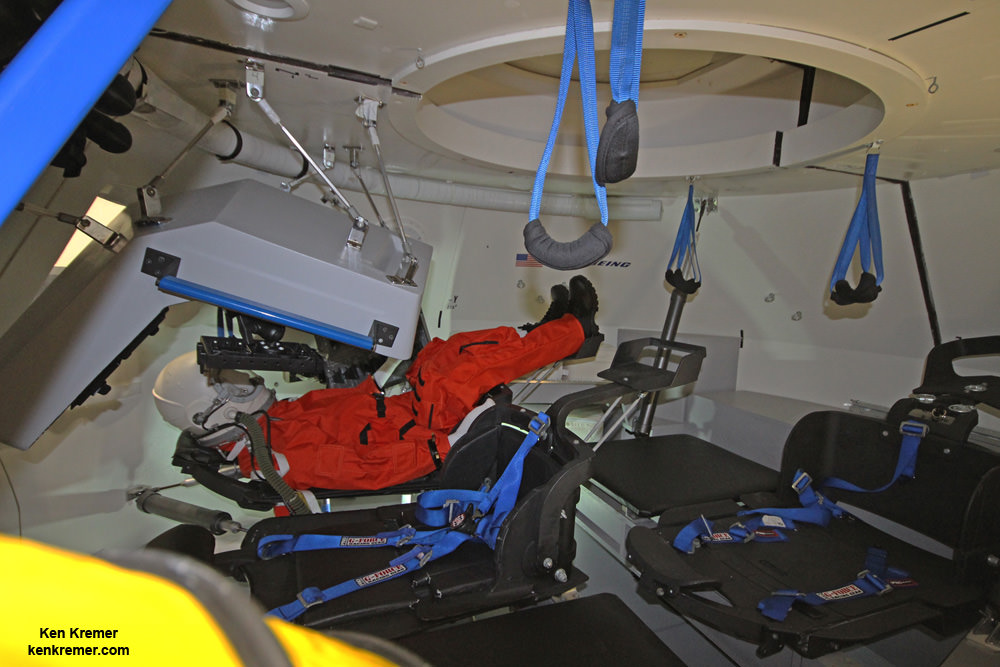

The SpaceX Crew Dragon is being manufactured at company headquarters in Hawthorne, California.
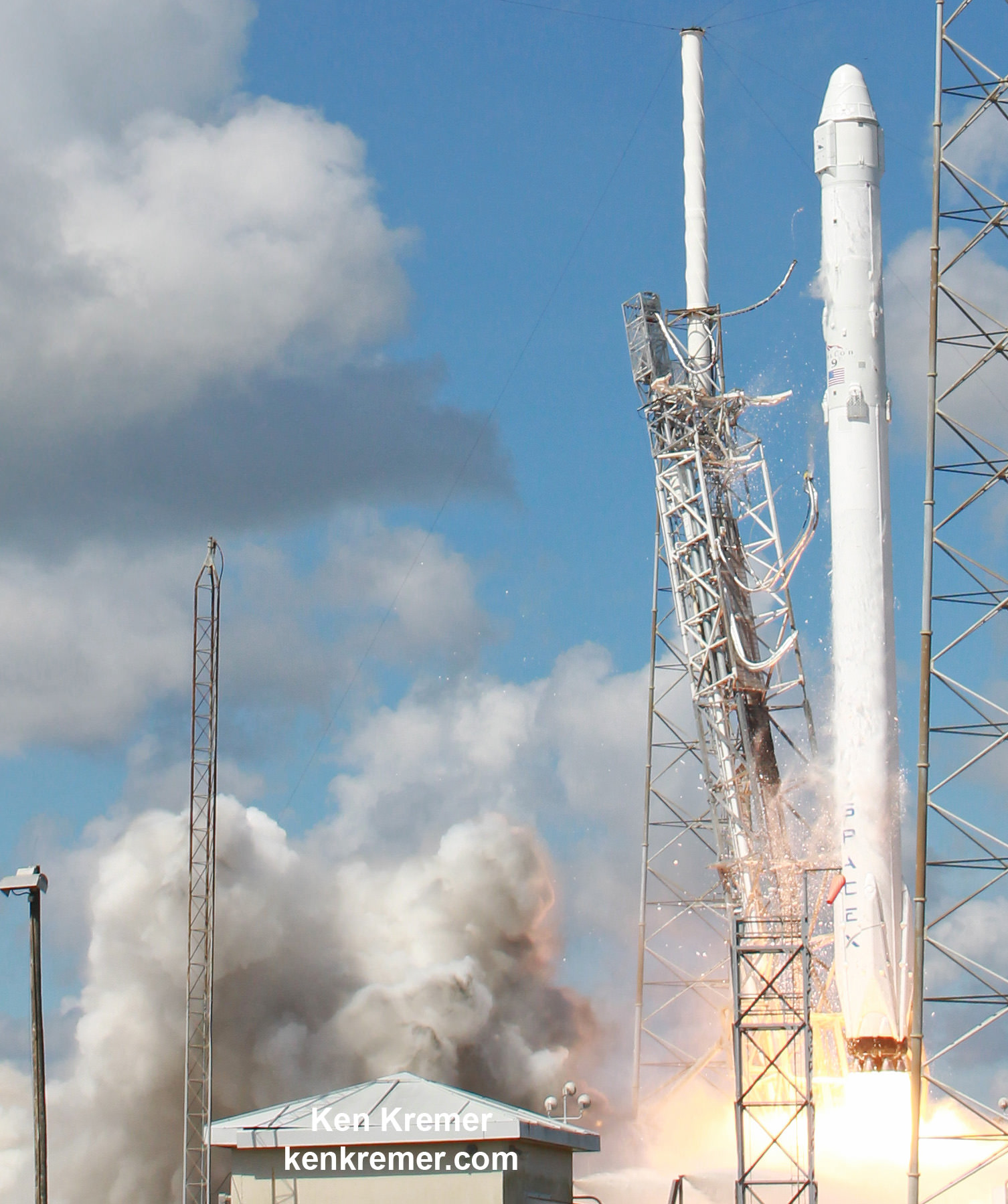
Blastoff of the first SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft on its first unmanned test flight, or Demonstration Mission 1, is postponed from May 2017 to November 2017, according to the latest quarterly revision just released by NASA last month in Dec. 2016.
Liftoff of the first piloted Crew Dragon with a pair of NASA astronauts strapped in has slipped from August 2017 to May 2018.
Launch of the first uncrewed Boeing Starliner, known as an Orbital Flight Test, has slipped to June 2018.
Liftoff of the first crewed Starliner is now slated for August 2018, possibly several months after SpaceX. But the schedules keep changing so it’s anyone’s guess as to when these commercial crew launches will actually occur.
Boeing’s uncrewed flight test, known as an Orbital Flight Test, is currently scheduled for June 2018 and its crewed flight test currently is planned for August 2018.
“Once the flight tests are complete and NASA certifies the providers for flight, the post-certification missions to the space station can begin,” NASA official said.

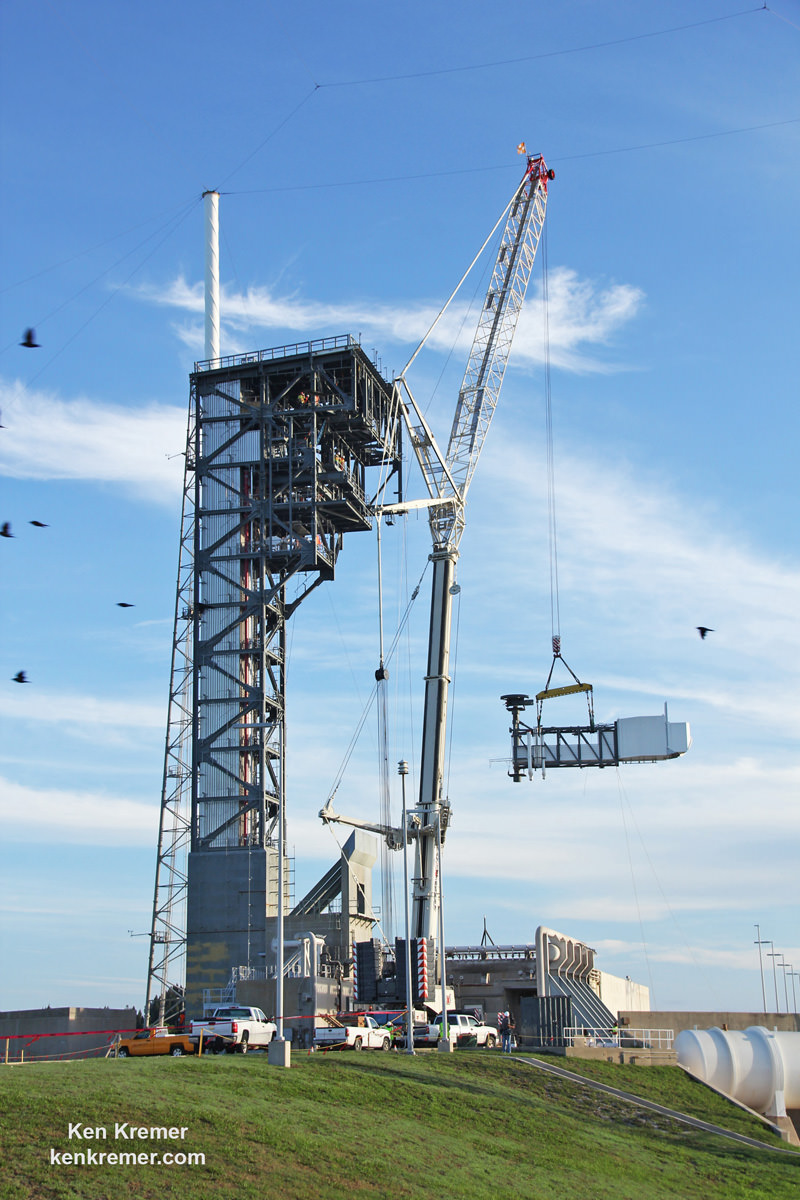
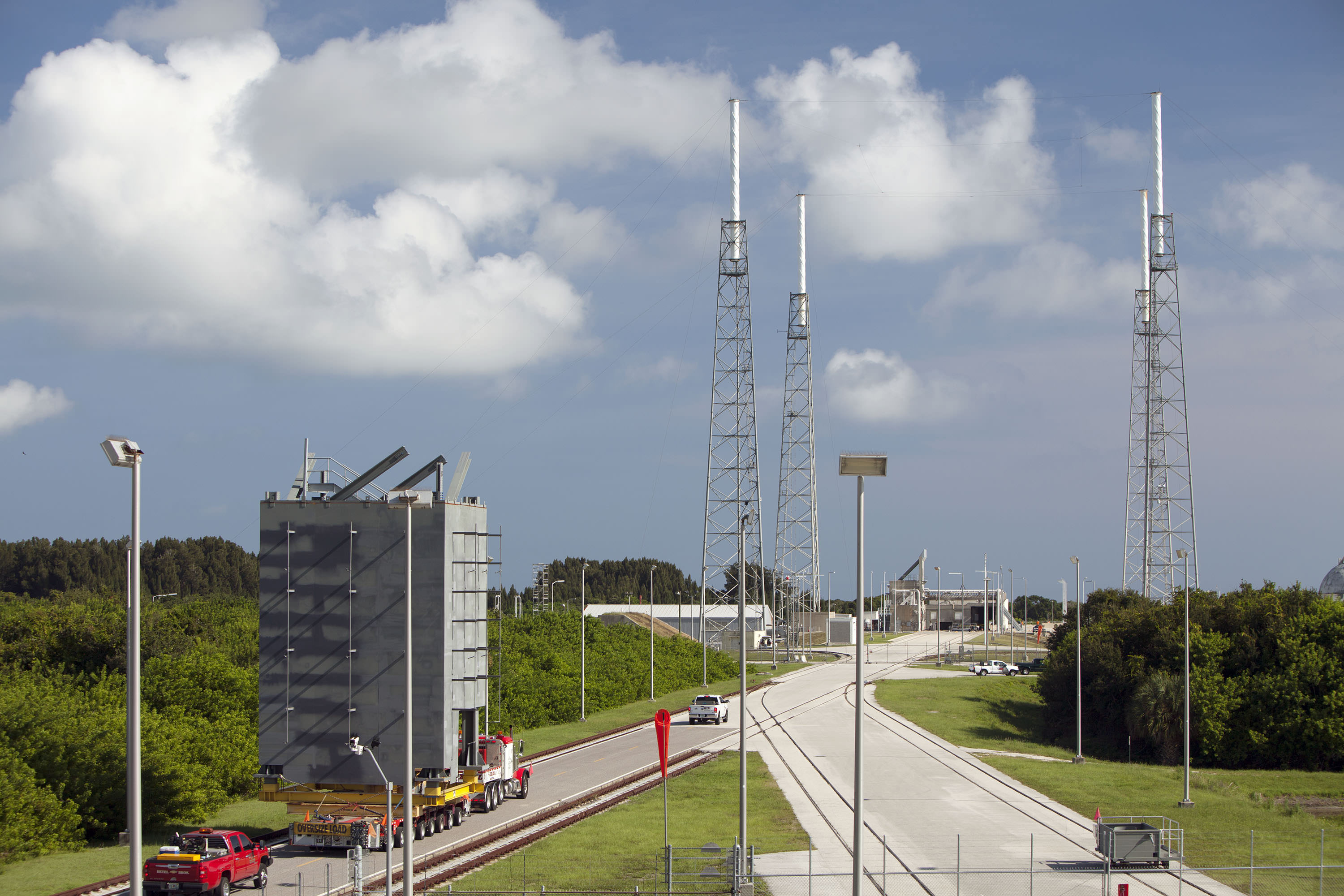
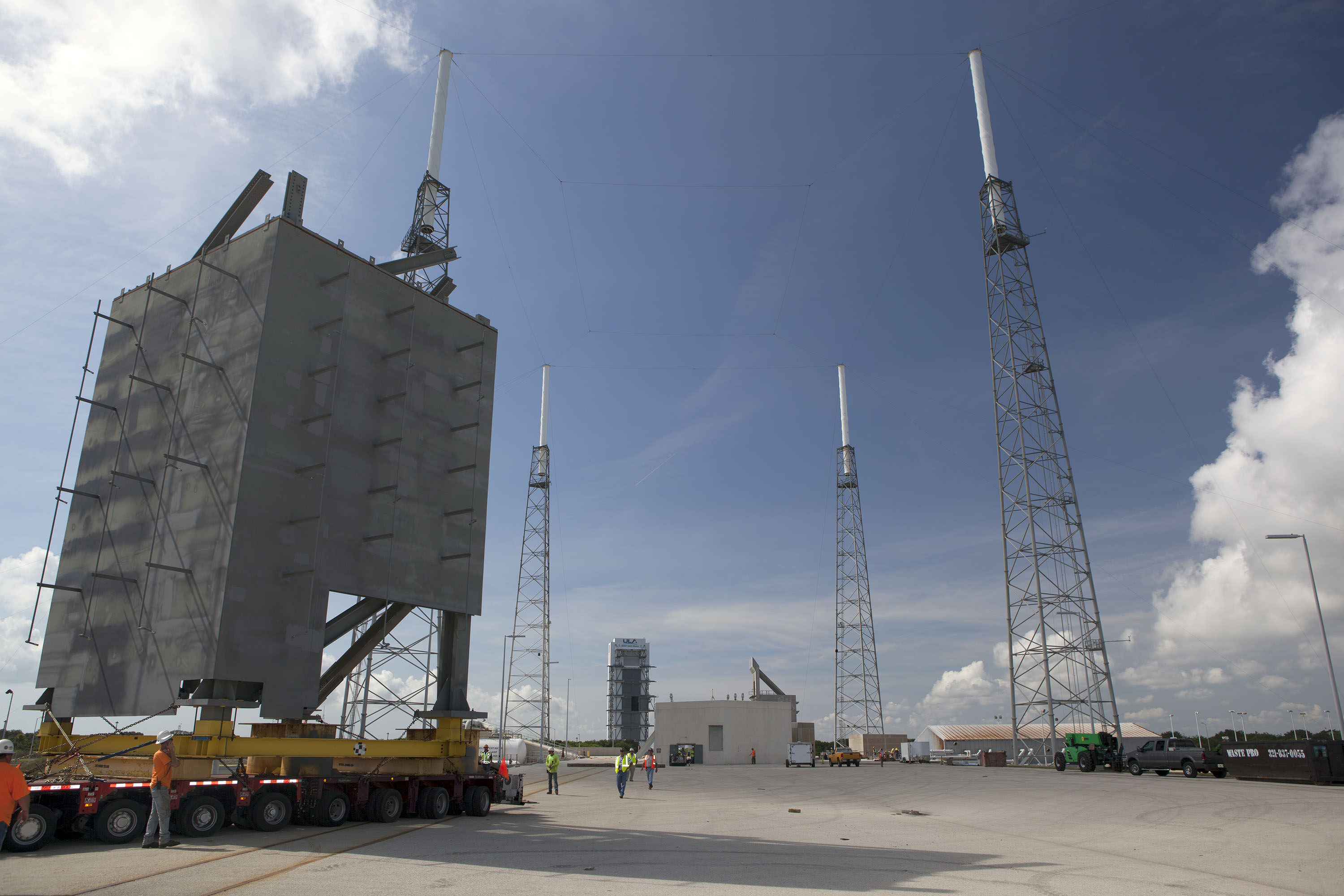
Meanwhile the rockets and launch pads for Boeing and SpaceX are also being developed, modified and refurbished as warranted.
The launch pads for both are located on Florida’s Space Coast.
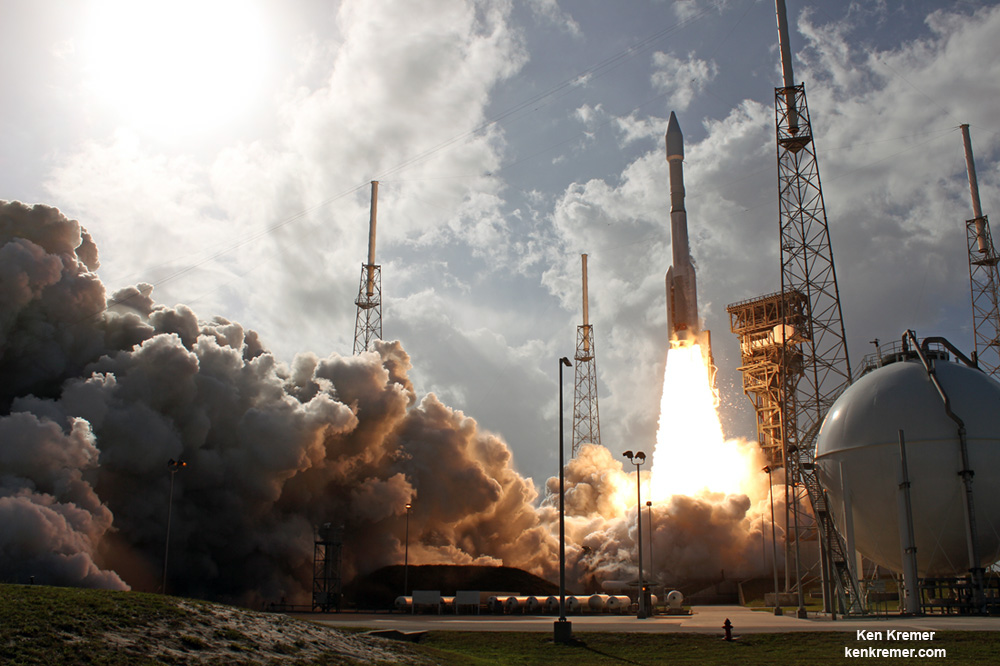
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
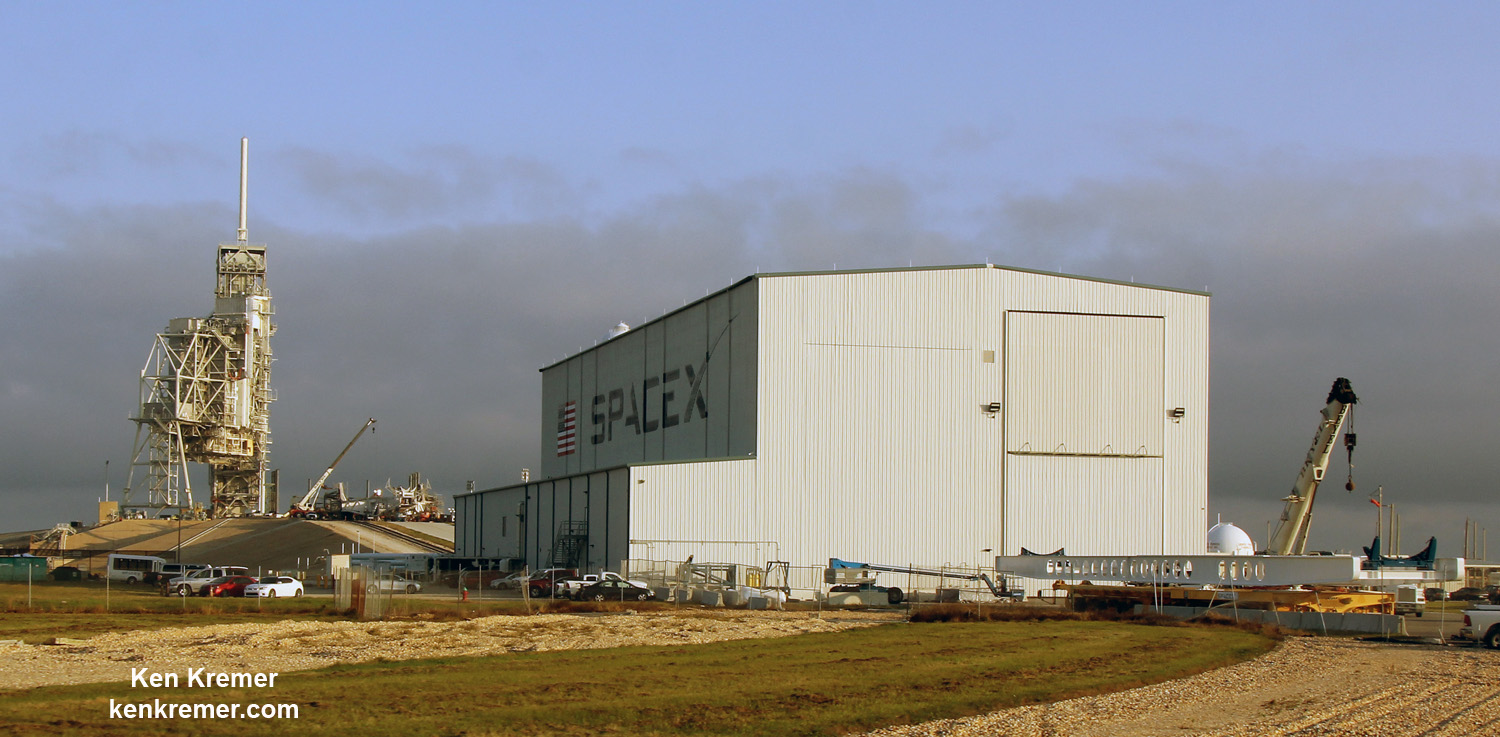
The SpaceX Crew Dragon will launch on the company’s own Falcon 9 from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.