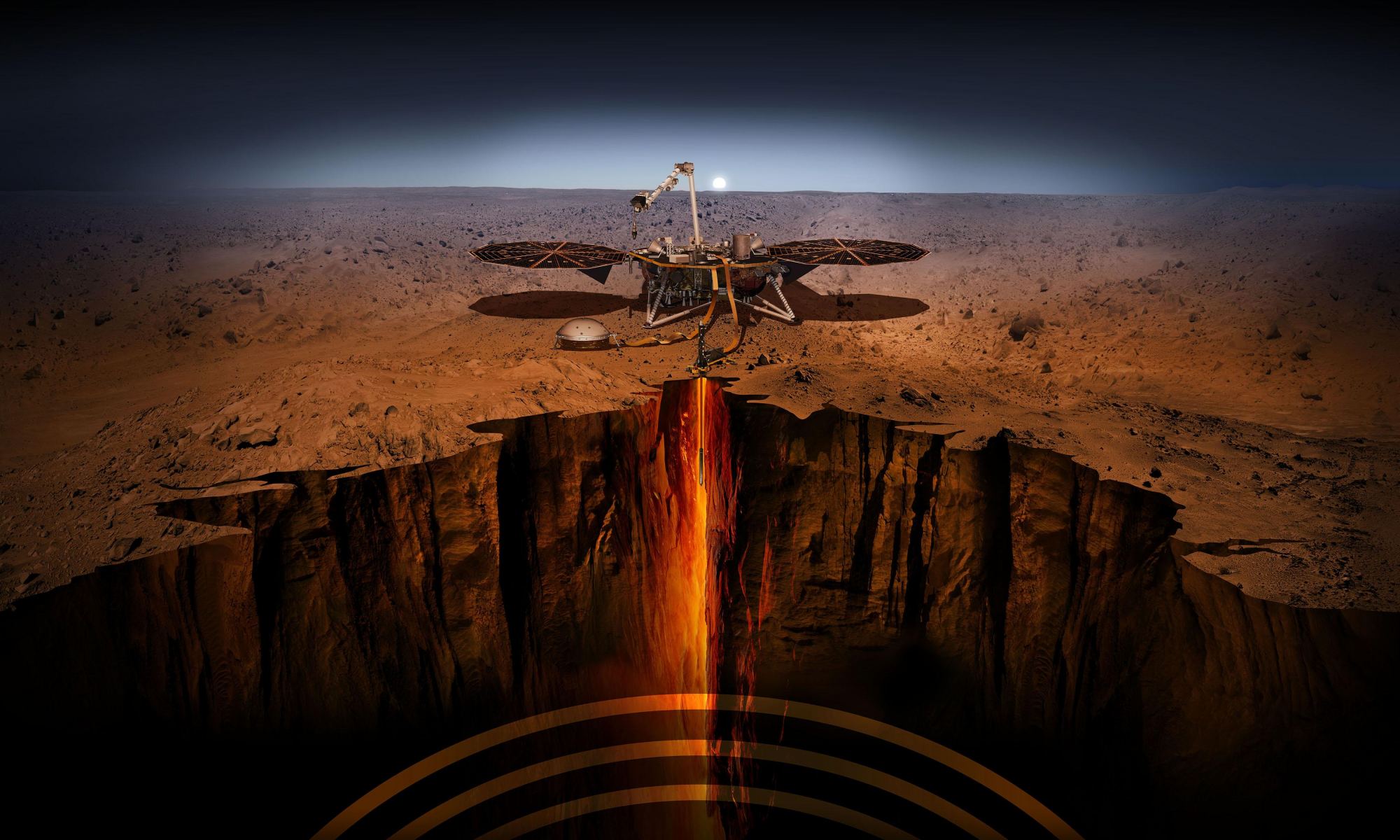
The InSight lander has been on Mars, gathering data for a thousand days now, working to give us a better understanding of the planet’s interior. It’s at Elysium Planitia, the second largest volcanic region on Mars. A newly-published paper based on seismic data from the lander shows something unexpected underground: a layer of sediment sandwiched between layers of lava flows.
Continue reading “InSight Peers Deep Below the Surface on Mars”InSight has Mapped out the Interior of Mars, Revealing the Sizes of its Crust, Mantle, and Core

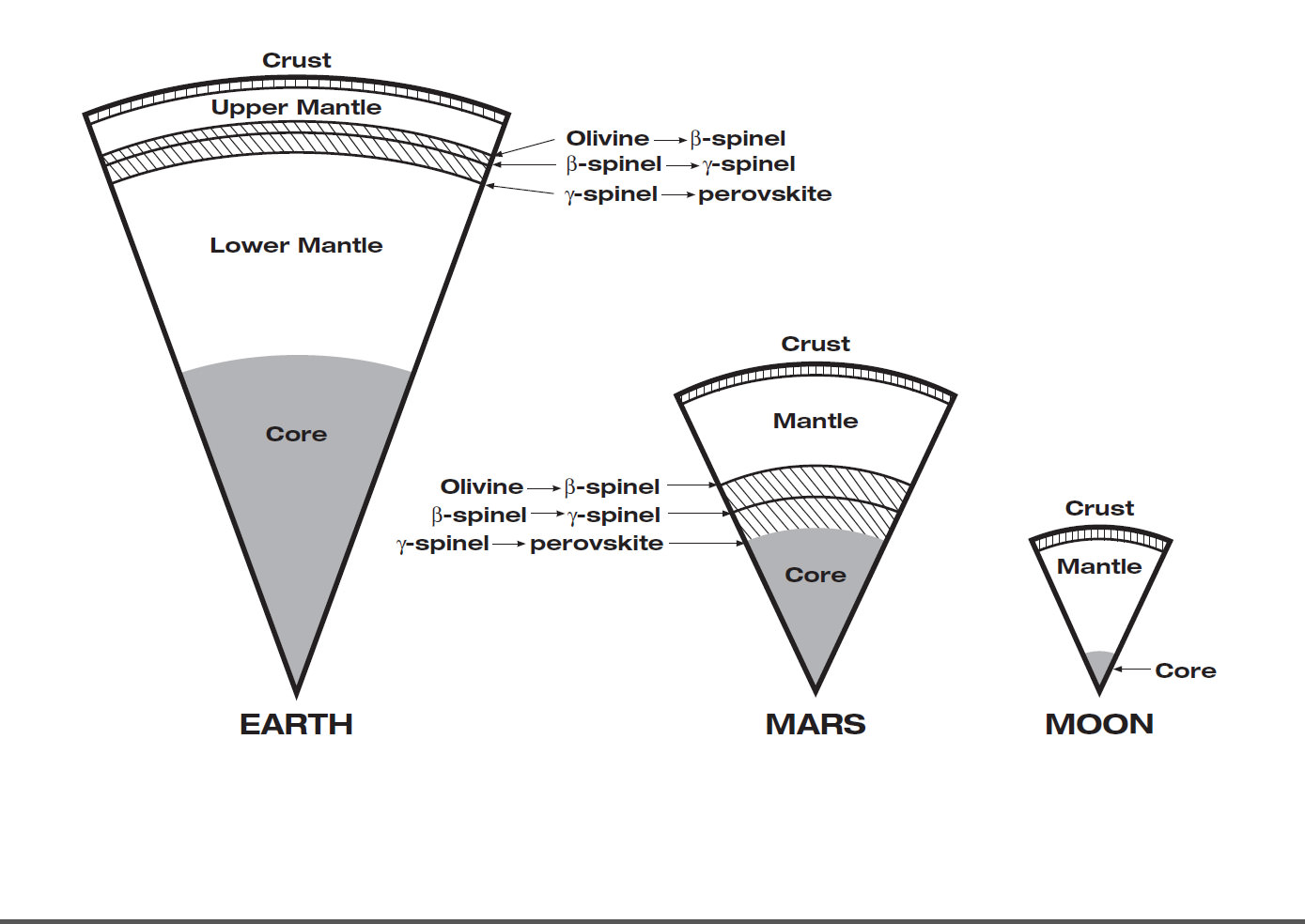
In May of 2018, NASA’s Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy, and Heat Transport (InSight) landed on the Martian surface. This mission is the first of its kind, as all previous orbiters, landers, and rovers focused on studying the surface and atmosphere of Mars. In contrast, InSight was tasked with characterizing Mars’ interior structure and measuring the core, mantle, and crust by reading its seismic activity (aka. “marsquakes”).
The purpose of this is to learn more about the geological evolution of Mars since it formed 4.5 billion years ago, which will also provide insight into the formation of Earth. According to three recently published papers, the data obtained by InSight has led to new analyses on the depth and composition of Mars’ crust, mantle and confirmed the theory that the planet’s inner core is molten.
Continue reading “InSight has Mapped out the Interior of Mars, Revealing the Sizes of its Crust, Mantle, and Core”InSight Has Already Detected 21 Marsquakes

The SEIS (Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure) instrument on NASA’s InSight lander has sensed 21 Marsquakes since it was deployed on December 19th, 2018. It actually sensed over 100 events to date, but only 21 of them have been identified as Marsquakes. SEIS is extremely sensitive so mission scientists expected these results.
SEIS is a key part of InSight, NASA’s mission to understand the interior of Mars. Along with other instruments, it’ll help scientists understand what’s going on inside Mars.
Continue reading “InSight Has Already Detected 21 Marsquakes”InSight Just Detected its First “Marsquake”
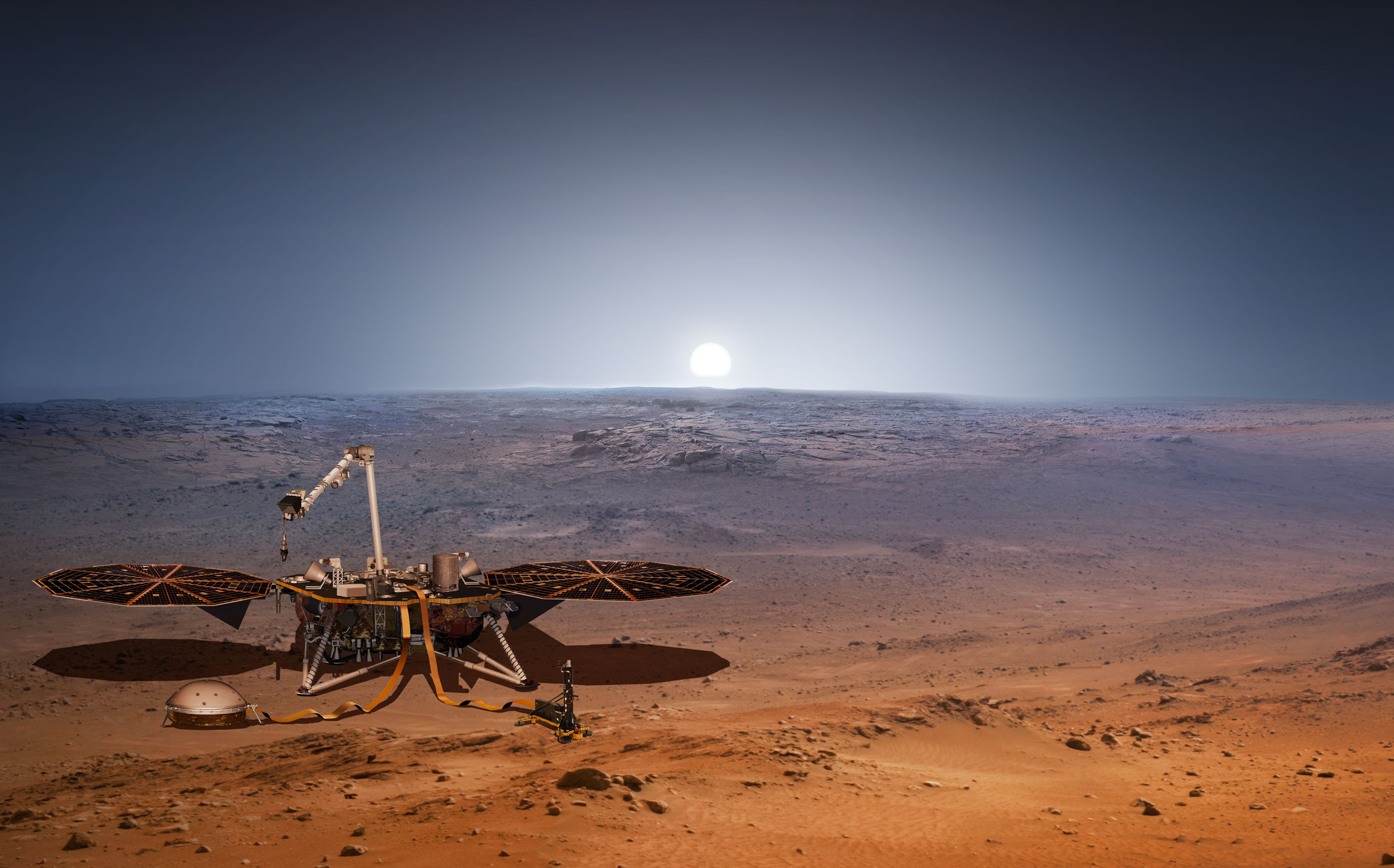

In November of 2018, the NASA Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) lander set down on Mars. Shortly thereafter, it began preparing for its science operations, which would consist of studying Mars’ seismology and its heat flow for the sake of learning how this planet – and all the other terrestrial planets in the Solar System (like Earth) – formed and evolved over time.
With science operations well-underway, InSight has been “listening” to Mars to see what it can learn about its interior structure and composition. A few weeks ago, mission controllers discovered that the lander’s Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) instrument detected its strongest seismic signal (aka. a “marsquake”) to date. This faint quake could reveal much about the Red Planet and how it came to be.
Continue reading “InSight Just Detected its First “Marsquake””InSight Just Put a Windshield Over its Seismometer
NASA’s InSight lander arrived on Mars on November 26th, 2018. Since then, it’s been busying itself studying its landing spot, and taking its time to carefully place its instruments. It spent several weeks testing the seismometer and adjusting it, and now it’s placed the domed, protective shield over the instrument.
Continue reading “InSight Just Put a Windshield Over its Seismometer”InSight Just Placed its Seismometer onto the Surface of Mars to Listen for Marsquakes
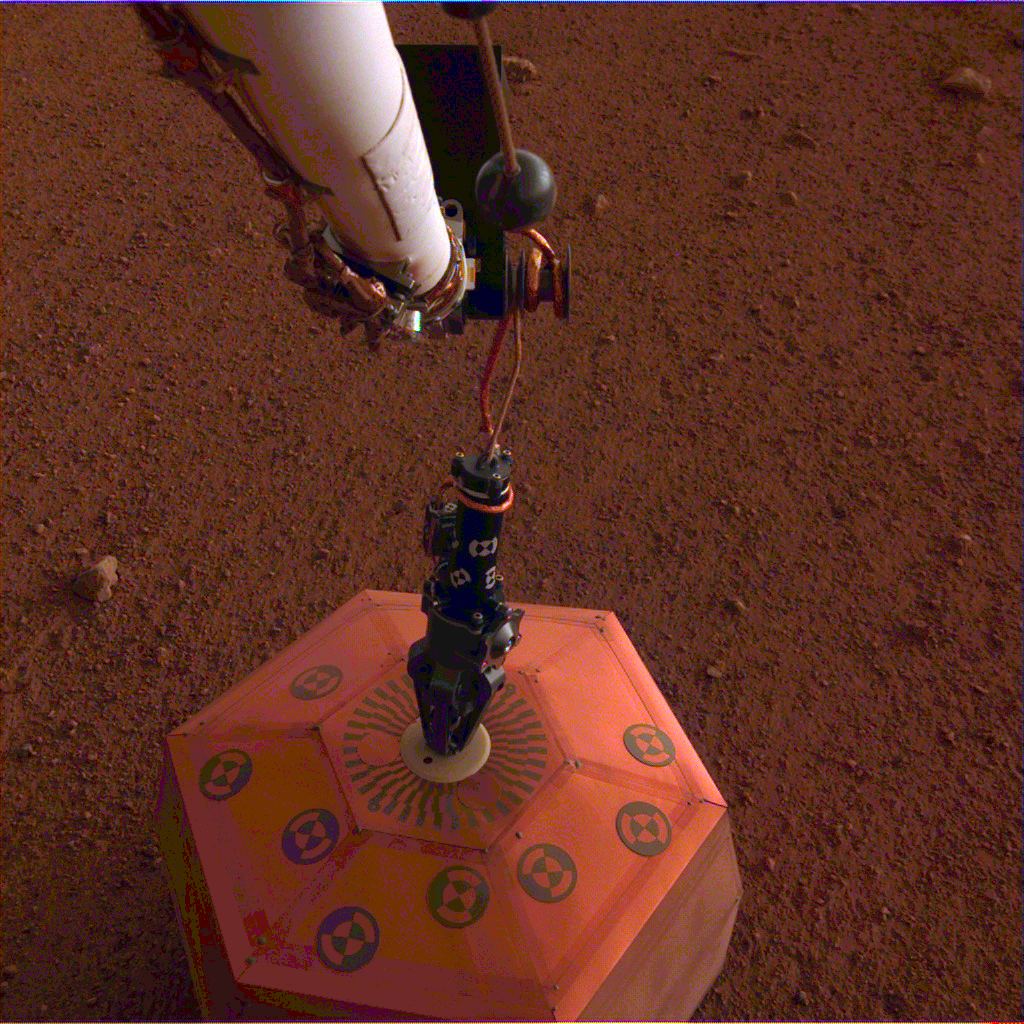
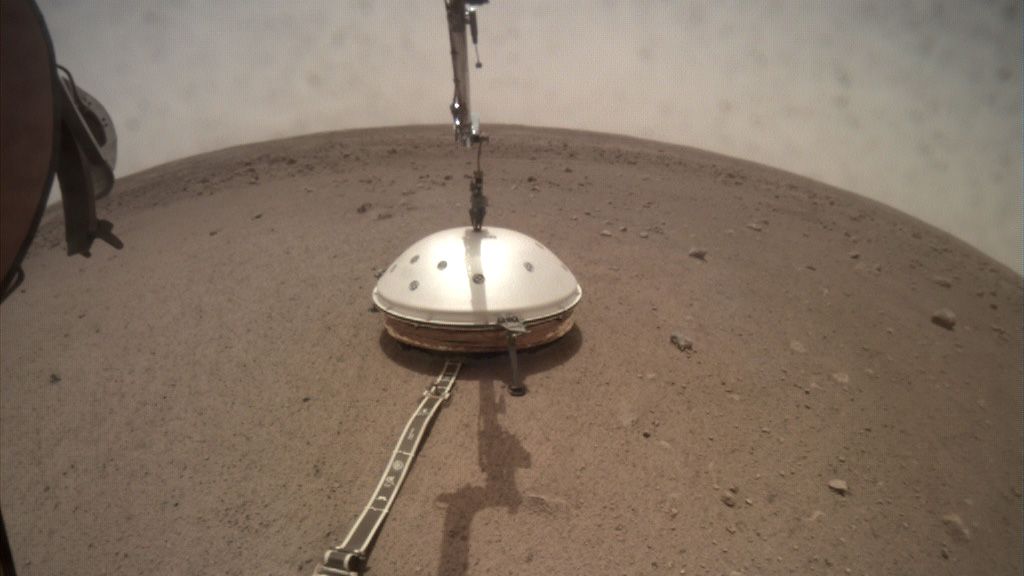
NASA’s InSight lander has deployed its first instrument on the surface of Mars. On December 19th, the stationary lander used its robotic arm to deploy the SEIS (Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure), marking the first time a seismometer has been placed on the surface of another planet. This is a milestone for the mission, and one that comes well ahead of schedule.
InSight landed on Mars at Elysium Planitia on November 26th. Since then, it’s been checking out its immediate surroundings with its cameras to find the perfect spot to deploy the seismometer, and its other deployable instrument, the HP3 (Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package.) Mission planners allocated several weeks for instrument site selection, so this is well ahead of schedule.
Continue reading “InSight Just Placed its Seismometer onto the Surface of Mars to Listen for Marsquakes”
InSight Uses its Seismometer to “Hear” the Sound of Wind on Mars

Just two weeks ago, NASA’s Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) lander touched down on the surface of Mars. In the hours that followed, mission controllers at NASA-JPL received confirmation that the lander had deployed its solar arrays and was commencing scientific operations.
And in what was sure to be a treat for space exploration enthusiasts, the lander recently provided the first ever experience of what it “sounds” like to be on Mars. The sounds were caught by an air pressure sensor inside the lander and the seismometer instrument that is awaiting deployment to the surface. Together, they recorded the low rumble caused by Martian winds that blew around the lander’s location on Dec. 1st.
Continue reading “InSight Uses its Seismometer to “Hear” the Sound of Wind on Mars”
NASA’s Insight Lander Spreads Its Solar Wings. It’ll Fly To Mars In May, 2018
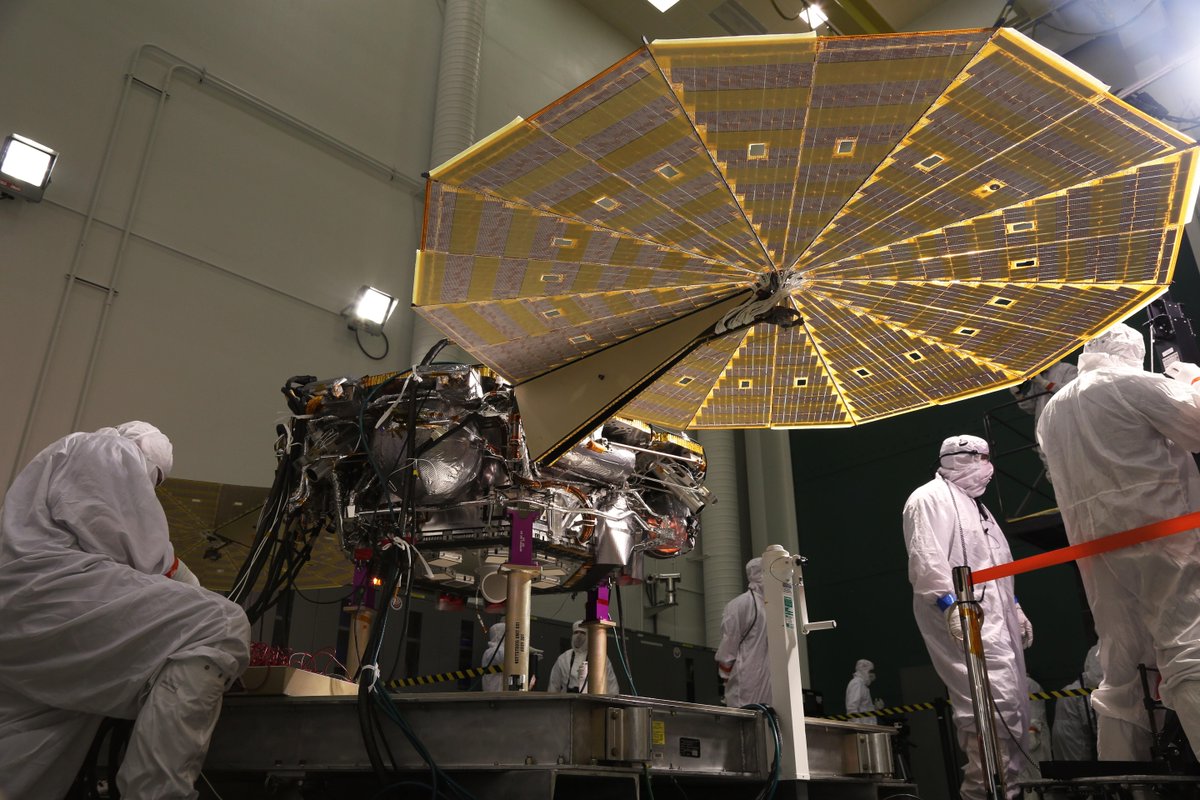

May 2018 is the launch window for NASA’s next mission to Mars, the InSight Lander. InSight is the next member of what could be called a fleet of human vehicles destined for Mars. But rather than working on the question of Martian habitability or suitability for life, InSight will try to understand the deeper structure of Mars.
InSight stands for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport. InSight will be the first robotic explorer to visit Mars and study the red planet’s deep interior. The work InSight does should answer questions about the formation of Mars, and those answers may apply to the history of the other rocky planets in the Solar System. The lander, (InSight is not a rover) will also measure meteorite impacts and tectonic activity happening on Mars currently.
This video helps explain why Mars is a good candidate to answer questions about how all our rocky planets formed, not just Mars itself.
InSight was conceived as part of NASA’s Discovery Program, which are missions focused on important questions all related to the “content, origin, and evolution of the solar system and the potential for life elsewhere”, according to NASA. Understanding how our Solar System and its planets formed is a key part of the Discovery Program, and is the question InSight was built to answer.

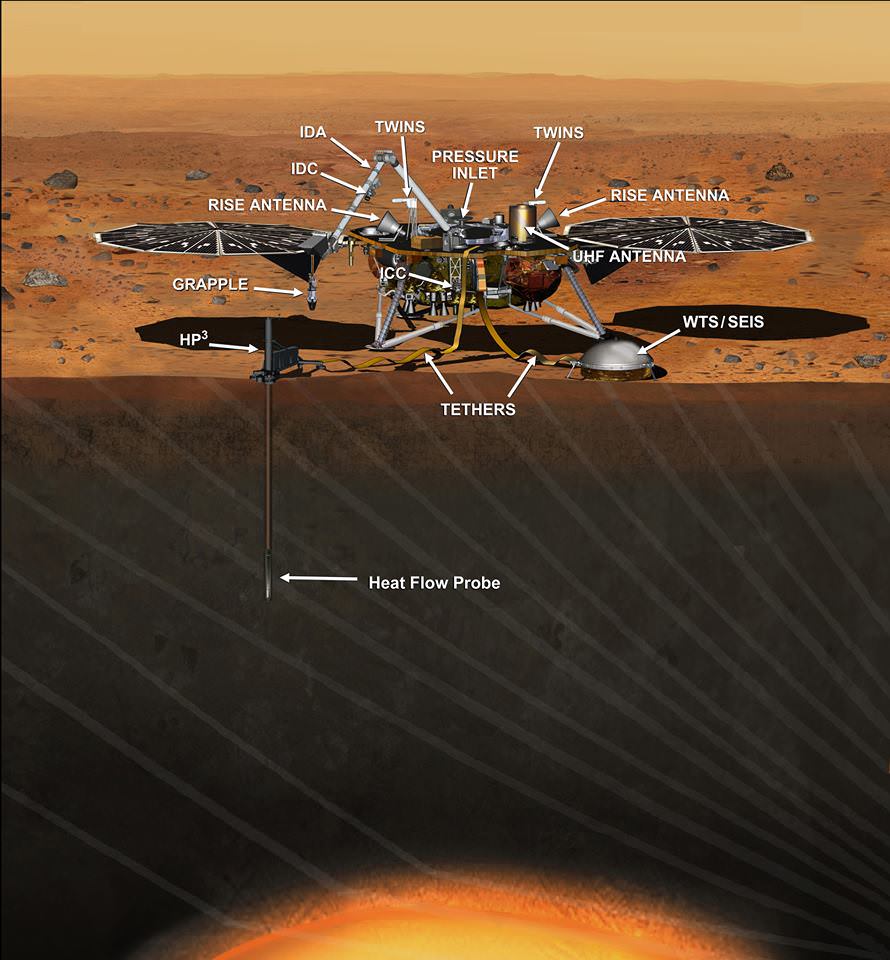
To do its work, InSight will deploy three instruments: SEIS, HP³, and RISE.
SEIS
This is InSight’s seismic instrument, designed to take the Martian pulse. It stands for Seismic Experiment for Internal Structure.
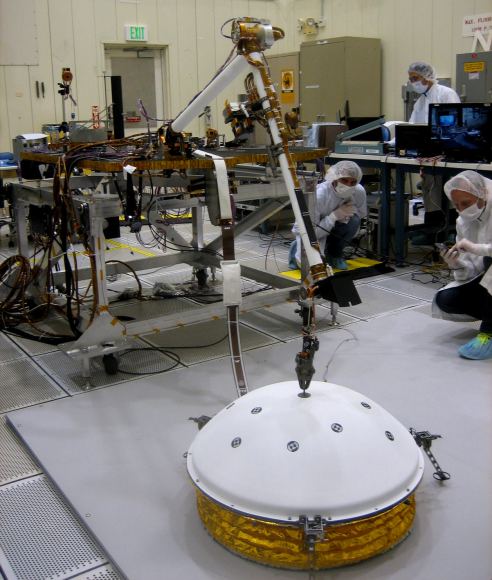

SEIS sits patiently under its dome, which protects it from Martian wind and thermal effects, and waits for something to happen. What’s it waiting for? For seismic waves caused by Marsquakes, meteorite impacts, or by the churning of magma deep in the Martian interior. These waves will help scientists understand the nature of the material that first formed Mars and the other rocky planets.
HP³
HP³ is InSight’s heat probe. It stands for Heat Flow and Physical Properties Probe. Upon deployment on the Martian surface, HP³ will burrow 5 meters (16 ft.) into Mars. No other instrument has ever pierced Mars this deeply. Once there, it will measure the heat flowing deeply within Mars.

Scientists hope that the heat measured by HP³ will help them understand whether or not Mars formed from the same material that Earth and the Moon formed from. It should also help them understand how Mars evolved after it was formed.
RISE
RISE stands for Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment. RISE will measure the Martian wobble as it orbits the Sun, by precisely tracking InSight’s position on the surface. This will tell scientists a lot about the deep inner core of Mars. The idea is to determine the depth at which the Martian core is solid. It will also tell us which elements are present in the core. Basically, RISE will tell us how Mars responds to the Sun’s gravity as it orbits the Sun. RISE consists of two antennae on top of InSight.

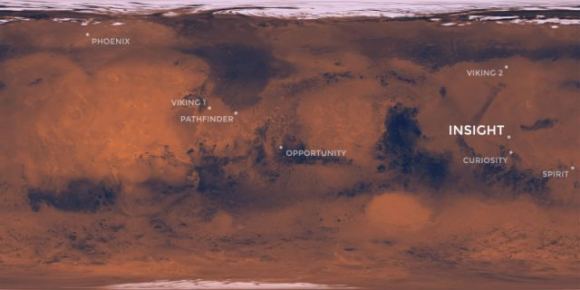
InSight will land at Elysium Planitia which is a flat and smooth plain just north of the Martian equator. This is considered a perfect location or InSight to study the Martian interior. The landing sight is not far from where Curiosity landed at Gale Crater in 2012.
InSight will be launched to Mars from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California by an Atlas V-401 rocket. The trip to Mars will take about 6 months. Once on the Martian surface, InSight’s mission will have a duration of about 728 Earth days, or just over 1 Martian year.
InSight won’t be launching alone. The Atlas that launches the lander will also launch another NASA technology experiment. MarCO, or Mars Cube One, is two suitcase-size CubeSats that will travel to Mars behind InSight. Once in orbit around Mars, their job is to relay InSight data as the lander enters the Martian atmosphere and lands. This will be the first time that miniaturized CubeSat technology will be tested at another planet.

If the MarCO experiment is successful, it could be a new way of relaying mission data to Earth. MarCO will relay news of a successful landing, or of any problems, much sooner. However, the success of the InSight lander is not dependent on a successful MarCO experiment.
NASA’s InSight Lander Approved for 2018 Mars Launch

Top NASA managers have formally approved the launch of the agency’s InSight Lander to the Red Planet in the spring of 2018 following a postponement from this spring due to the discovery of a vacuum leak in a prime science instrument supplied by France.
The InSight missions goal is to accomplish an unprecedented study of the deep interior of the most Earth-like planet in our solar system.
NASA is now targeting a new launch window that begins May 5, 2018, for the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight). mission aimed at studying the deep interior of Mars. The Mars landing is now scheduled for Nov. 26, 2018.
InSight had originally been slated for blastoff on March 4, 2016 atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California.
But the finding of a vacuum leak in its prime science instrument, the French-built Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS), in December 2015 forced an unavoidable two year launch postponement. Because of the immutable laws of orbital mechanics, launch opportunities to the Red Planet only occur approximately every 26 months.
InSight’s purpose is to help us understand how rocky planets – including Earth – formed and evolved. The science goal is totally unique – to “listen to the heart of Mars to find the beat of rocky planet formation.”
The revised launch date was approved by the agency’s Science Mission Directorate.
“Our robotic scientific explorers such as InSight are paving the way toward an ambitious journey to send humans to the Red Planet,” said Geoff Yoder, acting associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, in Washington, in a statement.
“It’s gratifying that we are moving forward with this important mission to help us better understand the origins of Mars and all the rocky planets, including Earth.”

Since InSight would not have been able to carry out and fulfill its intended research objectives because of the vacuum leak in its defective SEIS seismometer instrument, NASA managers had no choice but to scrub this year’s launch. For a time its outlook for a future revival seemed potentially uncertain in light of today’s constrained budget environment.
The leak, if left uncorrected, would have rendered the flawed probe useless to carry out the unprecedented scientific research foreseen to measure the planets seismic activity and sense for “Marsquakes” to determine the nature of the Red Planet’s deep interior.
“The SEIS instrument — designed to measure ground movements as small as half the radius of a hydrogen atom — requires a perfect vacuum seal around its three main sensors in order to withstand harsh conditions on the Red Planet,” according to NASA.
The SEIS seismometer instrument was provided by the Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) – the French national space agency equivalent to NASA. SEIS is one of the two primary science instruments aboard InSight. The other instrument measuring heat flow from the Martian interior is provided by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and is named Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3). The HP3 instrument checked out perfectly.
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) was assigned lead responsibility for the “replanned” mission and insuring that the SEIS instrument operates properly with no leaks.
JPL is “redesigning, developing and qualifying the instrument’s evacuated container and the electrical feedthroughs that failed previously. France’s space agency, the Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), will focus on developing and delivering the key sensors for SEIS, integration of the sensors into the container, and the final integration of the instrument onto the spacecraft.”
“We’ve concluded that a replanned InSight mission for launch in 2018 is the best approach to fulfill these long-sought, high-priority science objectives,” said Jim Green, director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division.
The cost of the two-year delay and instrument redesign amounts to $153.8 million, on top of the original budget for InSight of $675 million.
NASA says this cost will not force a delay or cancellation to any current missions. However, “there may be fewer opportunities for new missions in future years, from fiscal years 2017-2020.”
Lockheed Martin is the prime contractor for InSight and placed the spacecraft in storage while SEIS is fixed.
InSight is funded by NASA’s Discovery Program of low cost, focused science missions along with the science instrument funding contributions from France and Germany.
Meanwhile, NASA is preparing to launch its big planetary mission of 2018 on Thursday of this week ! – the OSIRIS-REx asteroid sample return probe blasts off on an Atlas V on Sept 8.
Watch for Ken’s continuing OSIRIS-REx mission and launch reporting from on site at the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, FL.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about OSIRIS-REx, InSight Mars lander, SpaceX missions, Juno at Jupiter, SpaceX CRS-9 rocket launch, ISS, ULA Atlas and Delta rockets, Orbital ATK Cygnus, Boeing, Space Taxis, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Sep 6-8: “OSIRIS-REx lainch, SpaceX missions/launches to ISS on CRS-9, Juno at Jupiter, ULA Delta 4 Heavy spy satellite, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings
InSight Mars Lander Saved from Termination, Reset to 2018 Blastoff


The Insight Mars lander has been saved from mission termination and will live to launch another day two years from now, NASA managers just announced following a thorough three month investigation into the causes of the last moment snafu involving the failure of its French-built seismometer science instrument that last December forced the agency to cancel its planned liftoff this month.
NASA is now targeting a new launch window that begins May 5, 2018, for the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission aimed at studying the deep interior of Mars.
The May 2018 launch amounts to an unavoidable 26 month launch delay from the originally planned launch on March 4, 2016. Because of the immutable laws of orbital mechanics, launch opportunities to the Red Planet only occur every 26 months.
Since InSight would not have been able to carry out and fulfill its intended research objectives because of a vacuum leak in its defective seismometer instrument, NASA managers had no choice but to scrub this year’s launch and its outlook for a future revival seemed potentially uncertain at best in today’s constrained budget environment.
“The spacecraft had been on track to launch this month until a vacuum leak in its prime science instrument prompted NASA in December to suspend preparations for launch,” said NASA officials.
The leak, if left uncorrected, would have rendered the flawed probe useless to carry out the unprecedented scientific research foreseen to measure the planets seismic activity and sense for “Marsquakes” to determine the nature of the Red Planet’s deep interior.
“The science goals of InSight are compelling, and the NASA and CNES plans to overcome the technical challenges are sound,” said John Grunsfeld, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
“The quest to understand the interior of Mars has been a longstanding goal of planetary scientists for decades. We’re excited to be back on the path for a launch, now in 2018.”
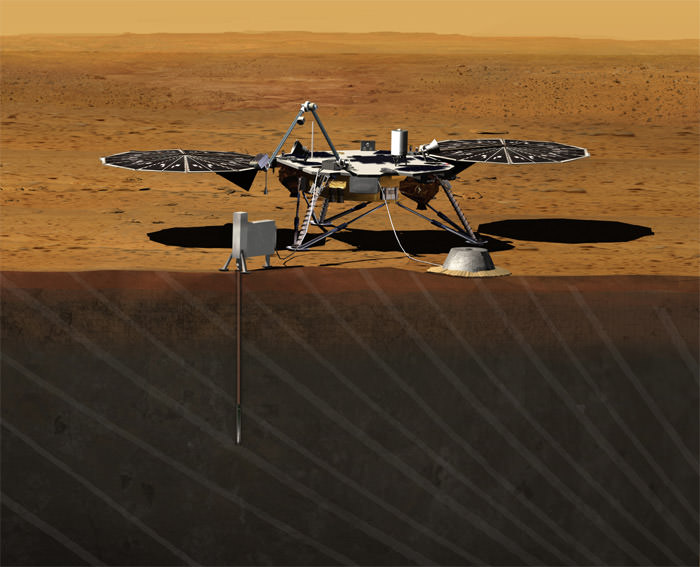

InSight is now slated for a Mars landing on Nov. 26, 2018.
The seismometer instrument is named Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) and was provided by the Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) – the French national space agency equivalent to NASA. SEIS is one of the two primary science instruments aboard InSight. The other instrument measuring heat flow from the Martian interior is provided by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and is named Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3).
“InSight project managers recently briefed officials at NASA and France’s space agency, Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), on a path forward; the proposed plan to redesign the science instrument was accepted in support of a 2018 launch,” said NASA.
JPL will assume lead responsibility for insuring that the SEIS instrument operates properly with no leak.
The cost of the 2 year delay is still being assessed but expected to be in the tens of millions of dollars, likely over $100 million. How that will be payed for has yet to be determined.
Lockheed Martin is the prime contractor for InSight and will place the spacecraft in storage while SEIS is fixed and until the 2018 launch date nears.
“We’re delighted that NASA has approved the launch of the InSight mission in May 2018,” Stu Spath, Lockhhed Martin spacecraft program manager told Universe Today.
“Currently, we are preparing the spacecraft to go into storage at our Space Systems facility near Denver.”
“Our team worked hard to get the InSight spacecraft built and tested, and although InSight didn’t launch this year as planned, we know ultimately the scientific knowledge it will bring us is crucial to our understanding of how Mars and other rocky planets formed.”

InSight is funded by NASA’s Discovery Program of low cost, focused science missions along with the science instrument funding contributions from France and Germany.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.


