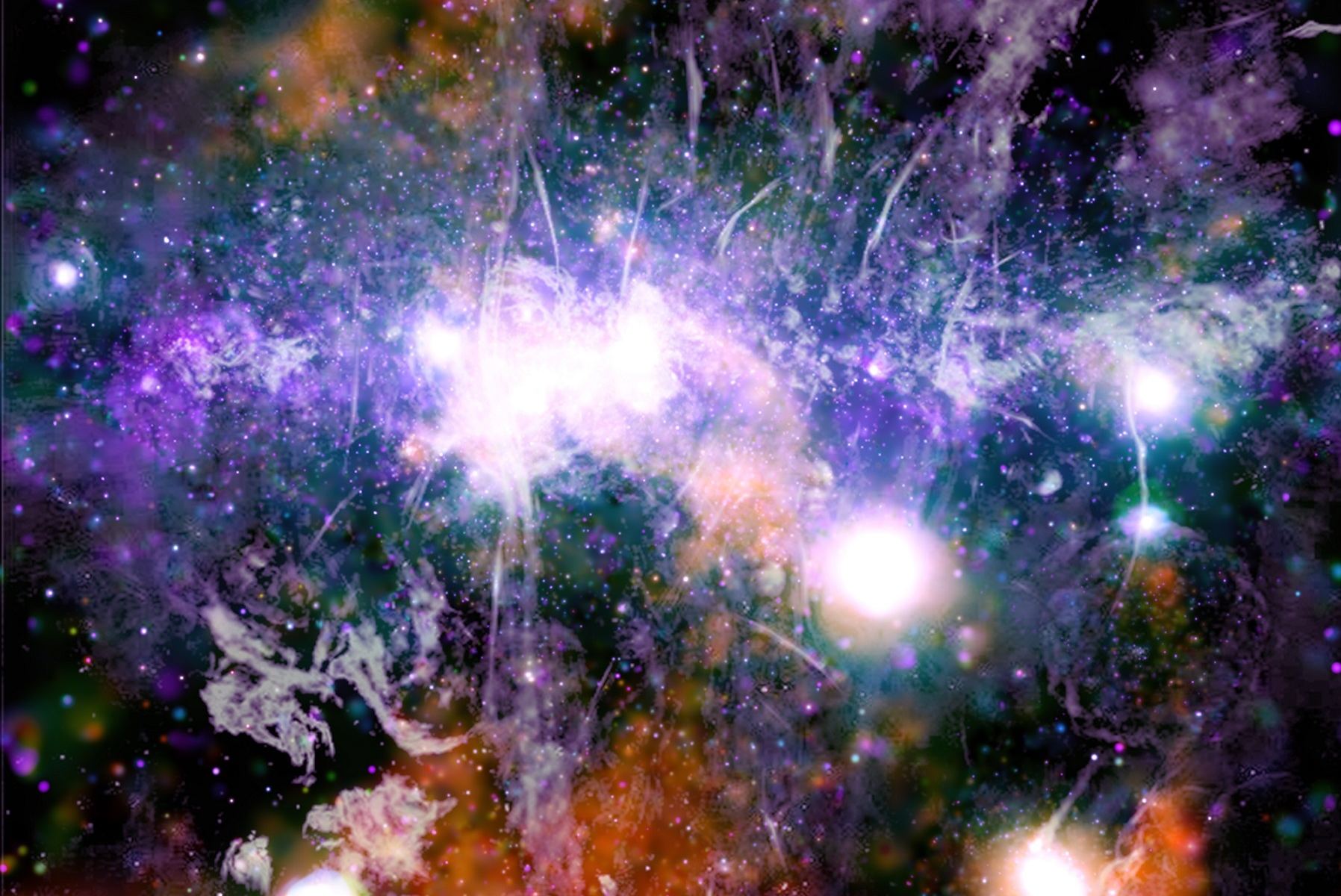
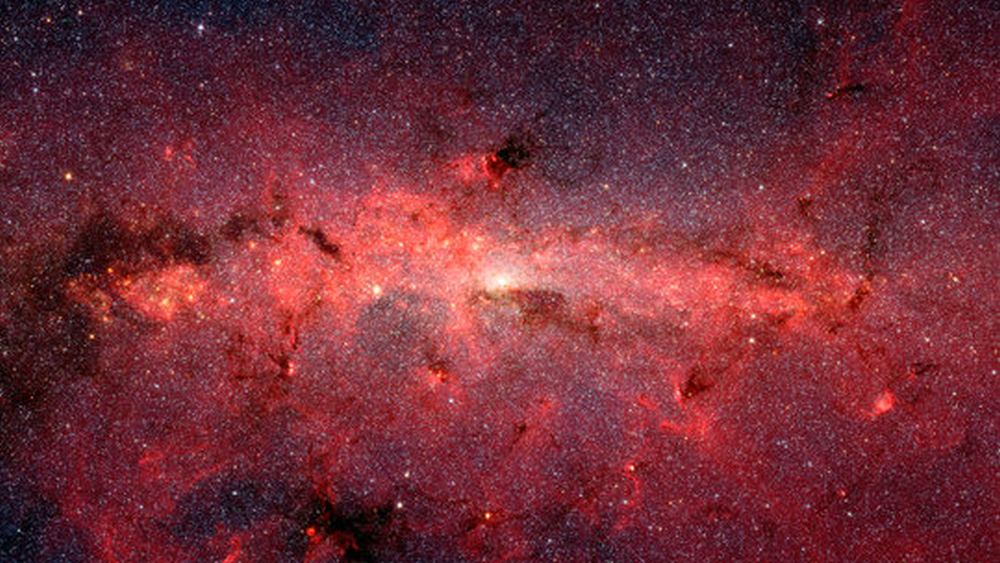
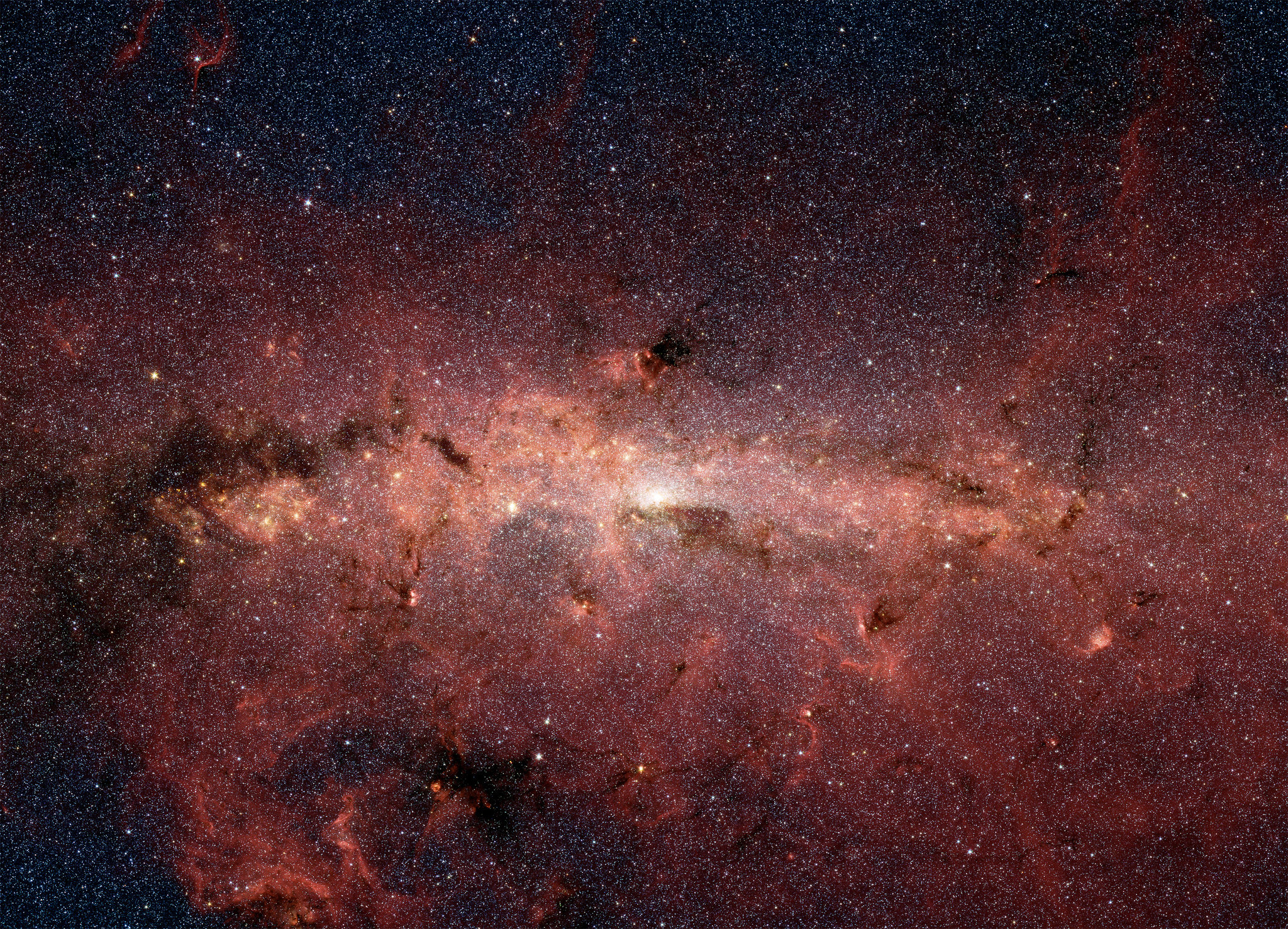
The core of the Milky Way Galaxy (aka. Galactic Center), the region around which the rest of the galaxy revolves, is a strange and mysterious place. It is here that the Supermassive Black Hole (SMBH) that powers the compact radio source known as Sagittarius A* is located. It is also the most compact region in the galaxy, with an estimated 10 million stars within 3.26 light-years of the Galactic Center.
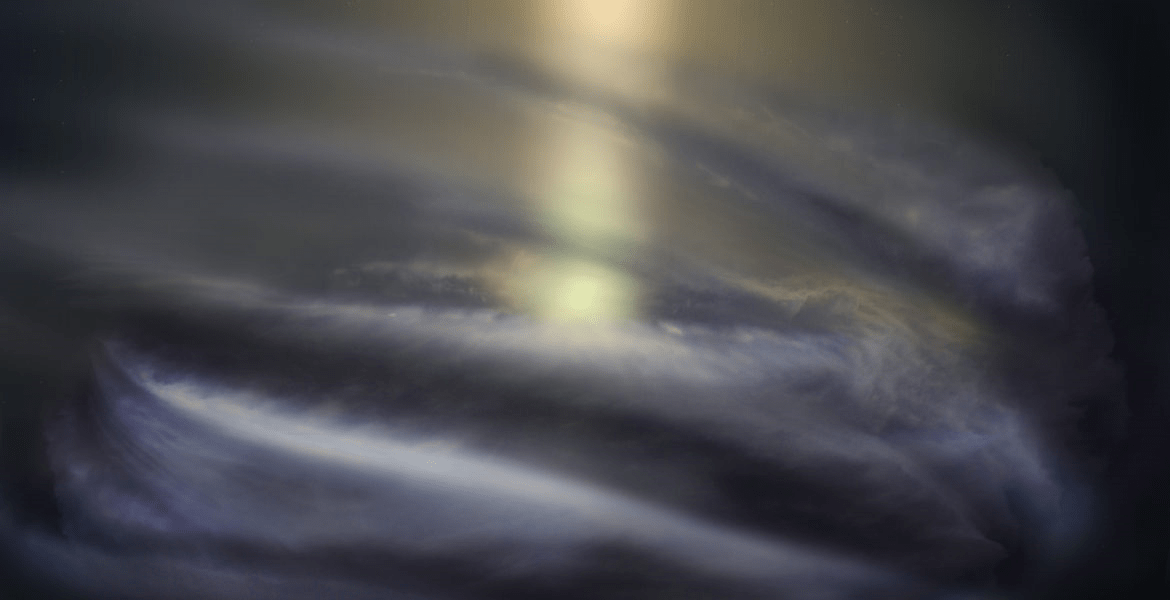
Using data from Chandra X-ray Observatory and the MeerKAT radio telescope, NASA and the National Research Foundation (NSF) of South Africa created a mosaic of the center of the Milky Way. Combining images taken in the x-ray and radio wavelengths, the resulting panoramic image manages to capture the filaments of super-heated gas and magnetic fields that (when visualized) shows the complex web of energy at the center of our galaxy.
Continue reading “New Mosaic Shows the Galactic Core From Opposite Sides of the Electromagnetic Spectrum”