[/caption]
Russia’s Space Agency, Roscosmos, has set November 9 as the launch date for the Phobos-Grunt mission to Mars and its tiny moon Phobos. Roscosmos has officially announced that the audacious mission to retrieve the first ever soil samples from the surface of Phobos will blastoff from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan atop a Zenit-2SB rocket at 00:16 a.m. Moscow time.
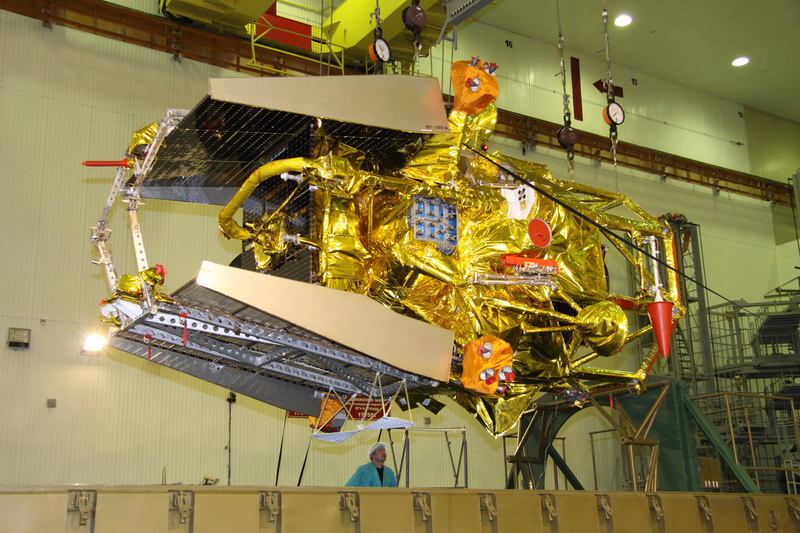
Roscosmos said that engineers have finished loading all the propellants into the Phobos-Grunt main propulsion module (cruise stage), Phobos lander and Earth return module at Facility 31 at Baikonur.
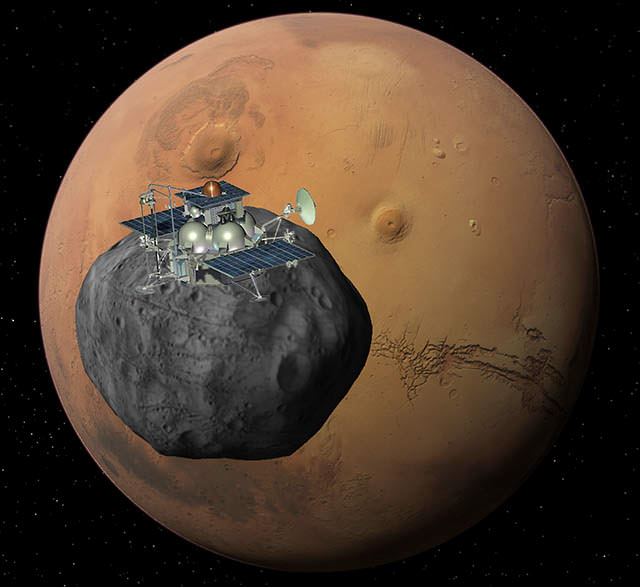
Phobos-Grunt is Russia’s first mission to Mars in almost two decades and a prelude to an ambitious program of even more interplanetary Russian science flights.
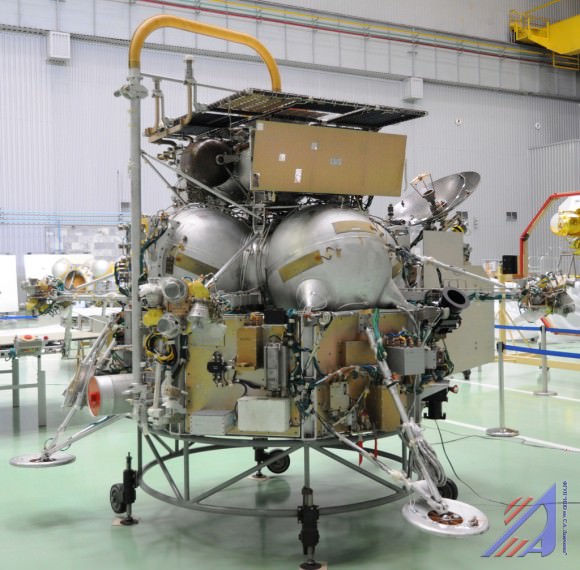

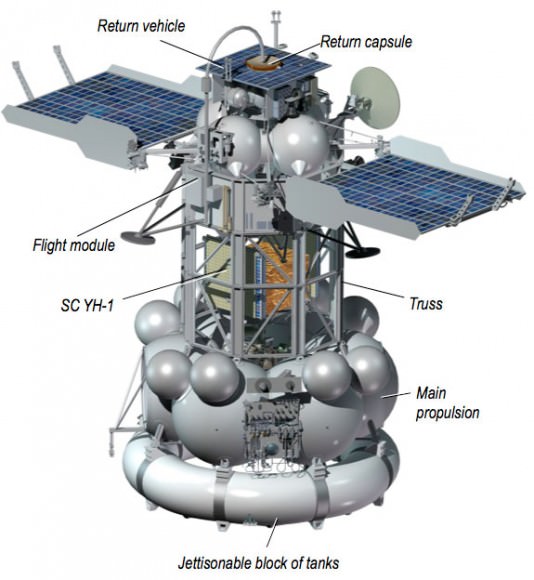
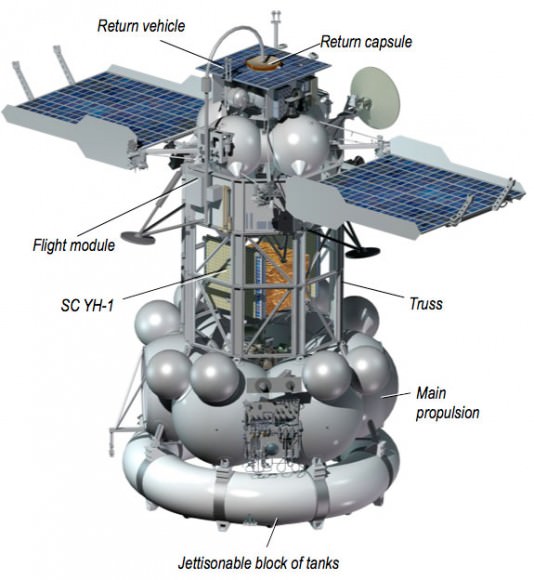
L-shaped soil sample transfer tube extends from Earth return module ( top -yellow) and solar panel to bottom (left) of lander module. 2 landing legs, communications antenna, sampling arm, propulsion tanks and more are visible. Credit Roscosmos
Technicians also fueled the companion Yinghou-1 mini-satellite, provided by China, that will ride along inside a truss segment between the MDU propulsion module and the Phobos-Grunt lander.
The 12,000 kg Phobos-Grunt interplanetary spacecraft is being moved to an integration and test area at Facility 31 for integration with the departure segments of the Zenit rocket.
The next step is to enclose Phobos-Grunt inside the protective payload fairing and transport it to Facility 42 for mating atop the upper stage of the stacked Zenit-2SB booster rocket.
After about an 11 month journey, the spaceship will enter Mars orbit and spend several months searching for a suitable landing site on Phobos. The goal of the bold mission is to retrieve up to 200 grams of soil and rock from Phobos and return them to Earth in August 2014. The samples will help unlock the mysteries of the origin and evolution of Phobos, Mars and the Solar System.
Scientists hope that bits of Martian soil will be mixed in with Phobos soil.
Phobos-Grunt is equipped with a powerful 50 kg payload of some 20 international science instruments.
The 110 kg Yinghou-1, which translates as Firefly-1, is China’s first spaceship to voyage to Mars. It will be jettisoned by Phobos-Grunt into a separate orbit about Mars. The probe will photograph the Red planet with two cameras and study it with a magnetometer to explore Mars’ magnetic field and science instruments to explore its upper atmosphere.
Earth’s other mission to Mars in 2011, NASA’s Curiosity rover, is set to blast off for Mars on Nov. 25
Read Ken’s continuing features about Russia’s Phobos-Grunt Mars mission here::
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghou-1 Arrive at Baikonur Launch Site to tight Mars Deadline
Phobos-Grunt: The Mission Poster
Daring Russian Sample Return mission to Martian Moon Phobos aims for November Liftoff
Read Ken’s continuing features about Curiosity starting here:
Curiosity Buttoned Up for Martian Voyage in Search of Life’s Ingredients
Assembling Curiosity’s Rocket to Mars
Encapsulating Curiosity for Martian Flight Test
Dramatic New NASA Animation Depicts Next Mars Rover in Action