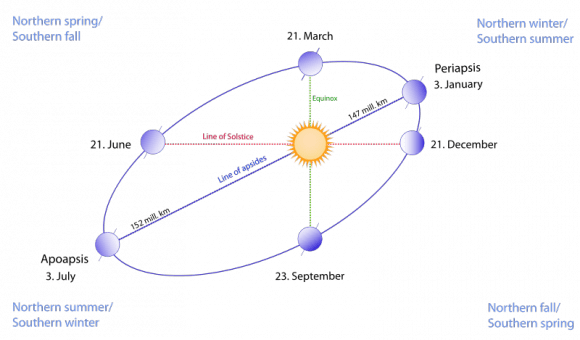
The planets are slowly returning into view this month, bashfully peeking out from behind the Sun in the dawn & dusk sky. This month offers a bonanza of photogenic conjunctions, involving the Moon, planets and bright stars.
The action begins tonight on July 8th, as the waxing crescent Moon joins the planet Venus in the dusk sky. The razor thin Moon will be a challenge on Monday night, as it just passed New on the morning of the 8th at 3:14AM EDT/7:14 Universal Time (UT). The record for spotting the thin crescent with the naked eye currently stands at 15 hours and 32 minutes, completed by Stephen O’Meara on May 1990. Binoculars help considerably in this endeavor. Wait until 15 minutes after local sunset, and then begin patiently sweeping the horizon.
Mr. Thierry Legault completed an ultimate photographic challenge earlier today, capturing the Moon at the precise moment of New phase!
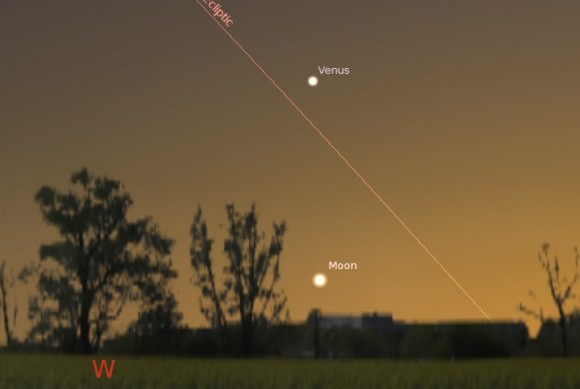
This week marks the start of lunation 1120. The Moon will be much easier to nab for observers worldwide on Tuesday night, July 9th for observers worldwide. The sighting of the waxing crescent Moon will also mark the start of the Muslim month of Ramadan for 2013. Due to the angle of the ecliptic in July, many northern hemisphere observers may not spot the Moon until Wednesday night on July 10th, about 6.7 degrees south west of -4.0 magnitude Venus.
Did you know? There are Guidelines for the Performance of Islamic Rites for Muslims aboard the International Space Station. It’s interesting to note that the timing of the rituals follows the point from which the astronaut originally embarked from the Earth, which is exclusively the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan for the foreseeable future of manned spaceflight.
Malaysia’s first astronaut, Sheikh Muszaphar Shukor observed Ramadan aboard the International Space Station in 2007.
From there, the crescent Moon fattens, meeting up with Saturn and Spica on the evenings of July 15th and 16th. The Moon will actually occult (pass in front of) the bright star Spica on the evening of July 15/16th at ~3:33UT/11:33PM EDT (on the 15th) for observers in Central America and western South America. The rest of us will see a near miss worldwide.
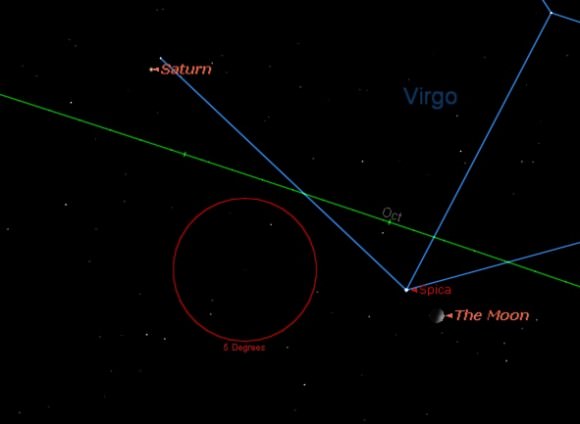
This is the 13th in a cycle of 18 occultations of Spica by our Moon spanning 2012-2013. Spica is one of four stars brighter than magnitude +1.4 that lie close enough to the ecliptic to be occulted by our Moon, the others being Antares, Regulus and Aldebaran. Saturn will lie 3 degrees from the Moon on the evening of July 16th.
Can you nab Spica and Saturn near the Moon with binoculars in the daytime around the 15th? It can be done, using the afternoon daytime Moon as a guide. Crystal clear skies (a rarity in the northern hemisphere summertime, I know) and physically blocking the Sun behind a building or hill helps.
The waxing gibbous Moon will also occult +2.8 Alpha Librae for South Africa on July 17th around 17:09UT & +4.4th magnitude Xi Ophiuchi for much of North America on the night of July 19th-20th.
And speaking of Regulus, the brightest star in the constellation Leo lies only a little over a degree (two Full Moon diameters) from Venus only the evenings of July 21st & the 22nd. 77.5 light years distant, Regulus is currently over 100 times fainter at magnitude +1.4. Can you squeeze both into the field of view of your telescope at low power? Venus’s mythical ‘moon’ Neith lives!
Venus can even occult Regulus on rare occasions, as last occurred on July 7th, 1959 and will happen next on October 1st, 2044.
But there’s morning action afoot as well. The planets Mars and Jupiter have emerged from solar conjunction on April 18th and June 19th, 2013 respectively, and can now be seen low in the dawn skies about 30 minutes before sunrise.
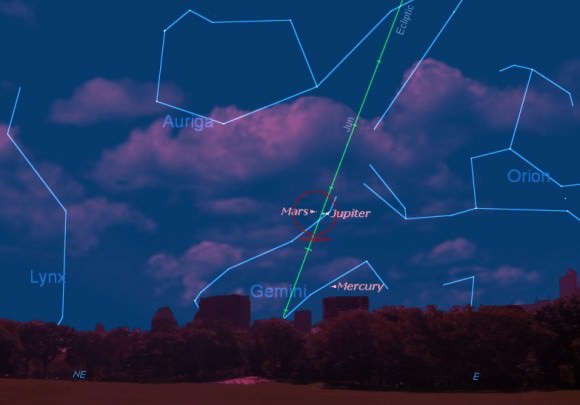
Mars approaches Jupiter in the dawn until the pair is only 0.79 degrees (about 48 arc minutes) apart on Monday, July 22nd. Mars shines at magnitude +1.6 and shows a tiny 3.9” disk, while Jupiter displays a 32.5” disk shining at magnitude -1.9 on this date. Conjunction occurs at about 7:00 UT/3:00 AM EDT, after which the two will begin to race apart. Mercury is visible beginning its morning apparition over 5 degrees to the lower right of the pair (see above).
Jupiter will reach opposition and reenter the evening sky on January 5th, 2014, while Mars won’t do the same until April 8th of next year. Weird factoid alert: neither Jupiter or Mars reach opposition in 2013! What effect does this have on terrestrial affairs? Absolutely none, well unless you’re a planetary imager/observer…
Mars also reaches its most northern declination of 2013 of 24 degrees in the constellation Gemini on July 16th at 7:00 AM EDT/11:00 UT. Mars can wander as far as declination 27 degrees north, as last happened in 1993.
Finally, are you observing from southern Mexico this week and up for a true challenge? The asteroid 238 Hypatia occults a +7.4 magnitude star from 10:13-10:49 UT on July 10th in the constellation Pisces for up to 29 seconds. This event will be bright enough to watch with binoculars- check out our best prospects for asteroid occultations of stars in 2013 here and here.
Good luck, clear skies, and be sure to post those astro-pics in the Universe Today’s Flickr community!