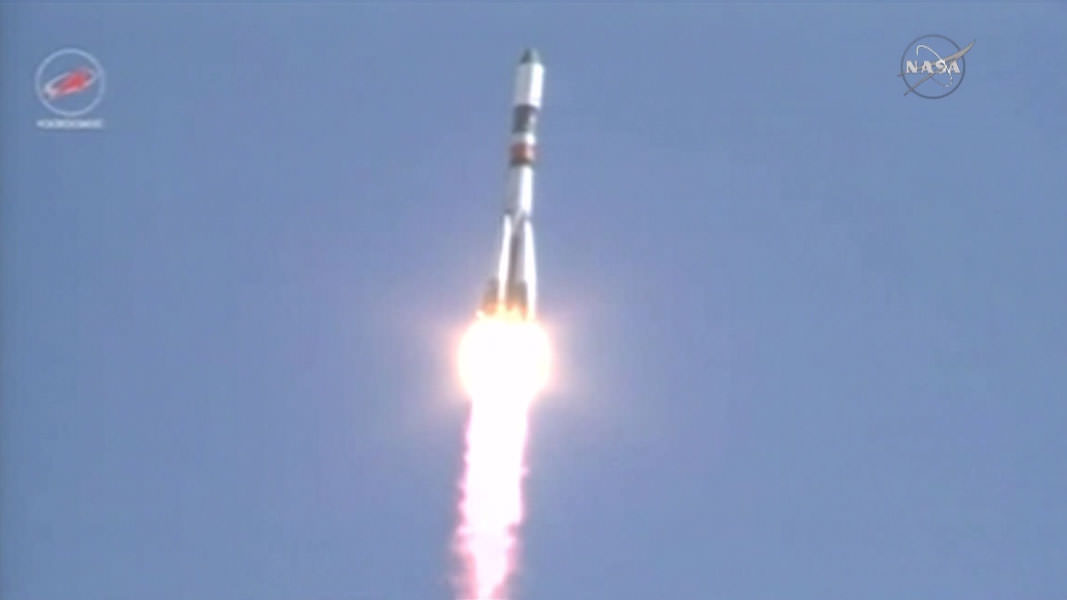
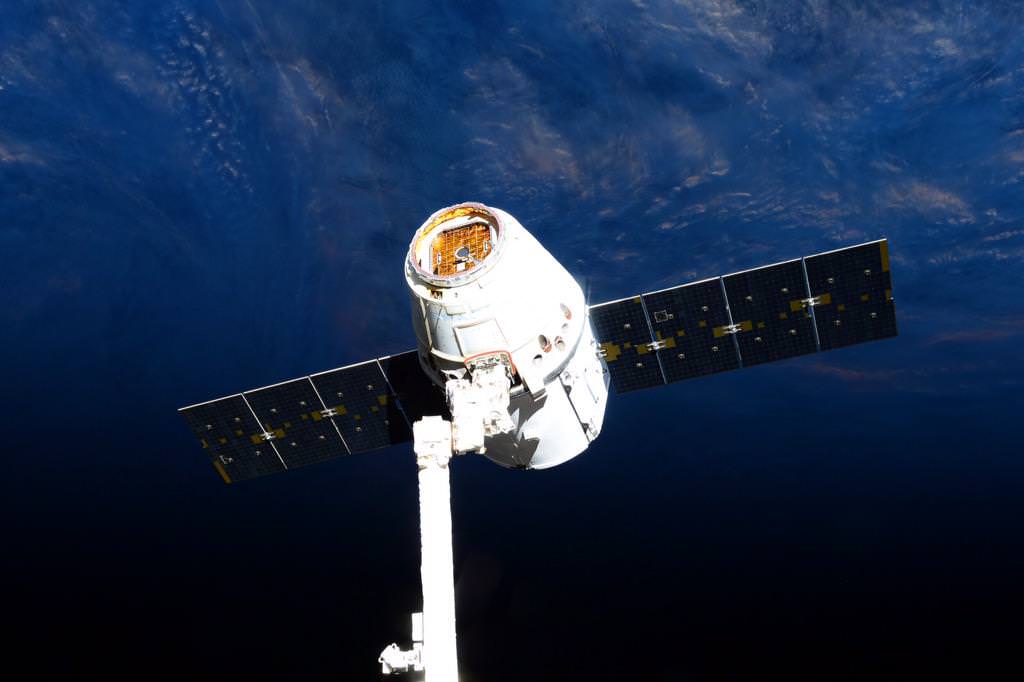
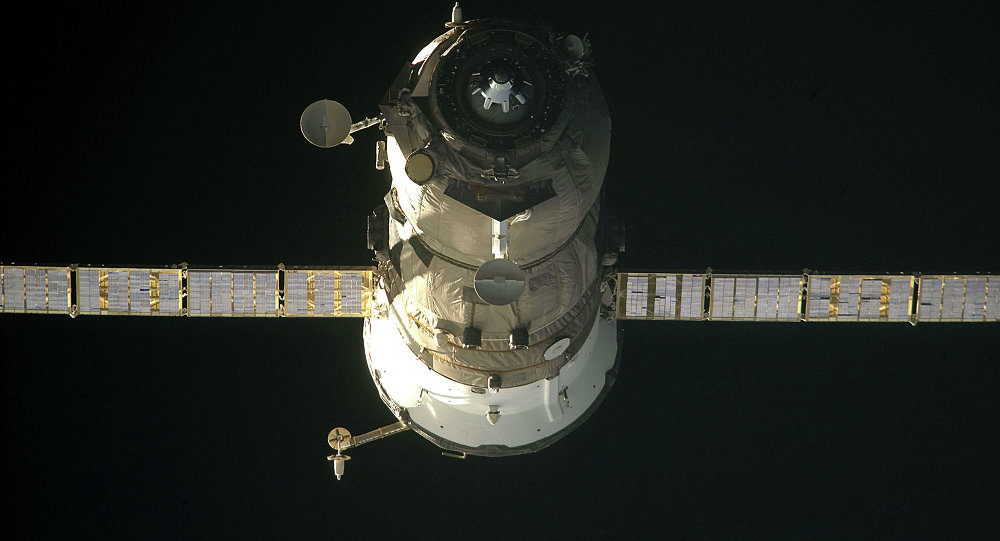
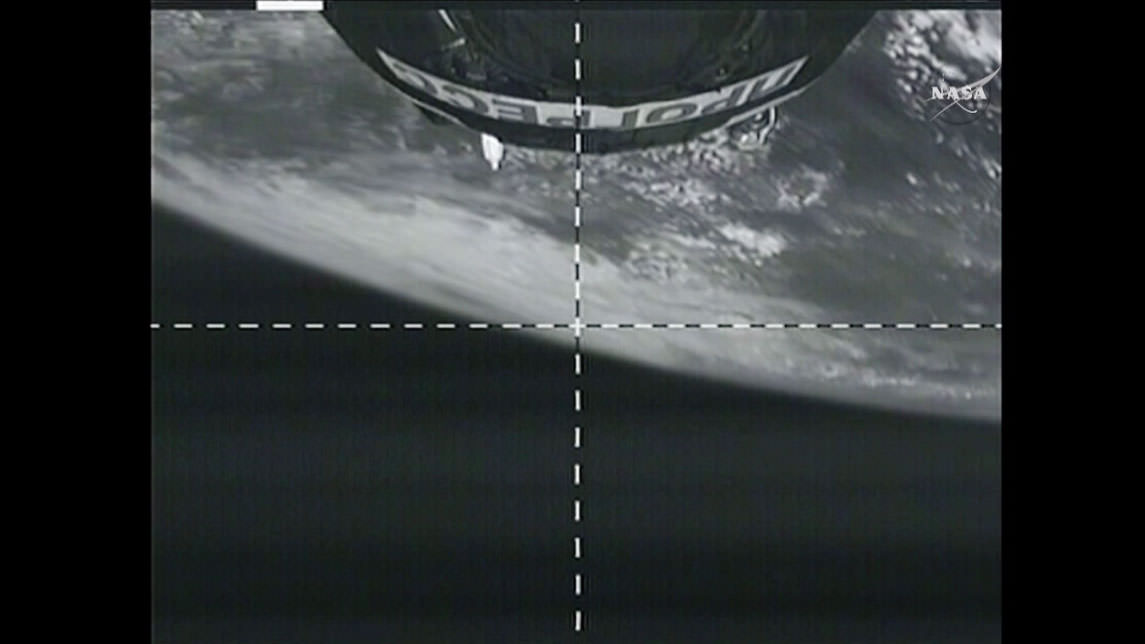
Over three tons of much needed supplies and equipment finally reached the crew living aboard the International Space Station (ISS), when an unmanned and highly anticipated Russian Progress cargo ship successfully docked at the orbiting outpost early this morning, Sunday July 5, at 3:11 a.m. EDT (10:11 MSK, Moscow local time)- to all the partners relief.
This follows two straight international resupply launch failures that significantly crimped the stations stockpiles and abruptly impacted upcoming crew rotations and station launches throughout the remainder of 2015.
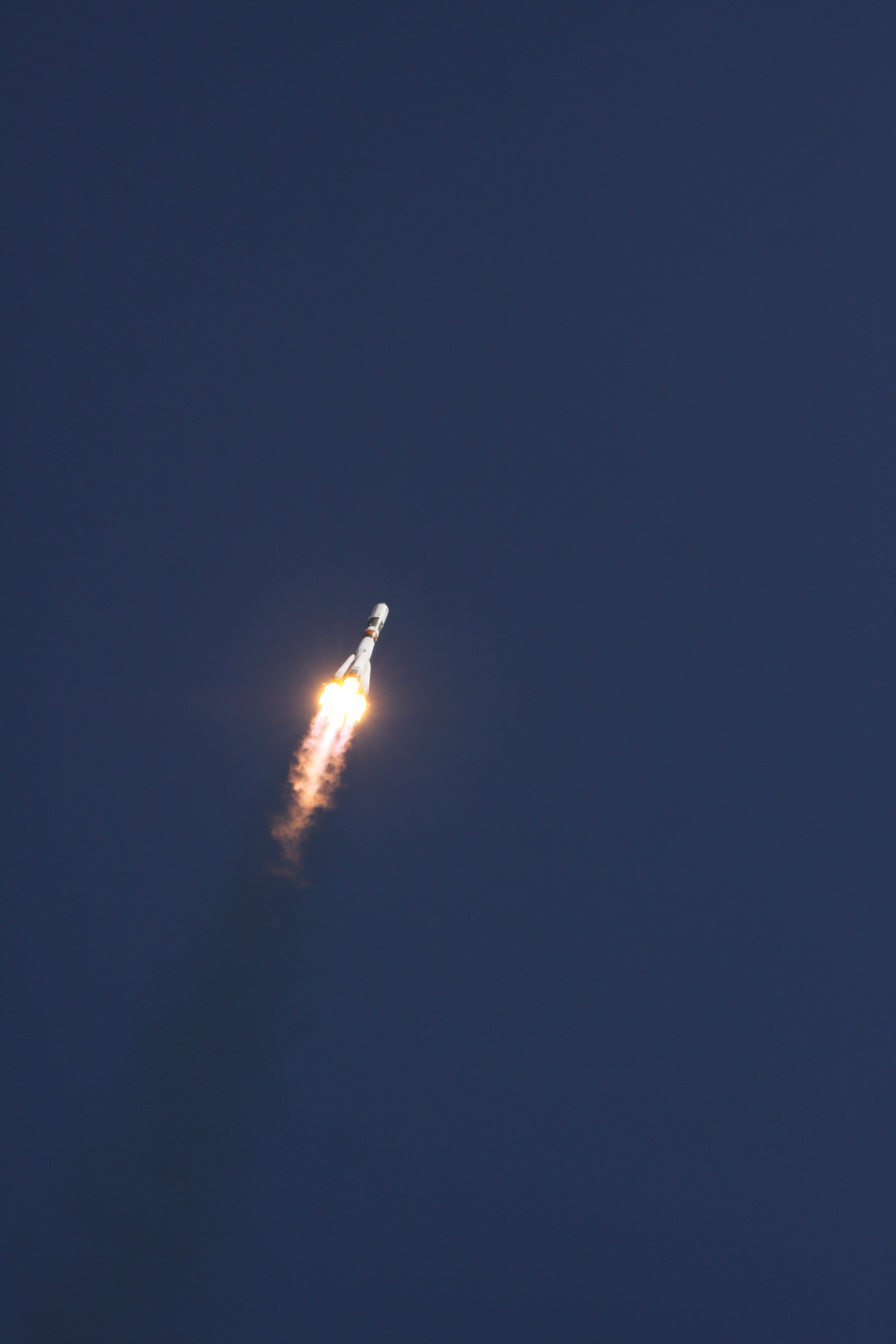
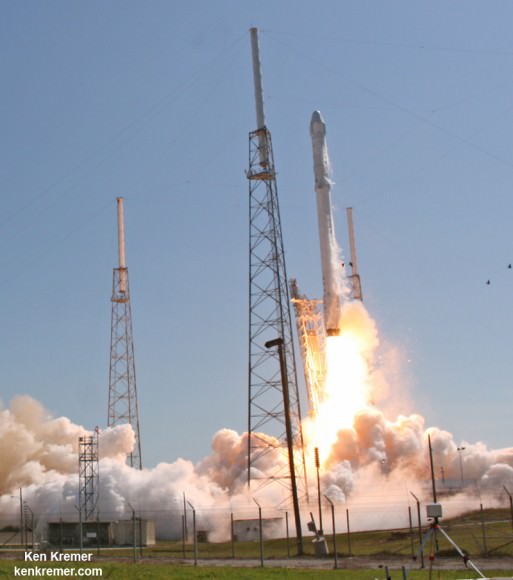
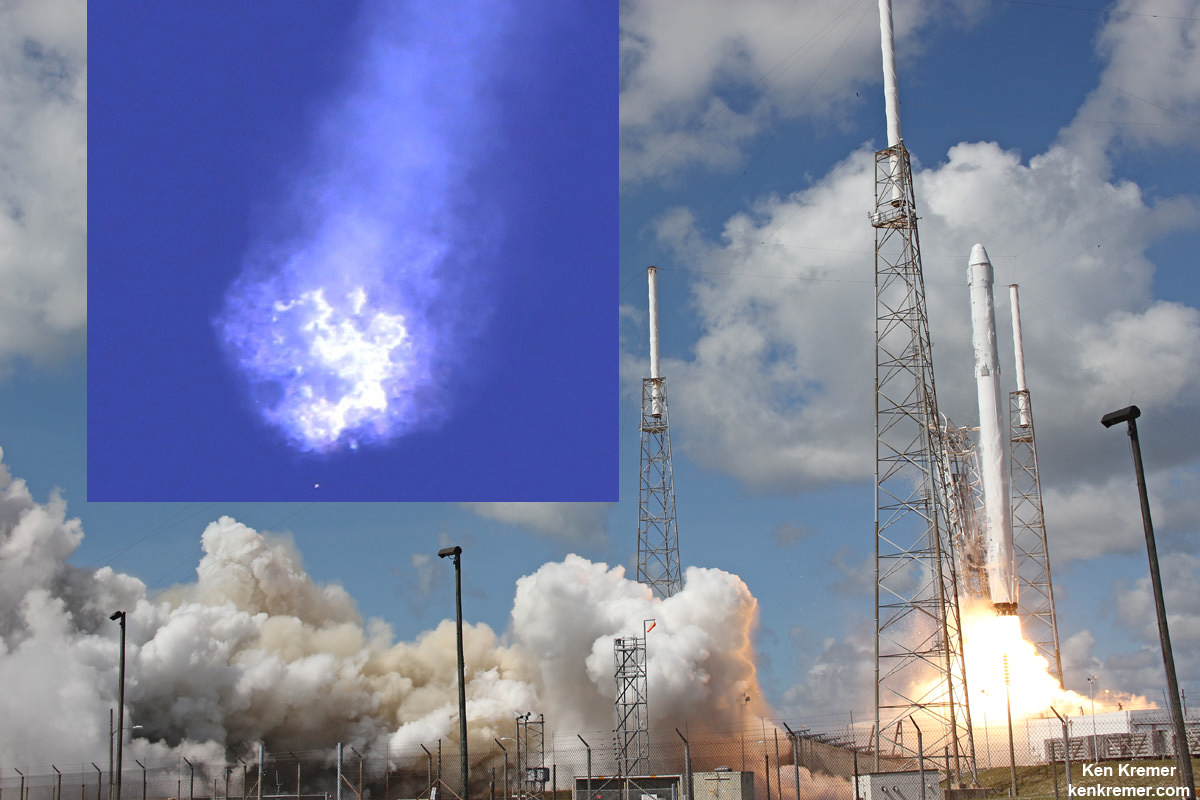
Today’s arrival of Russia’s Progress 60 (Progress M-28M) logistics vehicle ended a string of Russian and American resupply mission failures that began some two months ago with the devastating Soyuz rocket launch failure of the prior Progress 59 ship on April 28, and continued with the mid-air explosion of a commercial SpaceX Falcon 9 and unpiloted SpaceX Dragon CRS-7 cargo ship exactly one week ago on June 28.
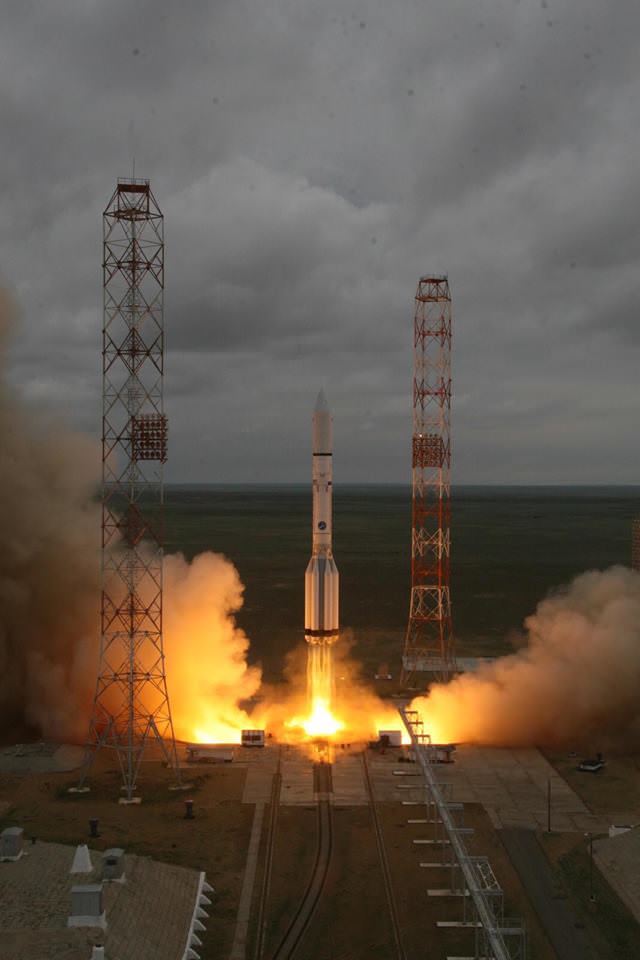
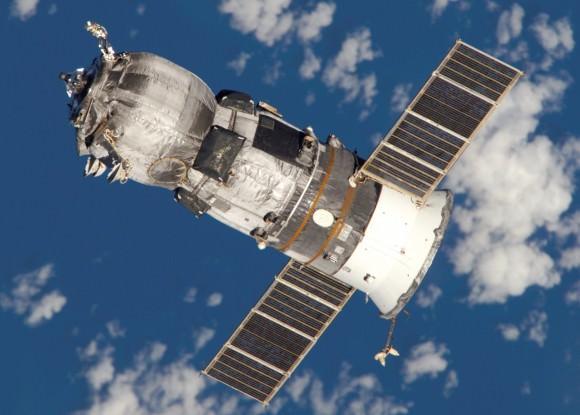
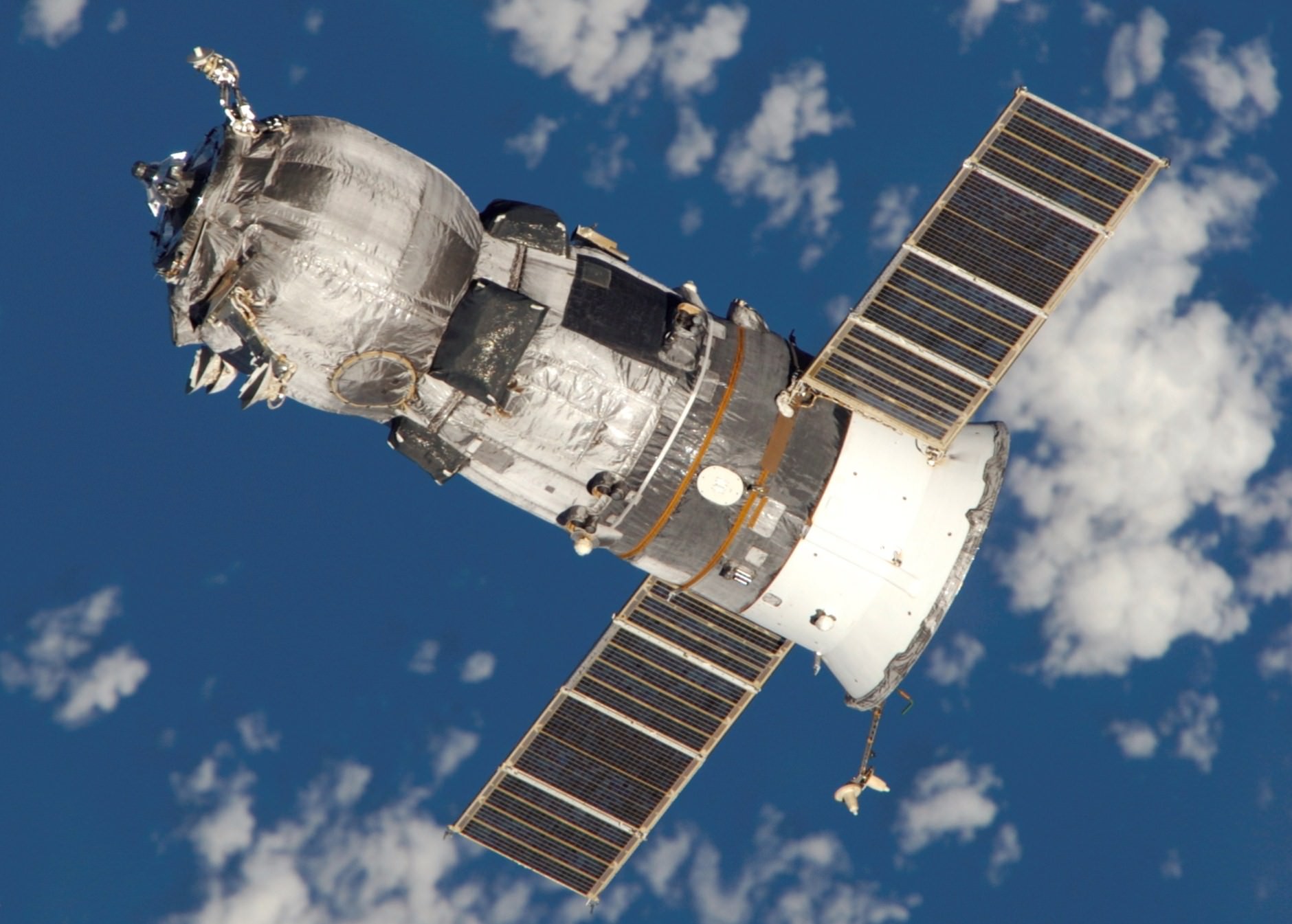
The Progress 60 was automatically docked at an earth facing port on the Russian “Pirs” docking module on the Russian segment of the ISS – that finally puts the station on the road to recovery with a stockpile of 6100 pounds (2770 kg) of new fuel, food, oxygen, research experiments and gear.
“The operation was carried out in an automated mode,” according to Russian Mission Control near Moscow.
The docking operation was conducted under the guidance of the Russian ISS Expedition 44 commander Gennady Padalka and flight engineer Mikhail Kornienko as well as experts at the Russian Mission Control Center, as the vehicles were soaring about 251 miles (400 km) over the south Pacific, southeast of New Zealand. NASA astronaut Scott Kelly is also aboard, rounding out the current three man crew.

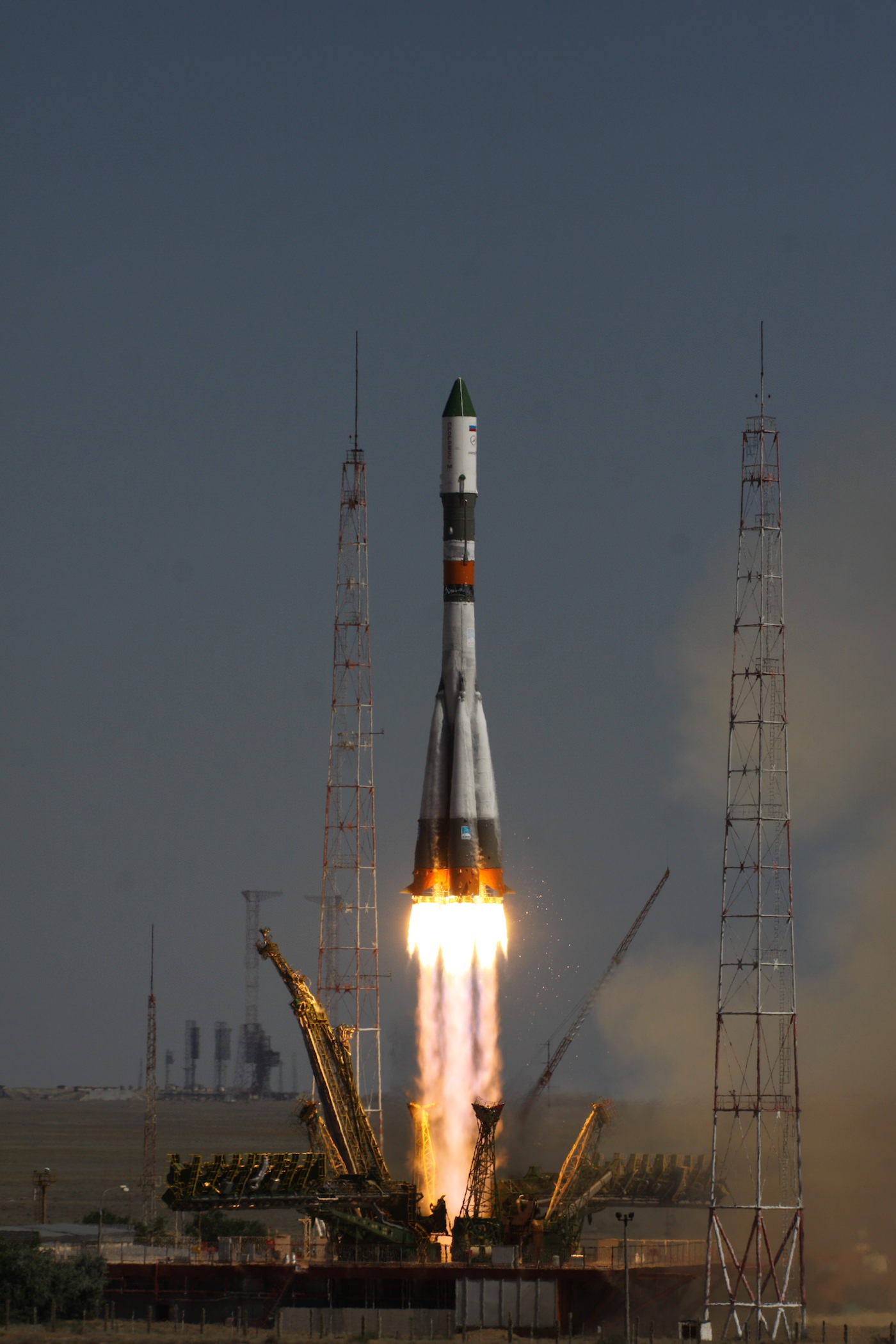
The successful docking came two days after the blastoff of the unmanned Progress 60 cargo freighter atop a Soyuz-U booster from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on July 3. This signifies the restoration of Russia’s critical cargo lifeline to the ISS and was like celebrating Christmas in July.
“Guys, congratulations. your cargo vehicle has arrived,” said Russian flight director Vladimir Solovyev from Russian mission control.
“We congratulate you as well,” cosmonaut Gennady Padalka replied from inside the station’s Russian-built Zvezda command module. “Thanks so much for sending it our way. It feels like Christmas in July.”
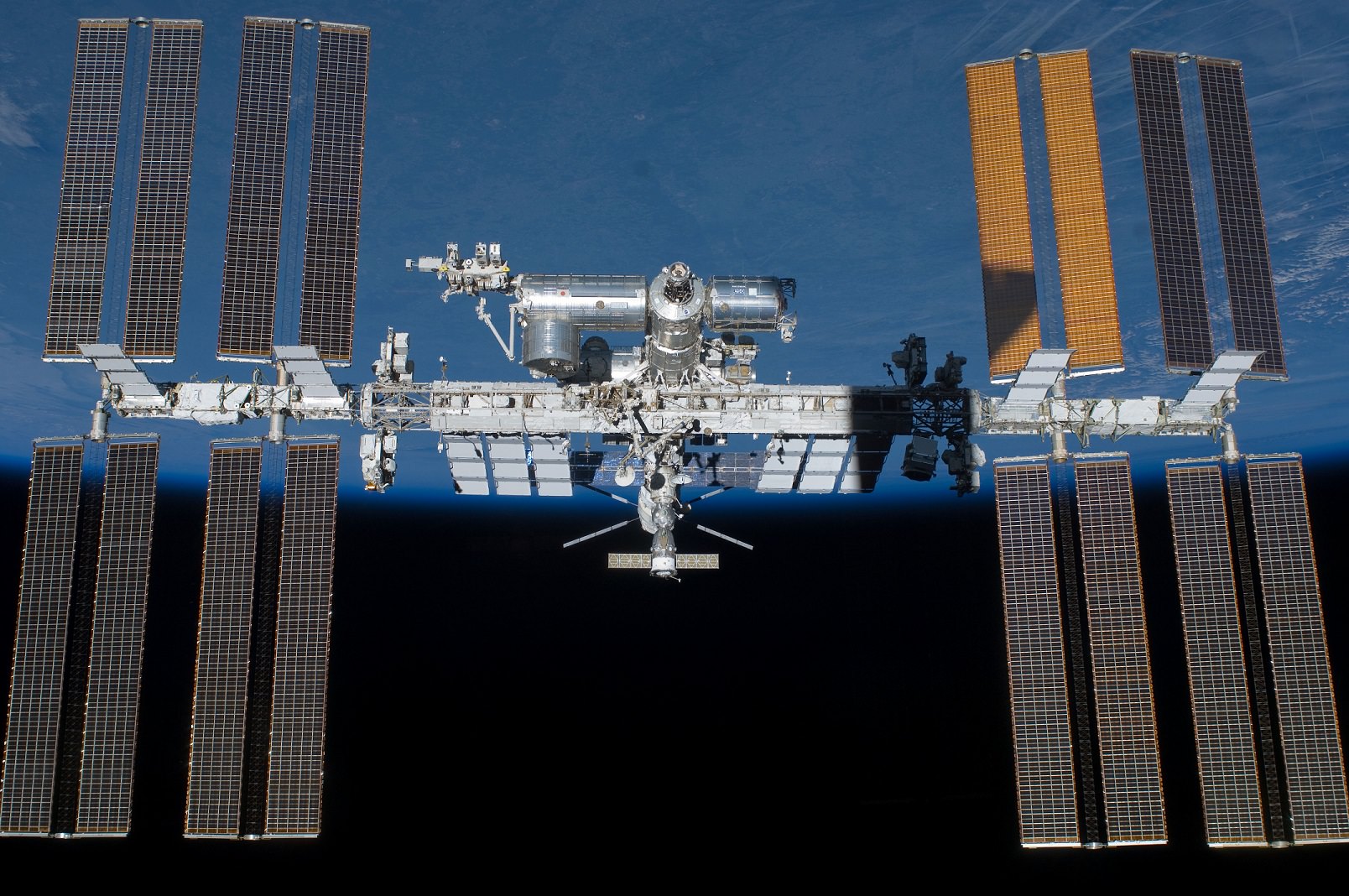
The station is totally dependent on a regular train of supply runs from the partner nations on Earth to operate with a crew and conduct research investigations that will aid in sending humans to deep space destinations.
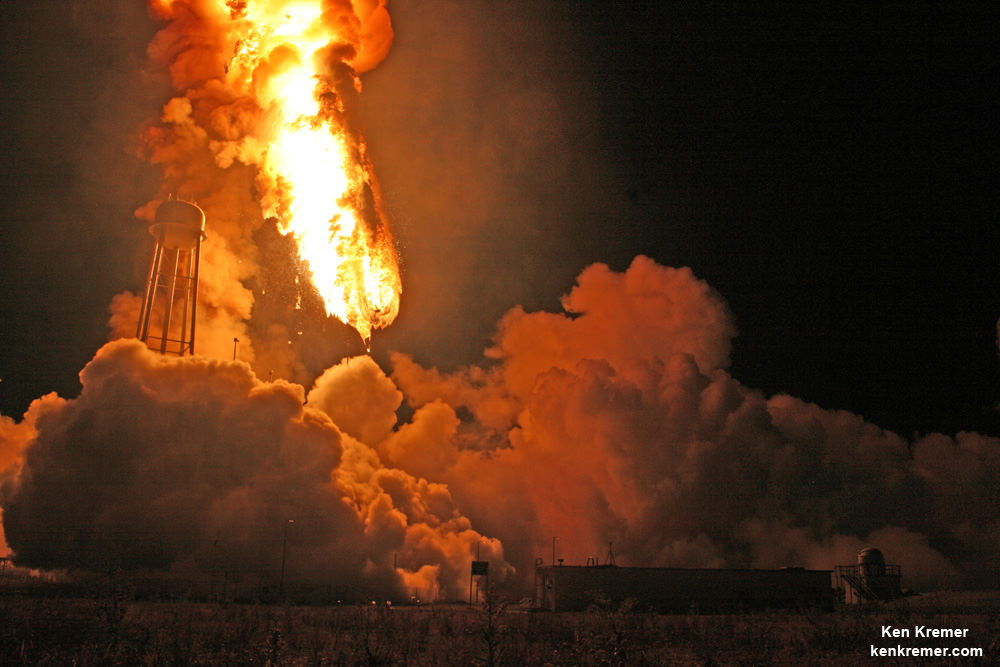
America’s cargo lifeline is currently on hold following the dual launch failures of both US commercial supply trains to low Earth orbit- involving the SpaceX Falcon 9 last week and the catastrophic Orbital ATK Antares/Cygnus Orb-3 mission launch disaster on October 28, 2014 which I saw at NASA Wallops.
The SpaceX Falcon 9 and Dragon exploded barely two minutes after liftoff from Cape Canaveral. The rocket disintegrated in mere moments as I watched from the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
All told, an unprecedented trio of launch failures with three different American and Russian rockets took place over the past eight months.

Progress 60 resupply ship was loaded with over three tons of food, fuel, oxygen, science experiments, water and supplies on a crucial mission for the International Space Station crew to keep them stocked with urgently needed life support provisions and science experiments in the wake of the twin launch failures in April and June.

The Progress was stuffed with 100 kg of additional food stocks to make up for the losses suffered from the twin Russian Progress 59 and SpaceX CRS-7 failures.
“As for food, 430 kilos of foodstuffs will be delivered to the ISS or 100 kilos more than the amount delivered by the previous spacecraft,” noted Mission Control.
“The Progress space freighter will deliver more food than usual so that it will suffice for everyone,” Alexander Agureyev, chief of the ISS crew nourishment department at the Institute of Medical and Biological Problems, told the Russian news agency TASS.
Progress 60 is scheduled to remain docked to Pirs for the next four months.
In the wake of the trio of American and Russian launch failures, the crew currently enjoys only about four months of reserves compared to the more desirable six months stockpile in case of launch mishaps.
Progress 60 will extend the station supplies by about a month’s time.
The next cargo ship now slated to launch is the Japanese HTV-5 on August 16.

The SpaceX CRS-7 Dragon was packed with over 4,000 pounds (1987 kg) of research experiments, an EVA spacesuit, water filtration equipment, spare parts, gear, computer equipment, high pressure tanks of oxygen and nitrogen supply gases, food, water and clothing for the astronaut and cosmonaut crews comprising Expeditions 44 and 45.
These included critical materials for the science and research investigations for the first ever one-year crew to serve aboard the ISS – comprising NASA astronaut Scott Kelly and Russian cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko.
The Dragon was also packed with the first of two new International Docking Adapters (IDS’s) required for the new commercial crew space taxis being built by Boeing and SpaceX to dock at the ISS starting in 2017.
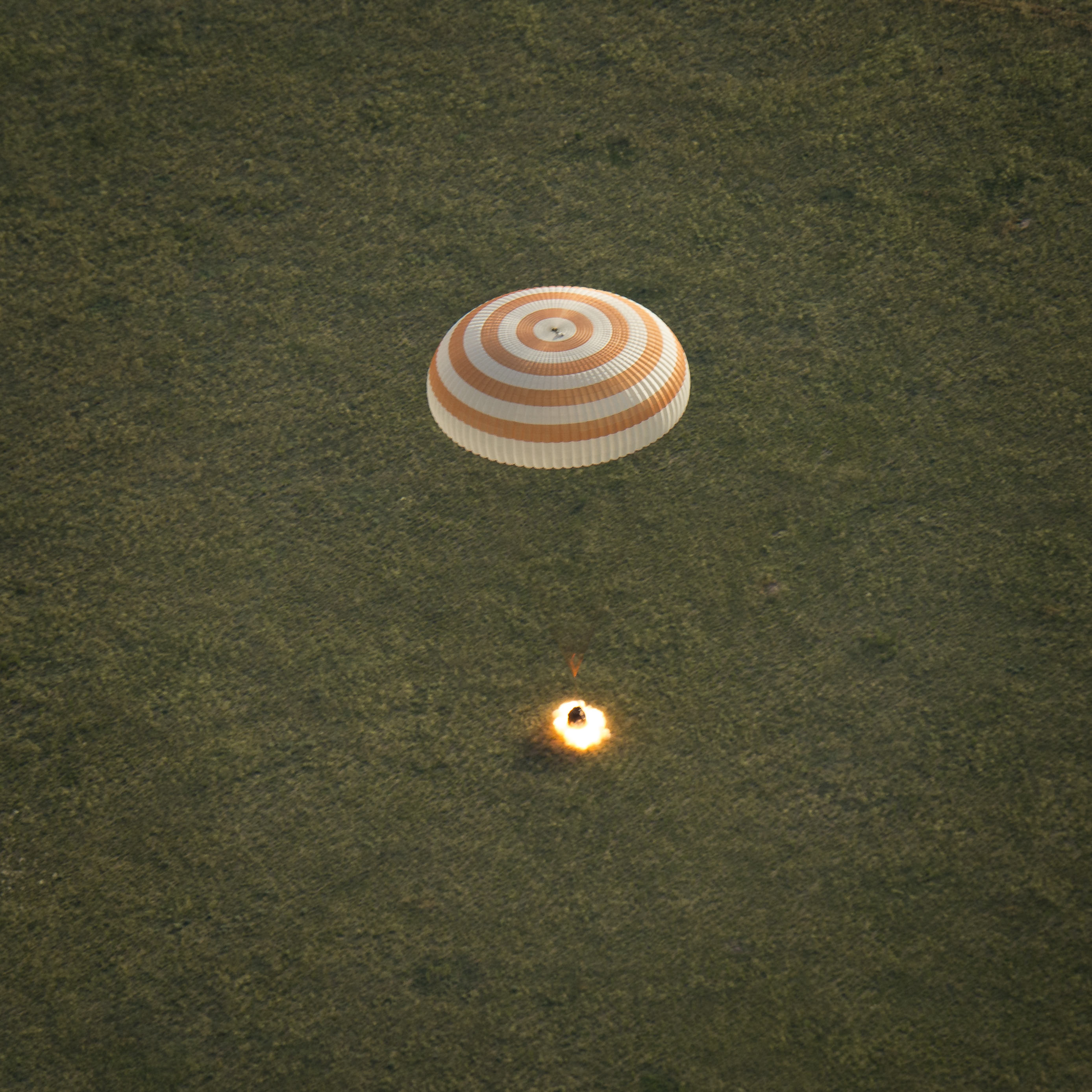
The next crewed launch to the station is set for July 22 aboard a Soyuz capsule with with an international trio comprising NASA astronaut Kjell Lindgren, Oleg Kononenko of the Russian Federal Space Agency and Kimiya Yui of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. Their flight was delayed from May 26 after the Progress 59 launch failure to ensure that there are no issues with the Soyuz rocket booster that will boost them to the ISS.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.