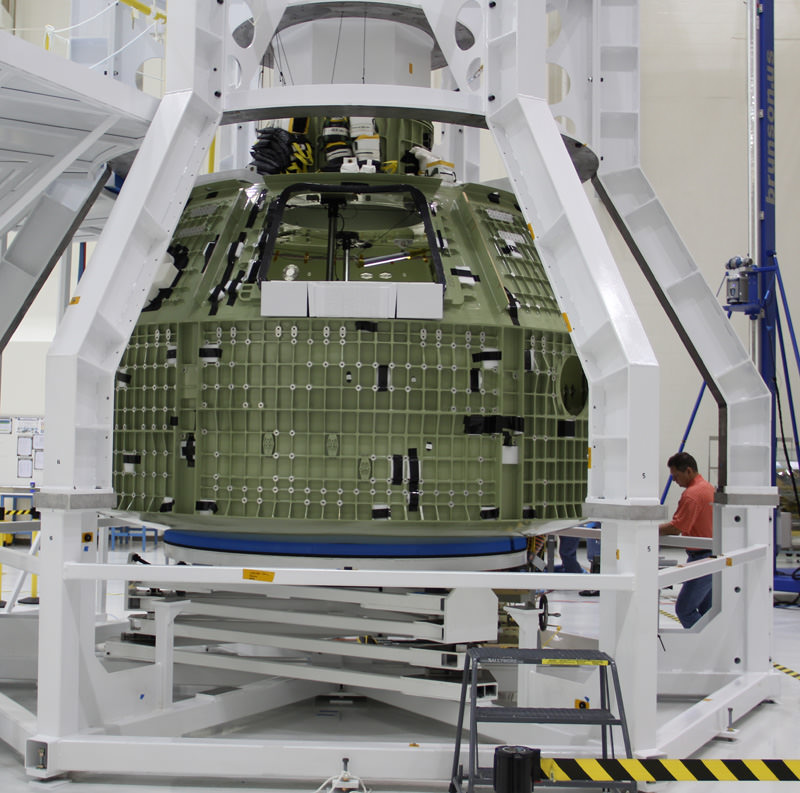
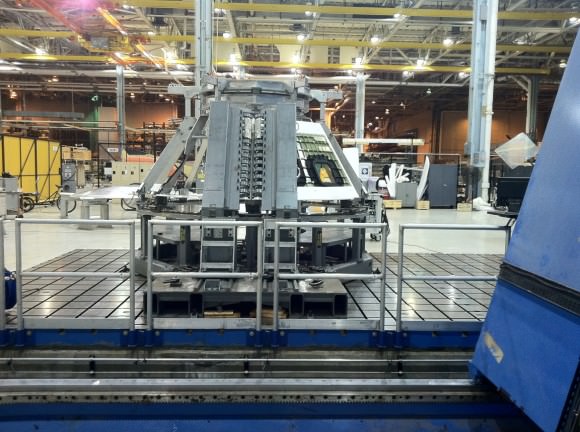
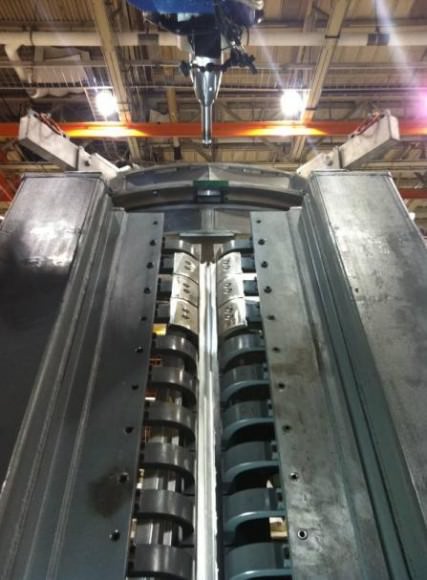
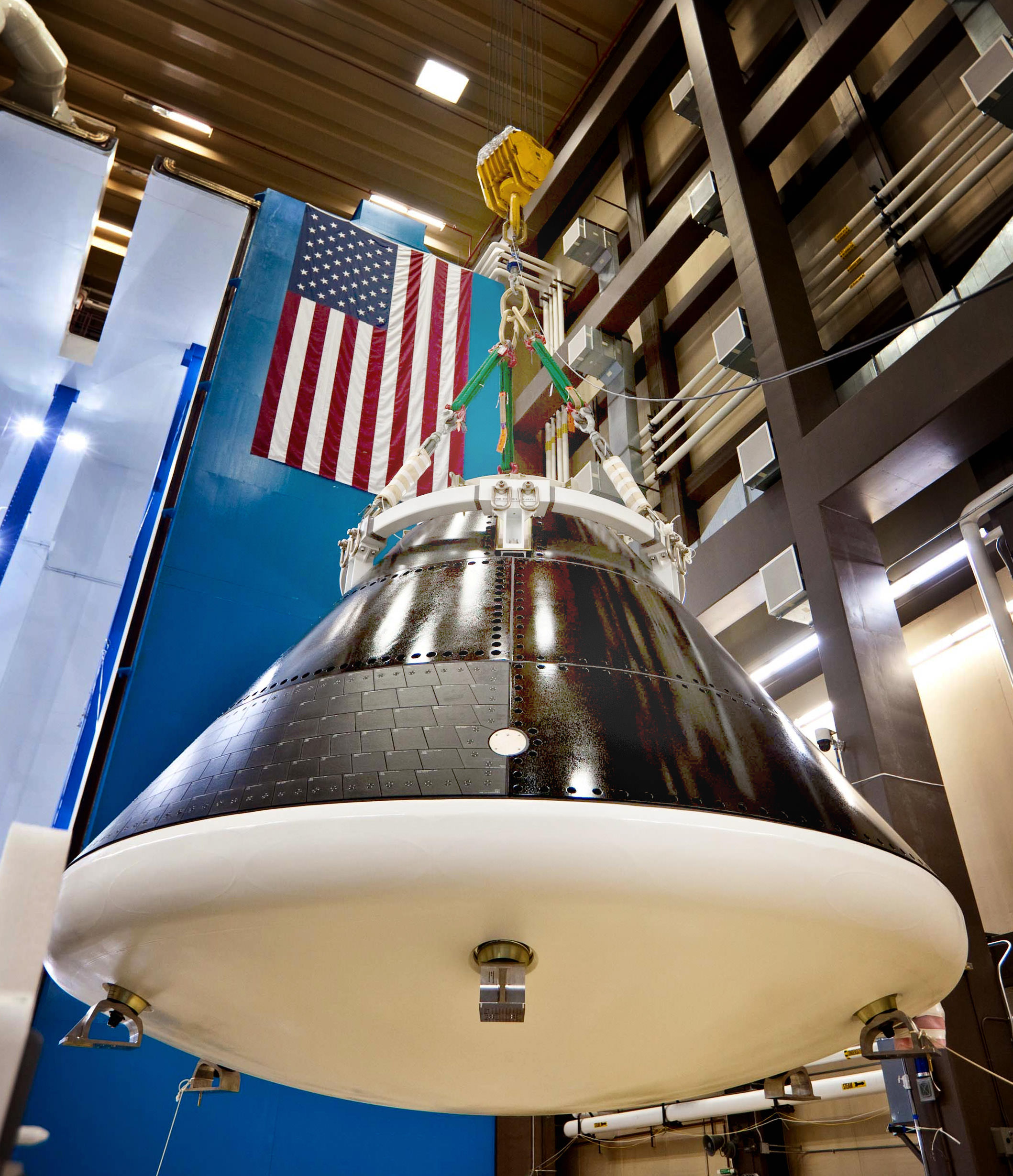
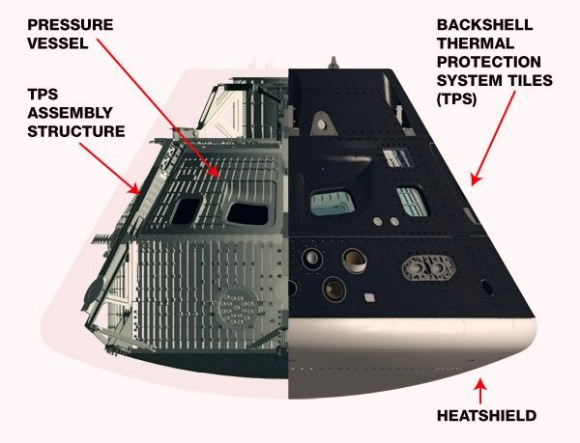
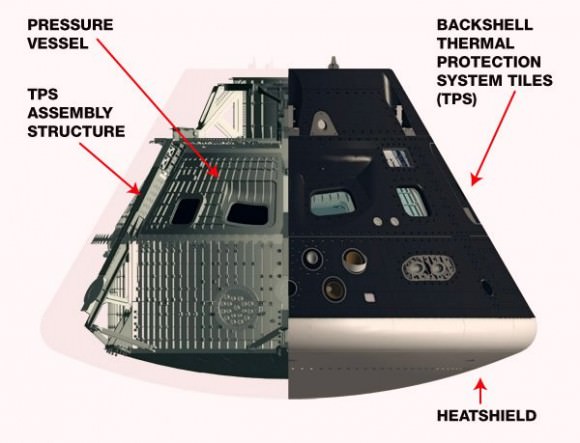
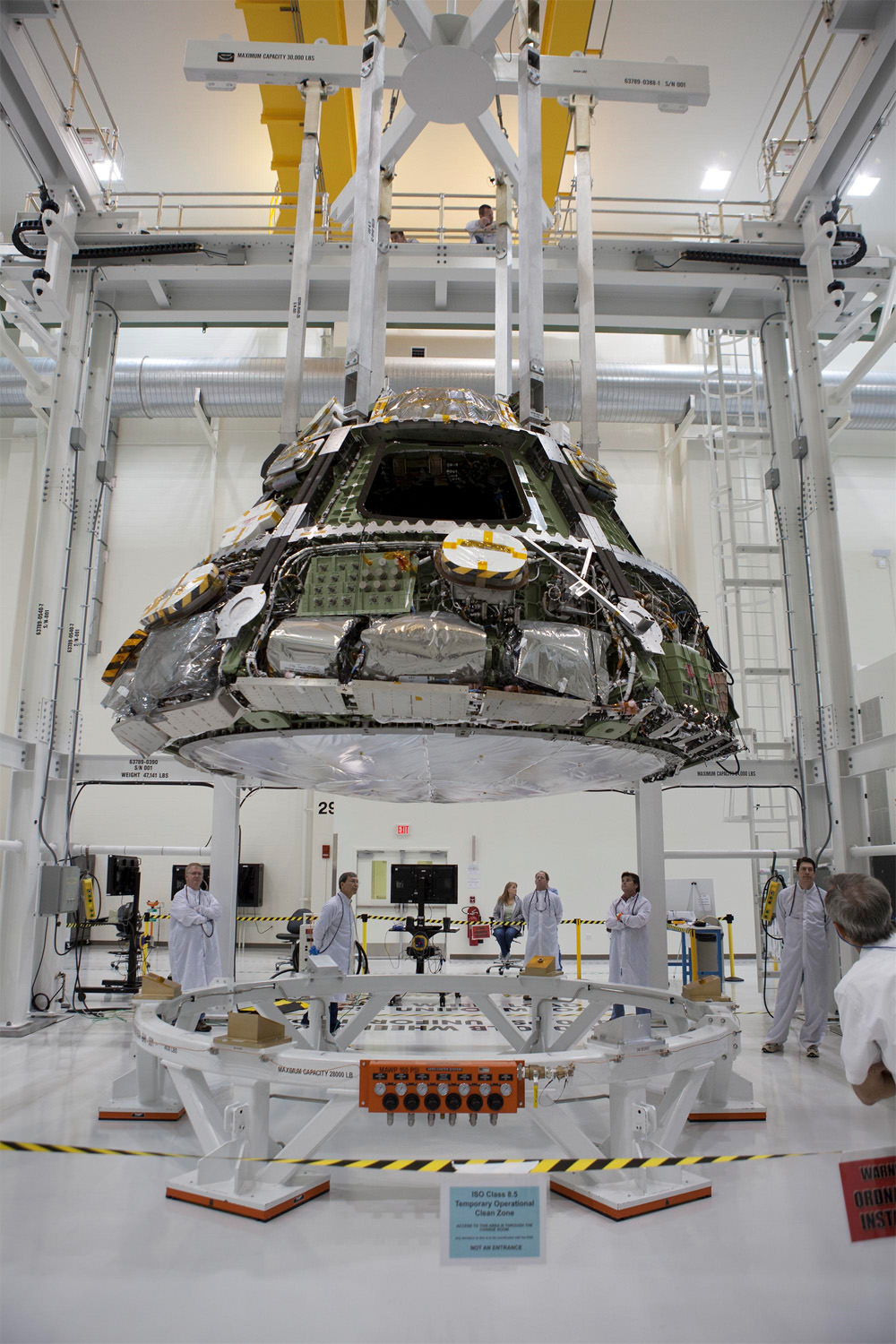
The Orion crew module for Exploration Flight Test-1 is shown in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) Cell, positioned over the service module just prior to mating the two sections together. Credit: NASA/Rad Sinyak
Story updated[/caption]
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL- Engineers have begun stacking operations for NASA’s maiden Orion deep space test capsule at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) achieving a major milestone leading to its first blastoff from the Florida Space Coast less than six months from today.
The excitement is mounting as final assembly of NASA’s Orion crew vehicle into its launch configuration started on Monday, June 9, inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at Kennedy.
Orion will eventually carry humans to destinations far beyond low Earth orbit on new voyages of scientific discovery in our solar system.
“Orion is the next step in our journey of exploration,” said NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot at a recent KSC media briefing.
“This mission is a stepping stone on NASA’s journey to Mars. The EFT-1 mission is so important to NASA.”
Orion is slated to launch on its inaugural unmanned test flight in December 2014 atop the mammoth, triple barreled United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV Heavy rocket.
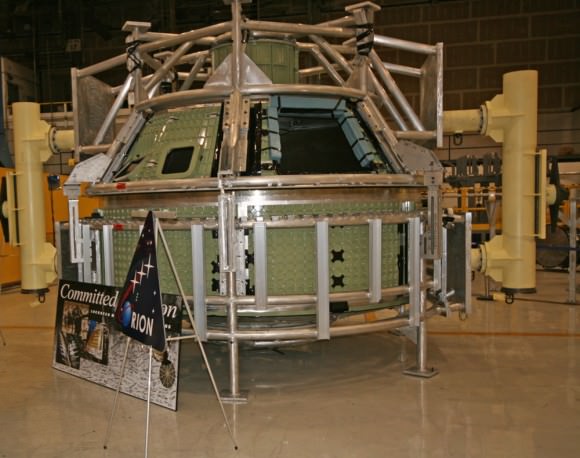
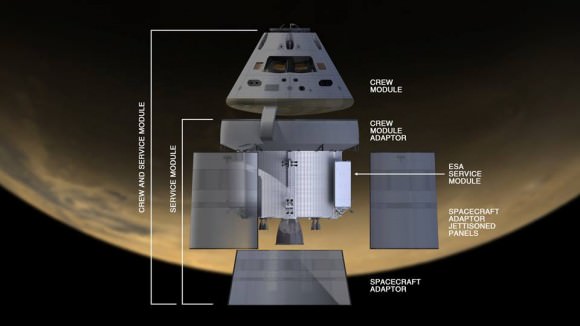
The main elements of the Orion spacecraft stack include the crew module (CM), service module (SM) and the launch abort system (LAS).
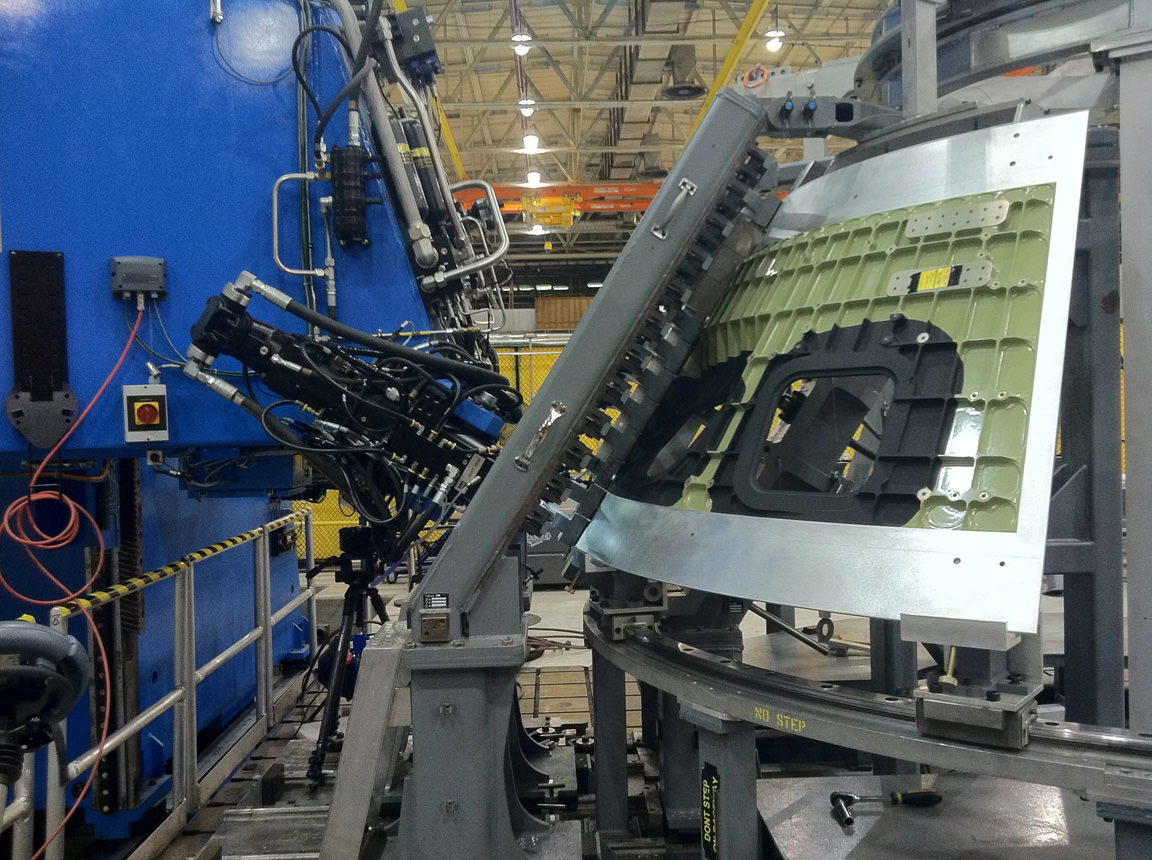
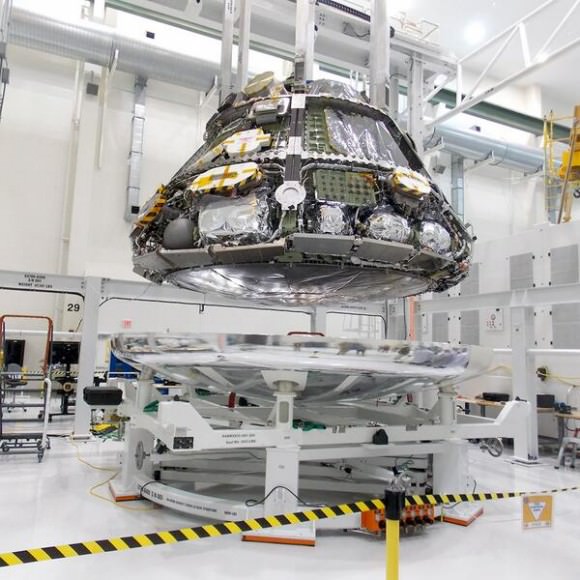
On Monday, technicians from Orion’s prime contractor Lockheed Martin began aligning and stacking the crew module on top of the already completed service module in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) Cell in the O & C facility at KSC.
“Ballast weights were added to ensure that the crew module’s center of gravity can achieve the appropriate entry and descent performance and also ensure that the vehicle lands in the correct orientation to reduce structural impact loads,” according to Lockheed Martin.
Engineers will remain busy throughout this week continuing to work at a 24/7 pace to get Orion ready for the December liftoff.
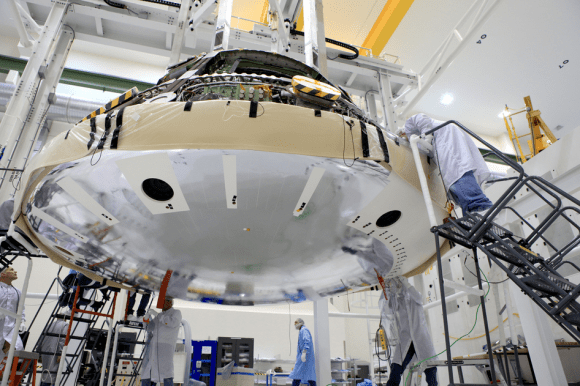
The next steps involve completing the power and fluid umbilical connections between the CM and SM and firmly bolting the two modules together inside the FAST cell.

An exhaustive series of electrical, avionic and radio frequency tests will follow. The team will then conduct final systems checks to confirm readiness for flight.
The LAS will then be stacked on top. The entire stack will then be rolled out to the launch pad for integration with the Delta IV Heavy rocket.
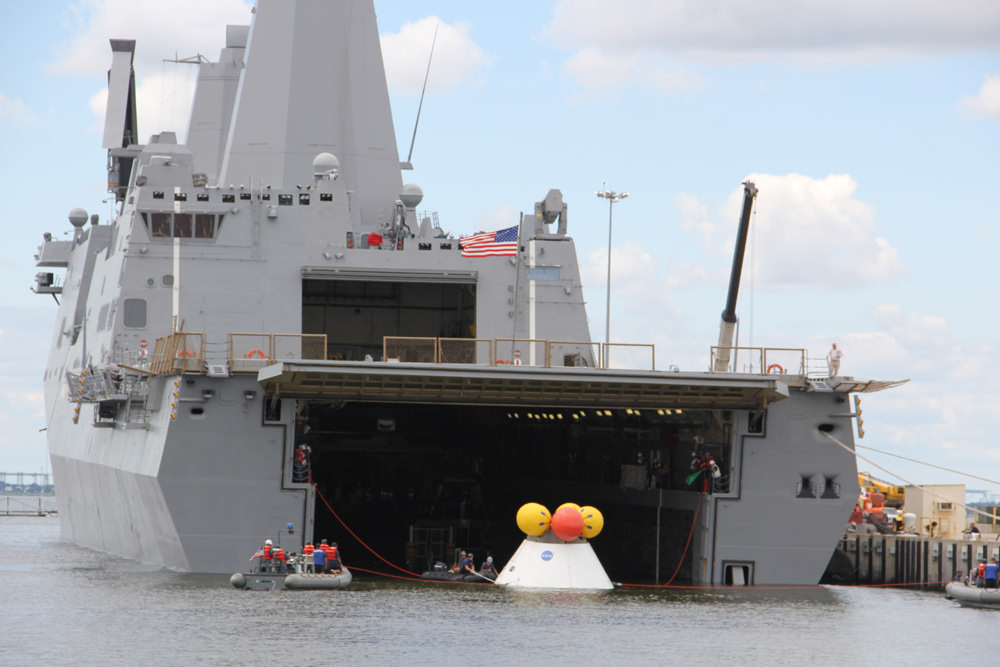
The CM/SM stacking operation was able to move forward following the successful attachment of the world’s largest heat shield onto the bottom of the CM in late May. Read my prior story – here.
“Now that we’re getting so close to launch, the spacecraft completion work is visible every day,” said Mark Geyer, NASA’s Orion Program manager in a statement.
“Orion’s flight test will provide us with important data that will help us test out systems and further refine the design so we can safely send humans far into the solar system to uncover new scientific discoveries on future missions.”

Orion is NASA’s next generation human rated vehicle now under development to replace the now retired space shuttle. The state-of-the-art spacecraft will carry America’s astronauts on voyages venturing farther into deep space than ever before – past the Moon to Asteroids, Mars and Beyond!
No humans have flown beyond low Earth orbit in more than four decades since Apollo 17, NASA’s final moon landing mission launched in December 1972.
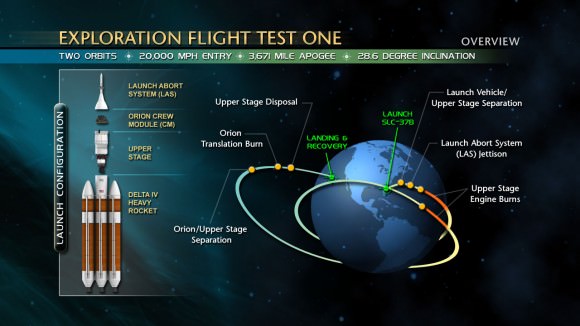
The two-orbit, four- hour EFT-1 flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.
One of the primary goals of NASA’s eagerly anticipated Orion EFT-1 uncrewed test flight is to test the efficacy of the heat shield in protecting the vehicle – and future human astronauts – from excruciating temperatures reaching 4000 degrees Fahrenheit (2200 C) during scorching re-entry heating.
At the conclusion of the EFT-1 flight, the detached Orion capsule plunges back and re-enters the Earth’s atmosphere at 20,000 MPH (32,000 kilometers per hour).
“That’s about 80% of the reentry speed experienced by the Apollo capsule after returning from the Apollo moon landing missions,” Scott Wilson, NASA’s Orion Manager of Production Operations at KSC, told me during an interview at KSC.
A trio of parachutes will then unfurl to slow Orion down for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
The EFT-1 mission will provide engineers with critical data about Orion’s heat shield, flight systems and capabilities to validate designs of the spacecraft, inform design decisions, validate existing computer models and guide new approaches to space systems development. All these measurements will aid in reducing the risks and costs of subsequent Orion flights before it begins carrying humans to new destinations in the solar system.
“We will test the heat shield, the separation of the fairing and exercise over 50% of the eventual software and electronic systems inside the Orion spacecraft. We will also test the recovery systems coming back into the Pacific Ocean,” said Lightfoot.
“Orion EFT-1 is really exciting as the first step on the path of humans to Mars,” said Lightfoot. “It’s a stepping stone to get to Mars.”
“We will test the capsule with a reentry velocity of about 85% of what to expect on returning [astronauts] from Mars.”

Concurrently, new American-made private crewed spaceships are under development by SpaceX, Boeing and Sierra Nevada – with funding from NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) – to restore US capability to ferry US astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) and back to Earth by late 2017.
Read my exclusive new interview with NASA Administrator Charles Bolden explaining the importance of getting Commercial Crew online to expand our reach into space- here.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, Curiosity, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more planetary and human spaceflight news.
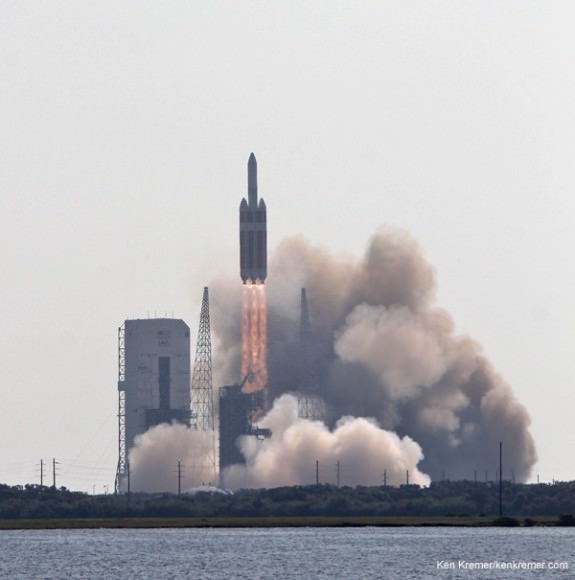






 Delta 4 Heavy rocket and super secret US spy satellite roar off Pad 37 on June 29, 2012 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Orion EFT-1 capsule will blastoff atop a similar Delta 4 Heavy Booster in December 2014. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com[/caption]
Delta 4 Heavy rocket and super secret US spy satellite roar off Pad 37 on June 29, 2012 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Orion EFT-1 capsule will blastoff atop a similar Delta 4 Heavy Booster in December 2014. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com[/caption]