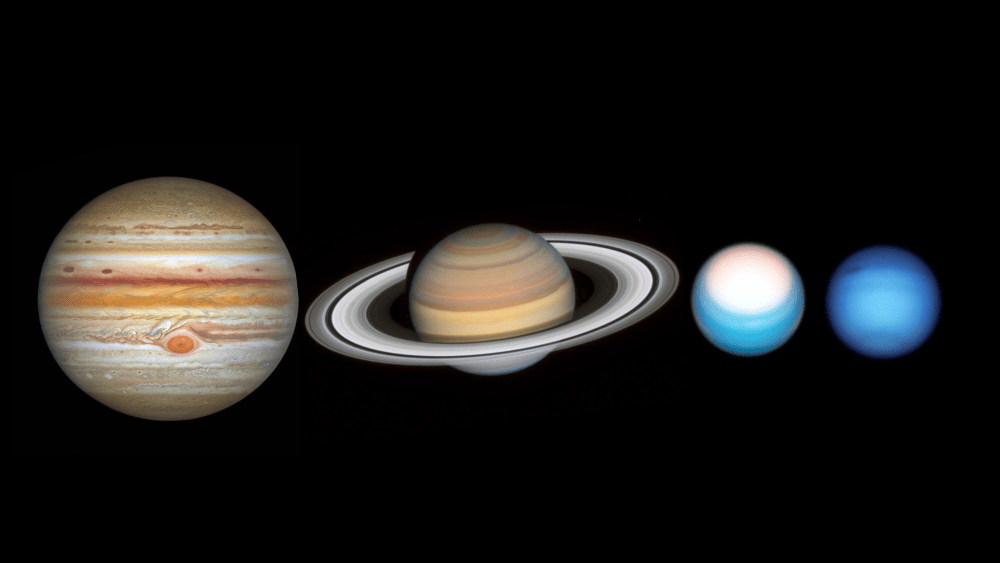
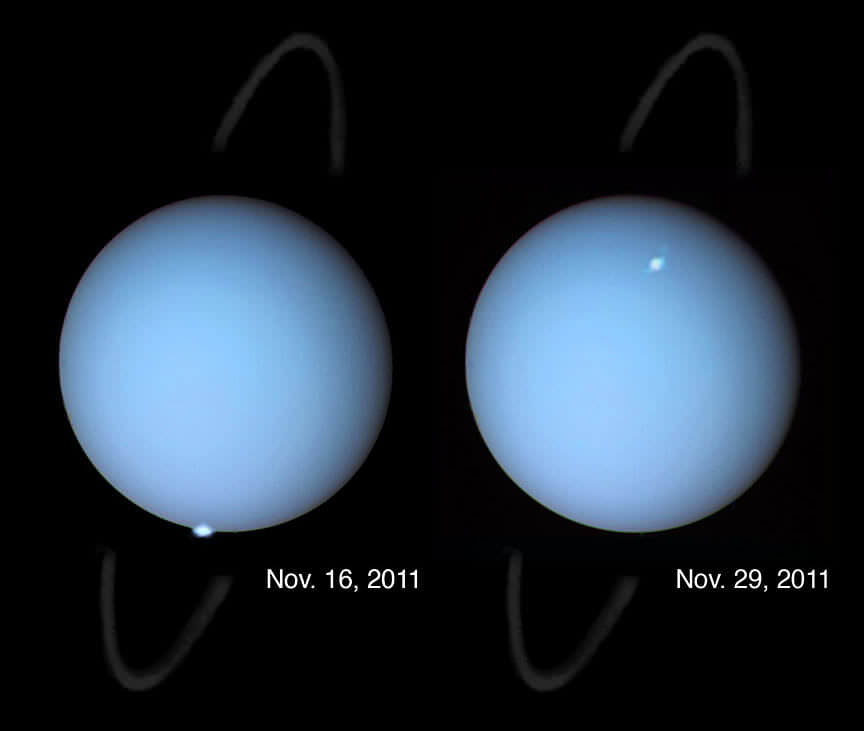
In the near future, astronomers will benefit from the presence of next-generation telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (RST). At the same time, improved data mining and machine learning techniques will also allow astronomers to get more out of existing instruments. In the process, they hope to finally answer some of the most burning questions about the cosmos.
For instance, the Dark Energy Survey (DES ), an international, collaborative effort to map the cosmos, recently released the results of their six-year survey of the outer Solar System. In addition to gathering data on hundreds of known objects, this survey revealed 461 previously undetected objects. The results of this study could have significant implications for our understanding of the Solar System’s formation and evolution.
Continue reading “A 6-Year Search of the Outer Solar System Turns up 461 new Objects (but no Planet 9)”