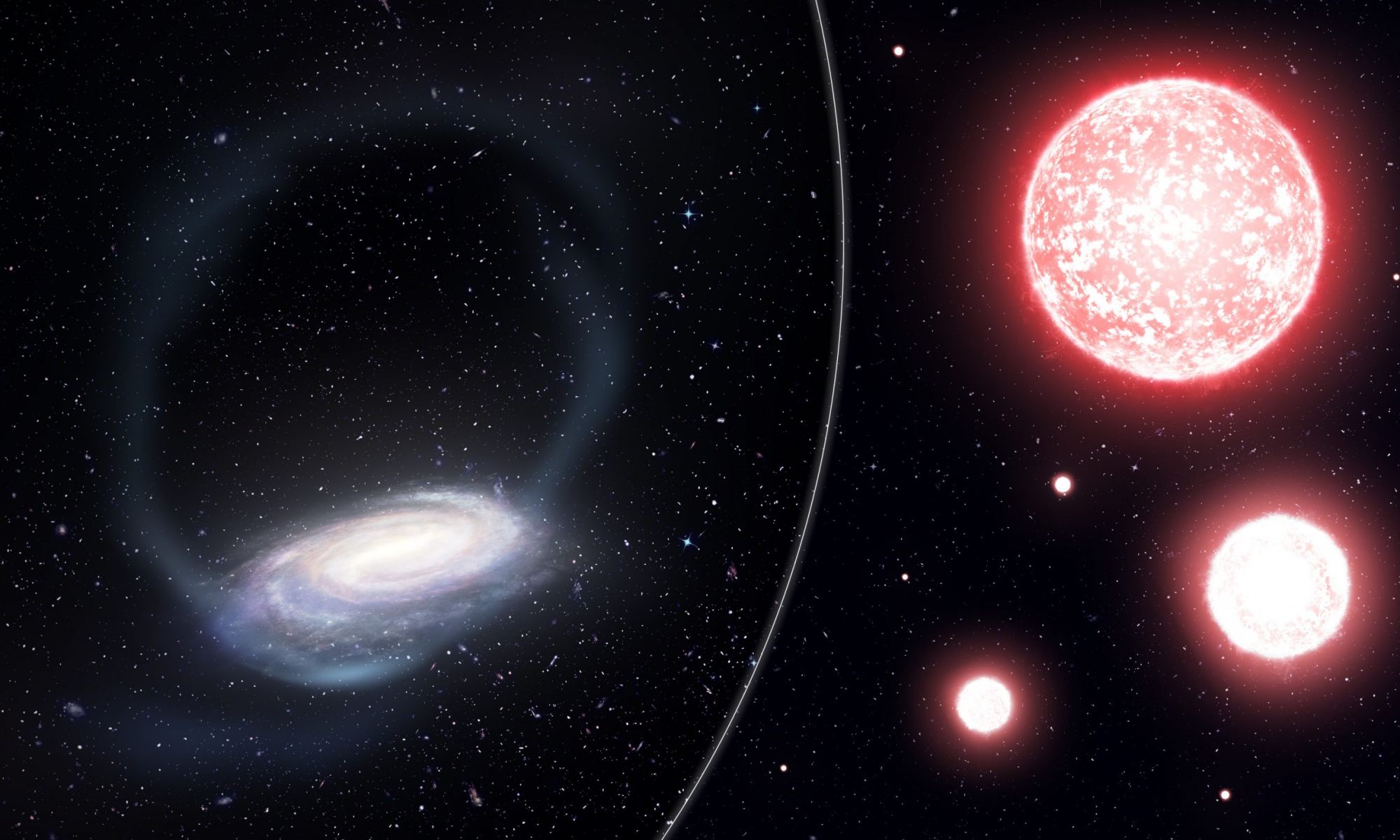
According to predominant theories of galaxy formation, the earliest galaxies in the Universe were born from the merger of globular clusters, which were in turn created by the first stars coming together. Today, these spherical clusters of stars are found orbiting around the a galactic core of every observable galaxy and are a boon for astronomers seeking to study galaxy formation and some of the oldest stars in the Universe.
Interestingly enough, it appears that some of these globular clusters may not have survived the merger process. According to a new study by an international team of astronomers, a cluster was torn apart by our very own galaxy about two billion years ago. This is evidenced by the presence of a metal-poor debris ring that they observed wrapped around the entire Milky Way, a remnant from this ancient collision.
Continue reading “A Globular Cluster was Completely Dismantled and Turned Into a Ring Around the Milky Way”