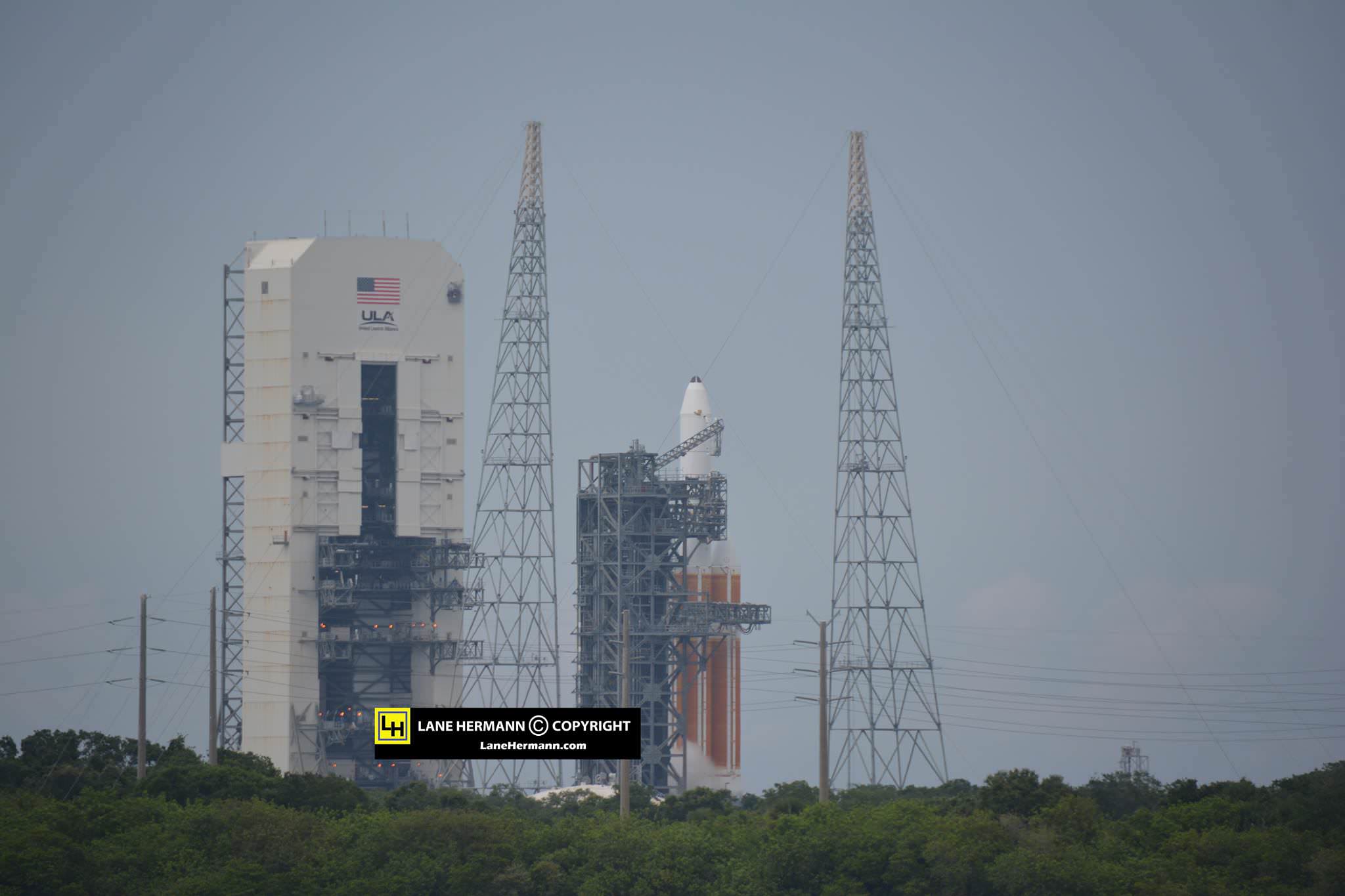
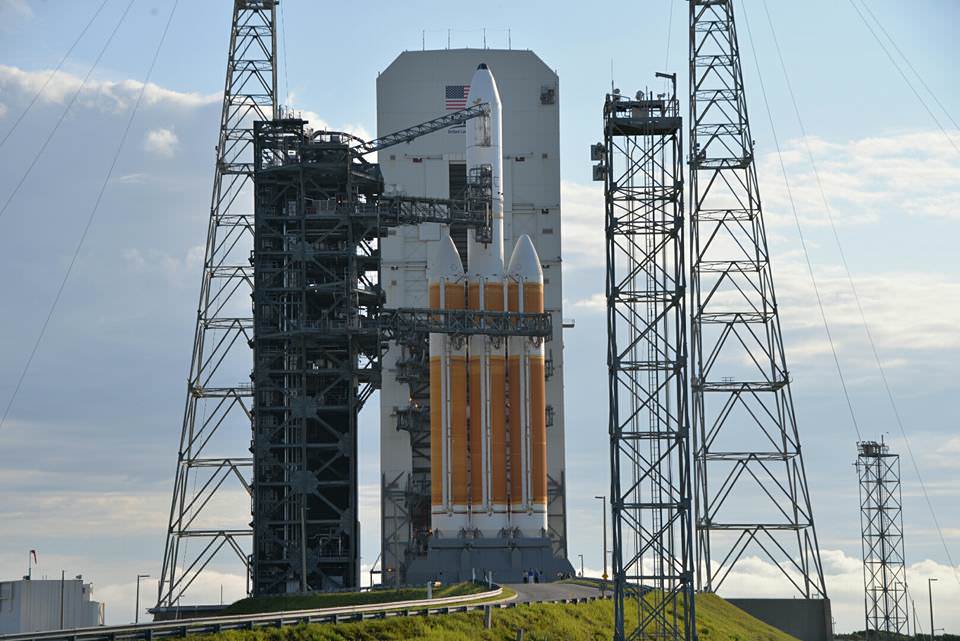
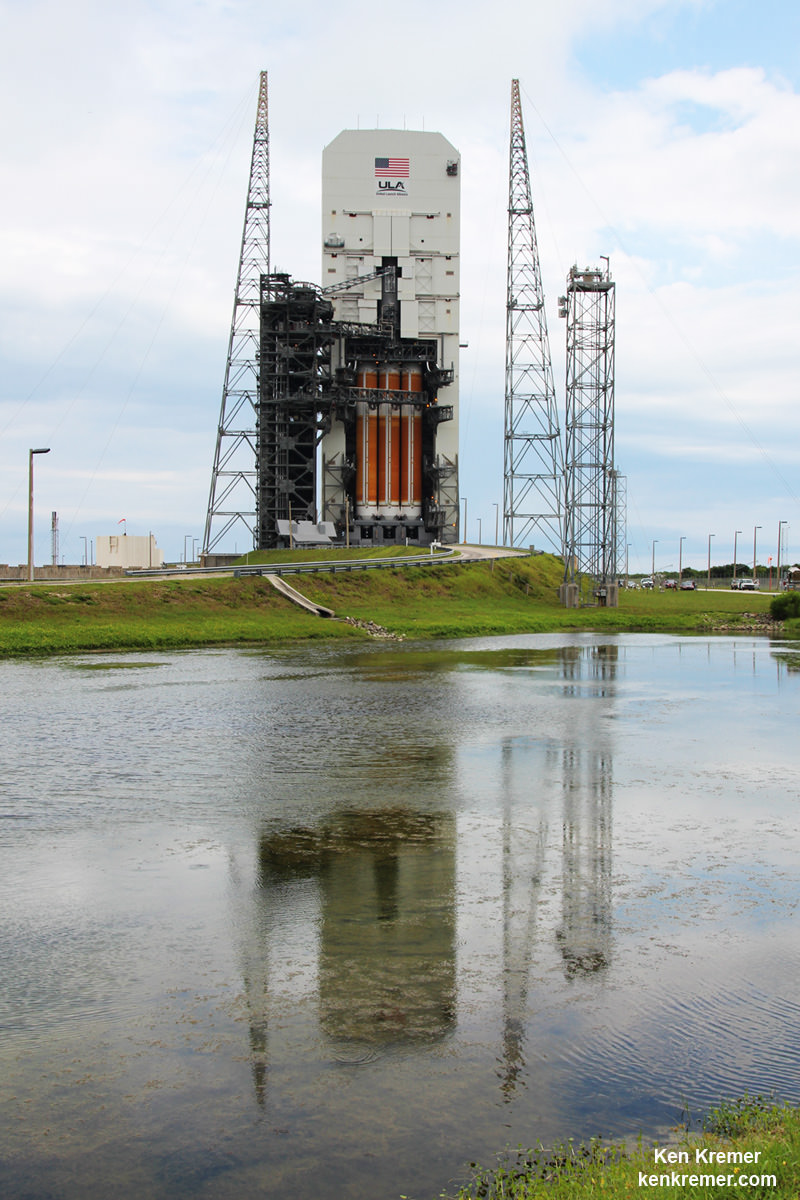
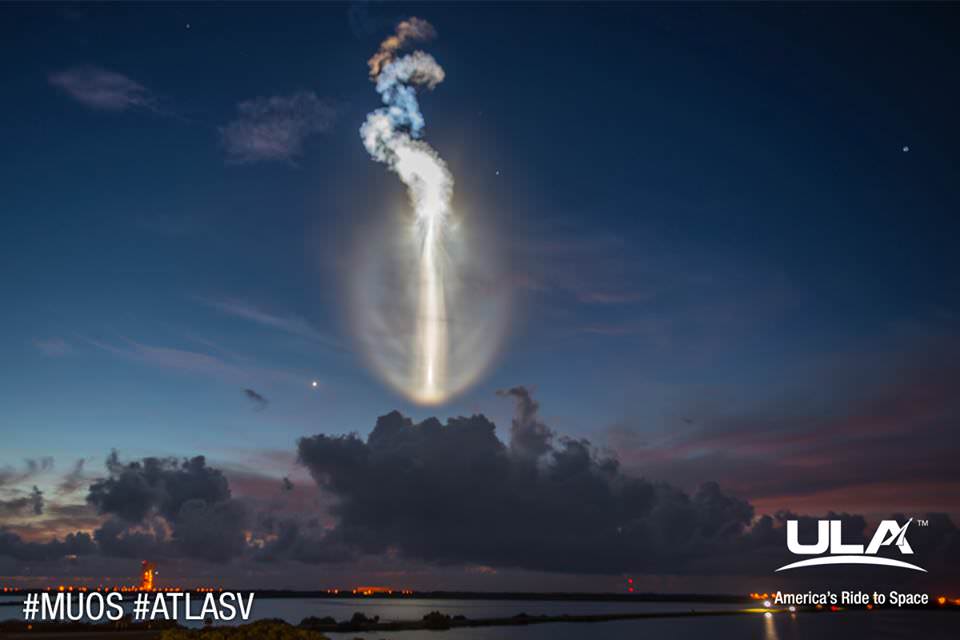
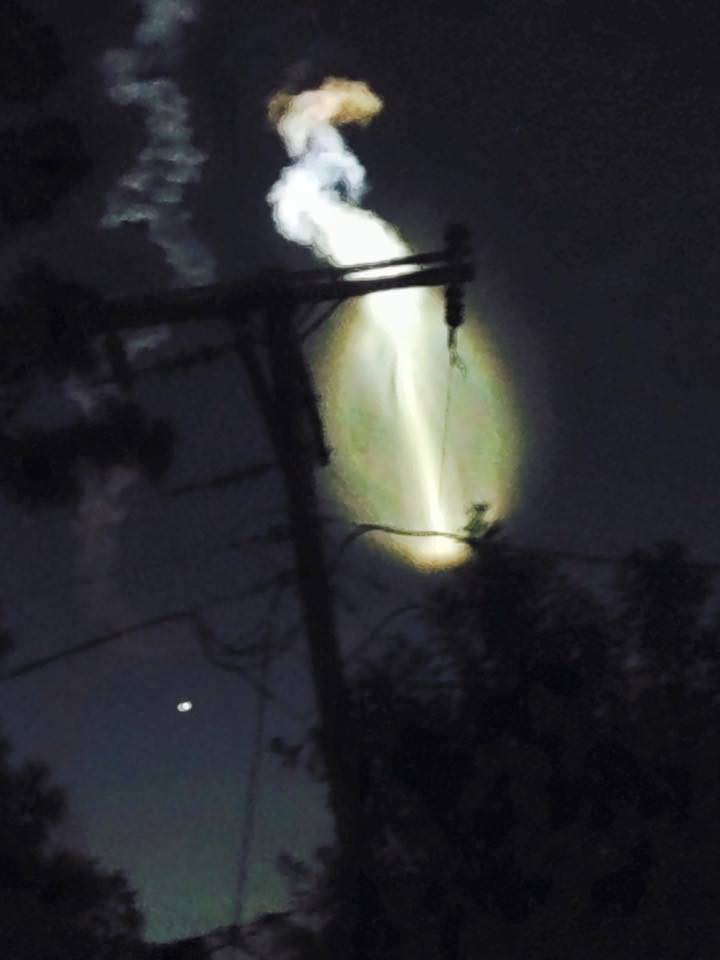
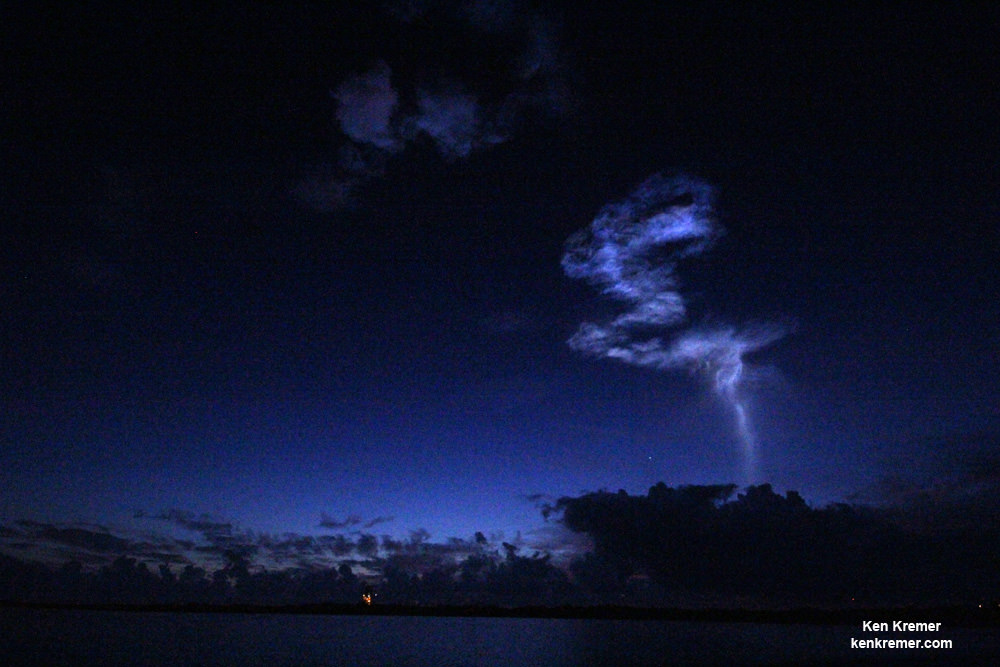
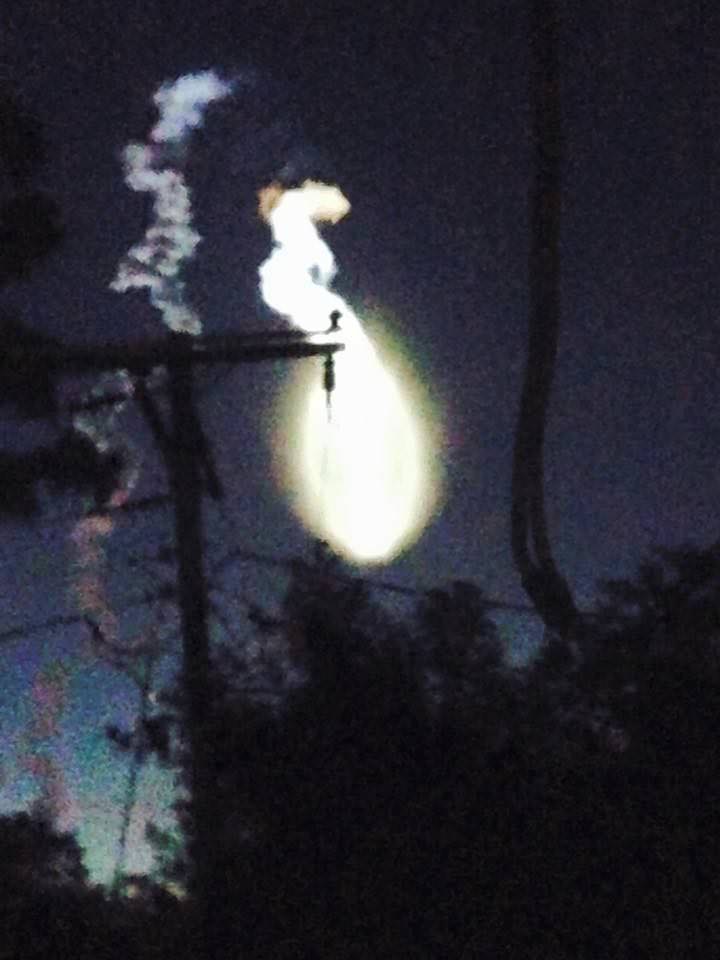
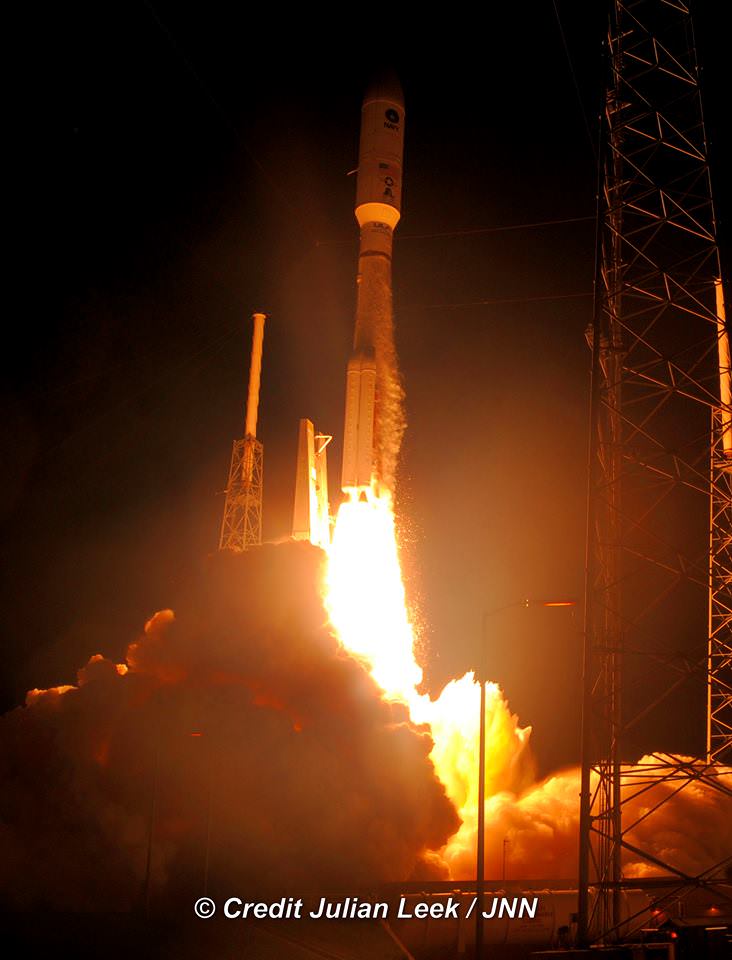
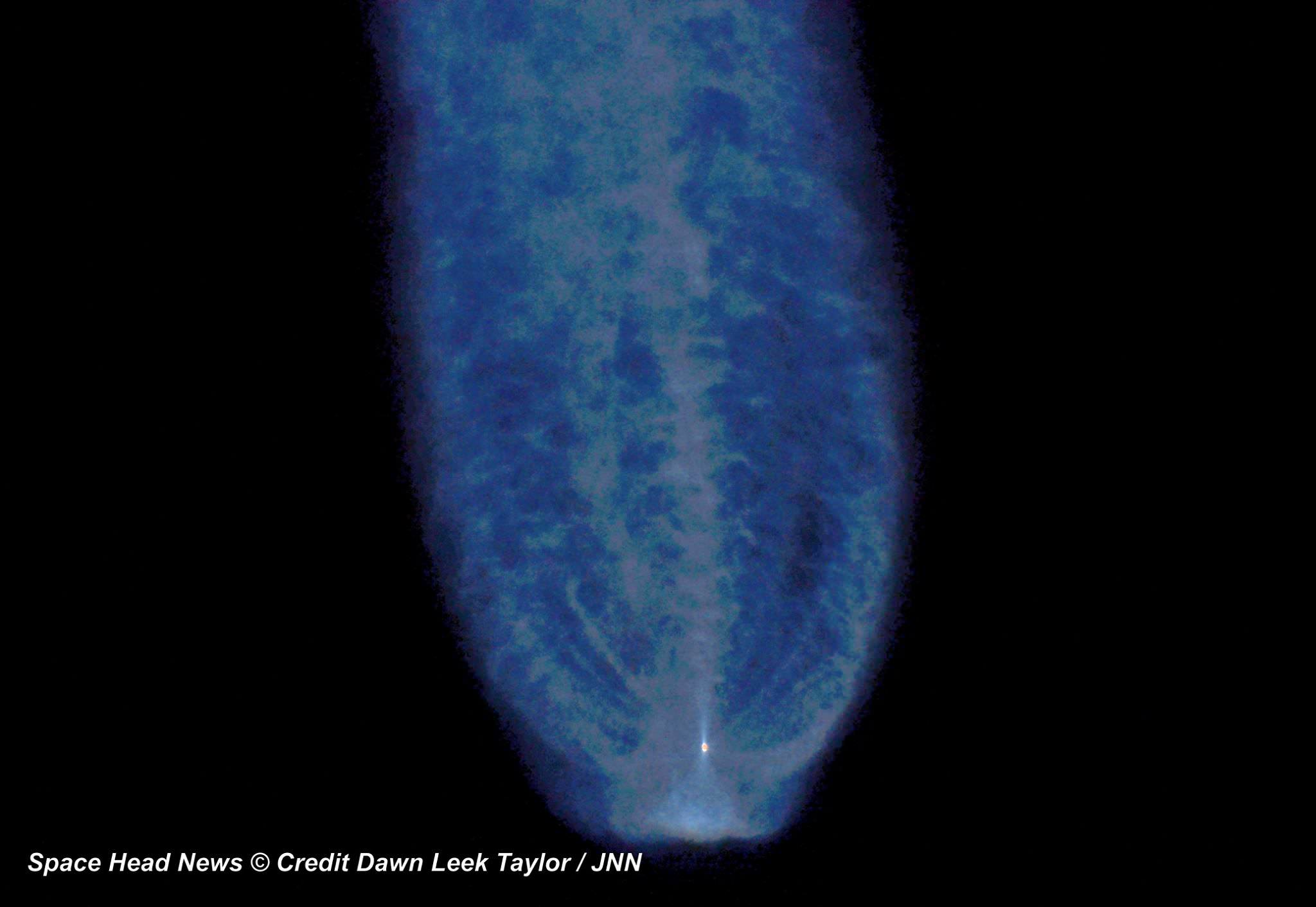
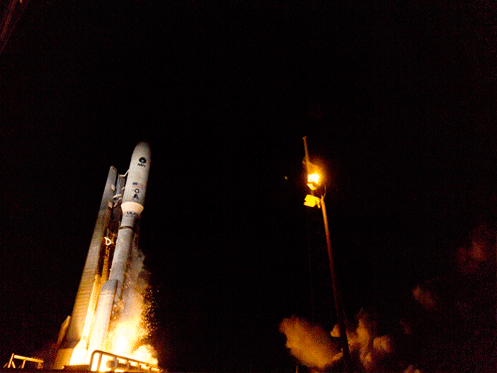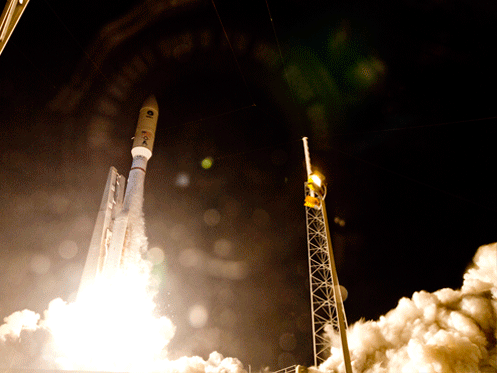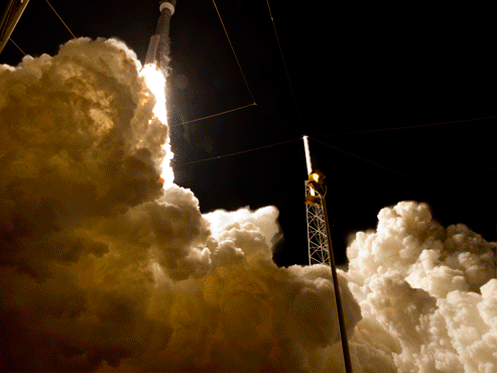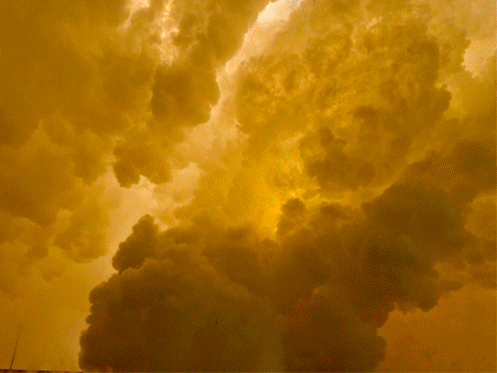
Today’s (June 24) spectacular launch of the most powerful version of the venerable Atlas V rocket from the sunshine state completes the orbital deployment of a constellation of advanced tactical communications satellites for the U.S. Navy.
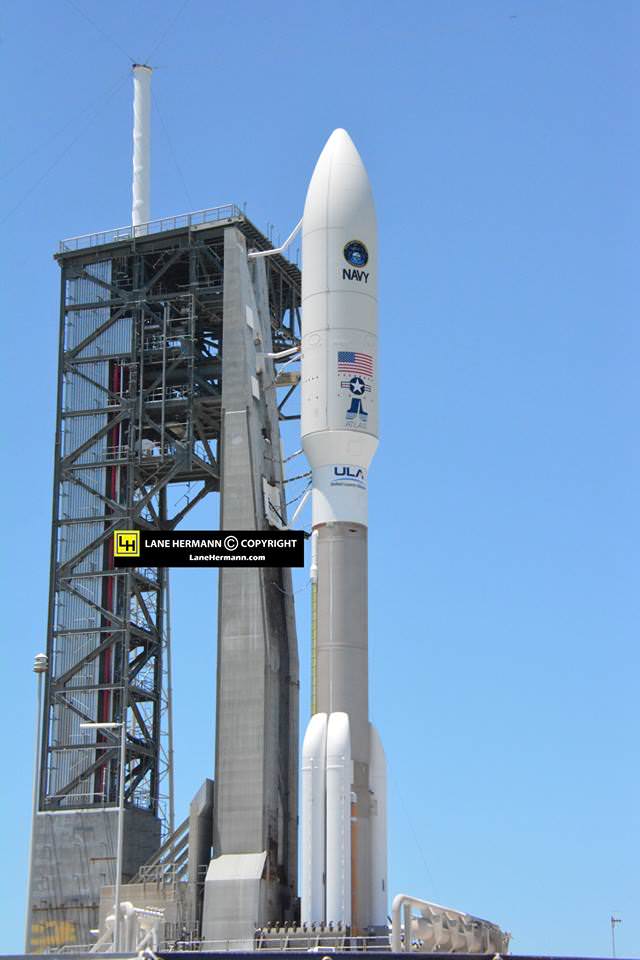
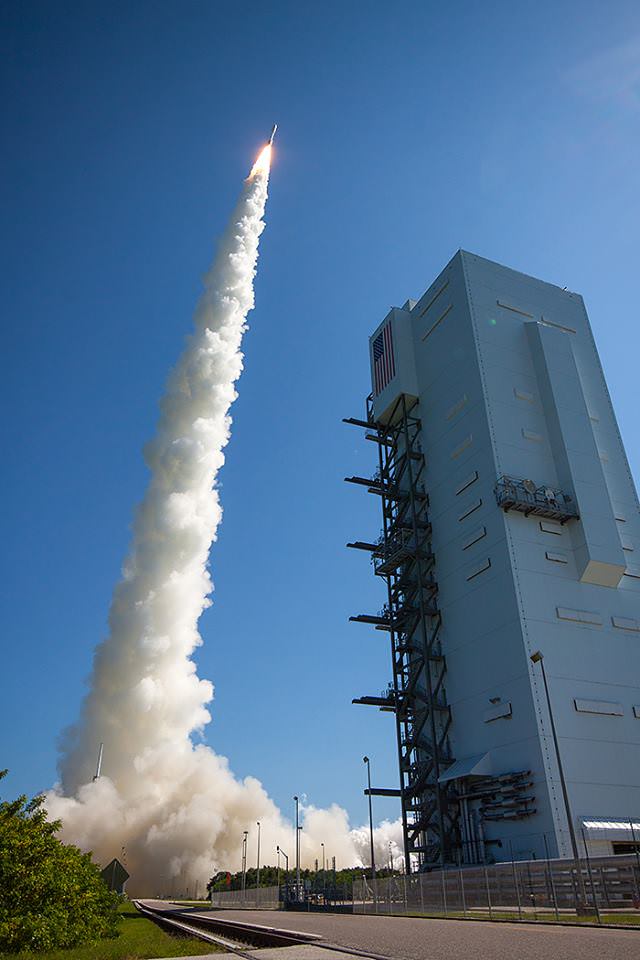
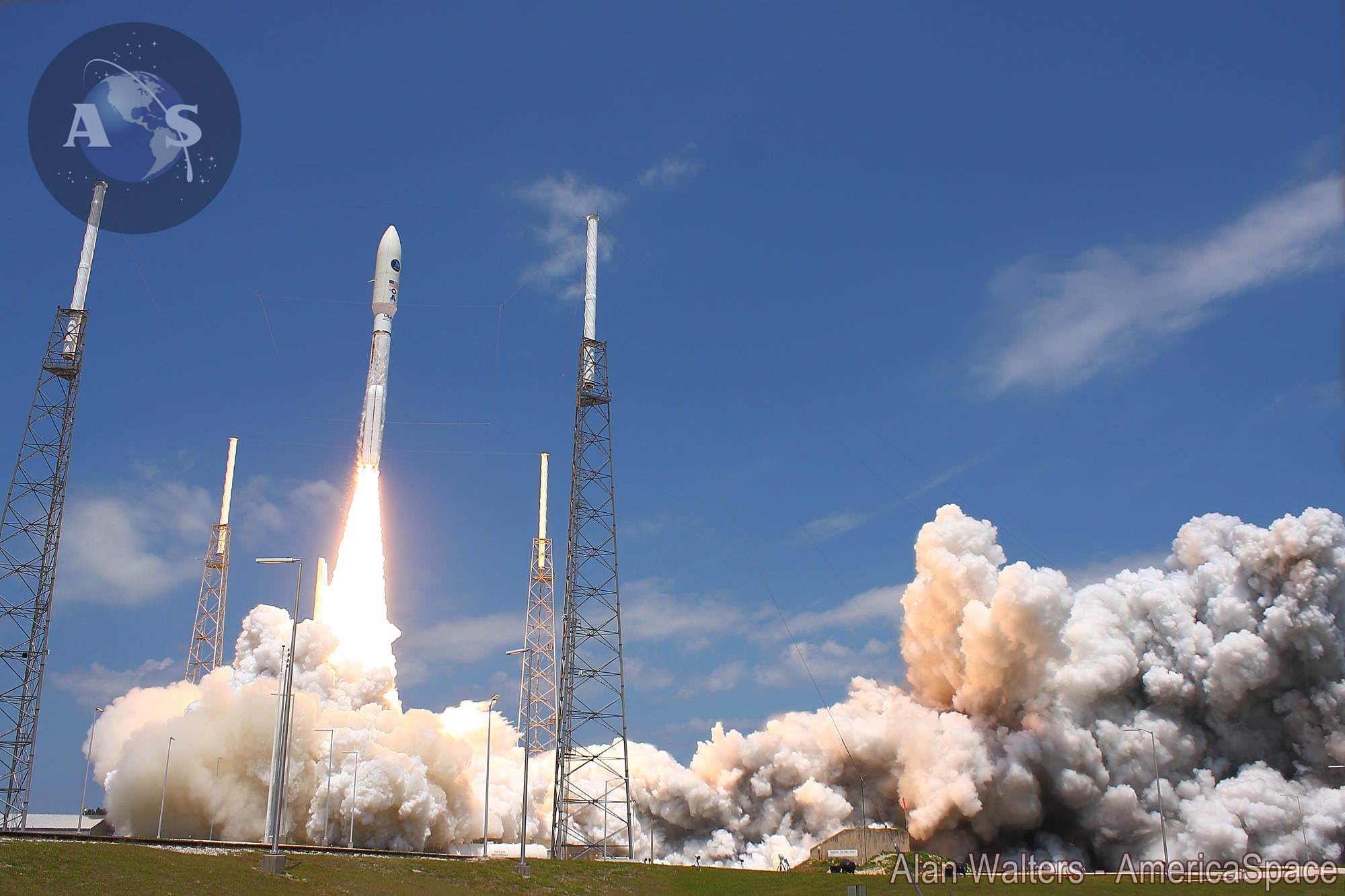
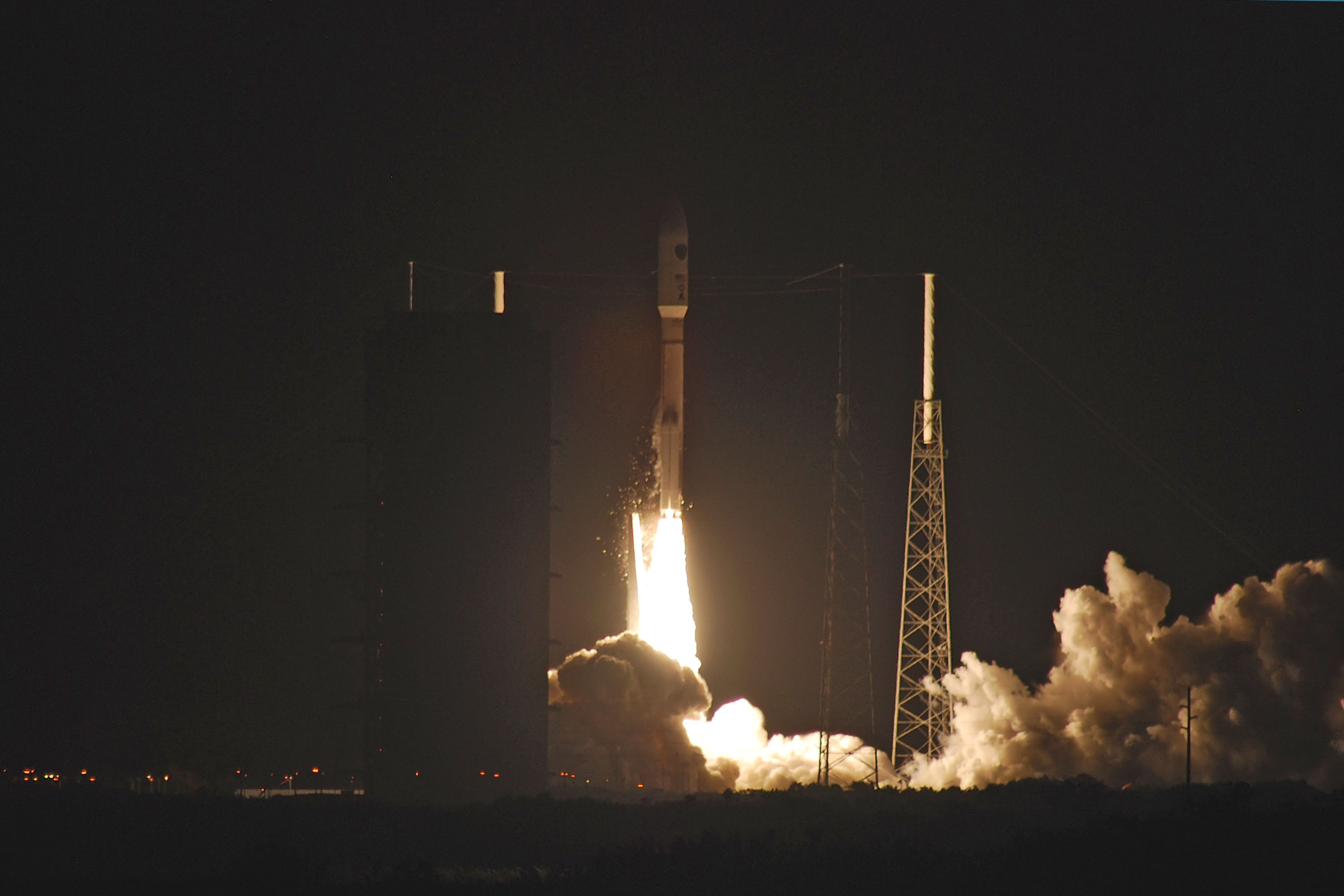
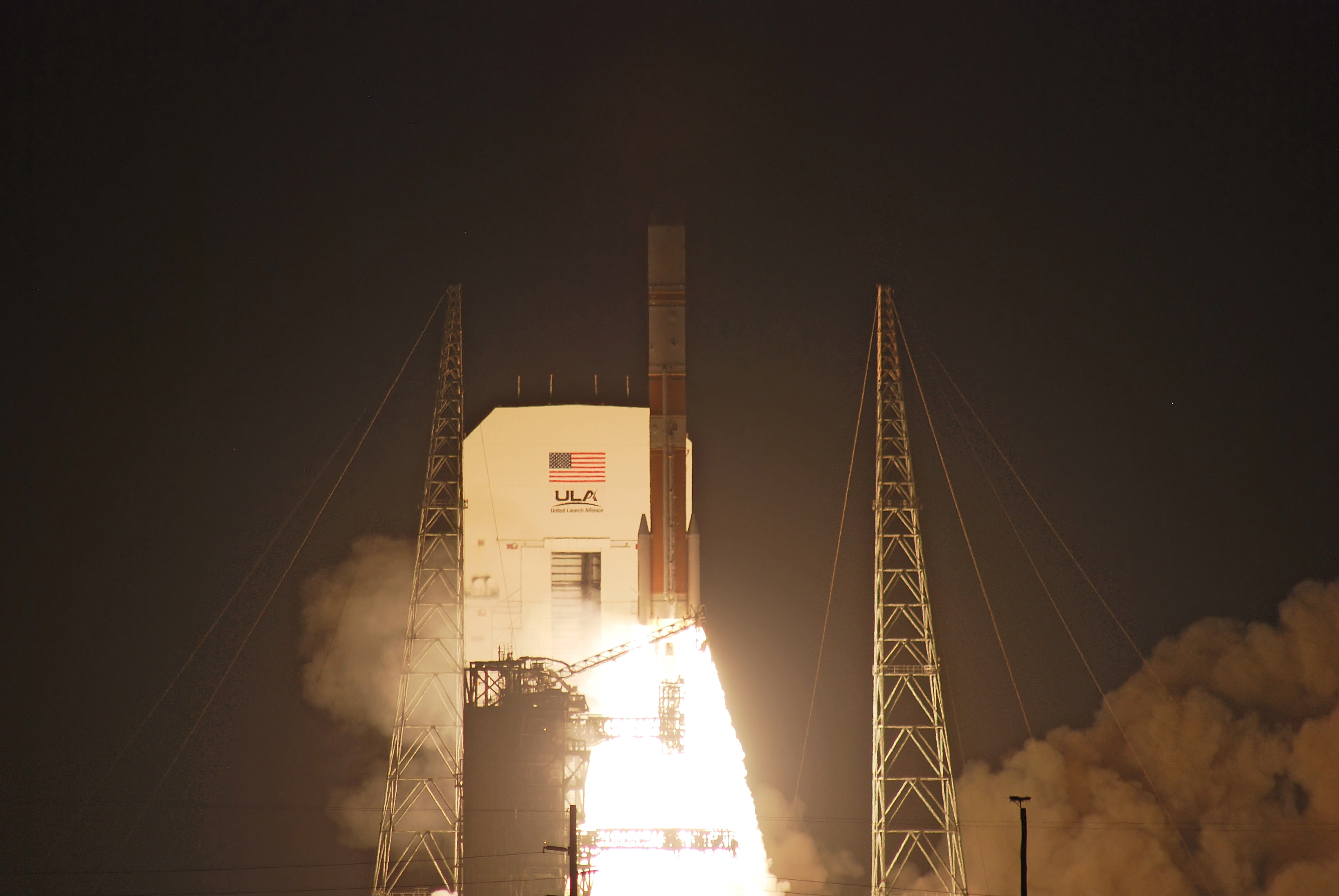
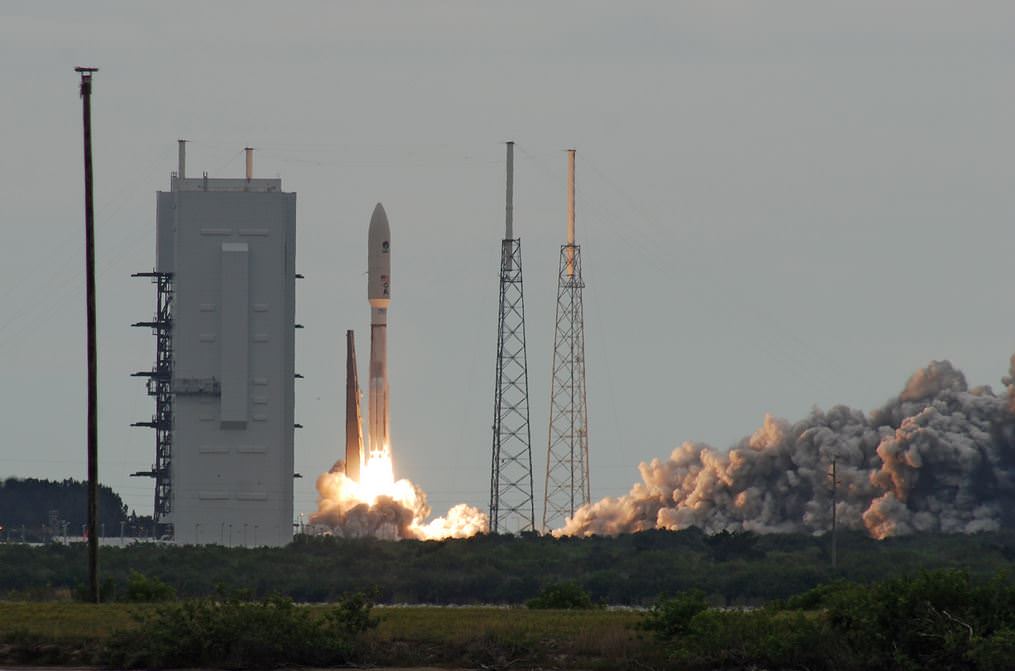
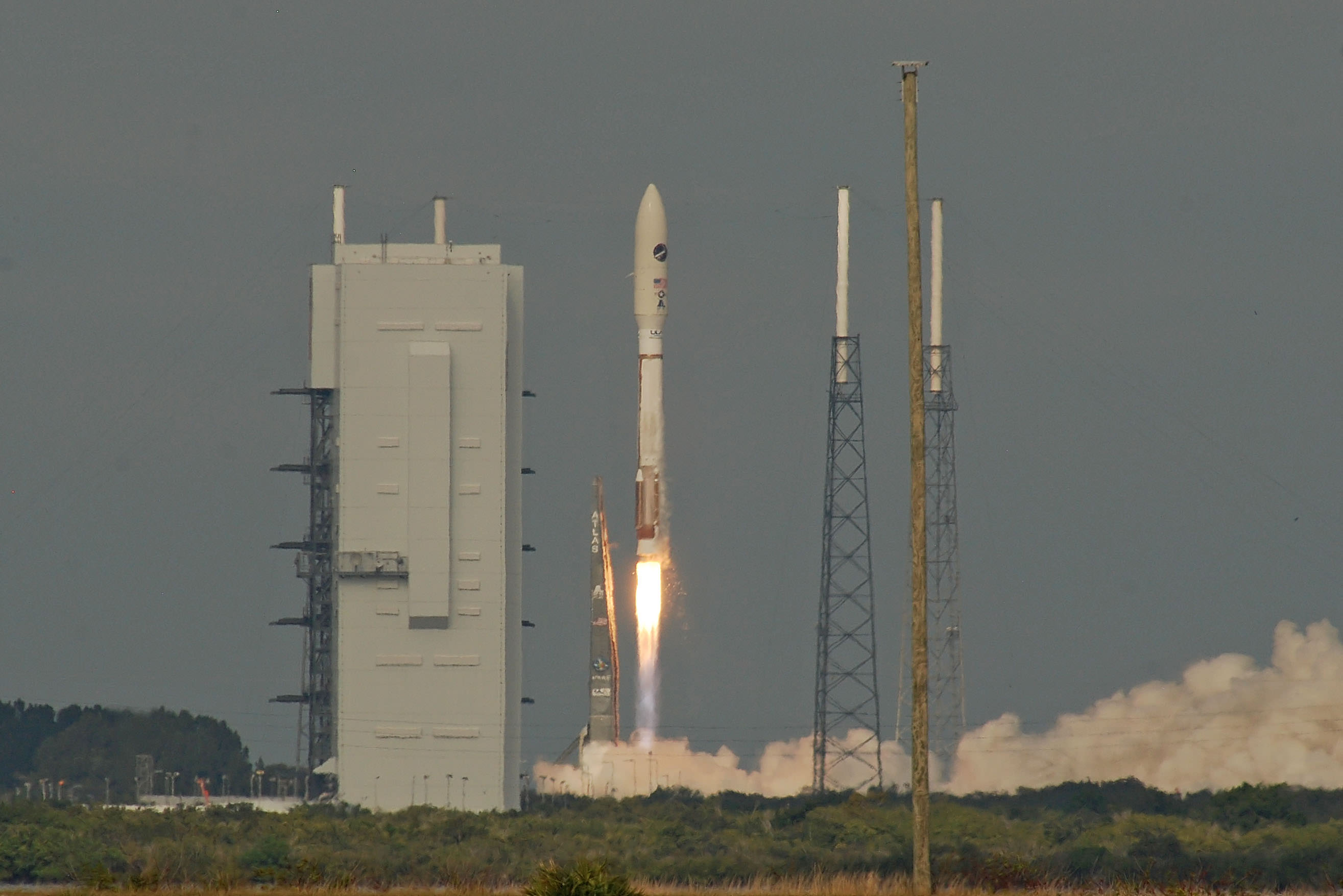
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket successfully launched the massive MUOS-5 satellite into clear blue skies from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, at 10:30 a.m. EDT – on its way to a geosynchronous orbit location approximately 22,000 miles (37,586 km) above the Earth.
Note: Check back again for an expanding gallery of launch photos and videos
The Mobile User Objective System-5 (MUOS-5) satellite is the last in a five-satellite constellation that will provide military forces with significantly improved and assured communications worldwide. Lockheed Martin is the prime contractor for the MUOS system.
As launch time neared the weather odds improved to 100% GO and Atlas rumbled off the pad for on time launch that took place at the opening of a 44 minute window.
The launch was broadcast live on a ULA webcast.
The 206 foot tall Atlas rocket roared to space on an expanding plume of smoke and crackling fire from the first stage liquid and solid fueled engines generating over 2.5 million pounds of liftoff thrust.
Their contribution complete, all 5 solid rocket motors were jettisoned with seconds about 2 minutes after liftoff as the liquid fueled first stage continued firing.
The spent first stage separated about 5 minutes after liftoff, as the Centaur second stage fires up for the first of three times over almost three hours to deliver the hefty payload to orbit.
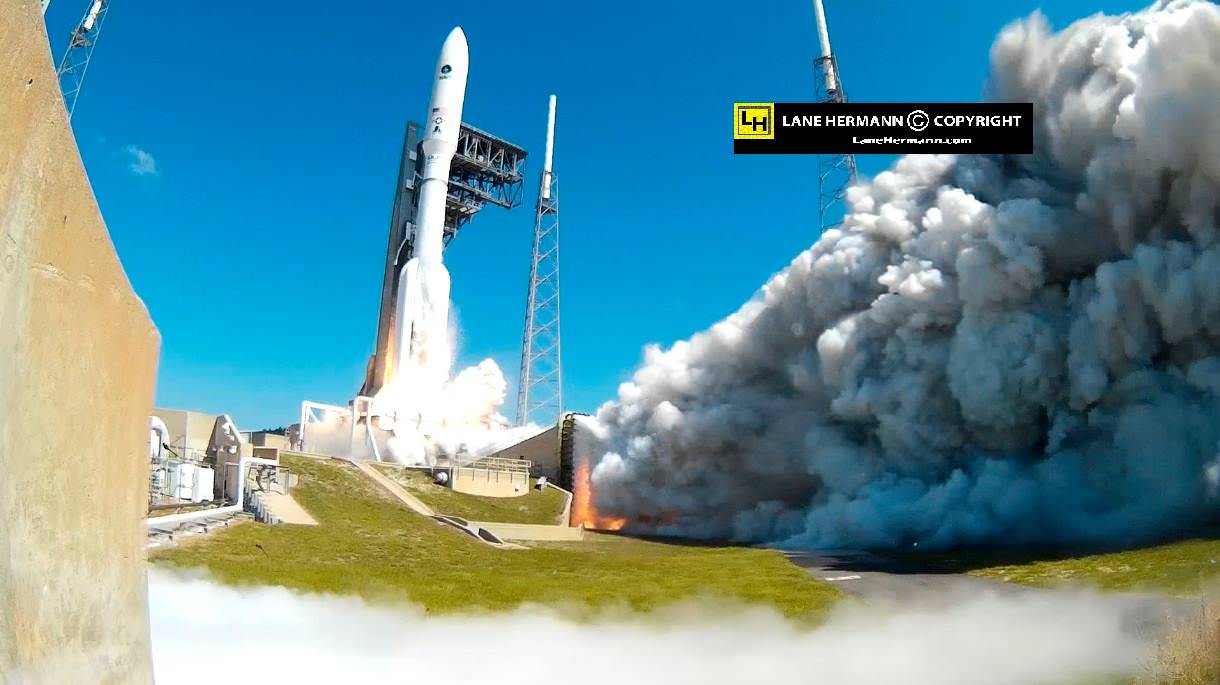

“We are honored to deliver the final satellite in the MUOS constellation for the U.S. Navy,” said Laura Maginnis, ULA vice president, Custom Services, in a statement.
“Congratulations to our navy, air force and Lockheed Martin mission partners on yet another successful launch that provides our warfighters with enhanced communications capabilities to safely and effectively conduct their missions around the globe.”
This is the fifth satellite in the MUOS series and will provide military users up to 16 times more communications capability over existing systems, including simultaneous voice, video and data, leveraging 3G mobile communications technology.
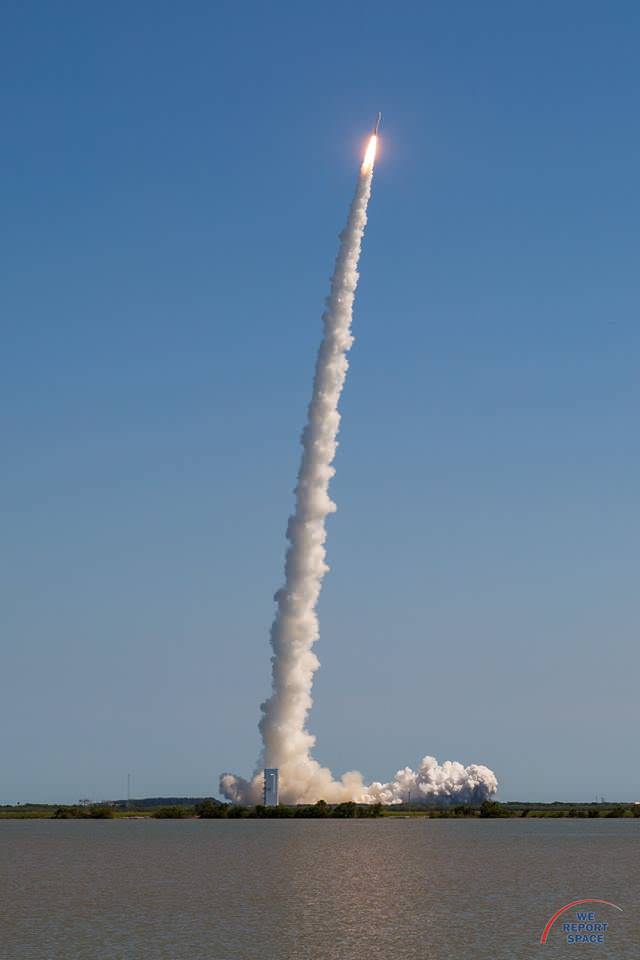

With MUOS-5 in orbit the system’s constellation is completed.
MUOS-5 will serve as an on orbit spare. It provides the MUOS network with near-global coverage. Communications coverage for military forces now extends further toward the North and South poles than ever before, according to Lockheed Martin officials.
“Like its predecessors, the MUOS-5 satellite has two payloads to support both new Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) waveform capabilities, as well as the legacy Ultra High Frequency (UHF) satellite system. On orbit, MUOS-5 will augment the constellation as a WCDMA spare, while actively supporting the legacy UHF system, currently used by many mobile forces today.”
The prior MUOS-4 satellite was launched on Sept. 2, 2015 – as I reported here.
The 20 story tall Atlas V launched in its most powerful 551 configuration and performed flawlessly.

The vehicle includes a 5-meter diameter payload fairing and five solid rocket boosters that augment the first stage. The Atlas booster for this mission was powered by the RD AMROSS RD-180 engine and the Centaur upper stage was powered by the Aerojet Rocketdyne RL10C-1 engine.
The RD-180 burns RP-1 (Rocket Propellant-1 or highly purified kerosene) and liquid oxygen and delivers 860,200 lb of thrust at sea level.
And the rocket needed all that thrust because the huge MUOS-5 was among the heftiest payloads ever lofted by an Atlas V booster, weighing in at some 15,000 pounds.
The Centaur upper stage was fired a total of three times.
For this mission the payload fairing was outfitted with an upgraded and advanced acoustic system to beet shield the satellite from the intense vibrations during the launch sequence.
This Atlas launch had been delayed several months to rectify a shortfall in the first stage thrust that occurred during the prior mission launching the Orbital ATK OA-6 cargo freighter in March 2016 on a contract mission for NASA to resupply the International Space Station (ISS).
The launch comes just two weeks after blastoff of the ULA Delta IV Heavy, the worlds most powerful rocket, on a mission to deliver a top secret spy satellite to orbit – as I witnessed and reported on here.
“I am so proud of the team for all their hard work and commitment to 100 percent mission success,” Maginnis added.
“It is amazing to deliver our second national security payload from the Cape in just two weeks. I know this success is due to our amazing people who make the remarkable look routine.”
The 15,000 pound MUOS payload is a next-generation narrowband tactical satellite communications system designed to significantly improve ground communications for U.S. forces on the move.
Here’s a detailed mission profile video describing the launch events:
Video caption: Atlas V MUOS-5 Mission Profile launched on June 24, 2016 from Cape Canaveral Air force Station. Credit: ULA
The launch was supported by the 45th Space Wing.
“Today’s successful launch is the culmination of the 45th Space Wing, Space and Missile Systems Center, Navy and ULA’s close partnership and dedicated teamwork,” said Brig. Gen. Wayne Monteith, 45th Space Wing commander and mission Launch Decision Authority, in a statement.
“We continue our unwavering focus on mission success and guaranteeing assured access to space for our nation, while showcasing why the 45th Space Wing is the ‘World’s Premiere Gateway to Space.”
Watch this exciting launch highlights video reel from ULA – including deployment of MUOS-5!
The MUOS-5 launch marked the 63rd Atlas V mission since the vehicle’s inaugural launch in August 2002. To date seven flights have launched in the 551 configuration. These include all four prior MUOS missions as well as NASA’s New Horizons mission to Pluto and the Juno mission to Jupiter.
Watch my up close remote launch video from the pad with hurling rocks:
Video caption: The sounds and fury of a ULA Atlas V 551 rocket blast off carrying Lockheed Martin built MUOS-5 tactical communications satellite to geosynchronous orbit for US Navy on June 24, 2016 at 10:30 a.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fl, as seen in this up close video from remote camera positioned at pad. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
Watch this compilation of dramatic launch videos from Jeff Seibert.
Video Caption: MUOS-5 launch compilation on ULA Atlas 5 rocket on 6/24/2016 from Pad 41 of CCAFS. Credit: Jeff Seibert
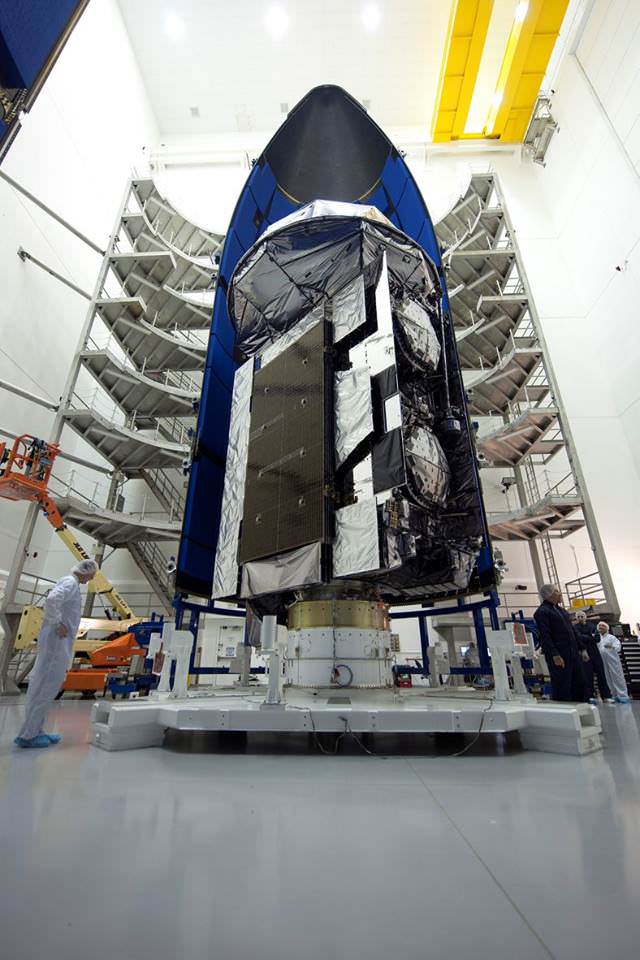

The next Atlas V launch is slated for July 28 with the NROL-61 mission for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO).

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.