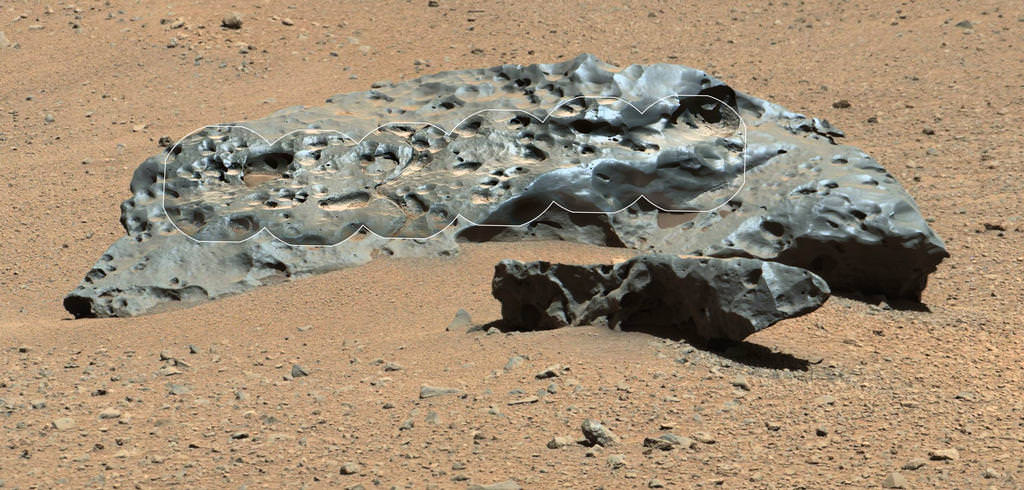
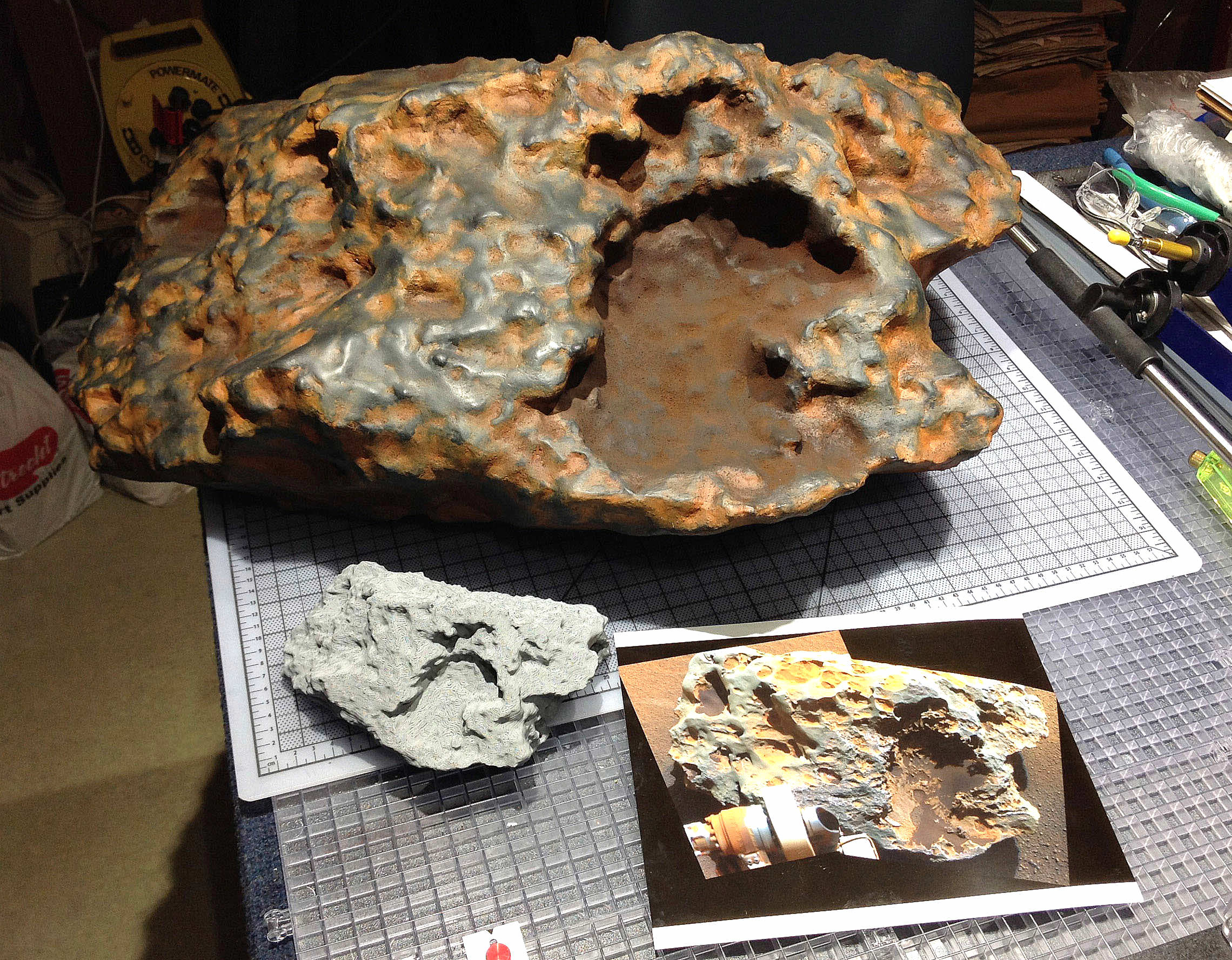
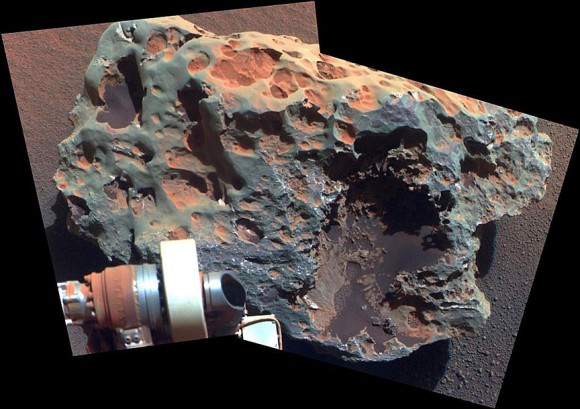
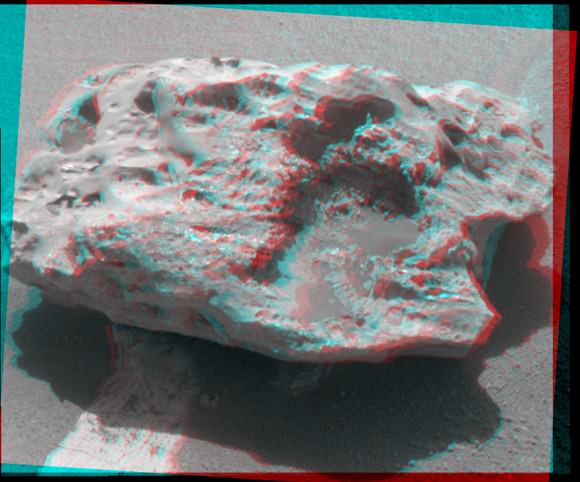
Talk about heavy metal! This shiny, lumpy rock spotted by NASA’s Curiosity rover is likely made mostly of iron — and came from outer space! It’s an iron meteorite, similar to ones found in years past by Curiosity’s forerunners Spirit and Opportunity, but is considerably larger than any of the ones the MER rovers came across… in fact, at 2 meters (6.5 feet) wide this may very well be the biggest meteorite ever discovered on Mars!
Click the image for a supermetallicious high-resolution version from JPL’s Planetary Photojournal.

The picture above was made by combining high-resolution circular images (outlined in white) acquired with the Remote Micro-Imager (RMI) of Curiosity’s ChemCam instrument with color and context from the rover’s Mastcam. The images were taken on mission Sol 640 (May 25, 2014) and have been adjusted to simulate more Earth-like illumination.
Dubbed “Lebanon,” the large meteorite has a smaller fragment lying alongside it, named “Lebanon B.”
While iron meteorites are fairly common on Earth, on Mars they are by far the most common types of meteorites that have been discovered — if just for the sheer fact that they are highly resistant to erosion.*
Find more news and images from the MSL mission on the JPL site here.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/LANL/CNES/IRAP/LPGNantes/CNRS/IAS/MSSS
Source: NASA
*Note: that isn’t to say iron meteorites can’t be eroded; on the contrary, much of their signature surface sheen and pitted texture comes from various erosion processes. See a related study from J. W. Ashley et al. here.