[/caption]
Greetings, fellow SkyWatchers! It’s International Dark Skies Week and a great time to enjoy astronomy! We’ll start off with an impressive galaxy for even small optics and enjoy two meteor showers. There are planets and planetary nebula to explore, as well as some awesome globular clusters. If you’re in the mood, there’s some history to learn and plenty of astronomy facts! Whenever you’re ready, meet me in the back yard…
Monday, April 16 – Before binocular observers begin to feel that we have deserted them, let’s drop in on a binocular and very small telescope galaxy that resides roughly a handspan below Spica – M83 (Right Ascension: 13 : 37.0 – Declination: -29 : 52). Starhop instructions are not easy for this one, but look for a pair of twin stars just west of the easily recognized “box” of Corvus – Gamma and R Hydrae. You’ll find it about four fingerwidths further south of R.
As one of the brightest galaxies around, the “Southern Pinwheel” was discovered by Lacaille in 1752. Roughly 10 million light-years distant, M83 has been home to a large number of supernova events – one of which was even detected by an amateur observer. To binoculars it will appear as a fairly large, soft, round glow with a bright core set in a delightful stellar field. As aperture increases, so do details – revealing three well defined spiral arms, a dense nucleus and knots of stars. It is truly a beauty and will become an observing favorite!
Tuesday, April 17 – Today in 1976, the joint German and NASA probe Helios 2 came closer to the Sun than any other spacecraft so far. One of its most important contributions helped us to understand the nature of gamma ray bursts.
Are you ready for even more meteors? Tonight is the peak of the Sigma Leonids. The radiant is located at the Leo/Virgo border, but has migrated to Virgo in recent years. Thanks to Jupiter’s gravity, this shower may eventually become part of the Virginid Complex as well. The fall rate is very low at around one to two per hour. While you’re watching this region of sky, be sure to check out the close pairing of Saturn and Spica!
With tonight’s dark skies, this would be a perfect time for larger telescopes to discover an unusual galaxy grouping in Hydra about 5 degrees due west of the Xi pairing (RA 10 36 35.72 Dec -27 31 03.2).
Centralmost are two fairly easy ellipticals, NGC 3309 and NGC 3311, accompanied by spiral NGC 3322. Far fainter are other group members, such as NGC 3316 and NGC 3314 to the east of the 7th magnitude star and NGC 3305 north of the 5th magnitude star. While such galaxy clusters are not for everyone, studying those very faint fuzzies is a rewarding experience for those with large aperture telescopes.
Wednesday, April 18 – Before we have any Moon to contend with, let’s head out in search of an object that is one royal navigation pain for the northern hemisphere, but makes up for it in beauty. Start with the southernmost star in Crater – Beta. If you have difficulty identifying it, it’s the brightest star east of the Corvus rectangle. Now hop a little more than a fistwidth southeast to reddish Alpha Antilae. Less than a fistwidth below, you will see a dim 6th magnitude star that may require binoculars in the high north. Another binocular field further southwest and about 4 degrees northwest of Q Velorum is our object – NGC 3132 (RA 10 07 01.76 – Dec -40 26 11.1). If you still have no luck, try waiting until Regulus has reached your meridian and head 52 degrees south.
More commonly known as the “Southern Ring” or the “Eight Burst Planetary,” this gem is brighter than the northern “Ring” (M57) and definitely shows more details. It can be captured in even small instruments, larger ones will reveal a series of overlapping shells, giving this unusual nebula its name.
Thursday, April 19 – Today in 1971, the world’s first space station was launched – the Soviet research vessel Salyut 1. Six weeks later, Soyuz 11 and its crew of three docked with the station, but a mechanism failed denying them entry. The crew carried out their experiments, but were sadly lost when their re-entry module separated from the return spacecraft and depressurized. Although the initial phase of Salyut 1 seemed doomed, the mission continued to enjoy success through the early 1980s and paved the way for Mir.
Tonight let’s try picking up a globular cluster in Hydra that is located about 3 fingerwidths southeast of Beta Corvus and just a breath northeast of double star A8612 – M68 (Right Ascension: 12 : 39.5 – Declination: -26 : 45).
This class X globular was discovered in 1780 by Charles Messier and first resolved into individual stars by William Herschel in 1786. At a distance of approximately 33,000 light-years, it contains at least 2000 stars, including 250 giants and 42 variables. It will show as a faint, round glow in binoculars, and small telescopes will perceive individual members. Large telescopes will fully resolve this small globular to the core!
Friday, April 20 – By 1850, Lord Rosse had used the 72 inch speculum-mirrored “Leviathon at Parsontown” (Birr Castle, Ireland) to catalogue fourteen previously indecipherable glowing clouds in deep space as “spiral nebulae.” The very first one resolved was originally a discovery of Charles Messier – found while chasing a comet on the night of October 13, 1773. That discovery, M51, had to wait 72 years until large reflecting telescopes unveiled its spiral form. It would take another 75 years before M51’s extragalactic nature became an indisputable fact. Interestingly, observers have now become so accustomed to seeing spiral structure in brighter galaxies that even mid-sized scopes can see M51 (Right Ascension: 13 : 29.9 – Declination: +47 : 12) – the Whirlpool Galaxy – as a “Grand Spiral.” Tonight see what Rosse saw for yourself.
Start in Ursa Major by locating Mizar (Zeta) and Alkaid (Eta), then rotate the line between these two 90 degrees south using Eta as the pivot. With the line oriented to the southwest, cut it in half. With good conditions and a mid-sized scope, you can be initiated into the mystery of the spiral nebulae – nebulae whose individual stars had to await the development of very large professional scopes and long-exposure photography to reveal their stellar nature to the questing human imagination!
Saturday, April 21 – It’s Saturday night and we’ve got New Moon! Tonight, let’s use our binoculars and telescopes and take a look at a spectacular stellar sphere. Let’s find one of the best northern hemisphere globular clusters – M3! You can locate M3 (Right Ascension: 13 : 42.2 – Declination: +28 : 23) easily by identifying Cor Caroli (Alpha Canes Venatici) and Arcturus. Sweep your binoculars along a line halfway between the two and you will uncover this condensed beauty just east of Beta Comae. With added inches and magnification, the stars are out to play!
Discovered by Charles Messier on May 3, 1764, this condensed ball of approximately a half million stars is one of the oldest formations in our galaxy. At 35-40,000 light years distant, this awesome globular cluster spans 220 light years and is believed to be 10 billion years old.
Now let’s check out a dandy little group of stars that are about a fistwidth southeast of Procyon and just slightly more than a fingerwidth northeast of M48. Called C Hydrae, this group isn’t truly gravitationally bound, but is a real pleasure to large binoculars and telescopes of all sizes. While they share similar spectral types, this mixed magnitude collection will be sure to delight you!
Sunday, April 22 – Today celebrates the birthday of Sir Harold Jeffreys, who was born in 1891. Jeffreys was an astrogeophysicist and the first person to envision Earth’s fluid core. He also helped in our understanding of tidal friction, general planetary structure, and the origins of our solar system.
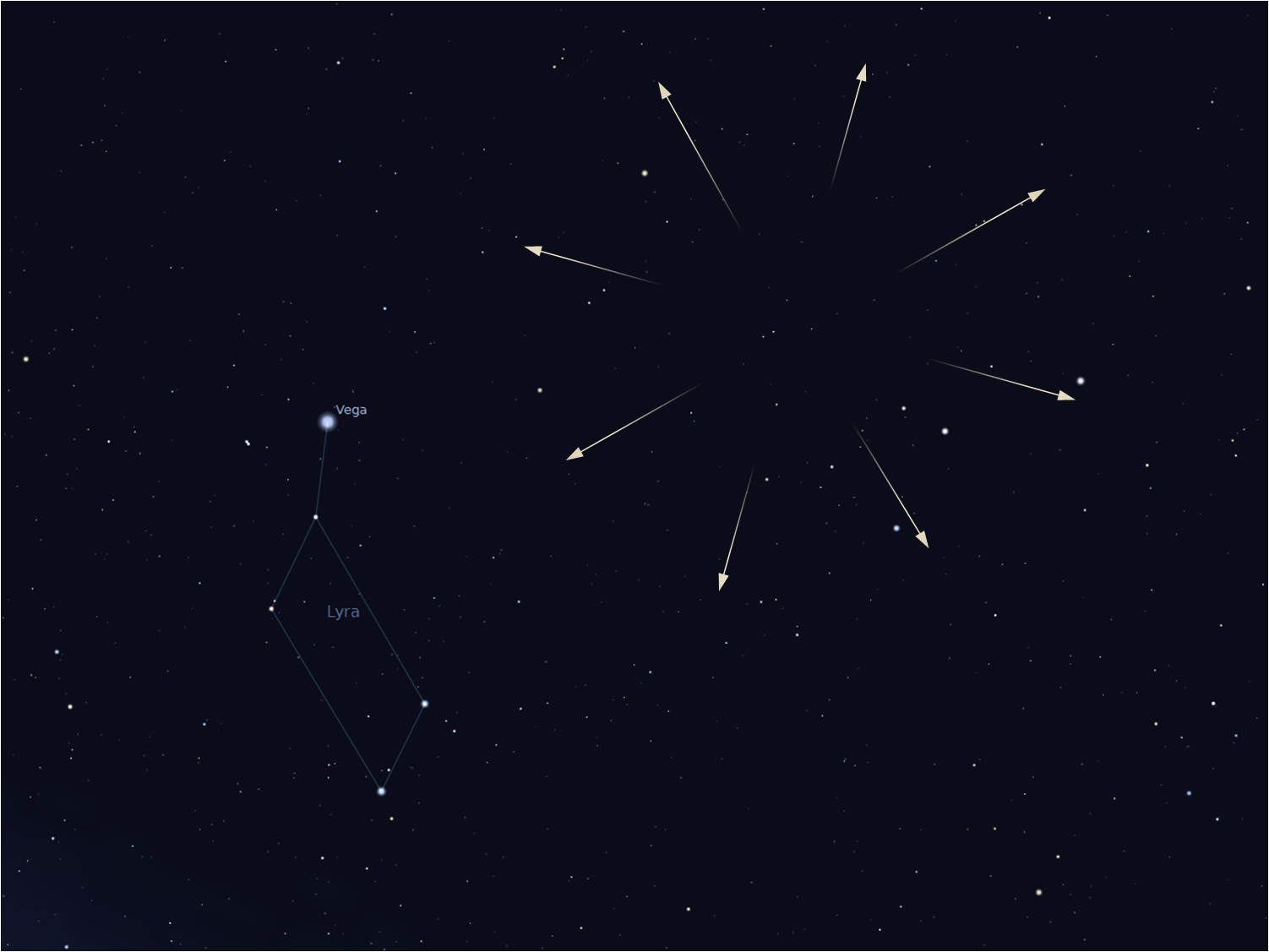
Start your moonless morning off before dawn with a chance to view the peak of the Lyrid meteor shower. Since the radiant is near Vega, you will improve your chances of spotting them when the constellation of Lyra is as high as possible. This stream’s parent is Comet Thatcher, and it produces around 15 bright, long-lasting meteors per hour!
Before you begin your observations tonight, be sure to check out the cool triangulation of Theta Leonis, Regulus and Mars!
Let’s begin tonight in eastern Hydra and pick up another combination Messier/Herschel object. You’ll find M48 (Right Ascension: 8 : 13.8 – Declination: -05 : 48) easily just a little less than a handspan southeast of Procyon.
Often called a “missing Messier,” Charles discovered this one in 1711, but cataloged its position incorrectly. Even the smallest of binoculars will enjoy this rich galactic cluster filled with more than 50 members including some yellow giants. Look for a slight triangle shape with a conspicuous chain of stars across its center. Larger telescopes should use lowest power since this will fill the field of view and resolve splendidly. Be sure to mark your notes for both a Messier object and Herschel catalog H VI 22!
Until next week? Dreams really do come true when you keep on reaching for the stars!