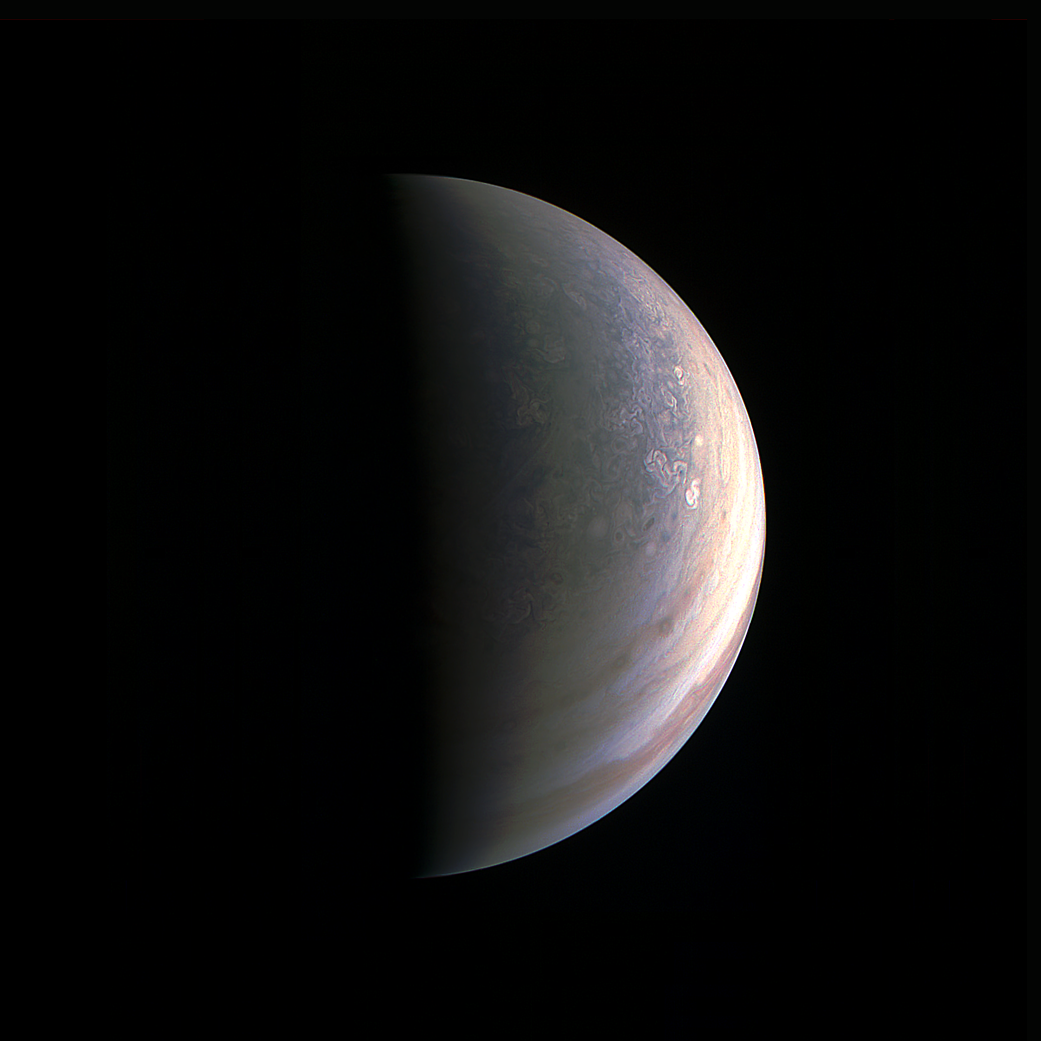
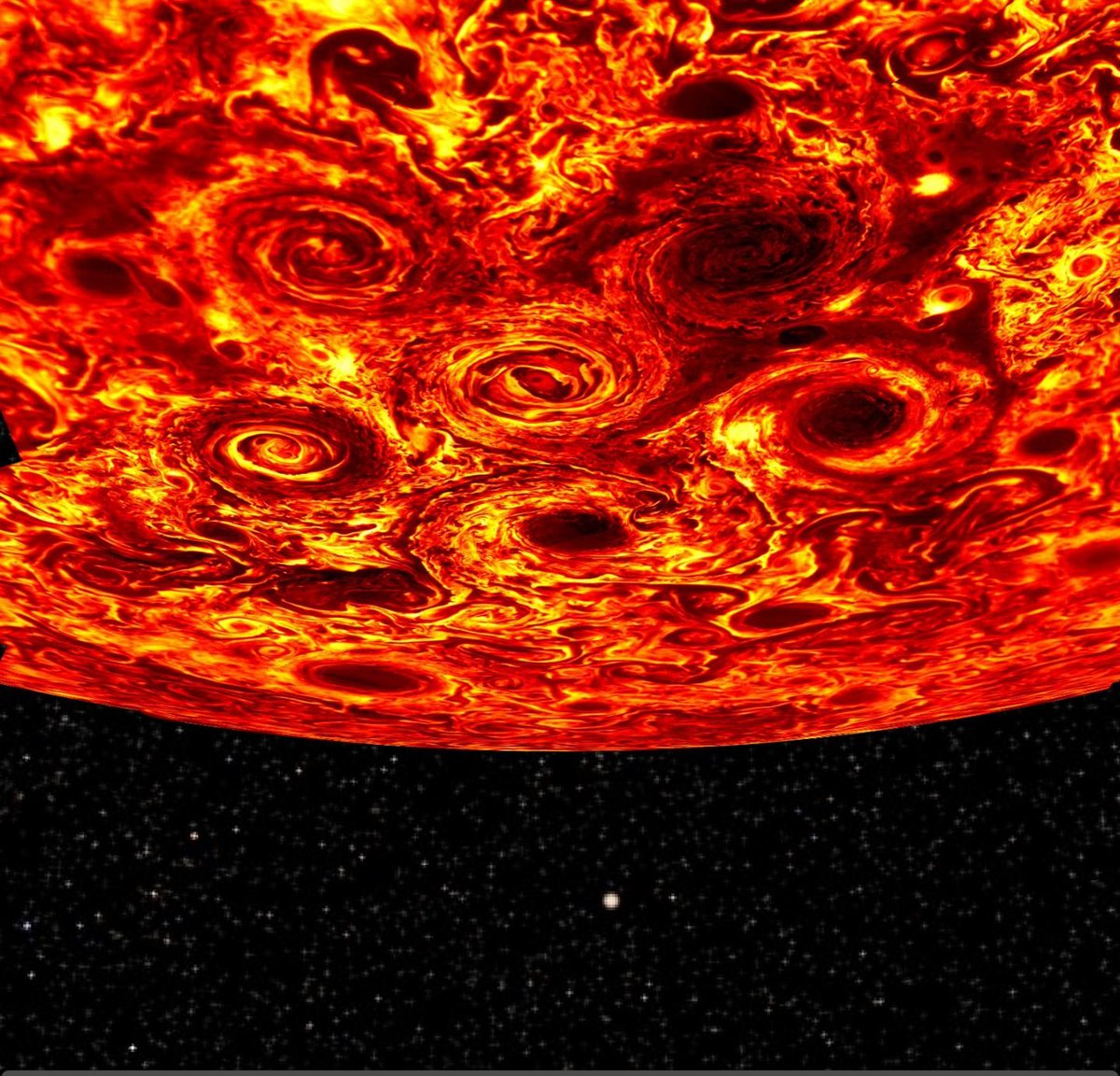
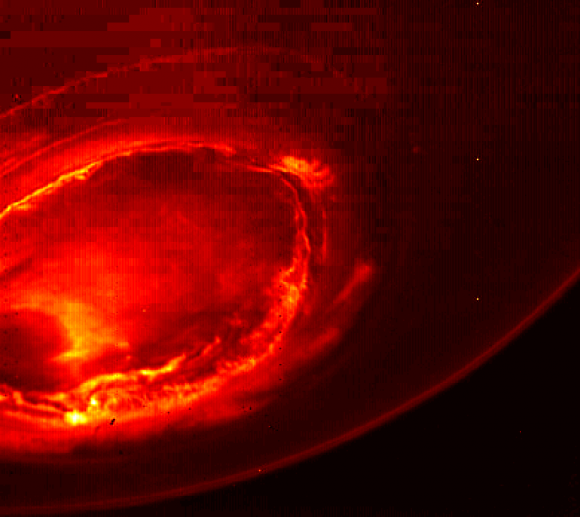
When the Juno spacecraft arrived at Jupiter in July 2016, it quickly got to work. Among the multitude of stunning images of the planet were our first ever images of Jupiter’s poles. And what we saw there was a huge surprise: geometric arrangements of cyclones in persistent patterns.
Jupiter’s polar regions have always been a mystery to Earth-bound observers. The planet isn’t tilted much, which means the poles are always tantalizingly out of view. Other spacecraft visiting Jupiter have focused on the equatorial regions, but Juno’s circumpolar orbit is giving us good, close-up views of Jupiter’s poles.
“They are extraordinarily stable arrangements of such chaotic elements. We’d never seen anything like it.” – Morgan O’Neill, University of Chicago
Juno has a whole suite of instruments designed to unlock some of the mysteries surrounding Jupiter, including an infrared imager and a visible light camera. The polar regions are a particular focus for the mission, and astronomers were looking forward to their first views of Jupiter’s hidden poles. They were not disappointed when they got them.
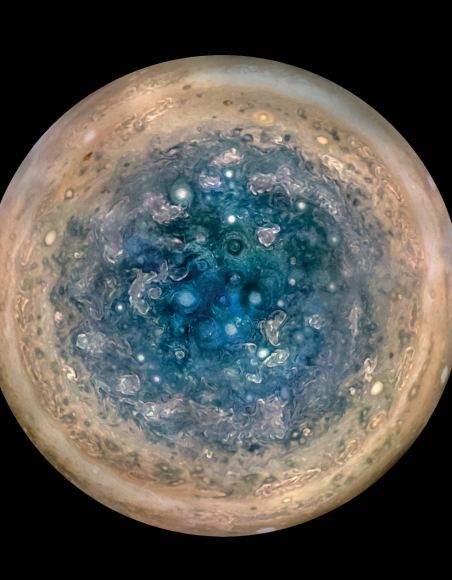
Each of Jupiter’s poles is a geometric array of large cyclones arranged in persistent, polygonal patterns. At the north pole, eight storms are arranged around a single polar cyclone. In the south, one storm is encircled by five others.
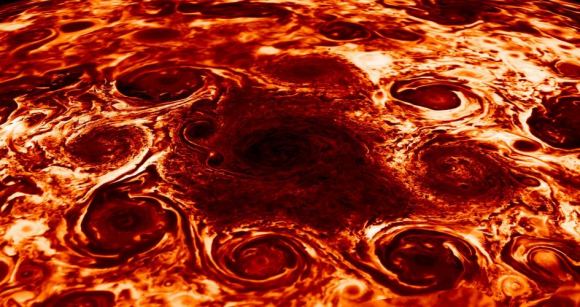
This was a stunning discovery, and quickly led to questions around the why and the how of these storm arrangements. Jupiter’s atmosphere is dominated by storm activity, including the well-known horizontal storm bands in the equatorial regions, and the famous Great Red Spot. But these almost artful arrangements of polar storms were something else.
The persistent arrangement of the storms is a puzzle. Our current understanding tells us that the storms should drift around and merge, but these storms do neither. They just turn in place.
A new paper published in Nature is looking deeper into these peculiar arrangements of storms. The paper is by scientists from an international group of institutions including the University of Chicago. It’s one of four papers dedicated to new observations from the Juno spacecraft.
One of the paper’s co-authors is Morgan O’Neill, a University of Chicago postdoctoral scholar. Remarking on the storms, she had this to say: “They are extraordinarily stable arrangements of such chaotic elements. We’d never seen anything like it.”

The strange geometrical arrangement of Jupiter’s polar storms reminded O’Neill of something from the library of strange physical phenomena only observed under laboratory conditions. Back in the ’90s, scientists had used electrons to simulate a frictionless, turbulent 2-D fluid as it cools. In those conditions, they observed similar behaviour. Rather than merging like expected, small vortices clumped together and formed equally spaced arrays around a center. They called these arrays “vortex crystals.”
This could help explain what’s happening at Jupiter’s poles, but it’s too soon to be certain. “The next step is: Can you create a model that builds a virtual planet and predicts these flows?” O’Neill said. That’ll be the next step in understanding the phenomenon.
Maybe it’s not surprising that these delicate-looking storms at the poles are so persistent. After all, the Great Red Spot on Jupiter has been visible for over 200 years. Maybe Jupiter is just huge and stable.
But the polar cyclones still require an explanation. And whatever that explanation is, understanding what’s happening on Jupiter will help us understand other planets better.