[/caption]
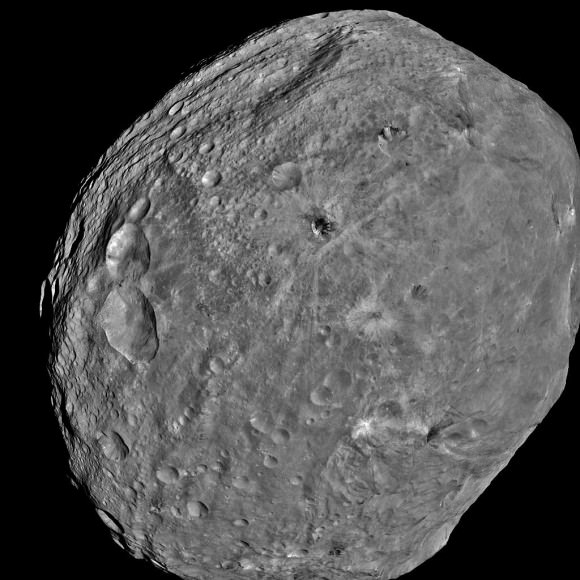
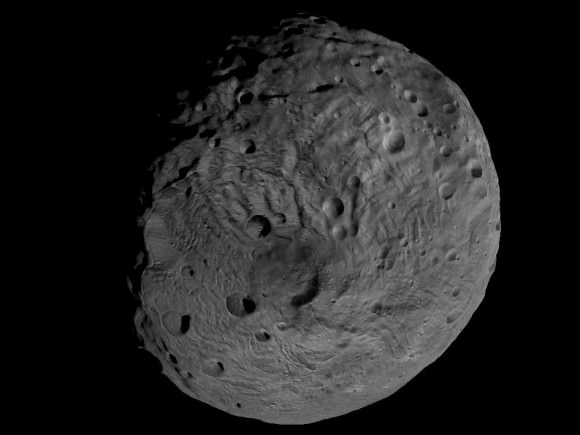
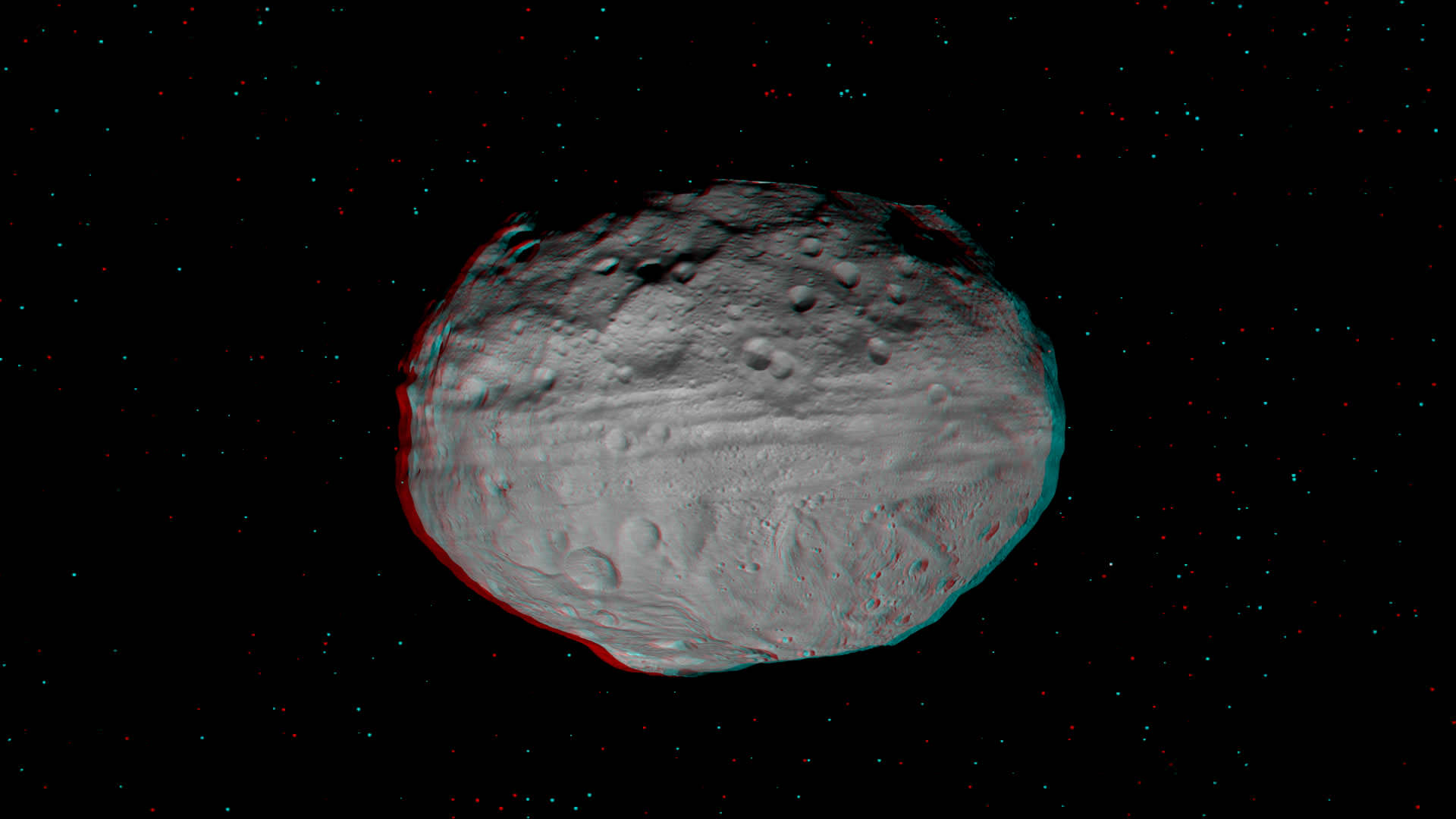
The giant Asteroid Vesta literally floats in space in a new high resolution 3-D image of the battered bodies Eastern Hemisphere taken by NASA’s Dawn Asteroid Orbiter.
Haul out your red-cyan 3-D anaglyph glasses and lets go whirling around Vesta and sledding down mountains to greet the alien Snowman! The sights are fabulous !
The Dawn imaging group based at the German Aerospace Center (DLR), in Berlin, Germany and led by team member Ralf Jaumann has released a trio of new high resolution 3-D images that are the most vivid anaglyphs yet published by the international science team.
The lead anaglyph shows the highly varied topography of the Eastern Hemisphere of Vesta and was taken during the final approach phase as Dawn was about 5,200 kilometers (3,200 miles) away and preparing to achieve orbit in July 2011.
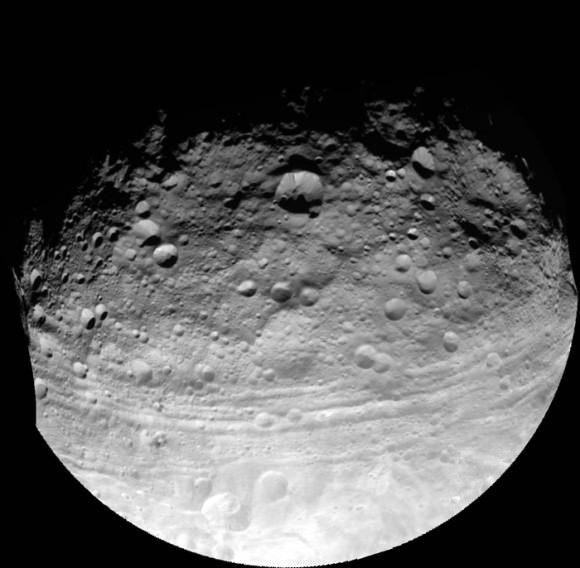
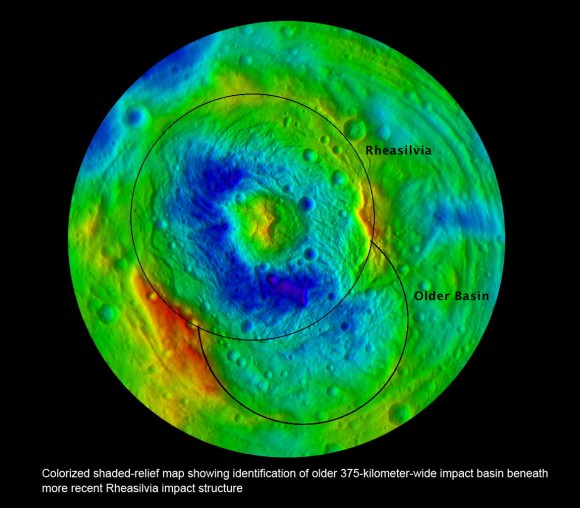
The heavily cratered northern region is at top and is only partially illuminated because of Vesta’s tilted angle to the Sun at that time of year. Younger craters are overlain onto many older and more degraded craters. The equatorial region is dominated by the mysterious troughs which encircle most of Vesta and may have formed as a result of a gargantuan gong, eons ago.
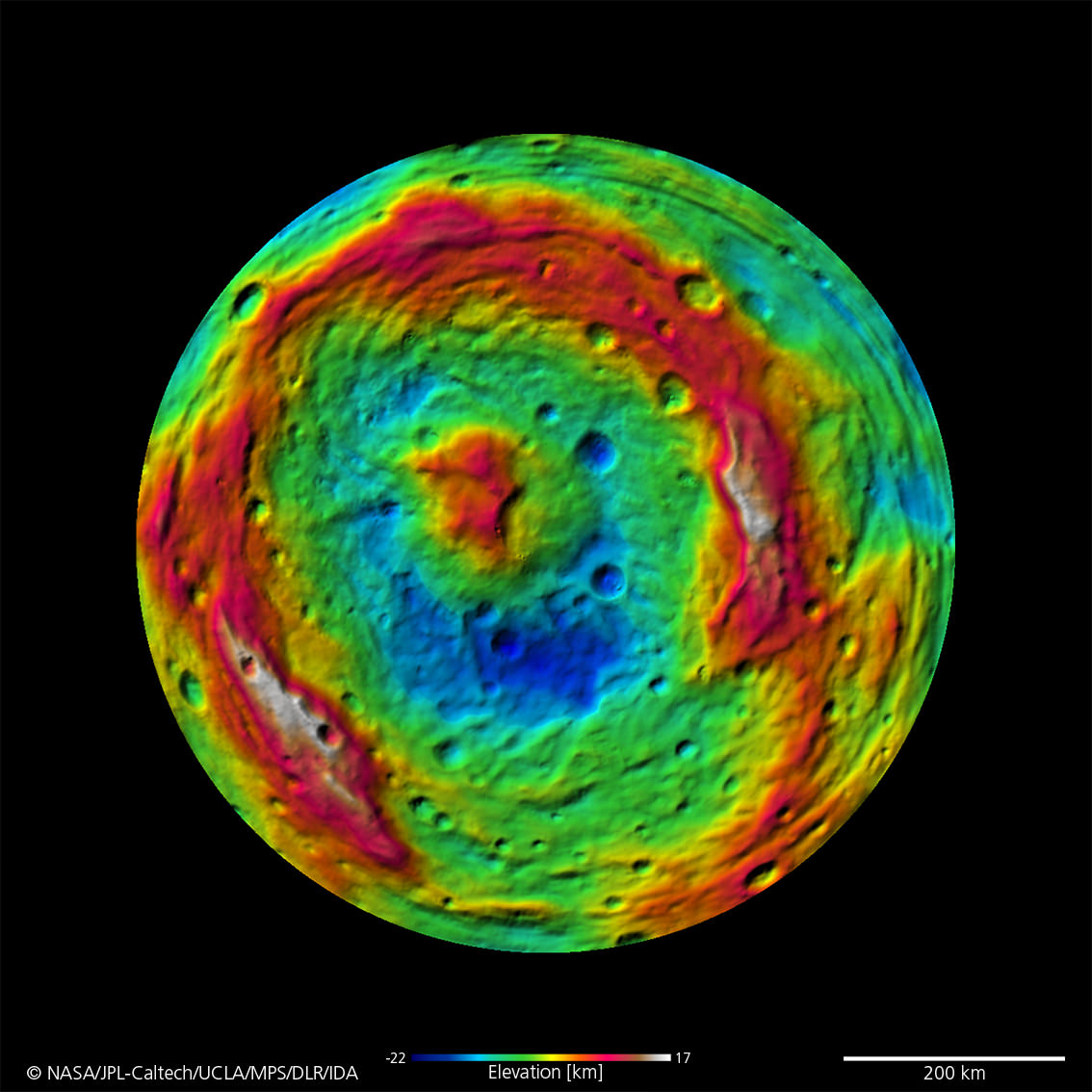
The southern hemisphere exhibits fewer craters than in the northern hemisphere. Look closely at the bottom left and you’ll see the huge central mountain complex of the Rheasilvia impact basin visibly protruding out from Vesta’s south polar region.
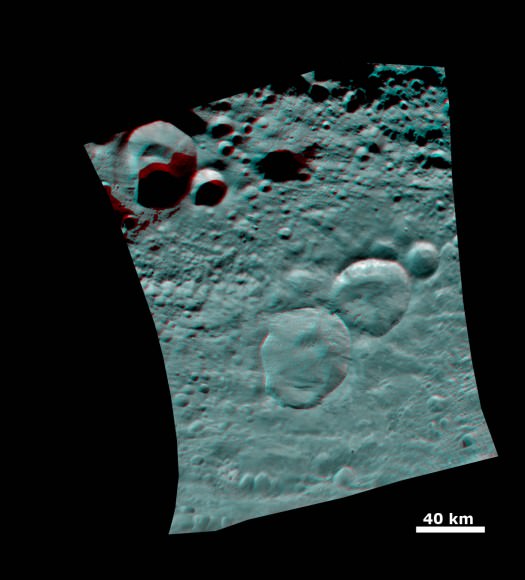
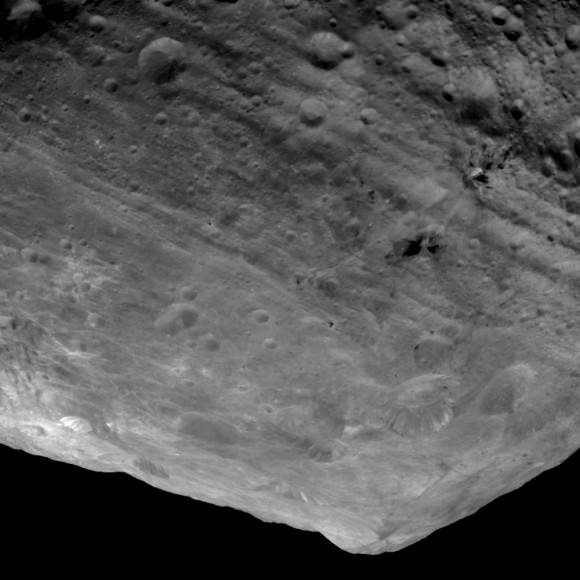
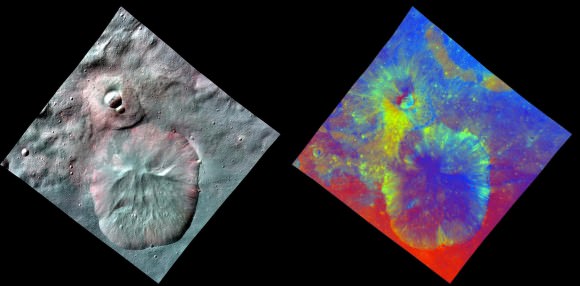
This next 3-D image shows a close-up of the South Pole Mountain at the center of the Rheasilvia Impact basin otherwise known as the “Mount Everest of Vesta”.
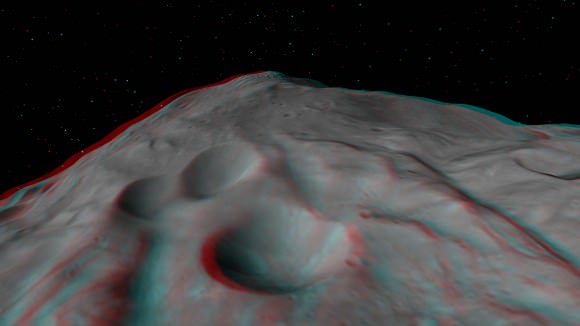
This anaglyph shows the central complex and huge mountain in Vesta’s Rheasilvia impact basin at the South Pole. Does water ice lurk beneath the South Pole ?
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA.
The central complex is approximately 200 kilometers (120 miles) in diameter and is approximately 20 kilometers (12 miles) tall and is therefore about two and a half times taller than Earth’s Mount Everest!
Be sure to take a long look inside the deep craters and hummocky terrain surrounding “Mount Everest”.
A recent study concludes that, in theory, Vesta’s interior is cold enough for water ice to lurk beneath the North and South poles.
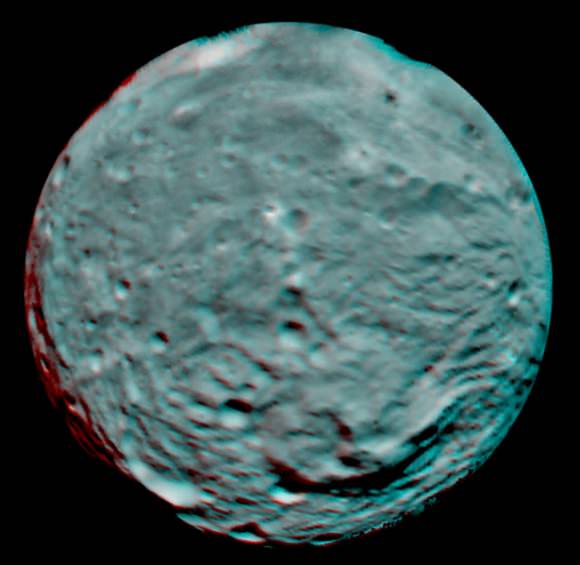
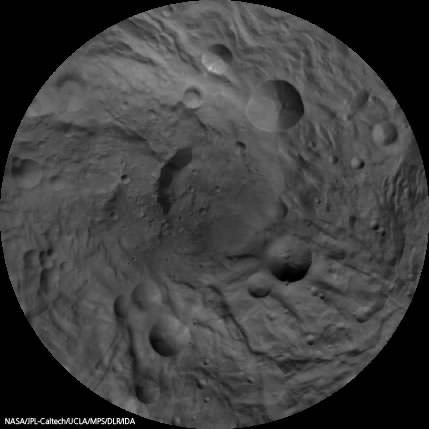
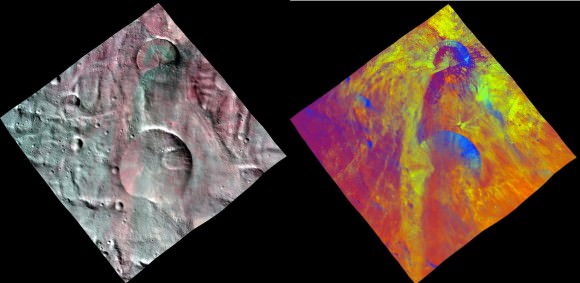
Finally lets gaze at the trio of craters that make up the “Snowman” in the 3-D image snapped in August 2011 as Dawn was orbiting at about 2,700 kilometers (1,700 miles) altitude. The three craters are named Minucia, Marcia and Calpurnia from top to bottom. Their diameters respectively are; 24 kilometers (15 miles), 53 kilometers (33 miles) and 63 kilometers (40 miles).

The three craters are named Minucia, Marcia and Calpurnia from top to bottom. They are 24 kilometers (15 miles), 53 kilometers (33 miles) and 63 kilometers (40 miles) in diameter, respectively. Image resolution is about 250 meters (820 feet) per pixel. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA.
It is likely that Marcia and Calpurnia formed from the impact of a binary asteroid and that Minucia formed in a later impact. The smooth region around the craters is the ejecta blanket.
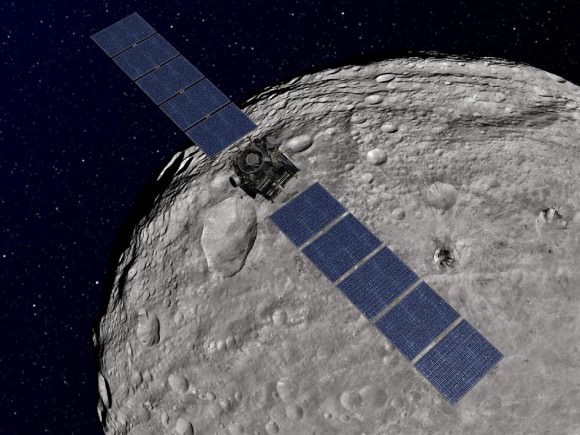

This artist's concept shows NASA's Dawn spacecraft orbiting the giant asteroid Vesta above the Snowman craters. The depiction of Vesta is based on images obtained by Dawn's framing cameras. Dawn is an international collaboration of the US, Germany and Italy. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Vesta is the second most massive asteroid in the main Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter. It is 330 miles (530 km) in diameter.
Dawn is the first spacecraft from Earth to visit Vesta. It achieved orbit in July 2011 for a year long mission. Dawn will fire up its ion propulsion thrusters in July 2012 to spiral out of orbit and sail to Ceres, the biggest asteroid of them all !
Vesta and Ceres are also considered to be protoplanets.