NEW JERSEY- The monstrous ‘Blizzard of 2016’ predicted by weather forecasters for days has struck a wide swath of the US East Coast from the Gulf coast to the Carolinas to New York and soon into New England, with full fury today, Friday, Jan. 22.
NASA and NOAA satellites are tracking the storm which is already inundating the biggest population centers, affecting some 85 million people in 20 states up and down the Atlantic Coast, as it moves in a northeasterly direction.
This afternoon, NASA and NOAA released a series of eyepopping satellite images showing the massive extent of the storm, which may drop historic amounts of snow on Washington DC and other cities over the next 24 to 48 hours.
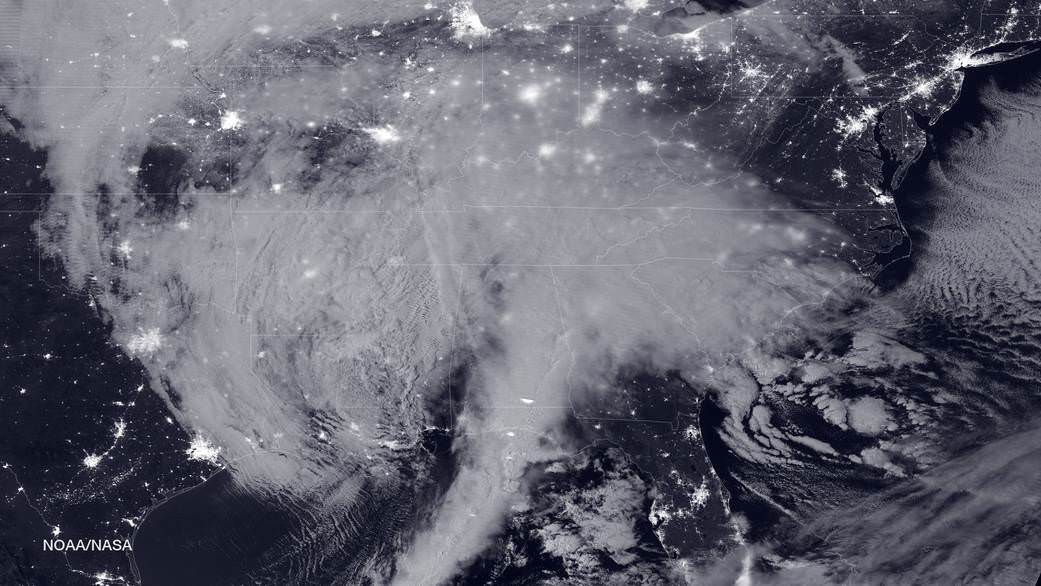
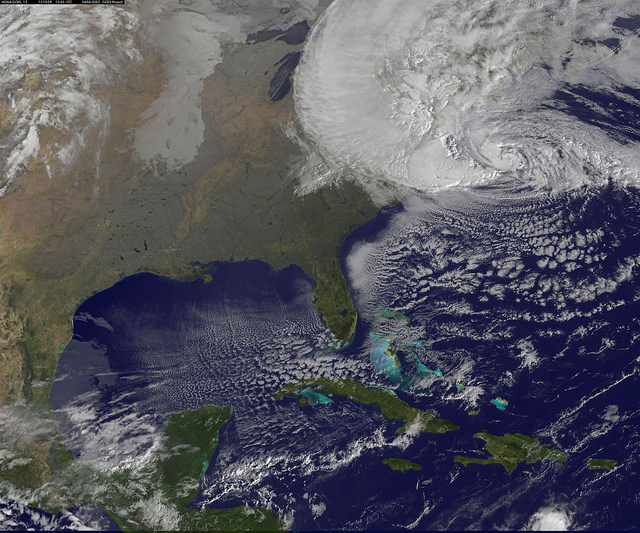
The two agencies released a particularly striking image, shown above, showing the storm swarming over virtually the entire eastern half of the continental US as it was barreling towards the East coast cites.
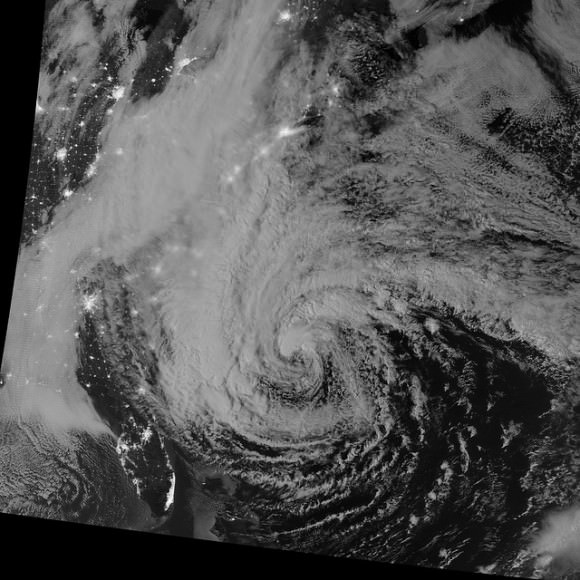
It was taken Friday afternoon by the NASA-NOAA’s Suomi NPP satellite showing the approaching blizzard around 2:35 a.m. EST on Jan. 22, 2016 using the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument’s Day-Night band.
States of Emergency have been declared by Governors of states from the mid-Atlantic to New England, including North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Kentucky, Georgia, Tennessee, West Virginia, the District of Columbia and the list is growing.
The heaviest snowfall is expected in and around Washington DC with estimates of 24 inches of snow or more. 18 to 24 inches may fall along the metropolitan Northeast corridor on Baltimore, Philadelphia, Trenton and New York City.
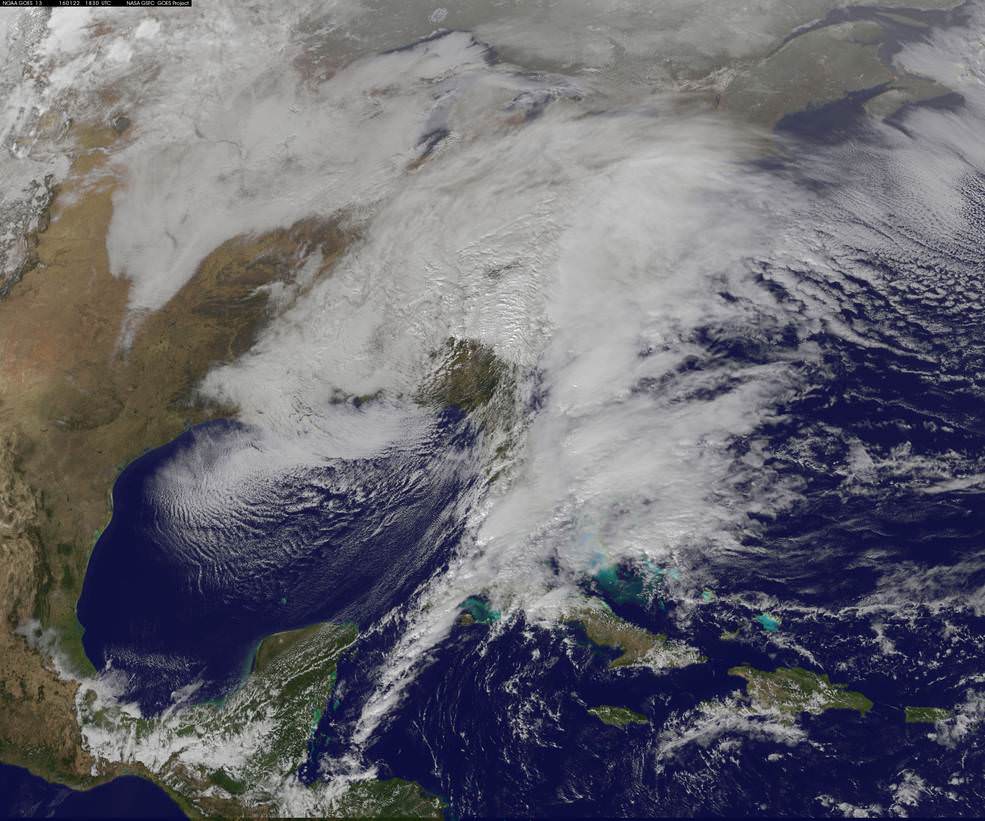

The heavy, blinding snow was already hitting Virginia and Washington by Friday afternoon. Governors, Mayors and Federal officials warned drivers to get off the roads by early Friday afternoon.
Stay off the roadways !!
Widespread treacherous driving with icy roads, sleet, rain, low visibility and whiteout conditions are causing numerous auto accidents as the blizzard bashes the region.
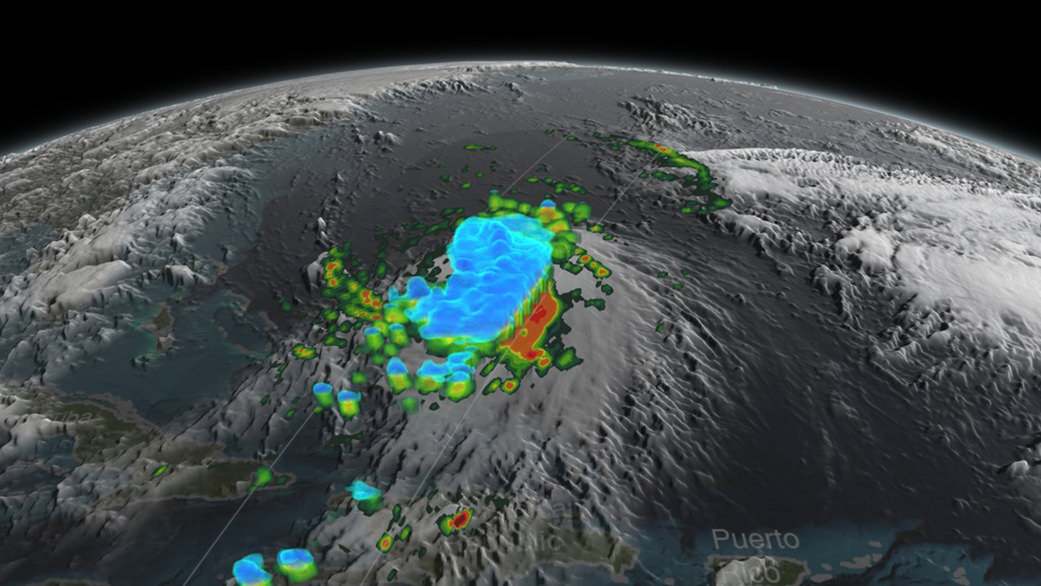
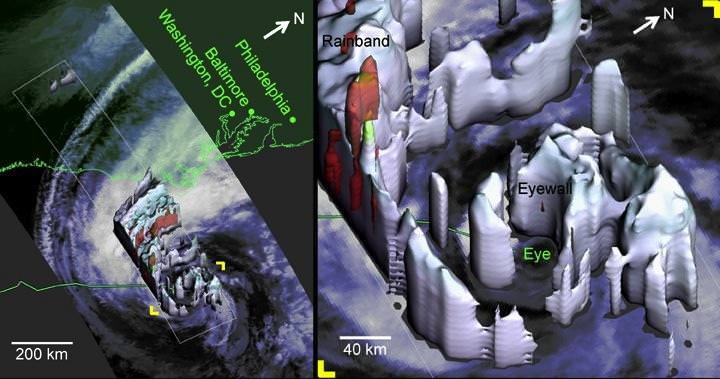
“The winter storm that caused damage during the night along the Gulf Coast has deepened and has started to spread heavy rain, freezing rain, sleet and snow northward into the Mid-Atlantic region. NASA’s GPM and NOAA’s GOES satellites are providing data on rainfall, cloud heights, extent and movement of the storm” wrote NASA’s Rob Gutro in an update on Friday.
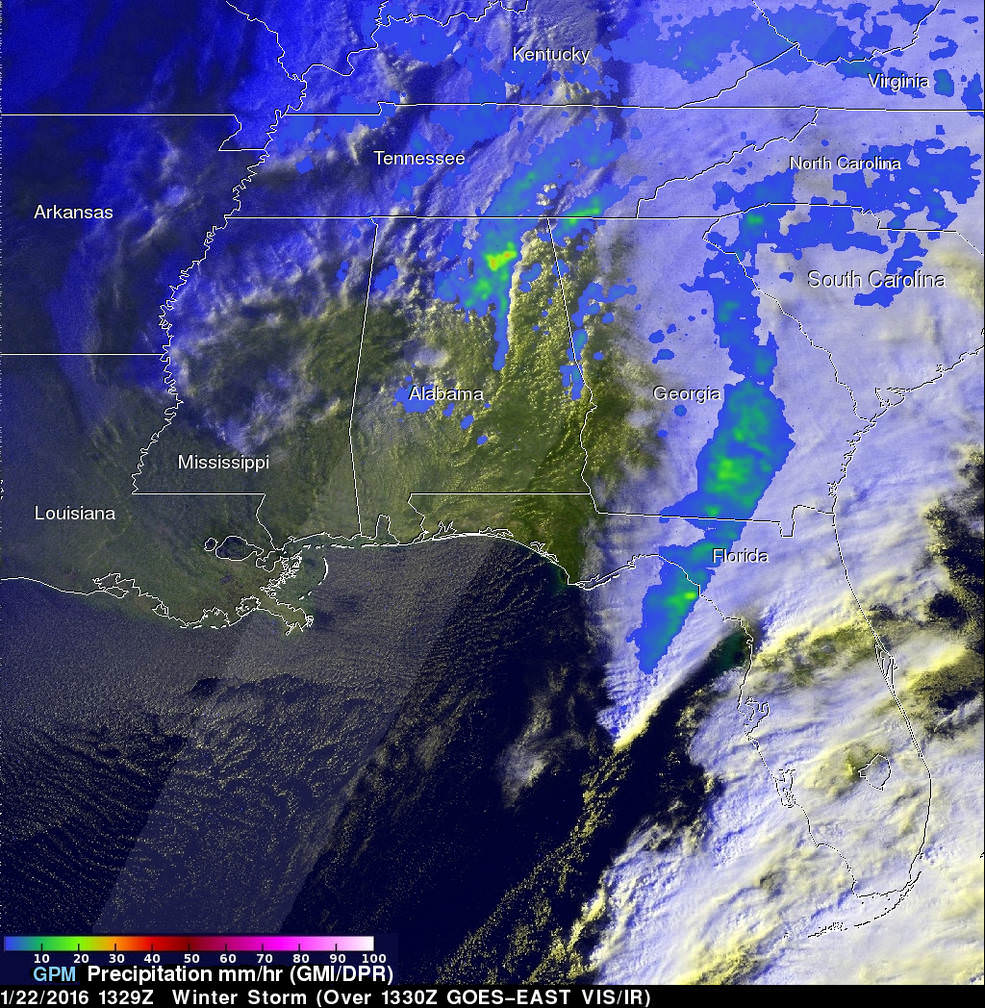
The National Weather Service (NWS) Weather Prediction Center in College Park, Maryland said “An area of low pressure centered over the southeastern U.S. will continue developing into a major winter storm which will impact a large portion of the East Coast from the southern Appalachians through the Mid-Atlantic States from Friday into the weekend. Snowfall totals may exceed 2 feet in portions of these areas, including the Baltimore and Washington D.C. metropolitan areas.”
The monster storm has already caused at least ten deaths. Thousands of motorists are stranded.
High winds up to 55 mph are expected to batter the New Jersey shore, causing significant beach erosion, coastal flooding and property destruction in the same areas devastated by Superstorm Sandy. Thousands of people have been evacuated.
The blizzard has also impacted the US Presidential campaigns and forced New Jersey Governor Chris Christie to temporary cancel campaign appearances in New Hampshire on Friday and Saturday, to deal first hand with the storm back home.
Heavy ice and snow accumulations could cause falling tress resulting in downed power lines and days long power outages during brutally cold temperatures.
Here’s a cool supercomputer animation model:
Video caption: A NASA Center for Climate Simulation supercomputer model that shows the flow of #Blizzard2016 thru Sunday, January 24, 2015. Credit: NASA
Many airports have been closed and some seven thousand flights have also been canceled.
The storm is expected to last into Sunday, Jan. 24

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
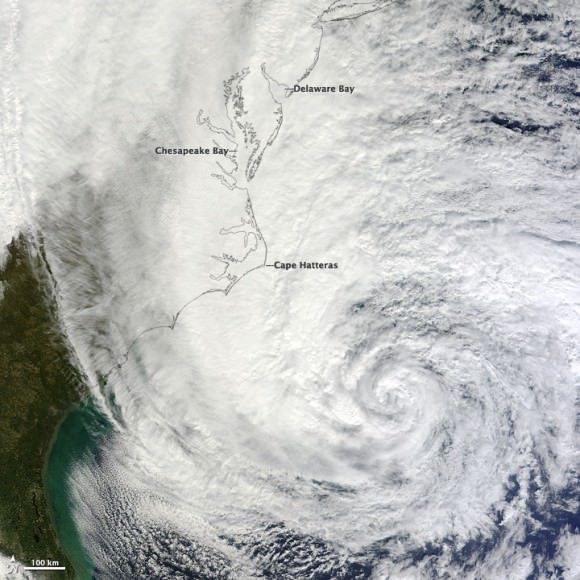




![Sandy_rainfall[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/Sandy_rainfall1-580x464.gif)