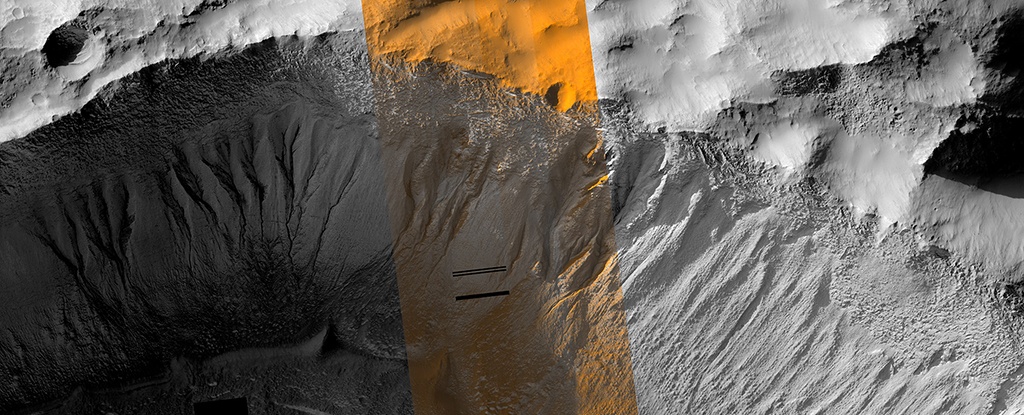
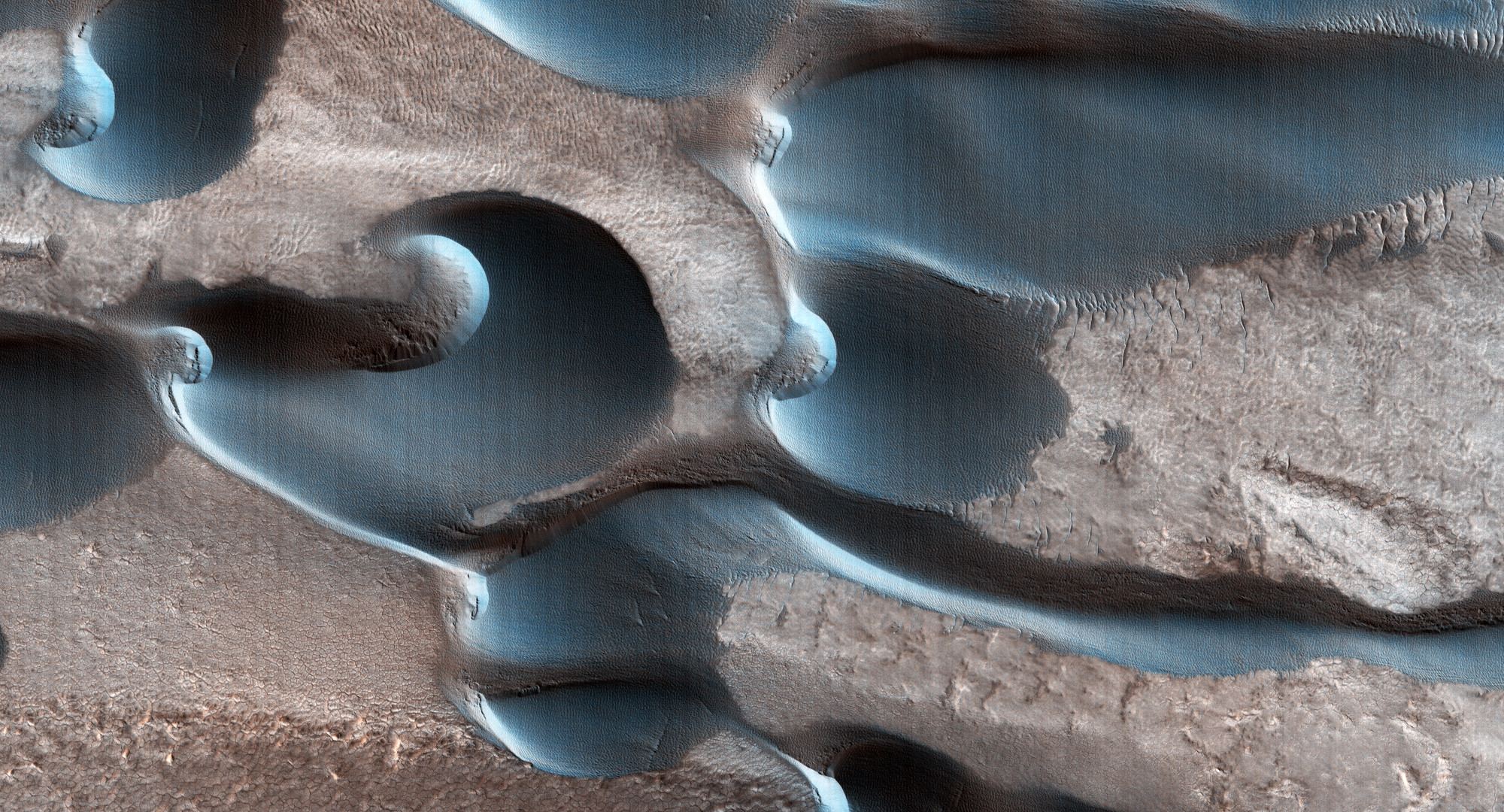
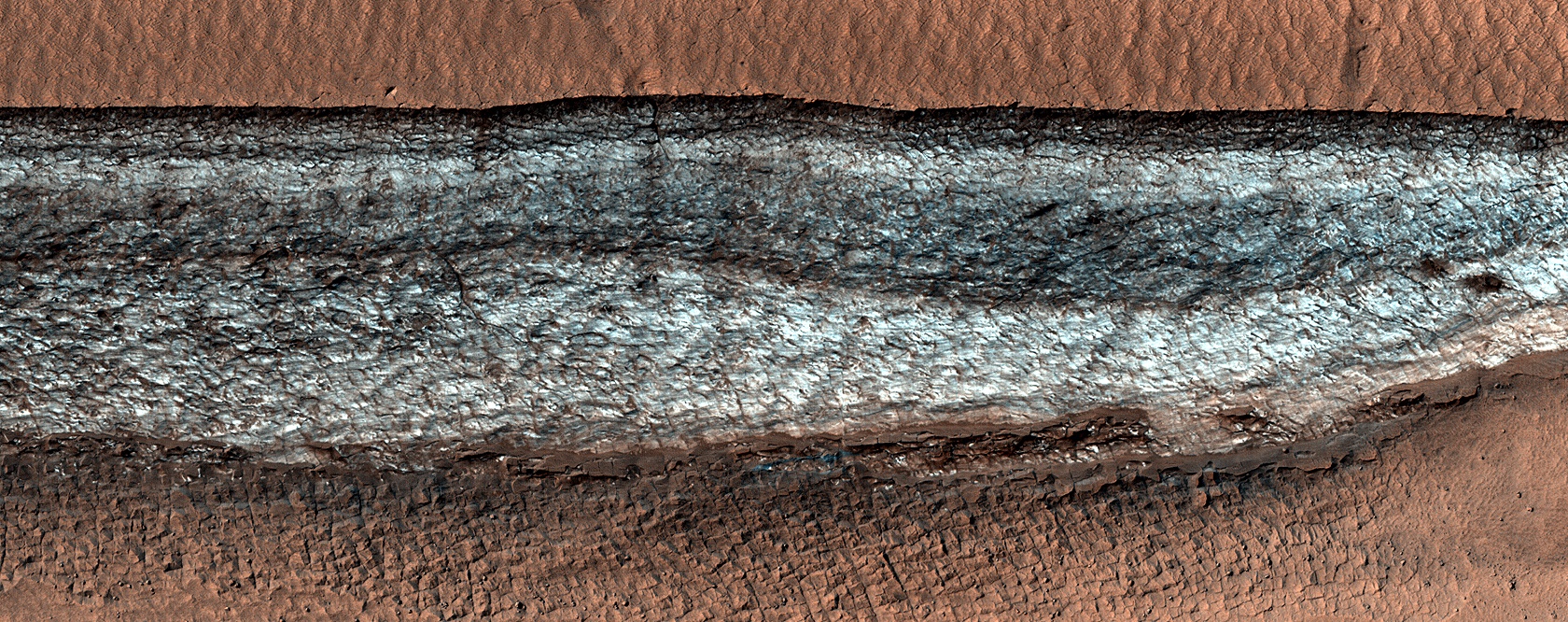
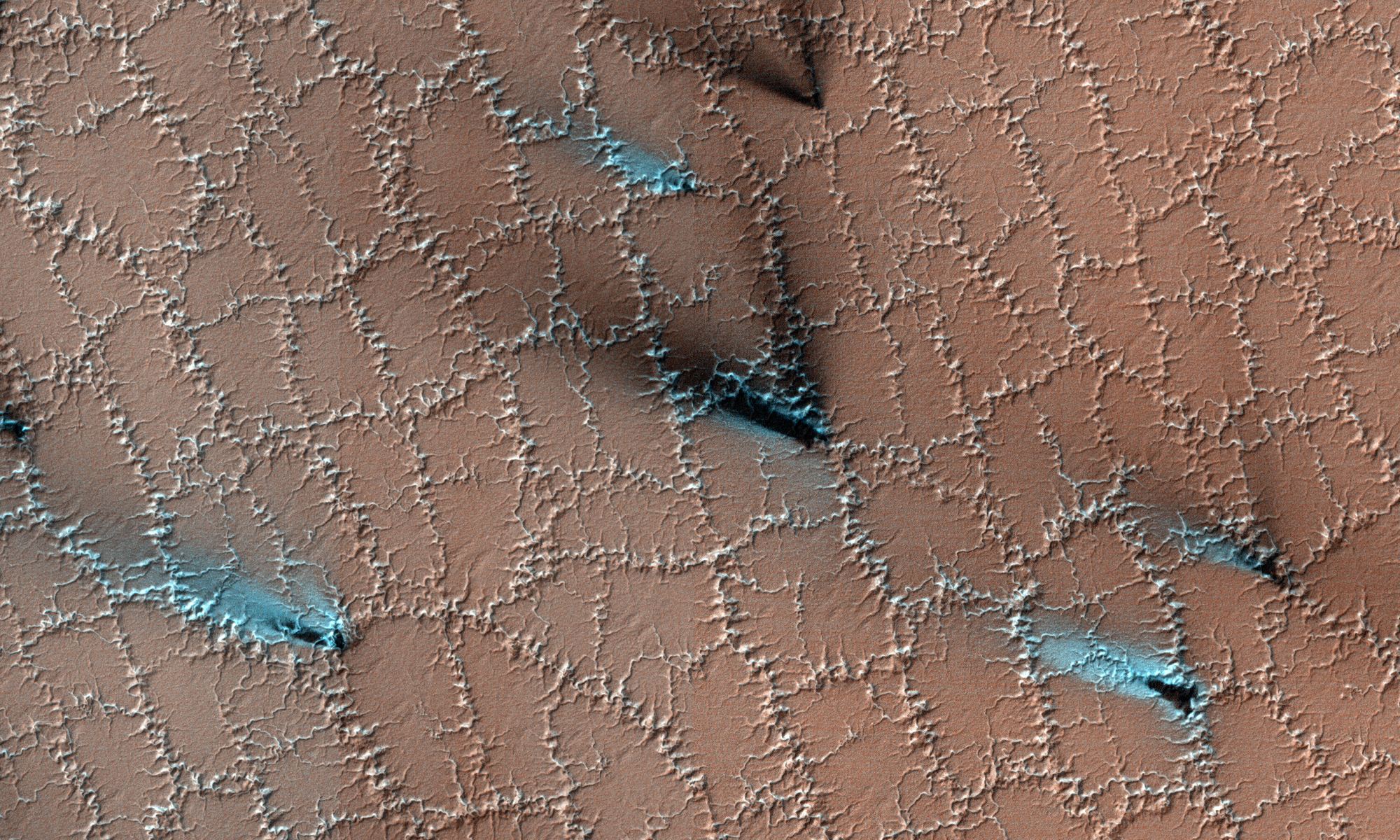
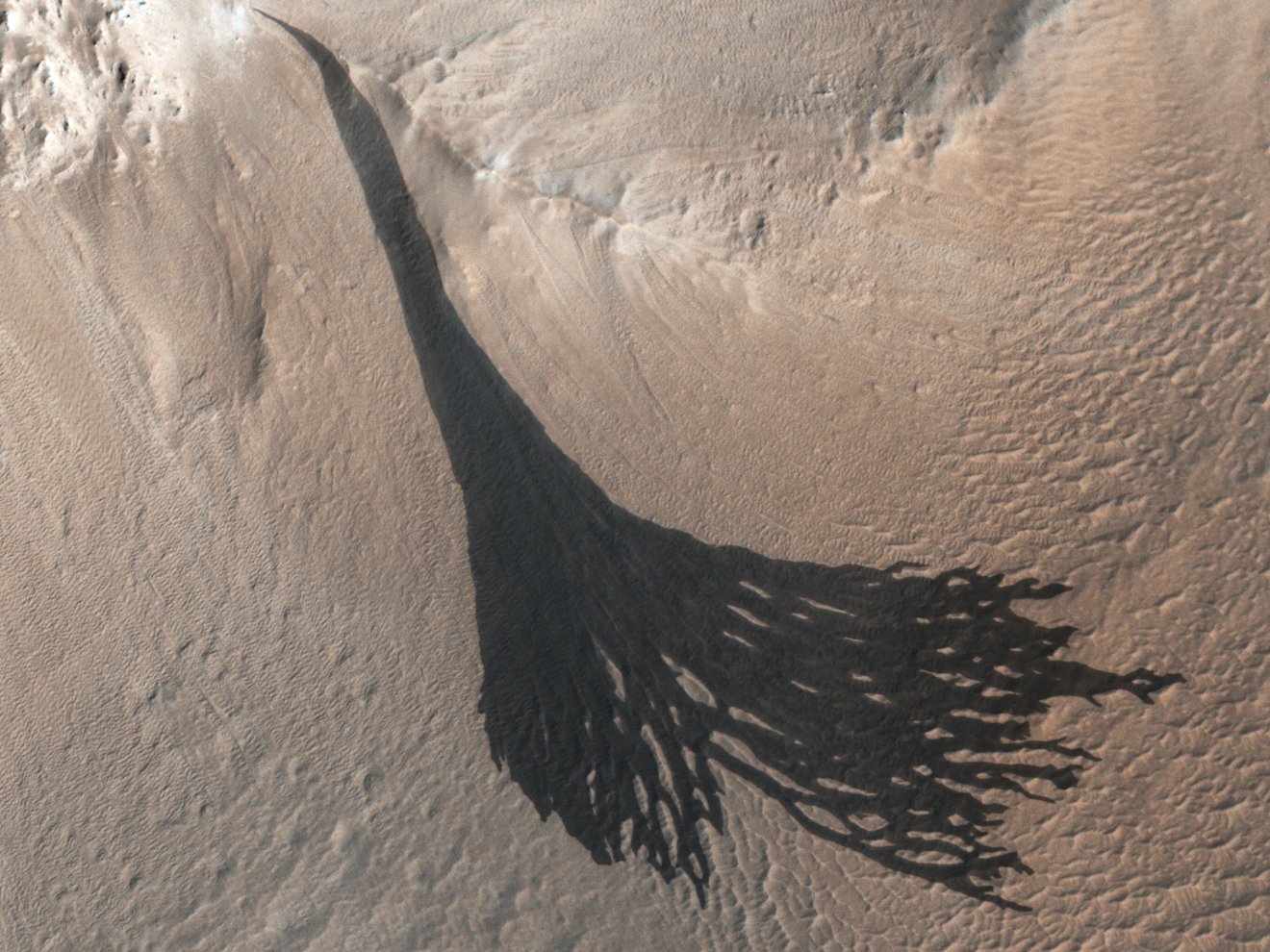
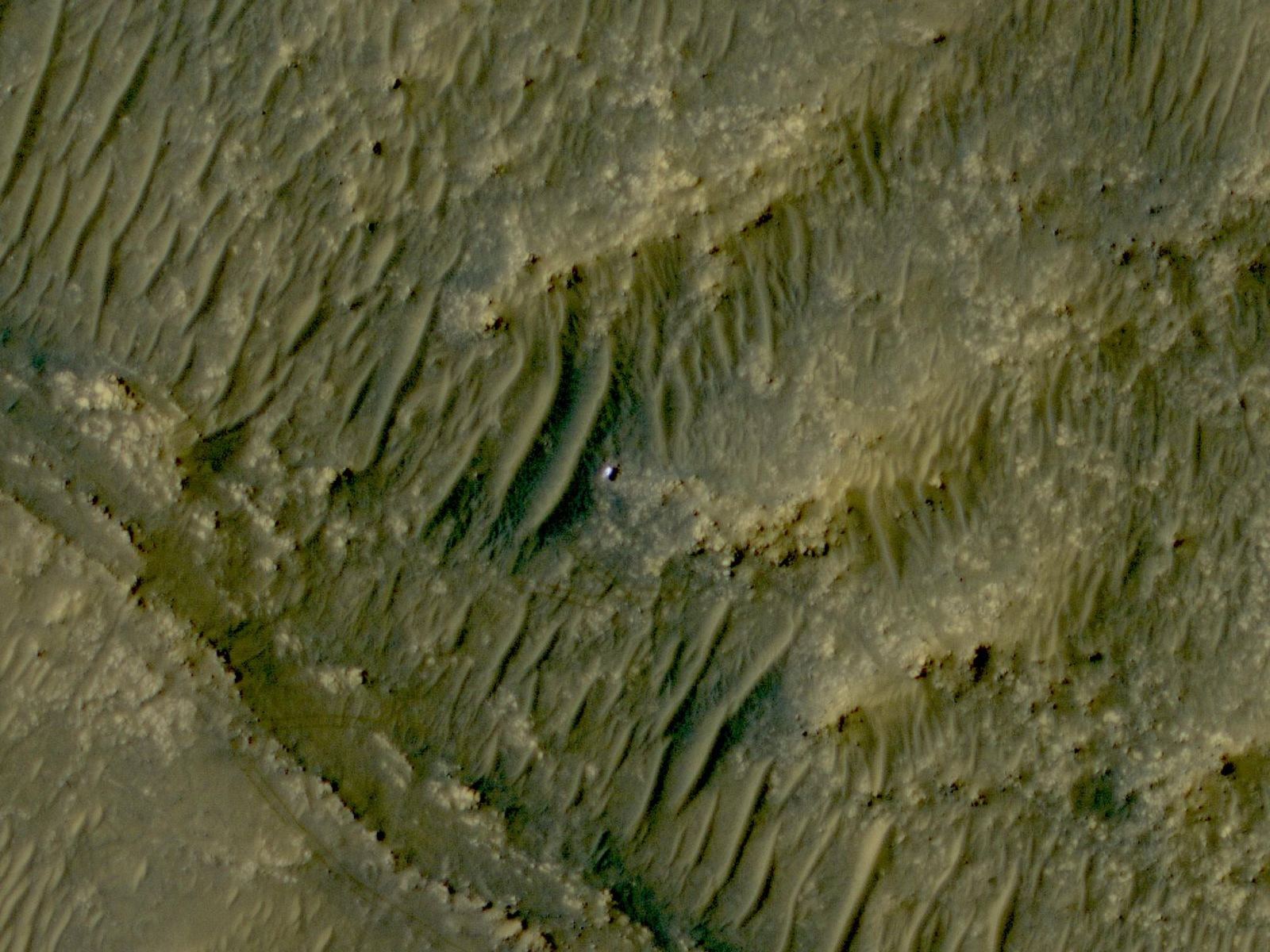
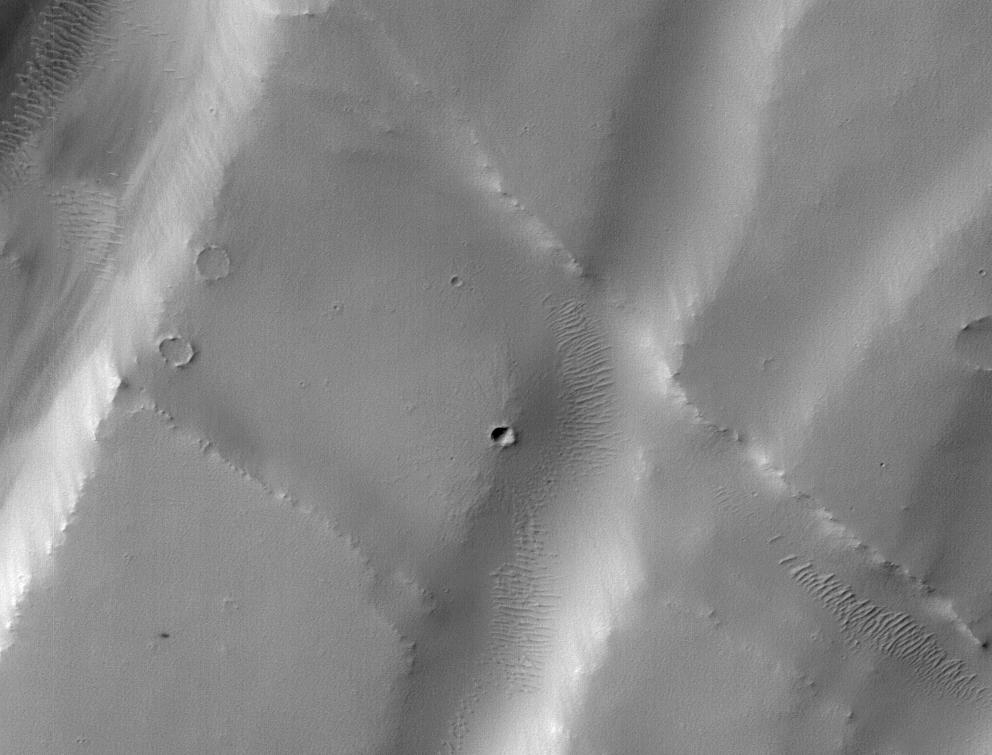
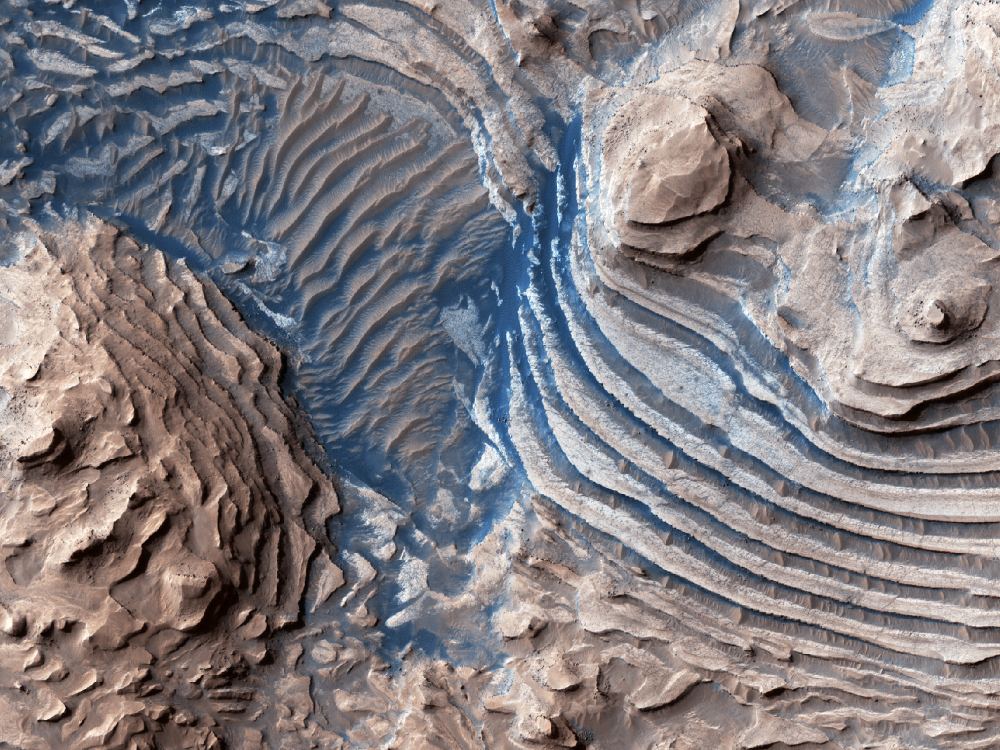
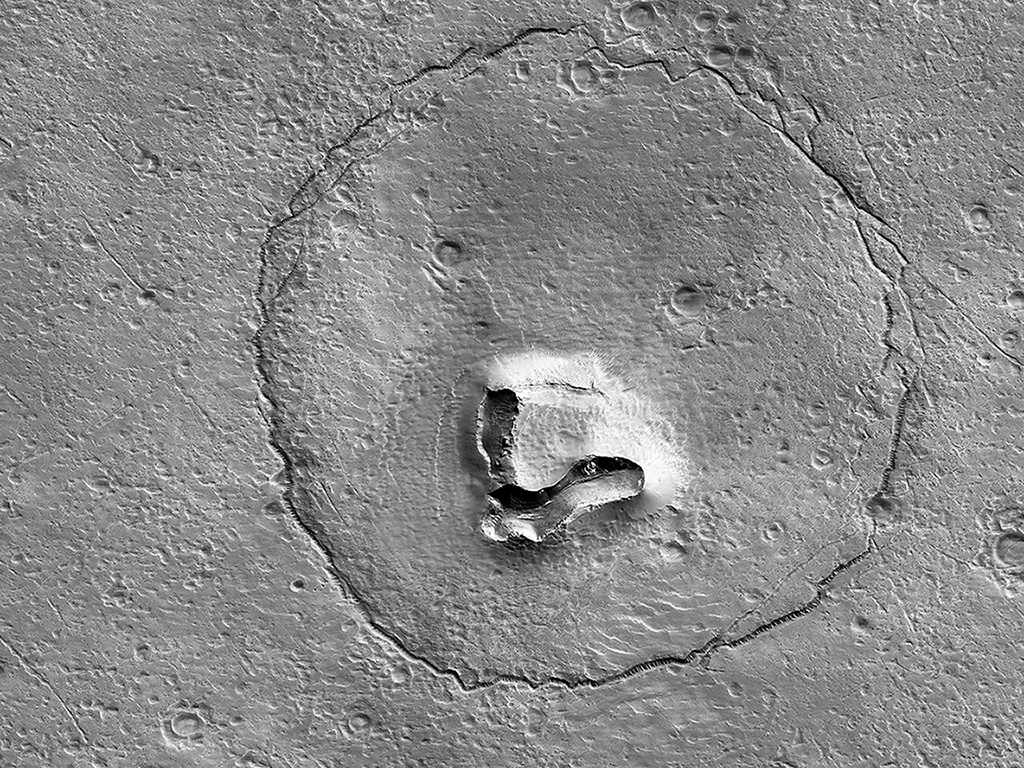
A recent study published in Science examines how thin channels inside impact craters on Mars could have formed from Martian gullies, which share similar characteristics with gullies on Earth and are typically formed from cascading meltwater, despite the Martian atmosphere being incapable of supporting liquid water on its surface. However, the researchers hypothesize these gullies could have formed during periods of high obliquity, also known as axial tilt, on Mars, which could have resulted in a brief rise in surface temperatures that could have melted some surface and subsurface ice, leading to meltwater cascading down the sides of impact craters across the planet.
Continue reading “Melting Water in Mars’ Past Could Have Created Martian Gullies”Melting Water in Mars’ Past Could Have Created Martian Gullies