Life on Earth depends on six critical elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, and Sulfur. These elements are referred to as CHNOPS, and along with several trace micronutrients and liquid water, they’re what life needs.
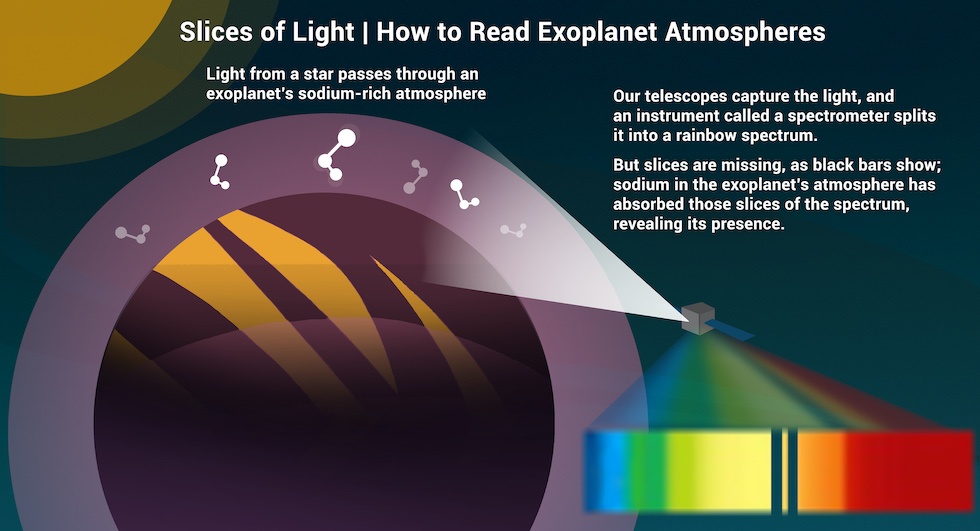
Scientists are getting a handle on detecting exoplanets that might be warm enough to have liquid water on their surfaces, habitability’s most basic signal. But now, they’re looking to up their game by finding CHNOPS in exoplanet atmospheres.
Continue reading “Measuring the Atmospheres of Other Worlds to See if There are Enough Nutrients for Life”