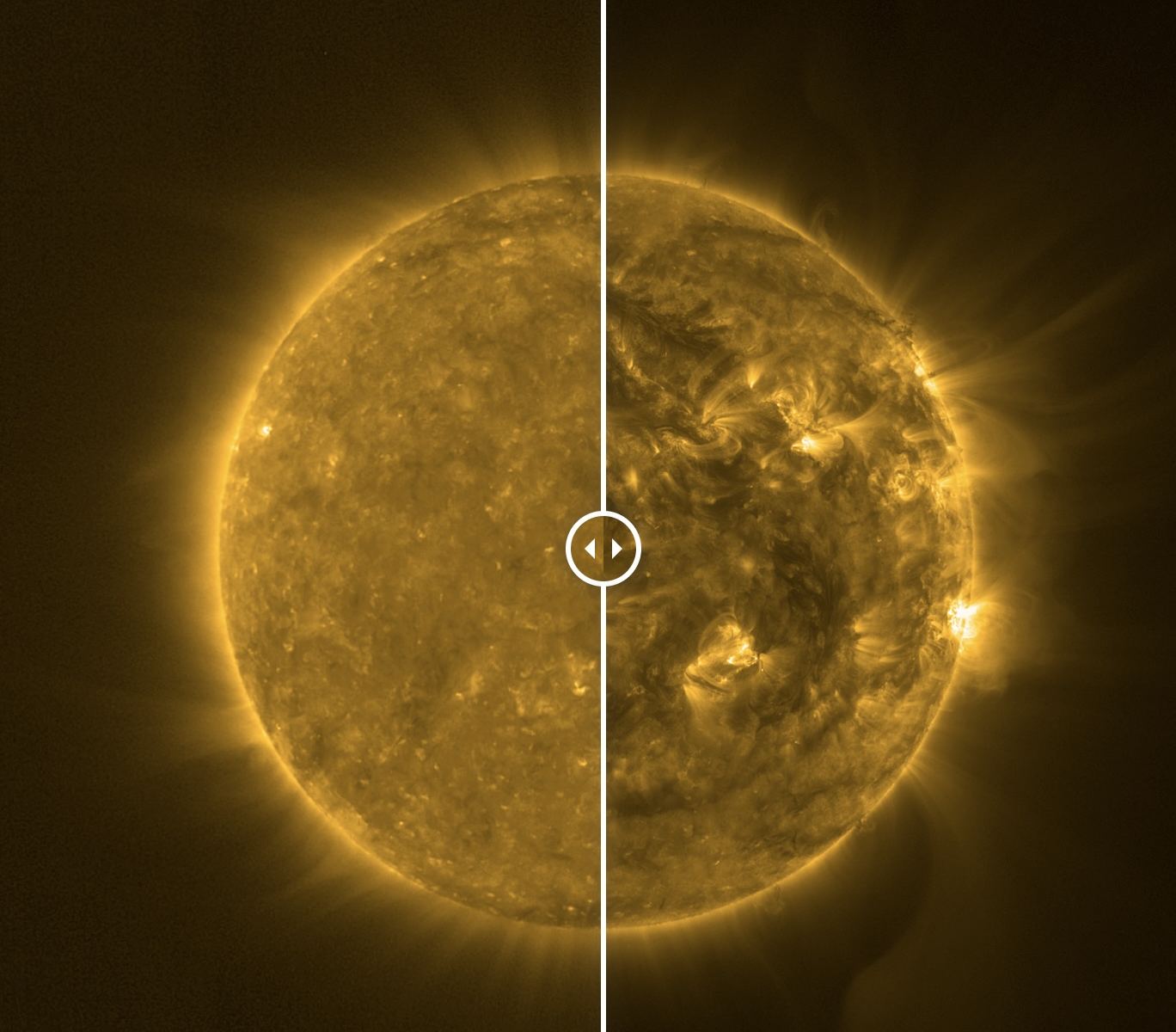
The solar cycle has been reasonably well understood since 1843 when Samuel Schwabe spent 17 years observing the variation of sunspots. Since then, we have regularly observed the ebb and flow of the sunspots cycle every 11 years. More recently ESA’s Solar Orbiter has taken regular images of the Sun to track the progress as we head towards the peak of the current solar cycle. Two recently released images from February 2021 and October 2023 show how things are really picking up as we head toward solar maximum.
Continue reading “Look at How Much the Sun Has Changed in Just Two Years”Juice is Fully Deployed. It’s Now in its Final Form, Ready to Meet Jupiter’s Moons in 2031
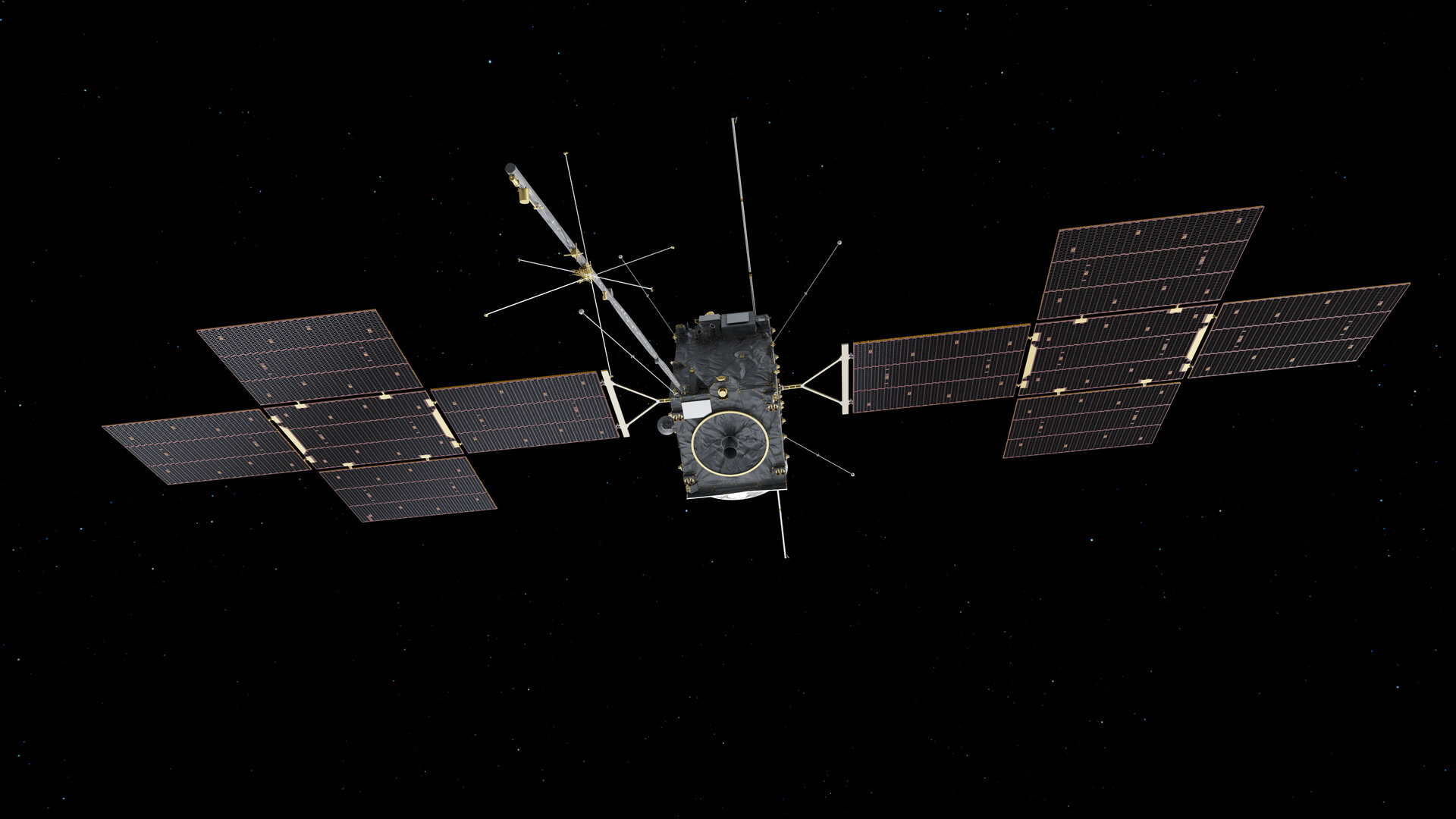

Launched on April 14, 2023, the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice; formerly known as JUICE) spacecraft has finally completed the unfurling of its solar panel arrays and plethora of booms, probes, and antennae while en route to the solar system’s largest planet.
Continue reading “Juice is Fully Deployed. It’s Now in its Final Form, Ready to Meet Jupiter’s Moons in 2031”Juice Looks Back at Earth During Its Space Odyssey to Jupiter’s Moons
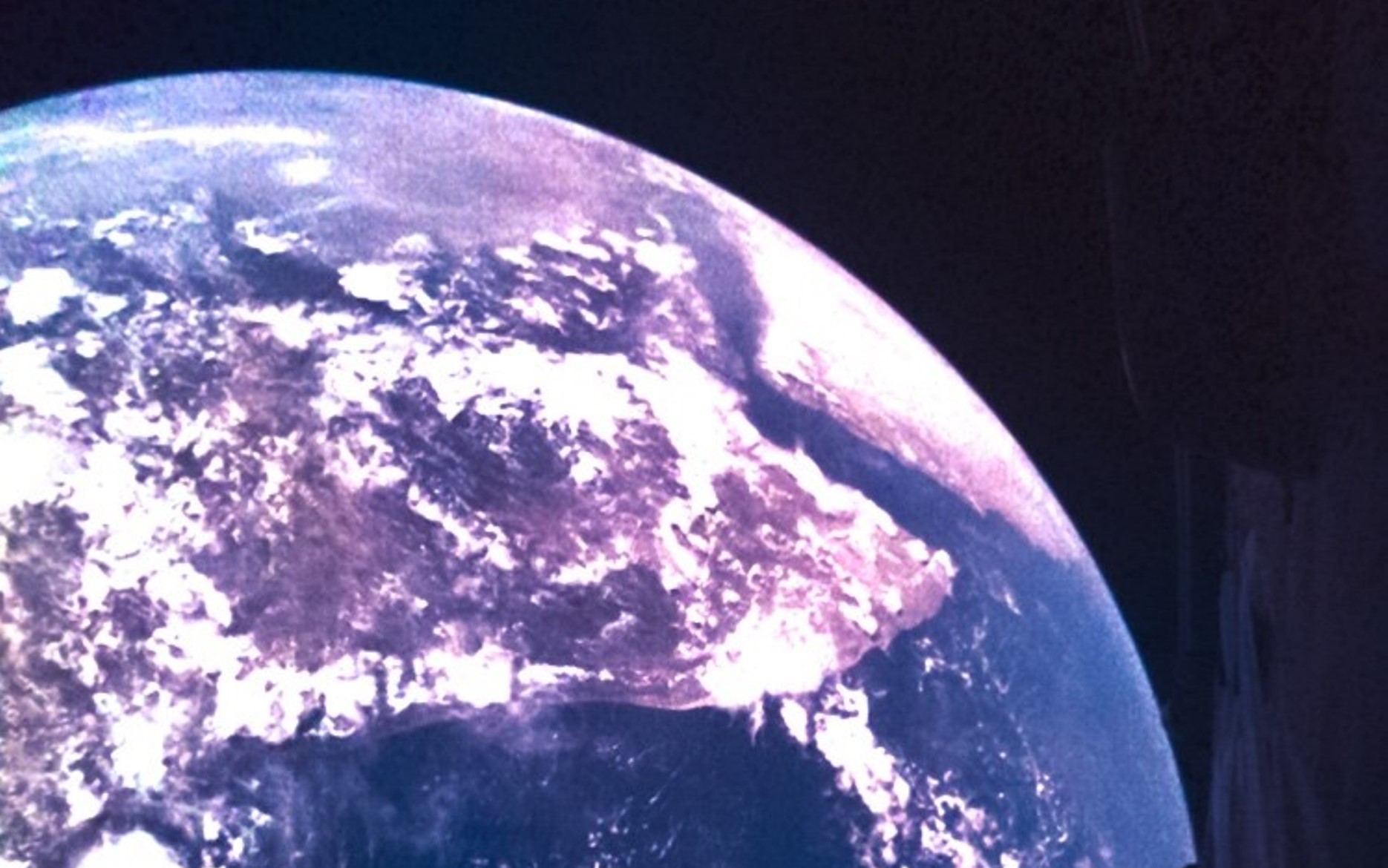

As the European Space Agency’s Juice spacecraft headed out on an eight-year trip to Jupiter’s icy moons, it turned back to snap some selfies with Earth in the background — and those awesome shots are just the start.
The bus-sized probe is due to make four slingshot flybys of Earth and Venus to pick up some gravity-assisted boosts to its destination — and ESA mission managers plan to have the monitoring cameras running during those close encounters.
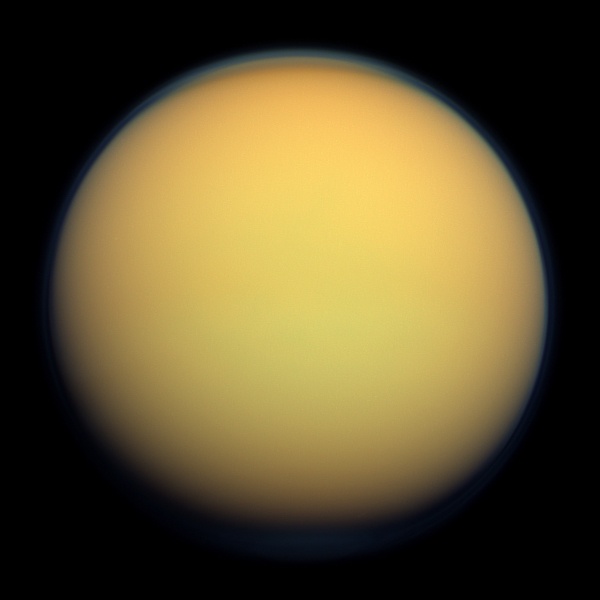
Continue reading “Juice Looks Back at Earth During Its Space Odyssey to Jupiter’s Moons”Will Titan finally answer, ‘Are we alone?’
We recently examined how and why Jupiter’s moon, Europa, could answer the longstanding question: Are we alone? While this small icy world gives plenty of reasons to believe why we could—and should—find life within its watery depths, it turns out our solar system is home to a myriad of places where we might find life. Much like how the Voyager missions gave us the first hints of an interior ocean swirling beneath Europa’s outer icy shell, it was only fitting that Voyager 1 also gave us the first hints of the potential for life on Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, as well.
Continue reading “Will Titan finally answer, ‘Are we alone?’”ESA Gives Green Light on its Comet Interceptor Mission
Comets, with their long, beautiful, bright tails of ice, are some of the most spectacular sightings in the night sky. This was most apparent when Comet NEOWISE passed by Earth in the summer of 2020, dazzling viewers from all over the planet while being mainly visible in the northern hemisphere. Even though the sky might look the same night after night, comets are a humble reminder that the universe is a very active and beautiful place.
Continue reading “ESA Gives Green Light on its Comet Interceptor Mission”ESA Is Going To Spend $102 Million To Remove a Single Piece of Space Junk
How much would you be willing to spend to remove a piece of space debris? Does $102 million sound like enough? That is how much a contract between the European Space Agency (ESA) and a Swiss start-up named ClearSpace SA is worth, and the entire contract is to simply remove a single piece of space debris.
Continue reading “ESA Is Going To Spend $102 Million To Remove a Single Piece of Space Junk”Gaia has Already Given Us 5 New Insights Into the Milky Way

The European Space Agency launched the Gaia mission in 2013. The mission’s overall goal was to discover the history of the Milky Way by mapping out the positions and velocities of one billion stars. The result is kind of like a movie that shows the past and the future of our galaxy.
The mission has released two separate, massive data sets for researchers to work through, with a third data release expected soon. All that data has spawned a stream of studies into our home galaxy.
Recently, the ESA drew attention to five new insights into the Milky Way galaxy. Allof these discoveries directly stemmed from the Gaia spacecraft.
Continue reading “Gaia has Already Given Us 5 New Insights Into the Milky Way”This Laser Powered Rover Could Stay in the Shadows on the Moon and Continue to Explore
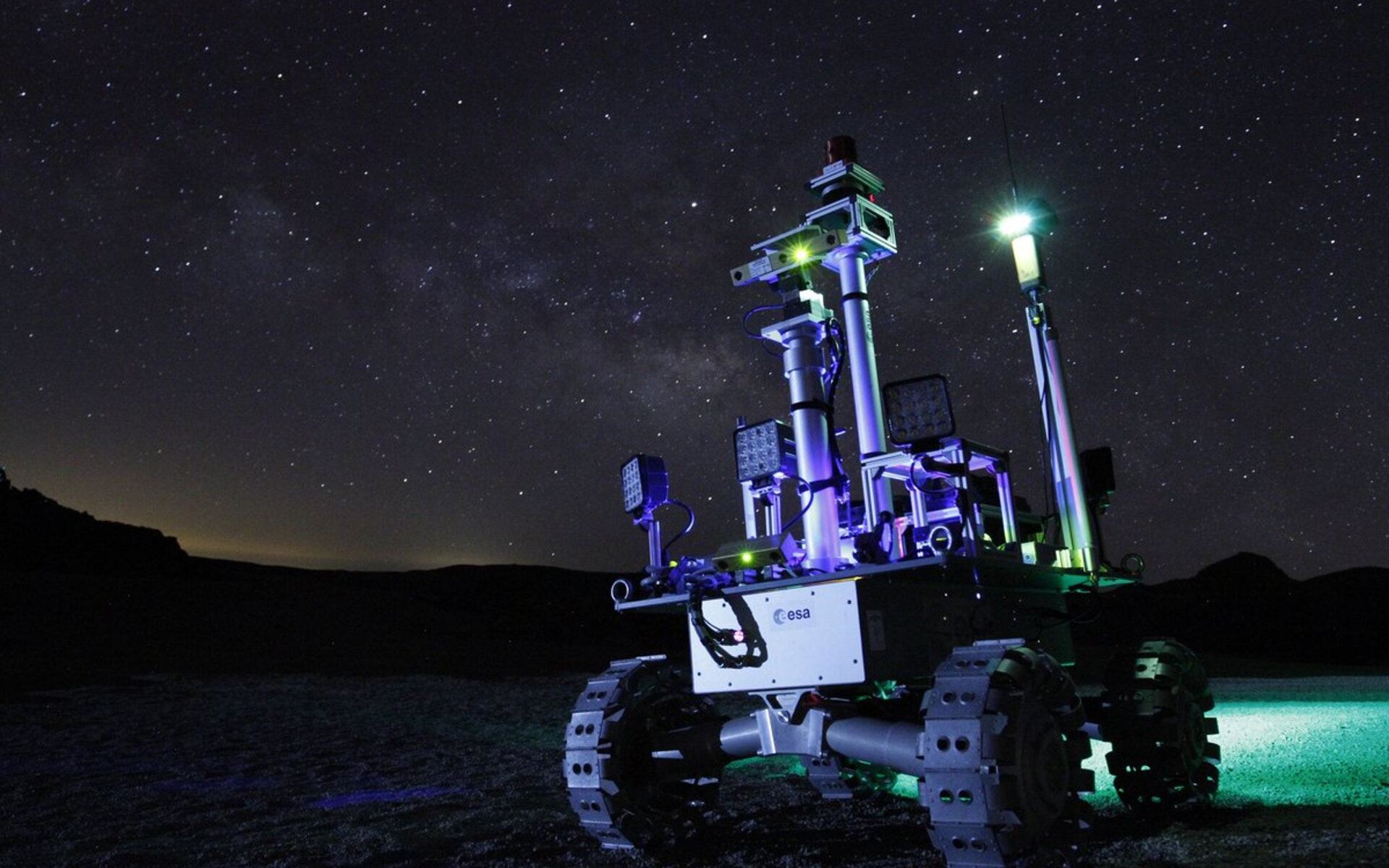
The craters on the Moon’s poles are in permanent shadow. But they’re also intriguing locations, due to deposits of water ice and other materials. The ESA is developing the idea for a rover that can explore these areas with power provided by lasers.
Continue reading “This Laser Powered Rover Could Stay in the Shadows on the Moon and Continue to Explore”Because of Coronavirus Lockdowns, Europe is Having the Same Drop in Pollution that we Saw in China
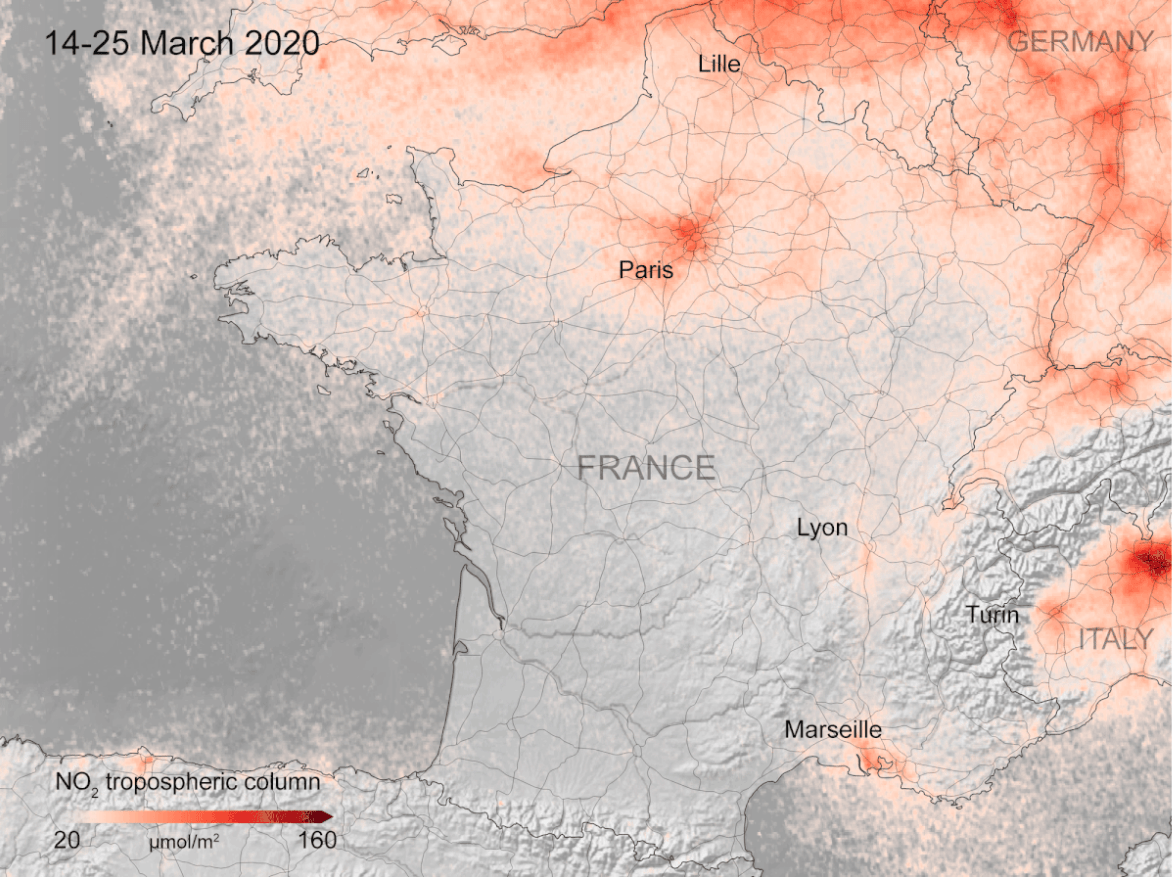
The pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus is creating all kinds of chaos for human society. But for the dear old Earth, and the humans and creatures that breathe its air, it’s a bit of a reprieve. Mirroring what happened in China during lock-down, Europe is now seeing the same drop in air pollution.
Continue reading “Because of Coronavirus Lockdowns, Europe is Having the Same Drop in Pollution that we Saw in China”New Image Shows the Rugged Landscape of Comet 67P
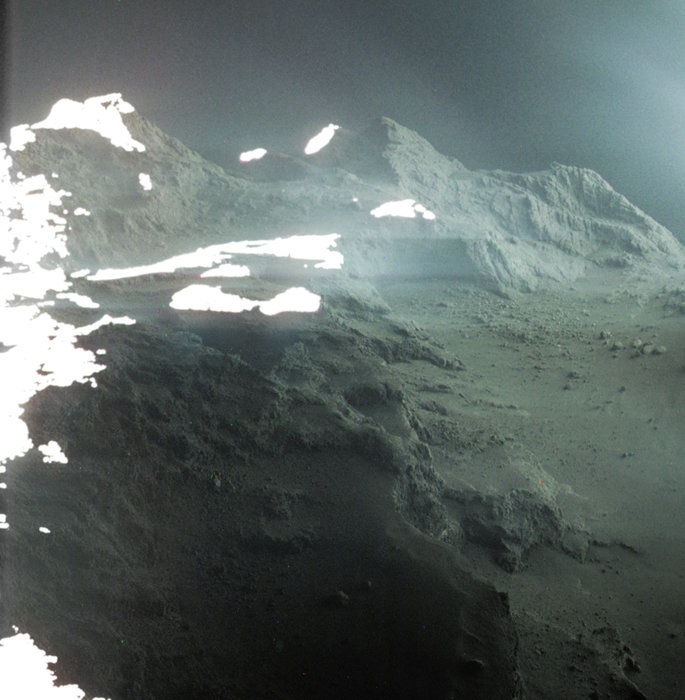

In March of 2004, the European Space Agency’s Rosetta spacecraft blasted off from French Guiana aboard an Ariane 5 rocket. After ten years, by November of 2014, the spacecraft rendezvoused with its target – Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (67P/C-G). Over the more than two years that followed, the spacecraft remained in orbit of this comet, gathering information on its surface, interior, and gas and dust environment.
And on September 30th, 2016, Rosetta came closer than ever to the surface of 67P/C-G and concluded its mission with a controlled impact onto the surface. Since that time, scientists have still been processing all the data the spacecraft collected during its mission. This included some awe-inspiring photographs of the comet’s surface that were obtained shortly after the spacecraft made its rendezvous with 67P/C-G.
Continue reading “New Image Shows the Rugged Landscape of Comet 67P”