A busy year of 13 space launches by rocket provider United Launch Alliance (ULA) in 2015 begins with a pair of blastoffs for the US Navy and NASA tonight and next week, emanating from both the US East and West Coasts.
The hefty manifest of 13 liftoffs in 2015 comes hot on the heels of ULA’s banner year in 2014 whereby they completed every one of the firm’s 14 planned launches in 2014 with a 100% success rate.
“What ULA has accomplished in 2014, in support of our customers’ missions, is nothing short of remarkable,” said ULA CEO Tory Bruno.
“When you think about every detail – all of the science, all of the planning, all of the resources – that goes into a single launch, it is hard to believe that we successfully did it at a rate of about once a month, sometimes twice.”
ULA’s stable of launchers includes the Delta II, Delta IV and the Atlas V. They are in direct competition with the Falcon 9 rocket from SpaceX founded by billionaire Elon Musk.
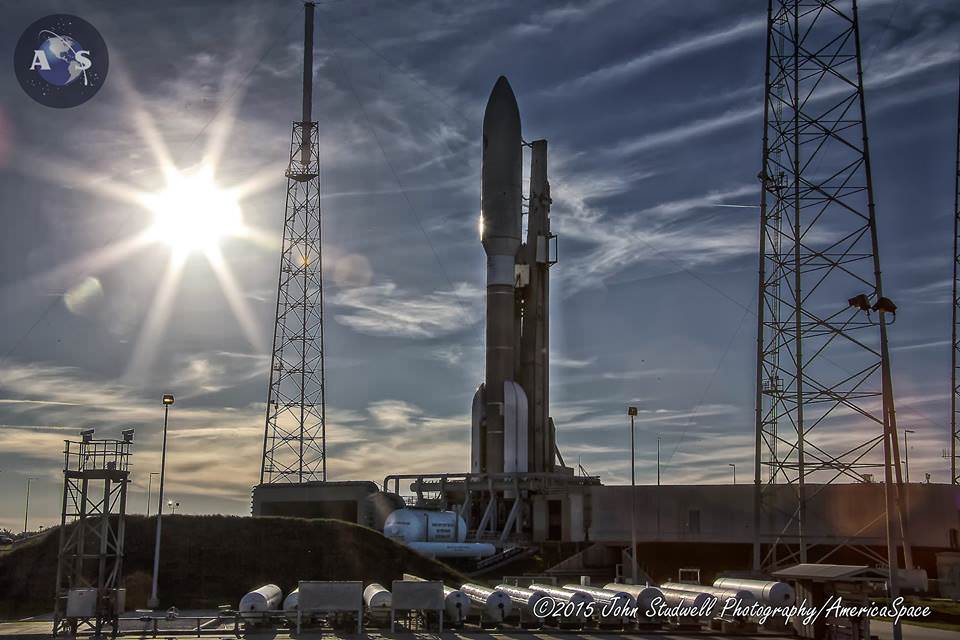
And ULA’s 2015 launch calendar begins tonight with a milestone launch for the US Navy that also marks the 200th launch overall of the venerable Atlas-Centaur rocket that has a renowned history dating back some 52 years to 1962 with multiple variations.
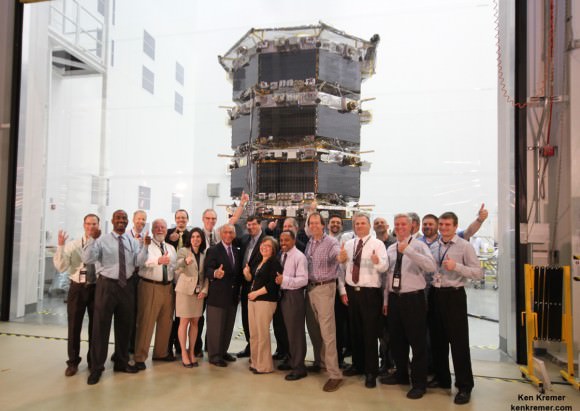
And tonight’s blastoff of the Multi-User Objective System (MUOS-3) satellite for the US Navy involves using the most powerful variant of the rocket, known as the Atlas V 551.
Liftoff of MUOS-3 is set for 7:43 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch window extends for 44 minutes and the weather outlook is very favorable. It will be carried live on a ULA webcast.

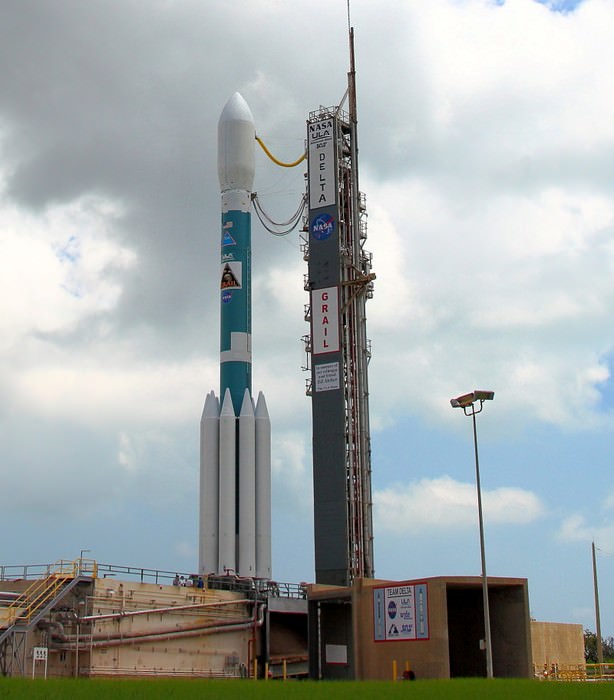
The second ULA launch of 2015 comes just over 1 week later on January 29, lofting NASA’s SMAP Earth observation satellite on a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
MUOS is a next-generation narrowband tactical satellite communications system designed to significantly improve ground communications for U.S. forces on the move, according to ULA.
This is the third satellite in the MUOS series and will provide military users 10 times more communications capability over existing systems, including simultaneous voice, video and data, leveraging 3G mobile communications technology.
ULA’s second launch in 2015 thunders aloft from the US West Coast with NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive mission (SMAP). It is the first US Earth-observing satellite designed to collect global observations of surface soil moisture.
SMAP will blastoff from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg AFB at 9:20 a.m. EST (6:20 a.m. PST) on ULA’s Delta II rocket.

“It goes without saying: ULA had a banner year,” Bruno said. “As we look ahead to 2015, we could not be more honored to continue supporting our nation in one of the most technologically complex, critical American needs: affordable, reliable access to space.”
ULA began operations in December 2006 with the merger of the expendable launch vehicle operations of Boeing and Lockheed Martin.
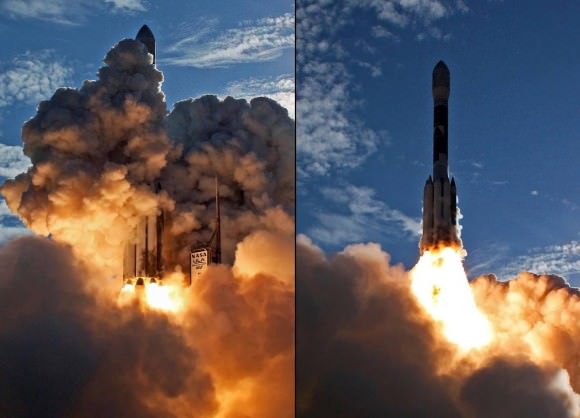
ULA’s Delta IV Heavy is currently the world’s most powerful rocket and flawlessly launched NASA’s Orion capsule on Dec. 5, 2014 on its highly successful uncrewed maiden test flight on the EFT-1 mission.
Overall, the 14-mission launch manifest in 2014 included 9 national security space missions, 3 space exploration missions, including NASA’s Orion EFT-1 and 2 commercial missions.

Beyond MUOS-3 and SMAP, the launch manifest on tap for 2015 also includes additional NASA science satellites, an ISS commercial cargo resupply mission as well as more GPS satellites for military and civilian uses and top secret national security launches using the Delta II, Delta IV and the Atlas V boosters.
NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale Mission (MMS) to study Earth’s magnetic reconnection is scheduled for launch on an Atlas V 421 booster on March 12 from Cape Canaveral. See my up close visit with MMS and NASA Administrator Charles Bolden at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center detailed in my story – here.

In March, June and September the GPS 2F-9, 2F-10 and 2F-11 navigation satellites will launch on Delta IV and Atlas V rockets from Cape Canaveral.
Two top secret NRO satellites are set to launch on a Delta IV and Atlas in April and August from Vandenberg.
An Air Force Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV) space plane may launch as soon as May atop an Atlas V from Cape Canaveral.
The MUOS-4 liftoff is set for August on another Atlas from the Cape.
The Morelos 3 communications satellite for the Mexican Ministry of Communications and Transportation is due to launch in October from the Cape.
In November, the Atlas V will be pressed into service for the first time to launch the Orbital Sciences Cygnus Orb-4 cargo vehicle to the International Space Station (ISS) as a replacement rocket for the Orbital Sciences Antares rocket which is grounded following its catastrophic Oct. 28 explosion on the Orb-3 mission from NASA Wallops.
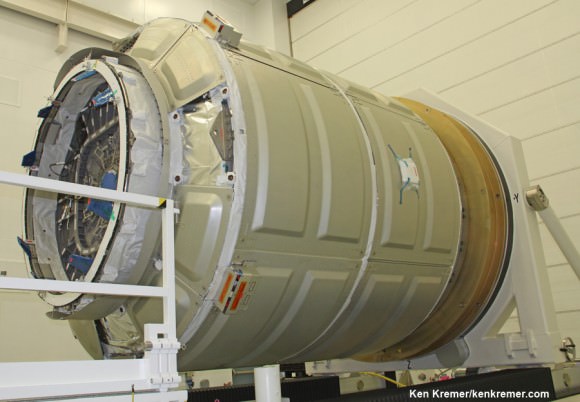

The Orb-4 launch also marks ULA’s first launch to the ISS. It may be followed by another Cygnus launch atop an Atlas V in 2016 as Orbital works to bring the Antares back into service.

In another major milestone down the road, the Atlas V is being man rated since it was chosen to launch the Boeing CST-100 space taxi which NASA selected as one of two new commercial crew vehicles to launch US astronauts to the ISS as soon as 2017.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.