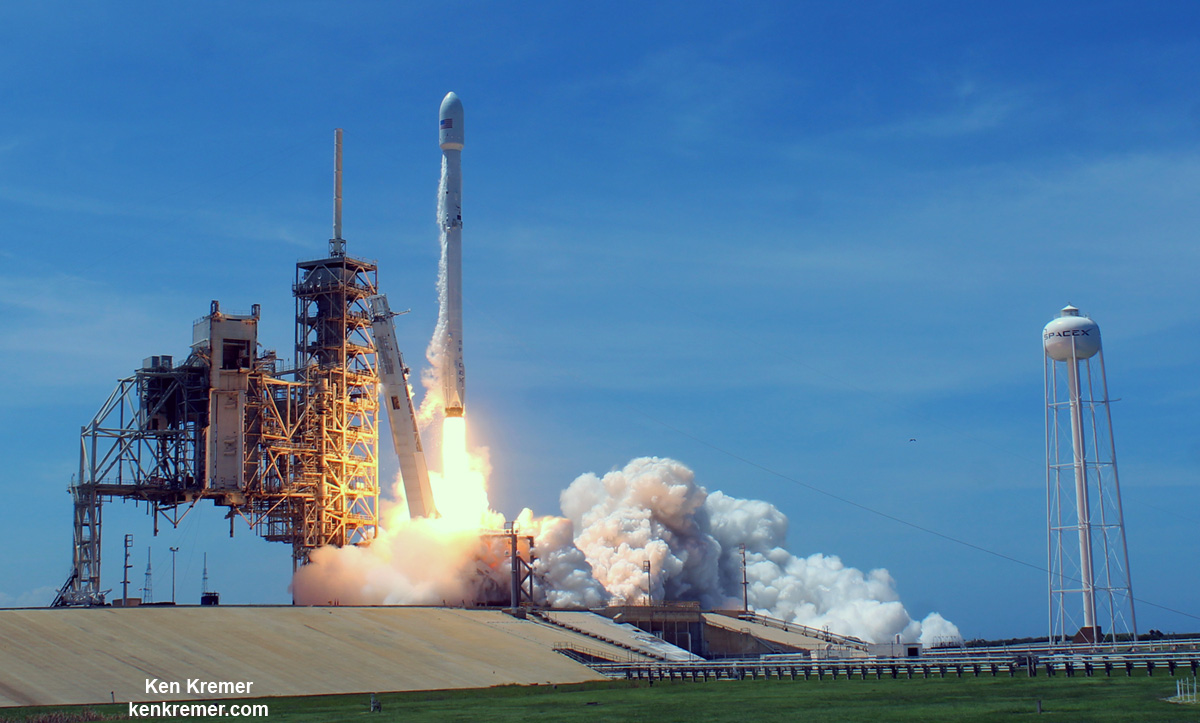
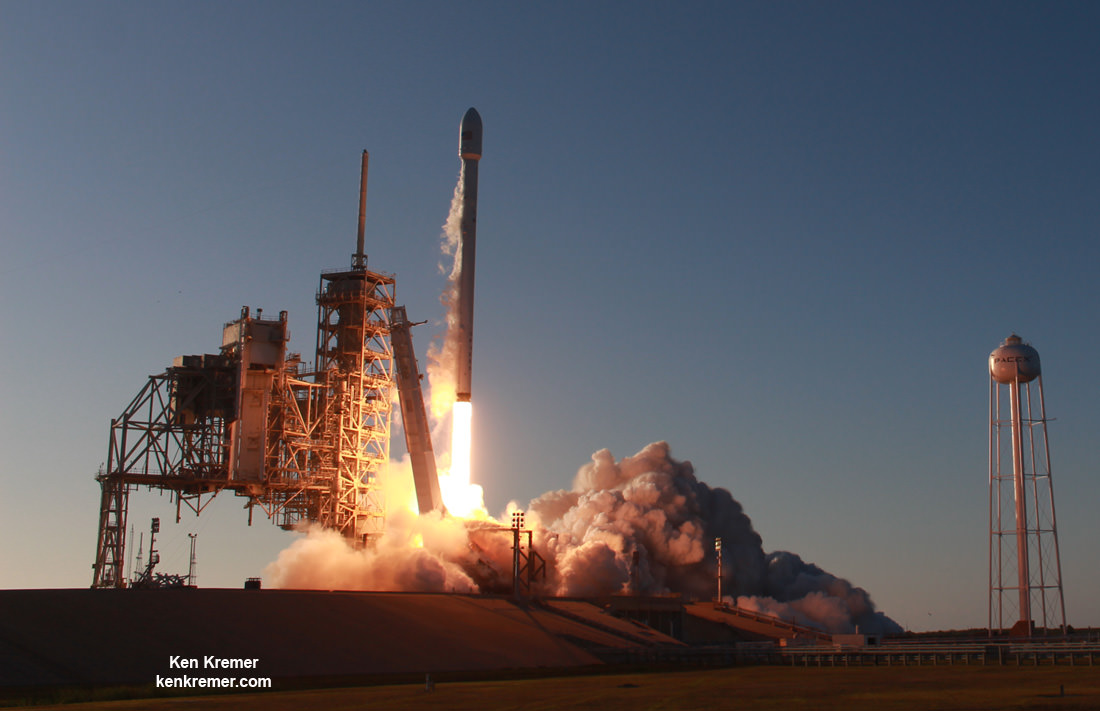
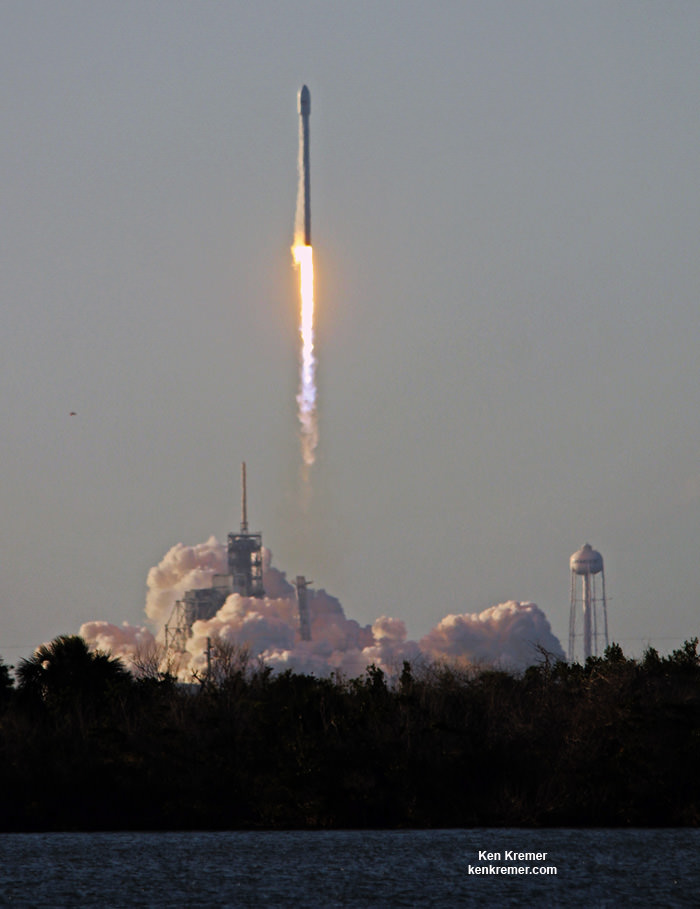
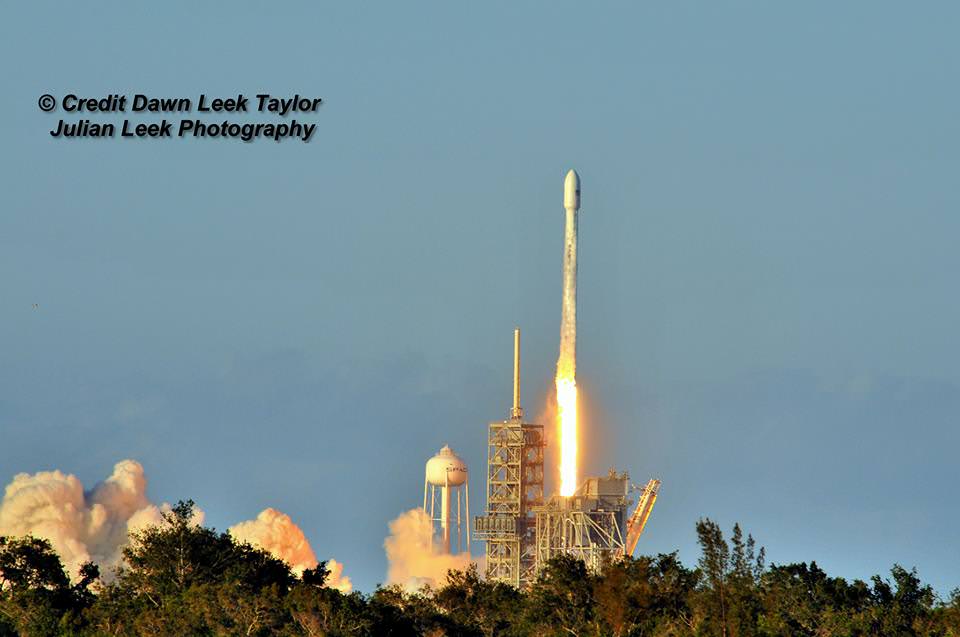
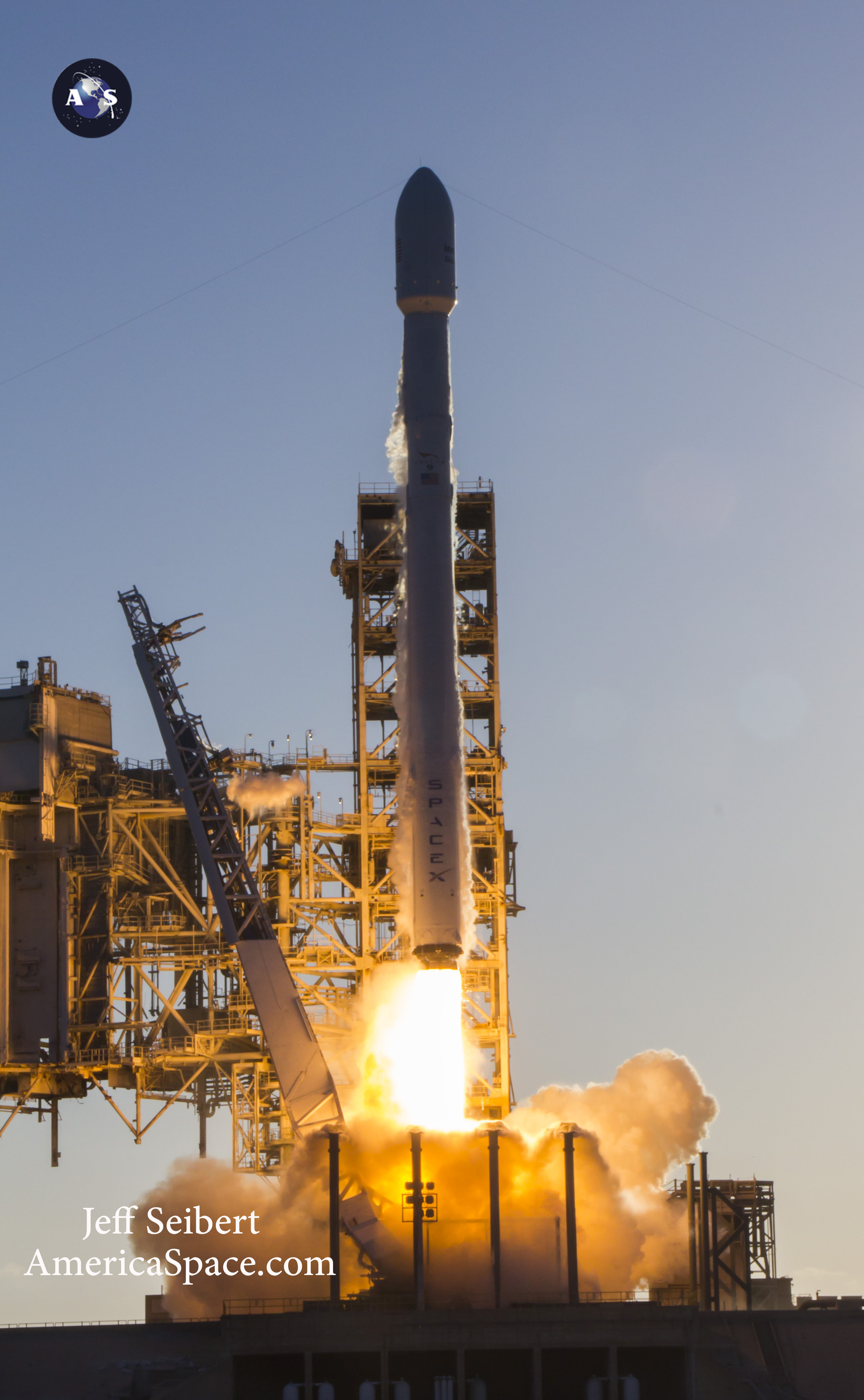
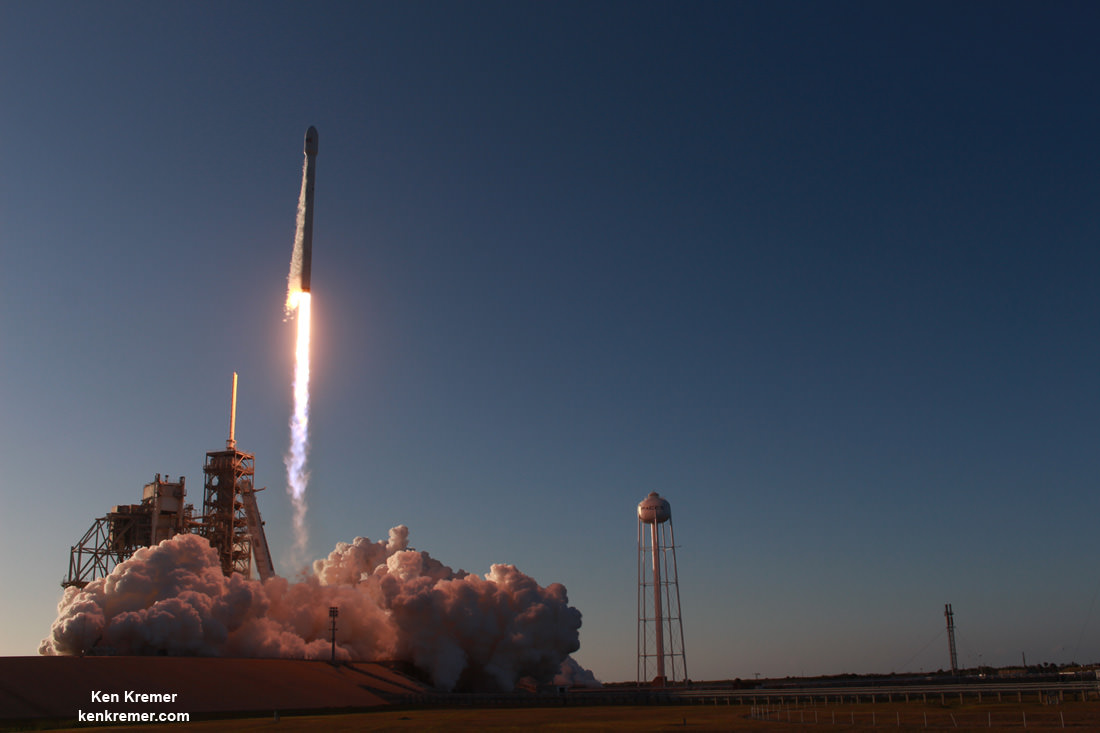
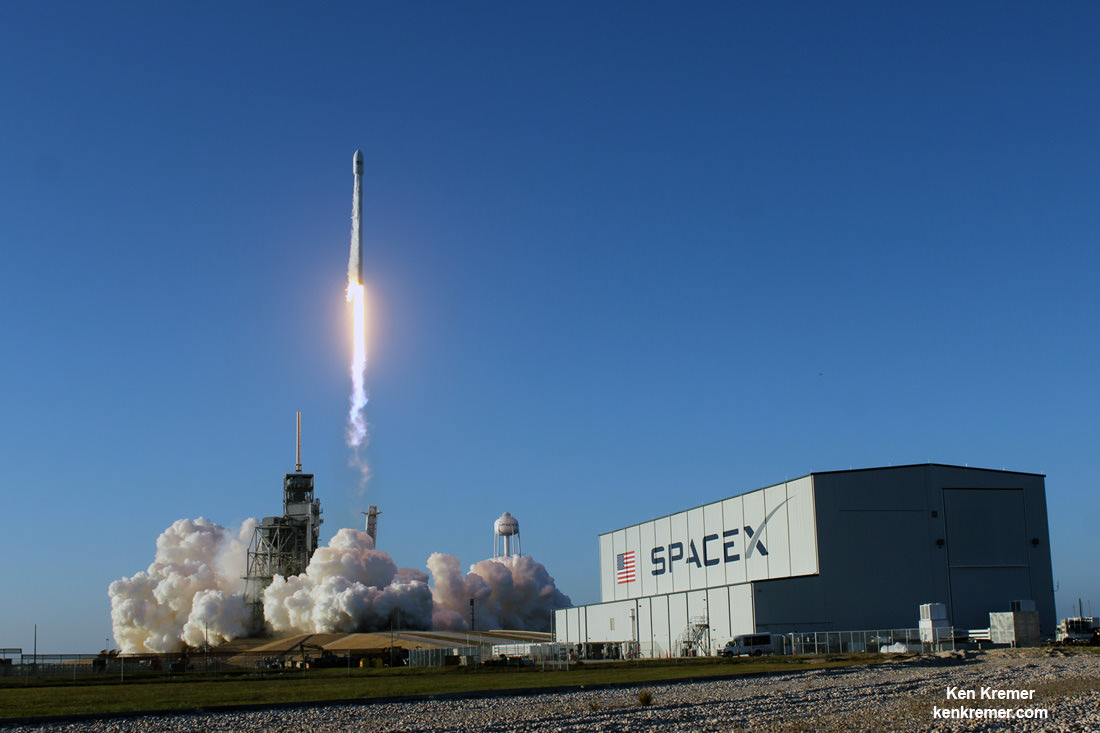
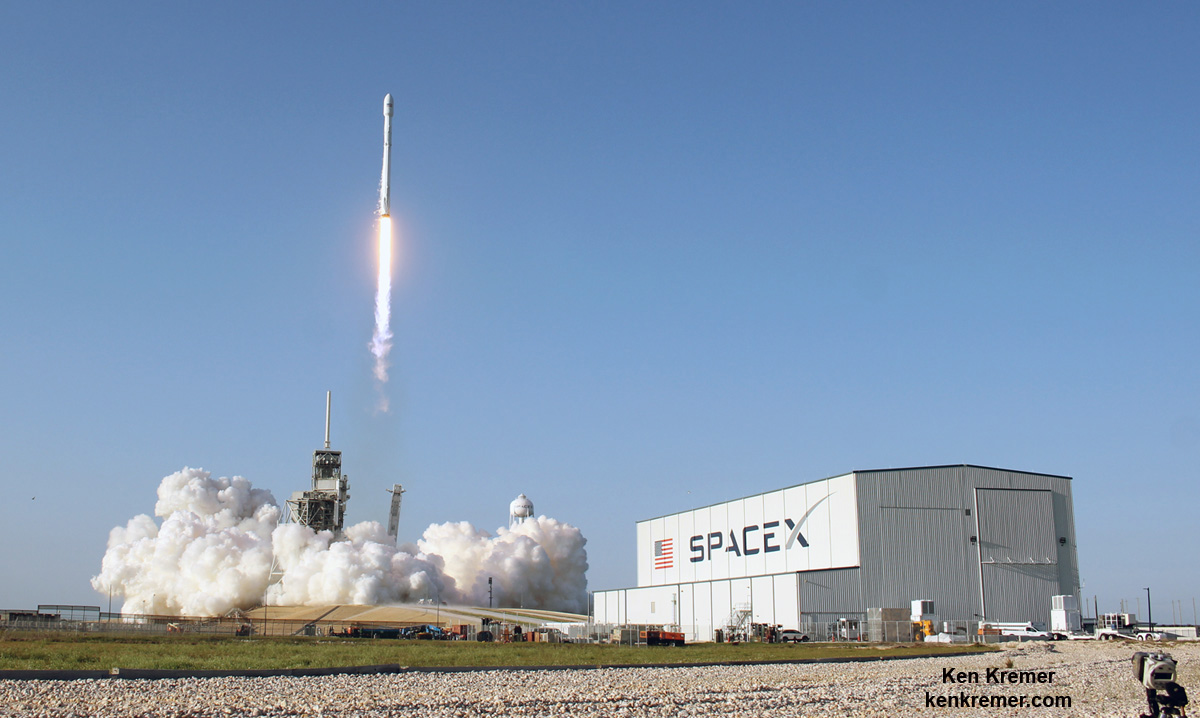
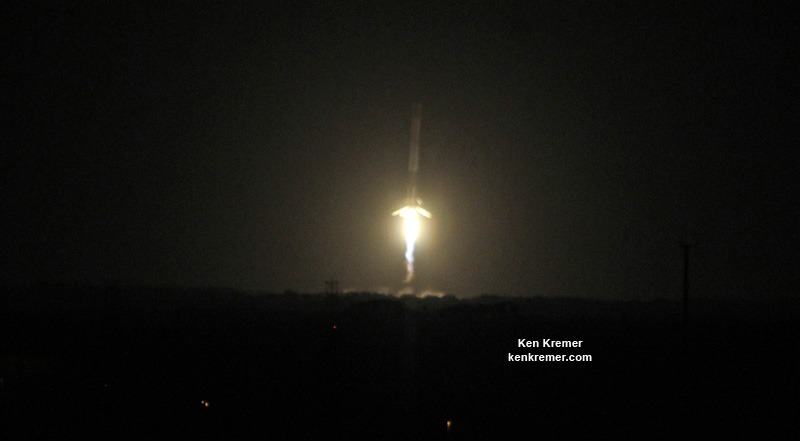
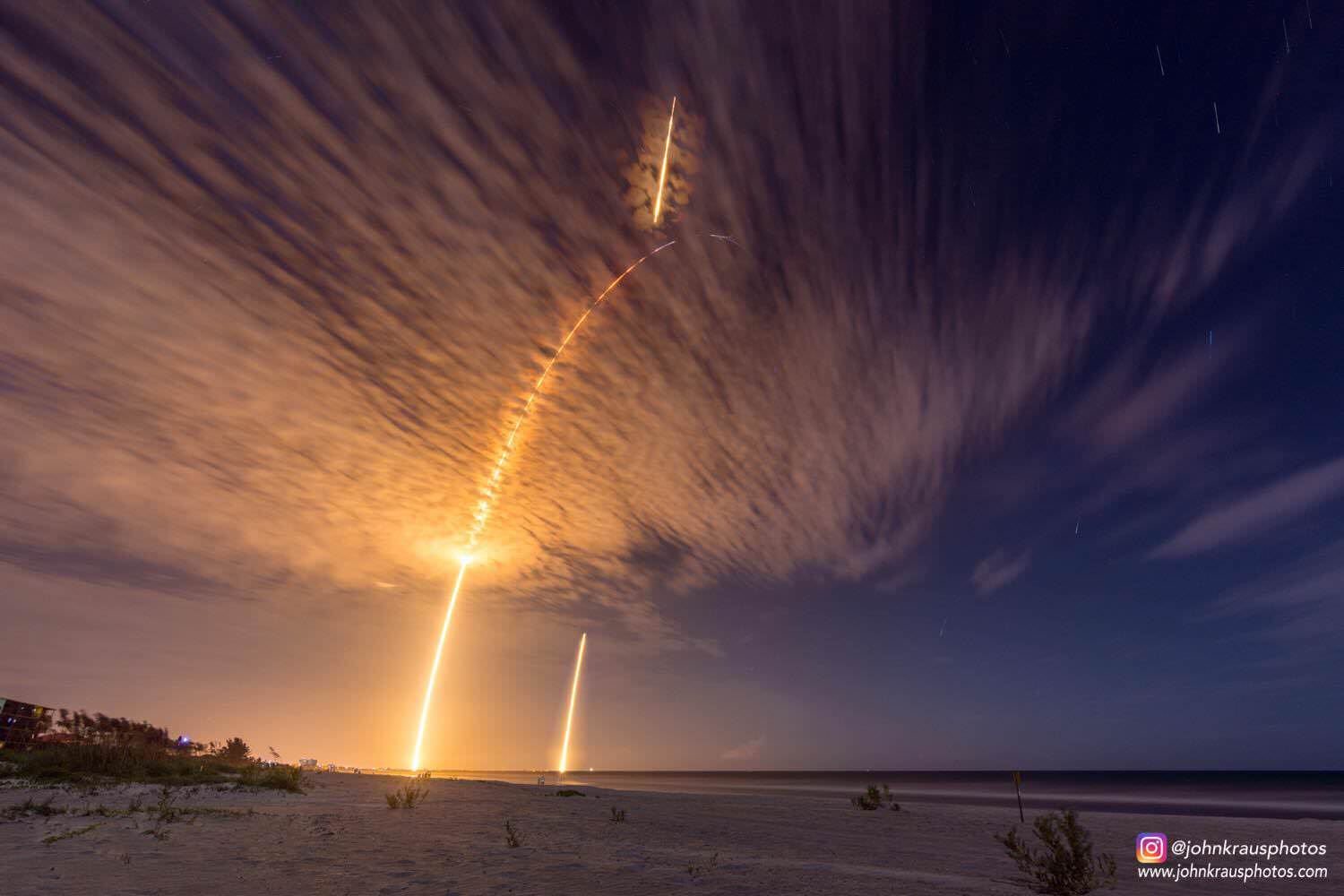
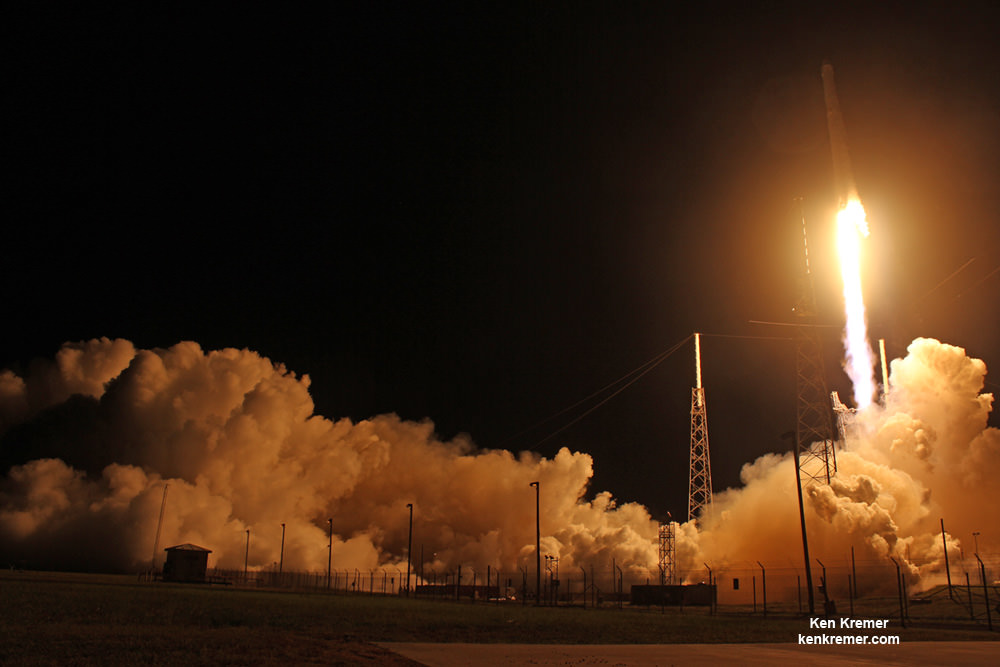
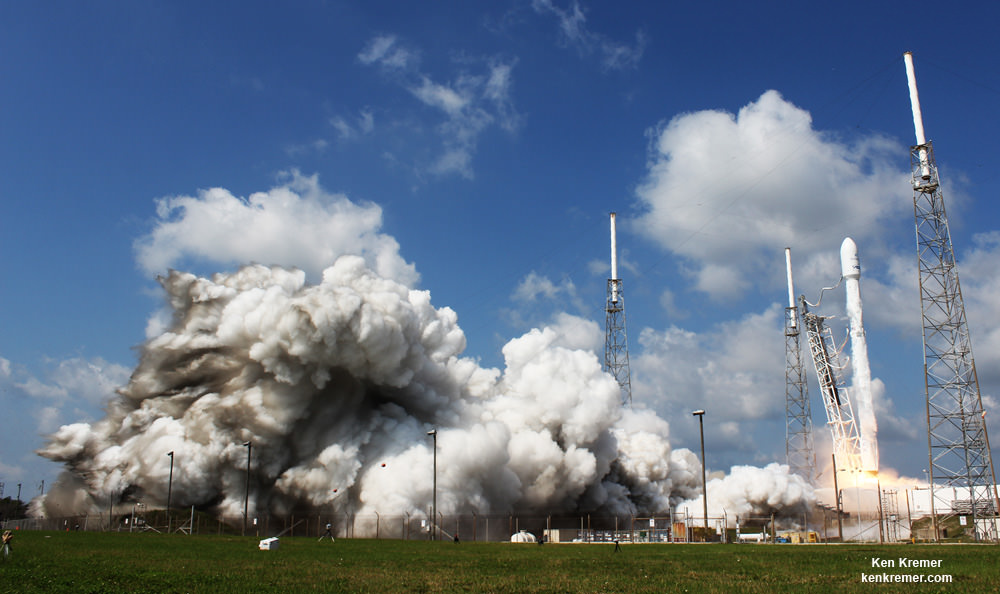
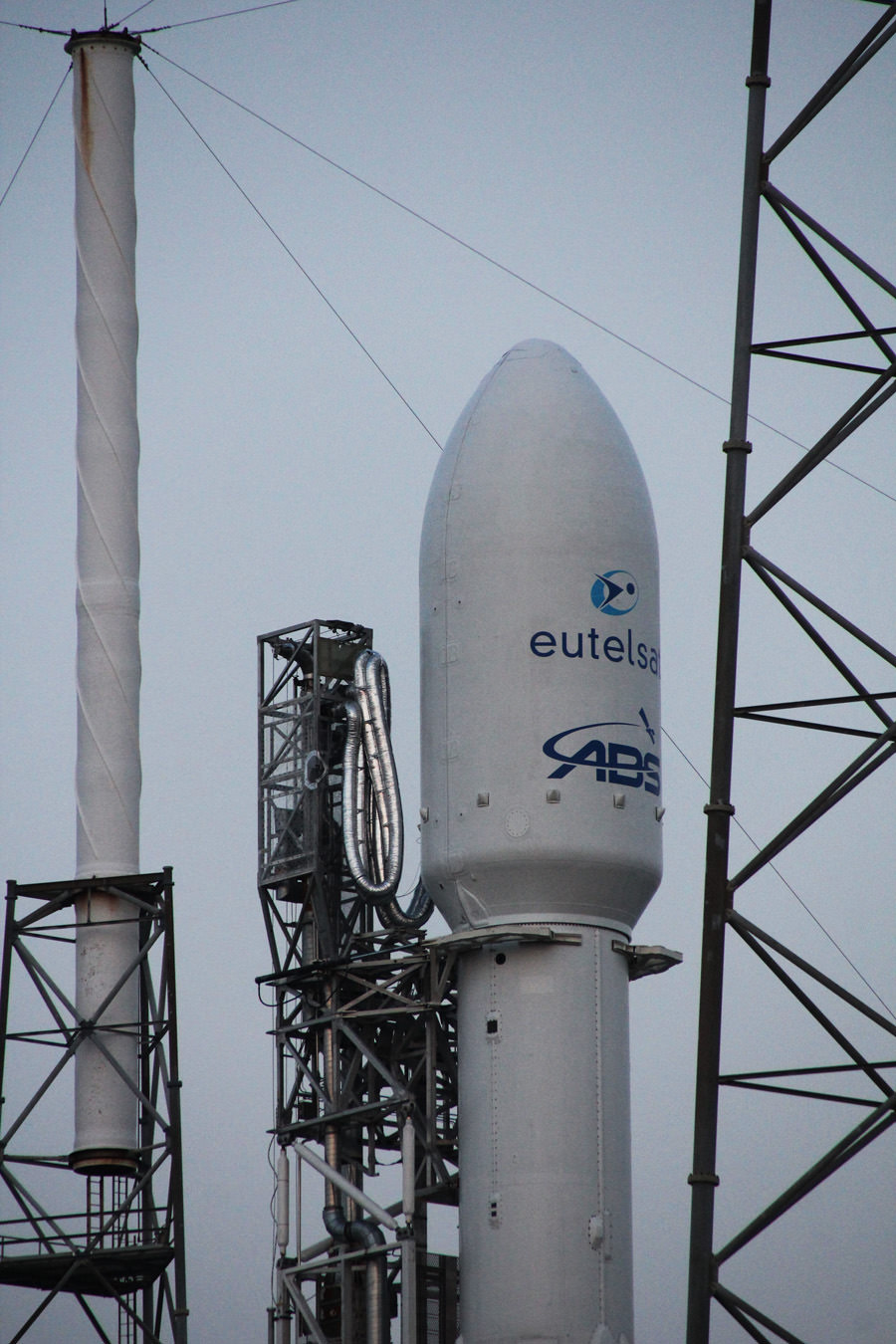
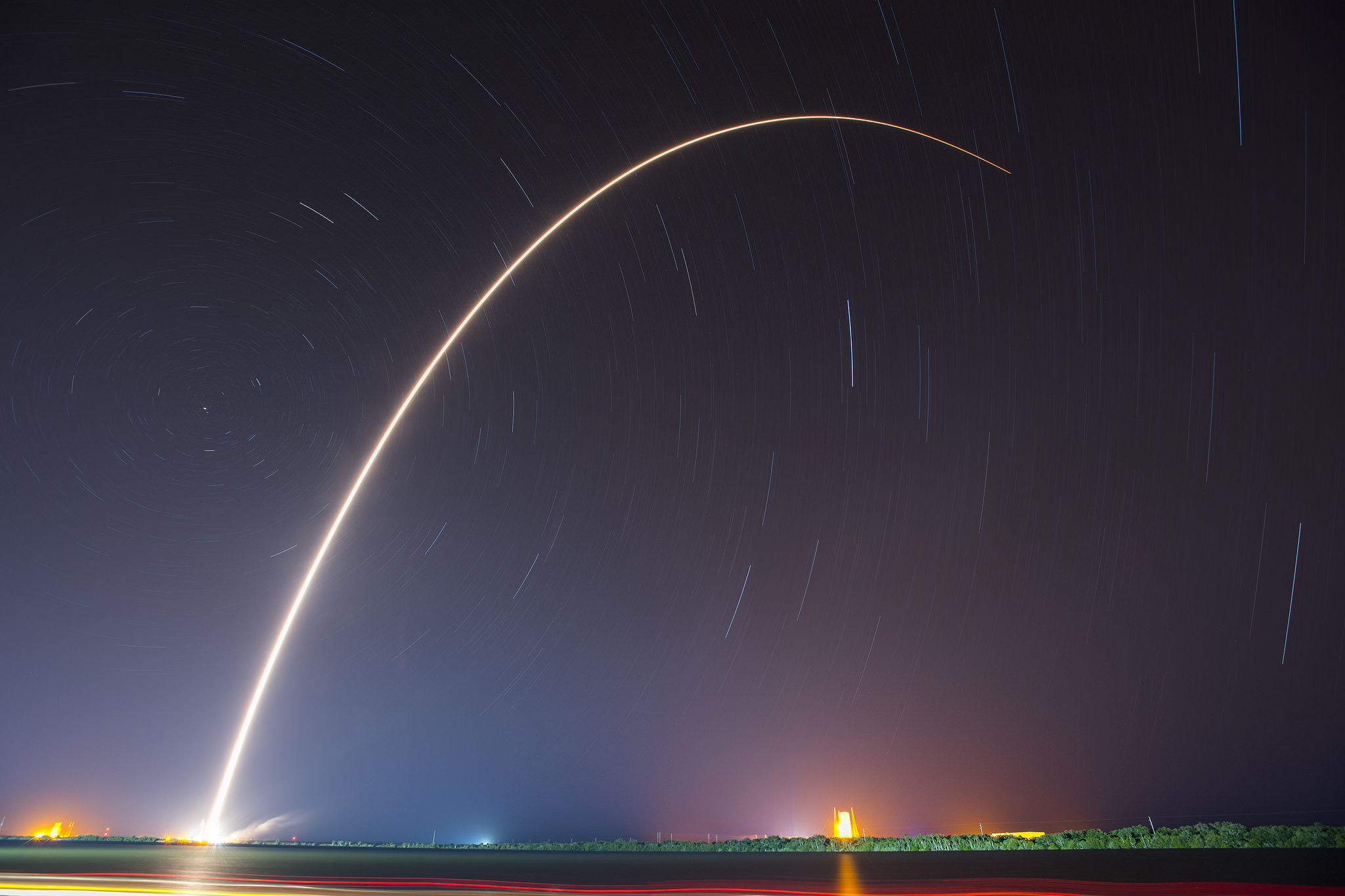
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – In another breakthrough milestone aimed at slashing the high cost of rocketry, the innovators at billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk’s SpaceX successfully launched a ‘used’ rocket for only the second time in history – that blazed a path to orbit with its BulgariaSat-1 commercial television comsat payload Friday afternoon, June 23, from the Kennedy Space Center and just minutes later landed upright and intact on an oceanic platform waiting offshore in the vast currents of the Atlantic ocean.
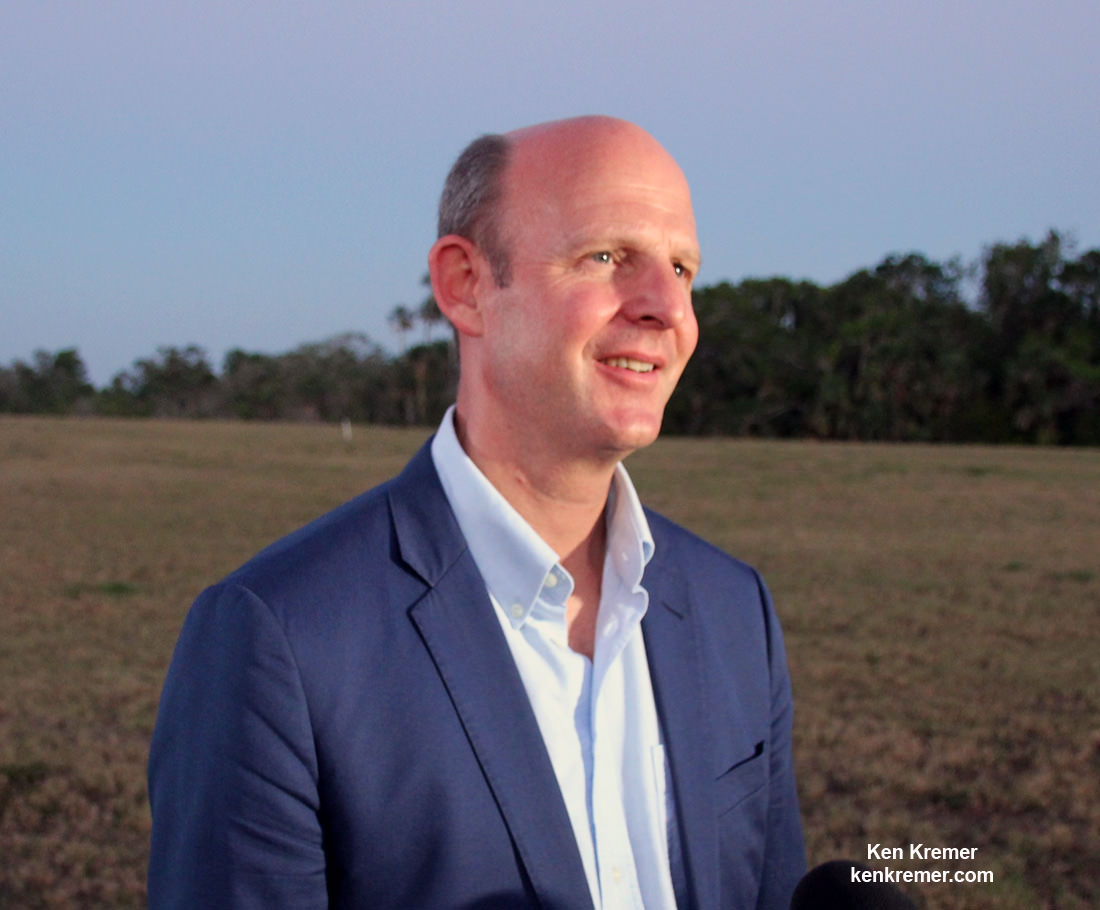
“This is really a great day for us,” Maxim Zayakov, CEO of BulgariaSat and Bulsatcom told Universe Today during pre and post launch interview’s onsite at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
“Everything is seeming to be a good success so far.”
To top that, SpaceX is targeting a bicoastal weekend doubleheader of launches signaling a remarkably rapid turnaround capability. Another Falcon 9 is scheduled for blastoff on Sunday, June 25 at 1:25 p.m. PDT (4:25 p.m. EDT; 2025 UTC) from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on the Iridium-2 mission, less than 48 hours apart – which would set a new launch turnaround record for SpaceX.
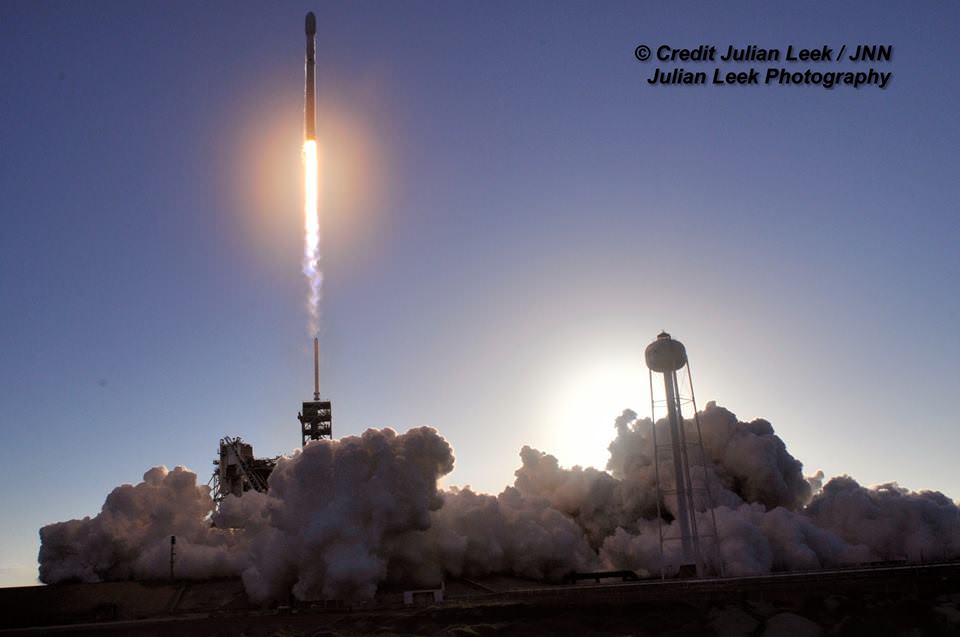
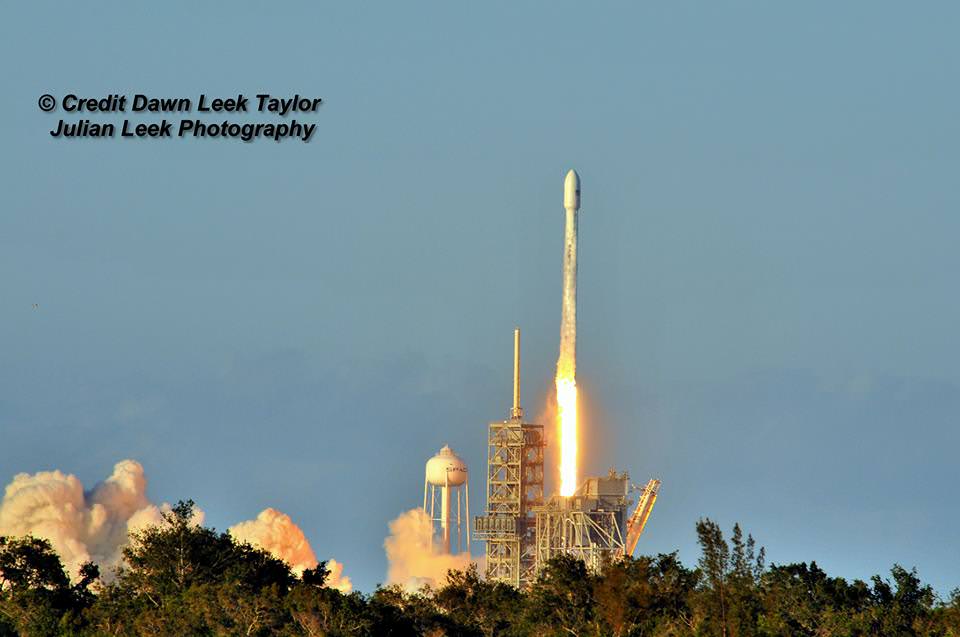
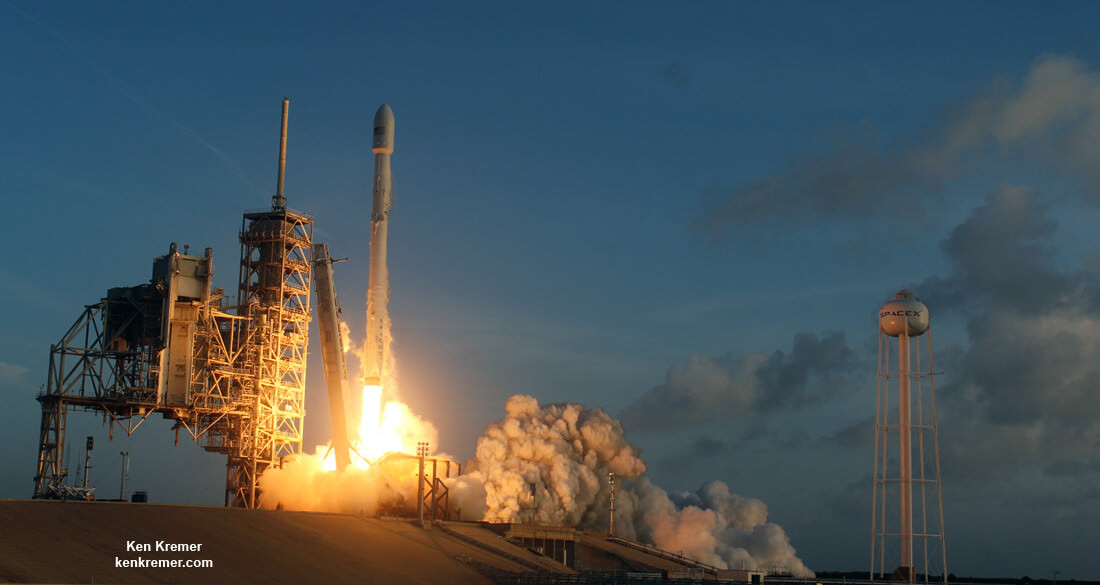
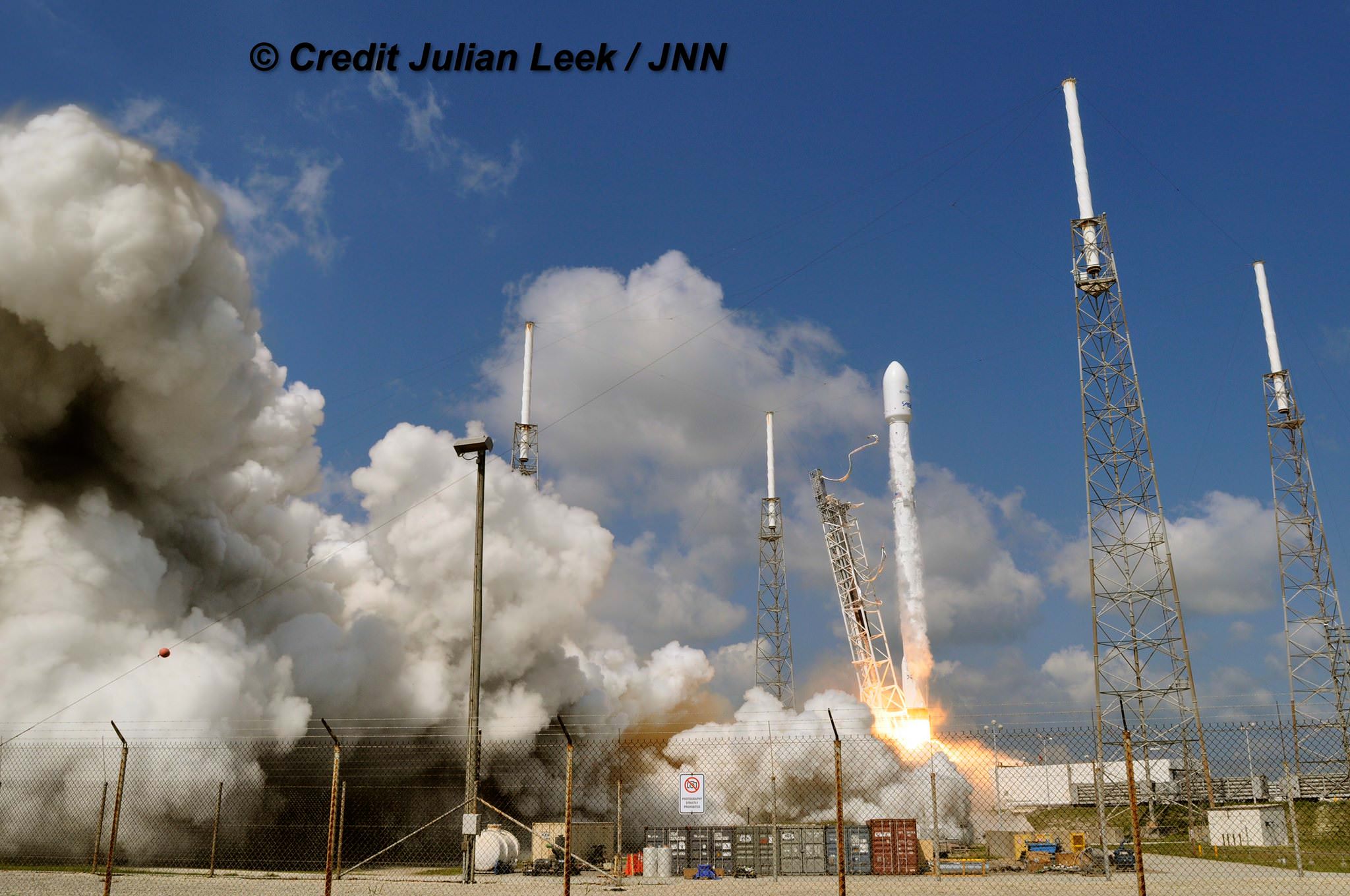
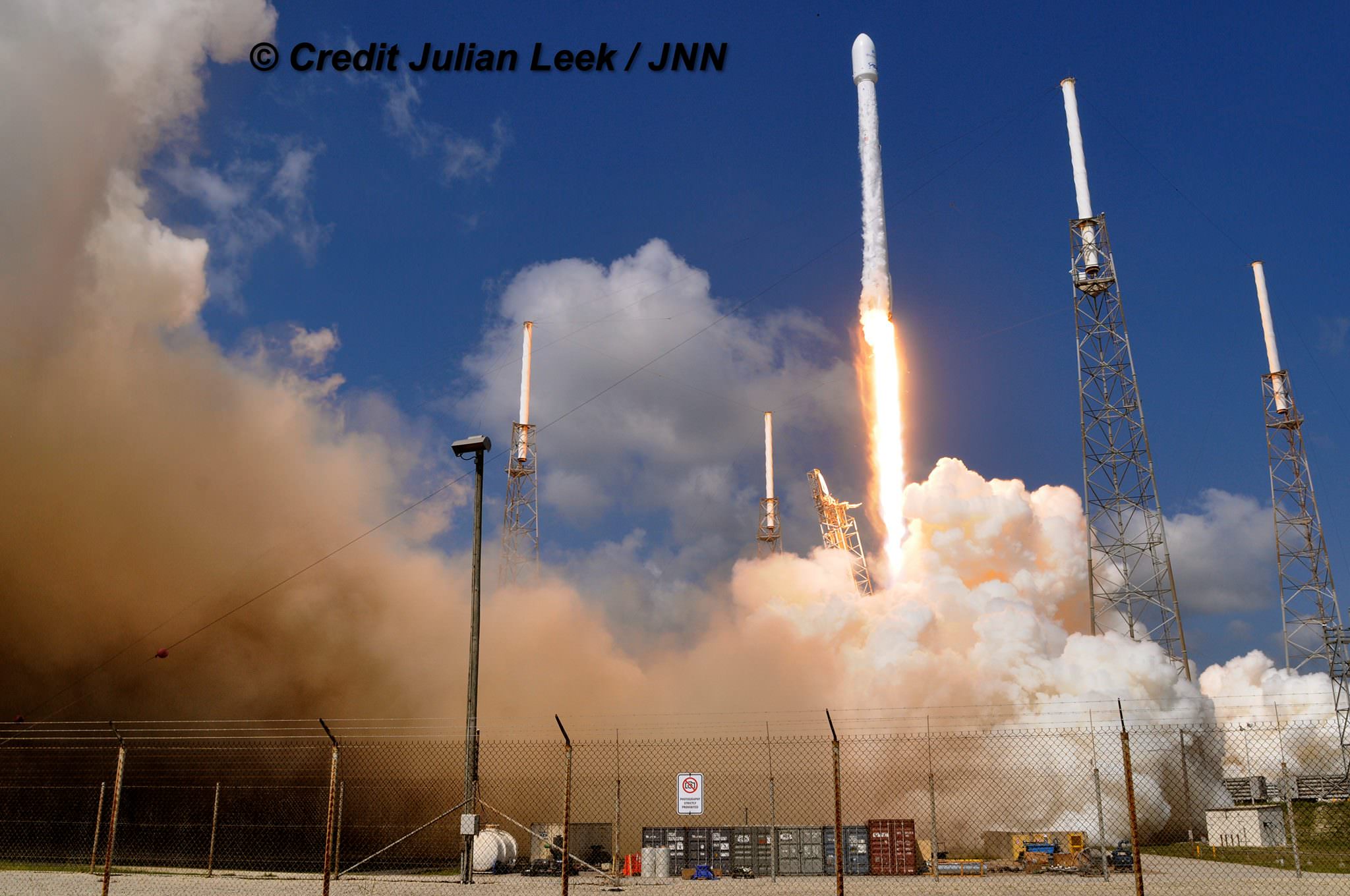
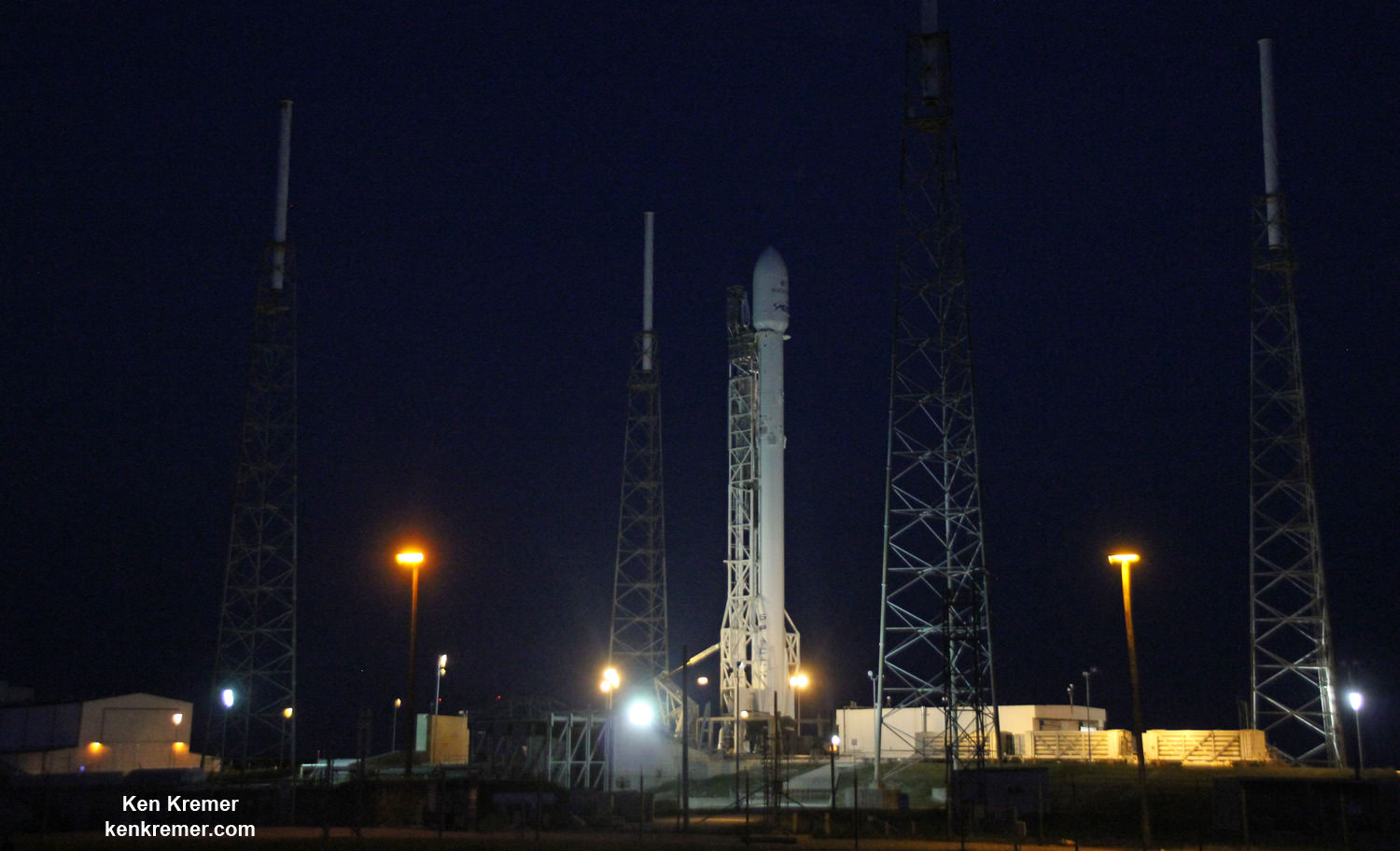
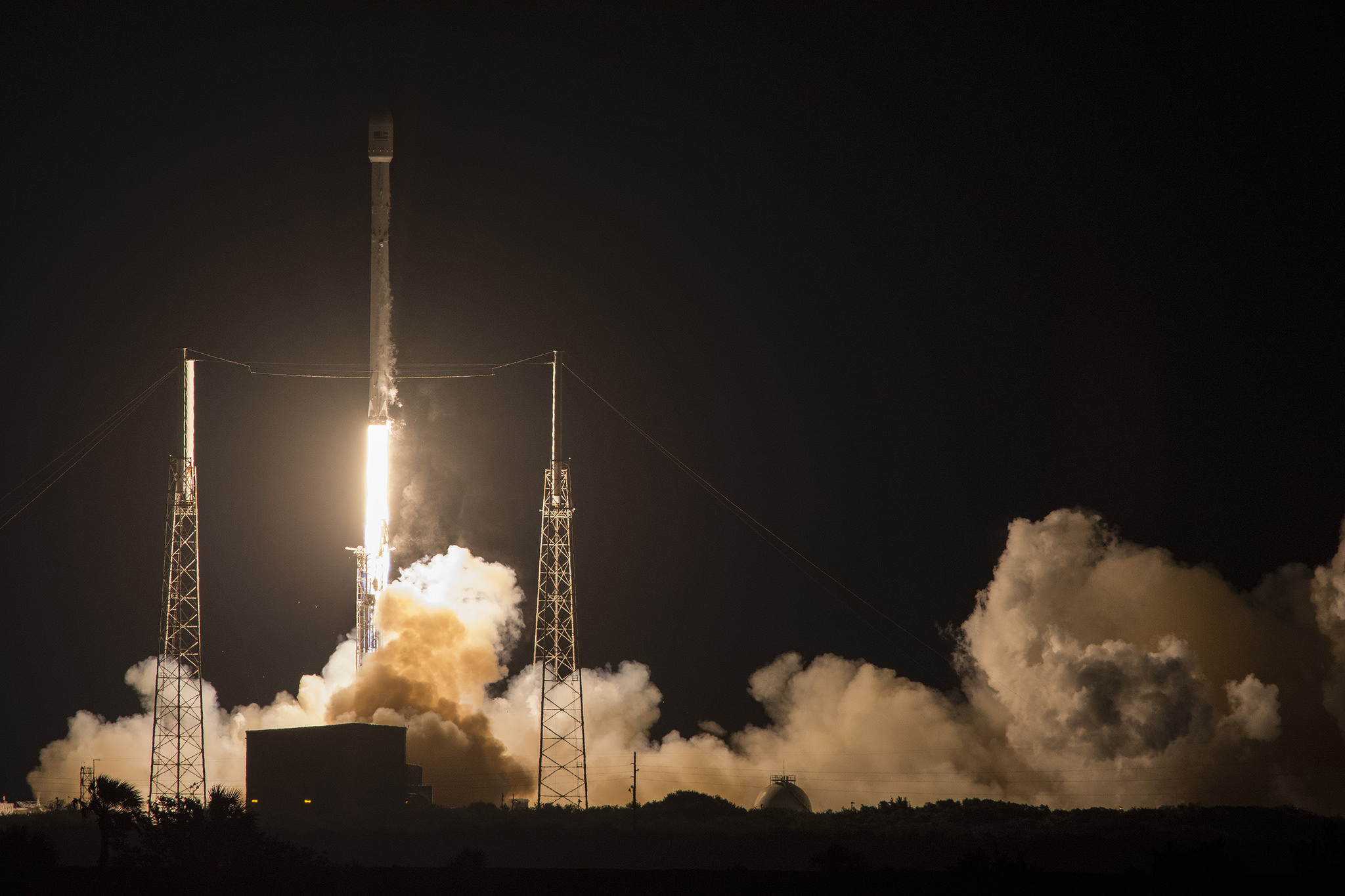
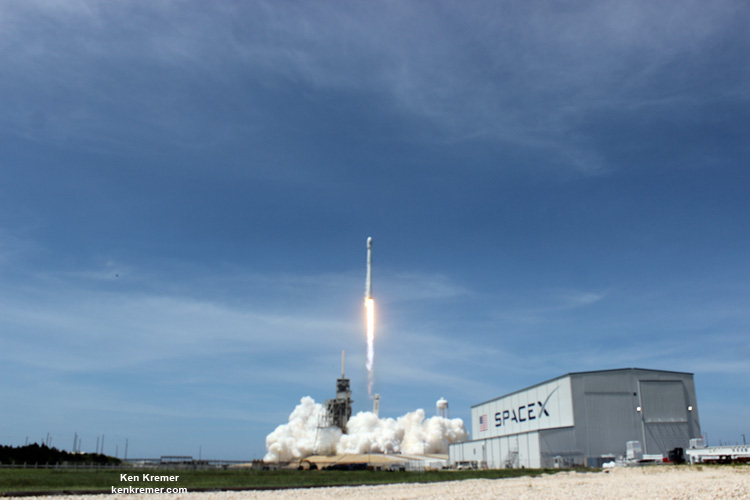
The picture perfect liftoff of the BulgariaSat-1 communications satellite for East European commercial broadband provider BulgariaSat began at 3:10 p.m. EDT, or 19:10 UTC, June 23, with ignition of all nine of the ‘flight-proven’ Falcon 9 first stage engines on SpaceX’s seaside Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

BulgariaSat is an affiliate of Bulsatcom, Bulgaria’s largest digital television provider.
“Everything went down just as we expected,” BulgariaSat CEO Zayakov told me. “Of course there was a lot of excitement. And there are a lot of excited and scared feelings [with launches].”
“At the end of the day it not only worked out just as expected with the launch but the satellite also already reported in telemetry that she is doing fine,” Zayakov elaborated.
BulgariaSat-1 is the first geostationary communications satellite orbited for the nation of Bulgaria.
“We will start using it as soon as we can, in about one and a half months.”
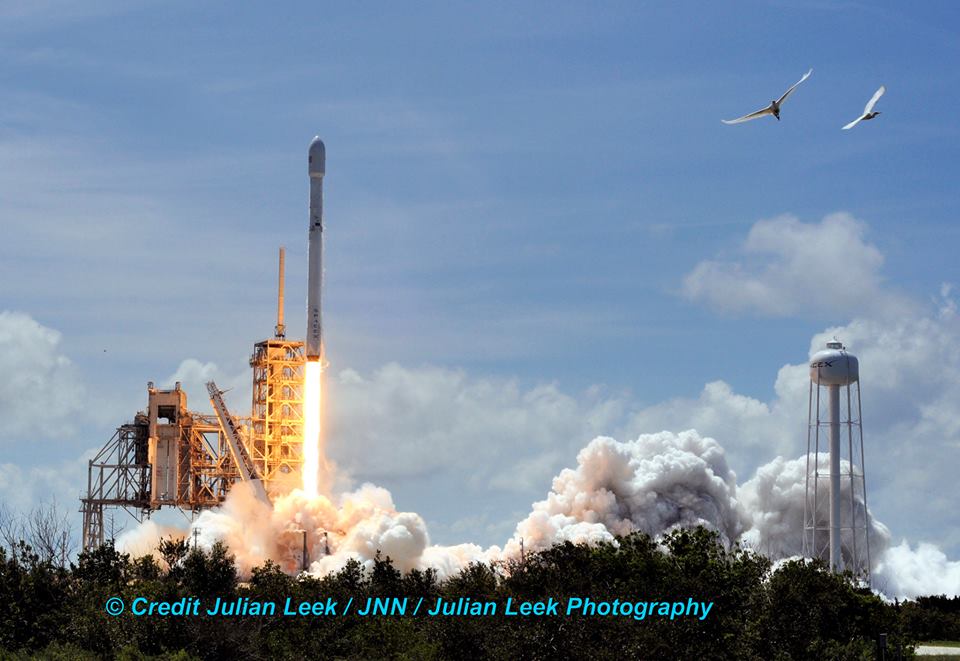

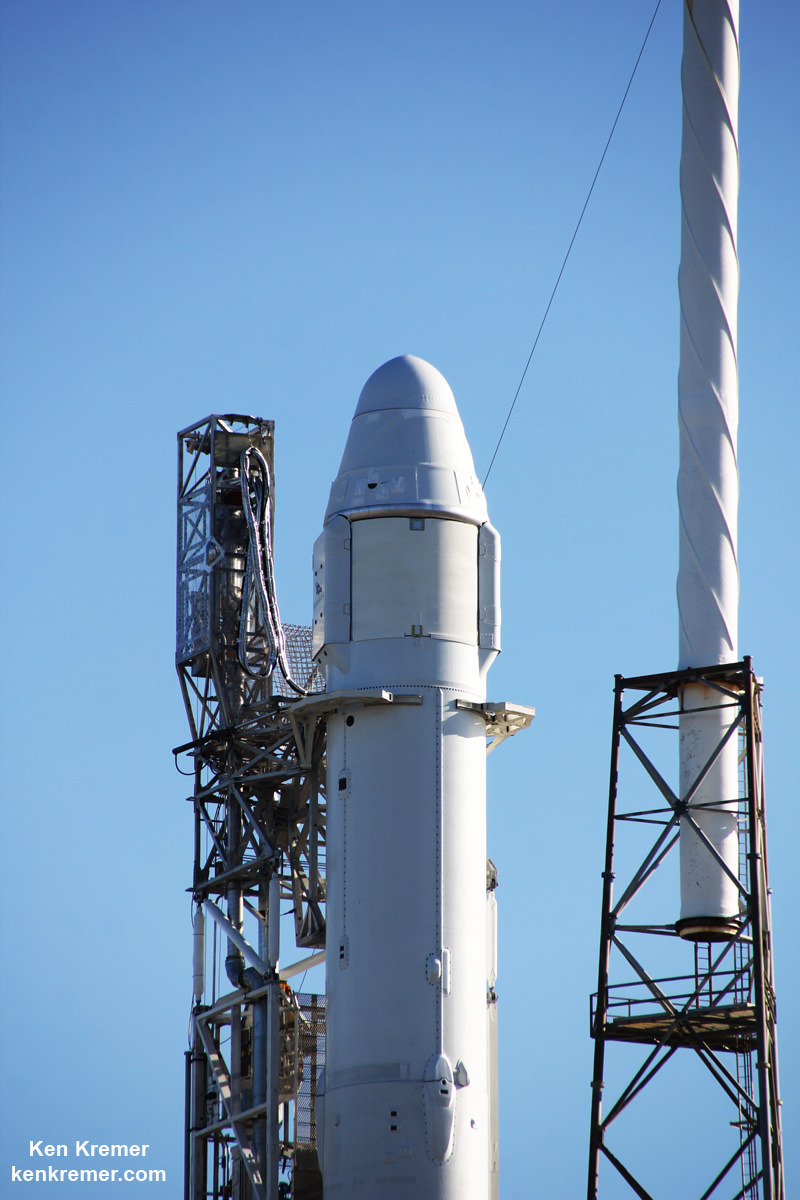
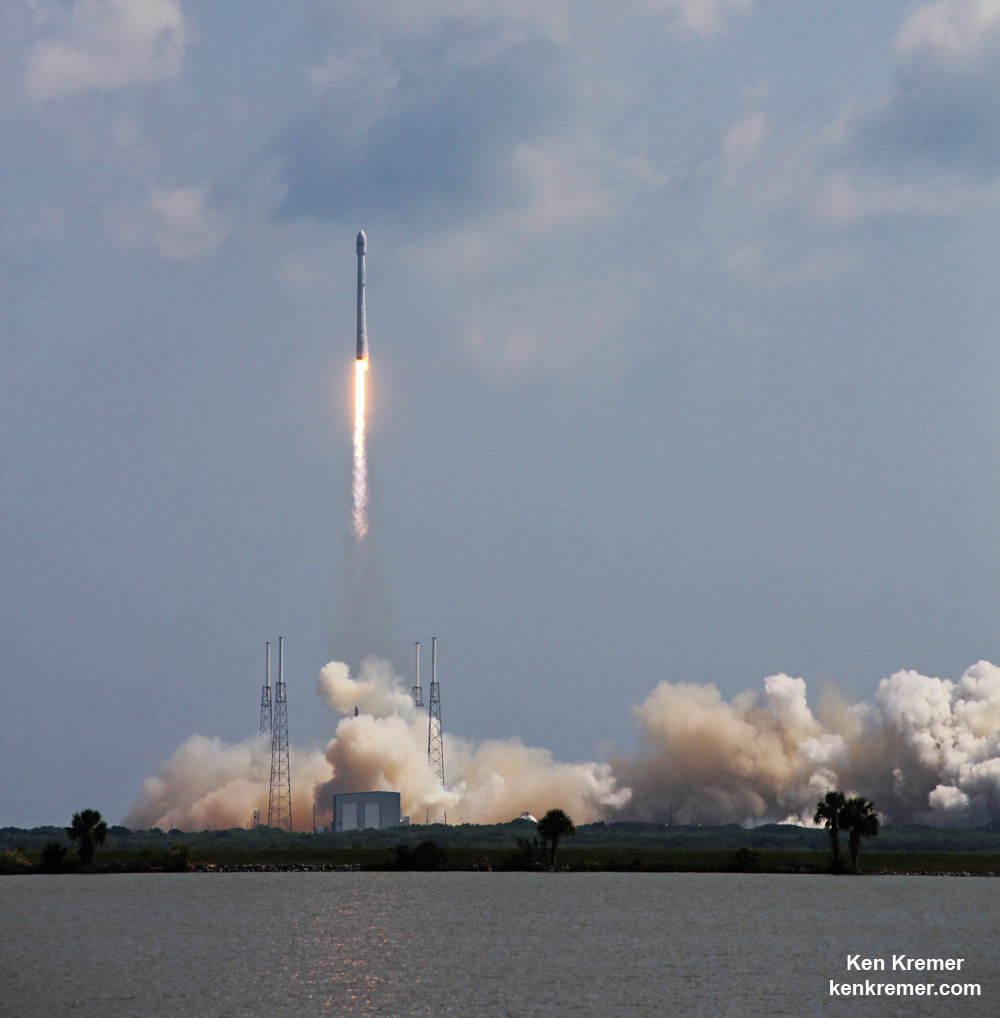
The used 229-foot-tall (70-meter) SpaceX Falcon 9 carrying BulgariaSat-1 soared off historic pad 39A into brilliant mid-afternoon blue skies drenching the Florida Space Coast with beloved sunshine to the delight of hordes of spectators gathered from across the globe – including a Bulgarian TV crew witnessing their first launch.
History’s first ‘flight-proven’ Falcon 9 booster was successfully launched by SpaceX this past March for Luxembourg based telecommunications giant SES on the SES-10 mission – likewise from pad 39A.
Some 35 minutes after blastoff, BulgariaSat-1 was successfully separated as planned from the Falcon 9 second stage and deployed to its targeted initial geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
“So now she is on her way to the orbital position. The solar arrays deployed about 30 minutes after spacecraft separation from the second stage.”

Would you launch with Space X again?
“Yes looking to the future we would be happy to use SpaceX again in the future, certainly why not. SpaceX is definitely up there,” Zayakov replied.
BulgariaSat-1 will be located at the Bulgarian orbital position at 1.9 degrees East longitude and will provide reliable satellite communications solutions to broadcast, telecom, corporate and government customers.
How many customers will be served? I asked Zayakov.
“BulgariaSat-1 will serve about 800,000 customers in Bulgaria and about another million subscribers elsewhere in eastern Europe and the Balkans,” Zayakov elaborated.
The BulgariaSat-1 geostationary comsat will provide direct-to-home television (DTH) and data communications services to Southeastern Europe, including Serbia, the Balkans and other European regions.
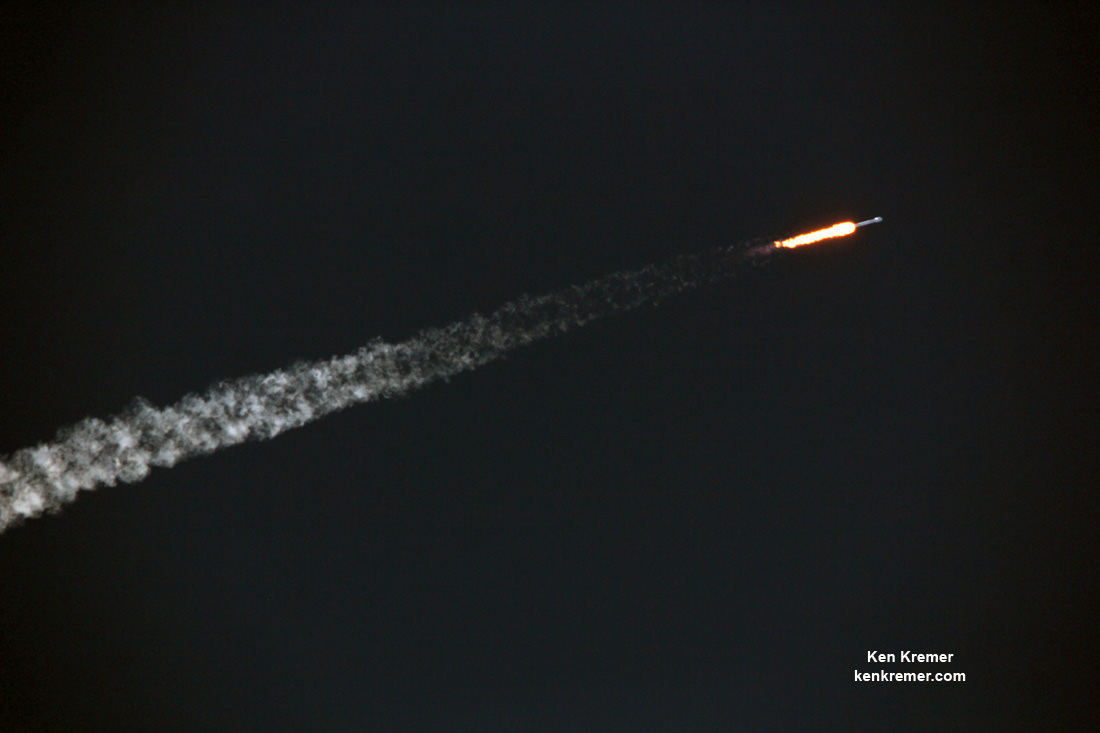
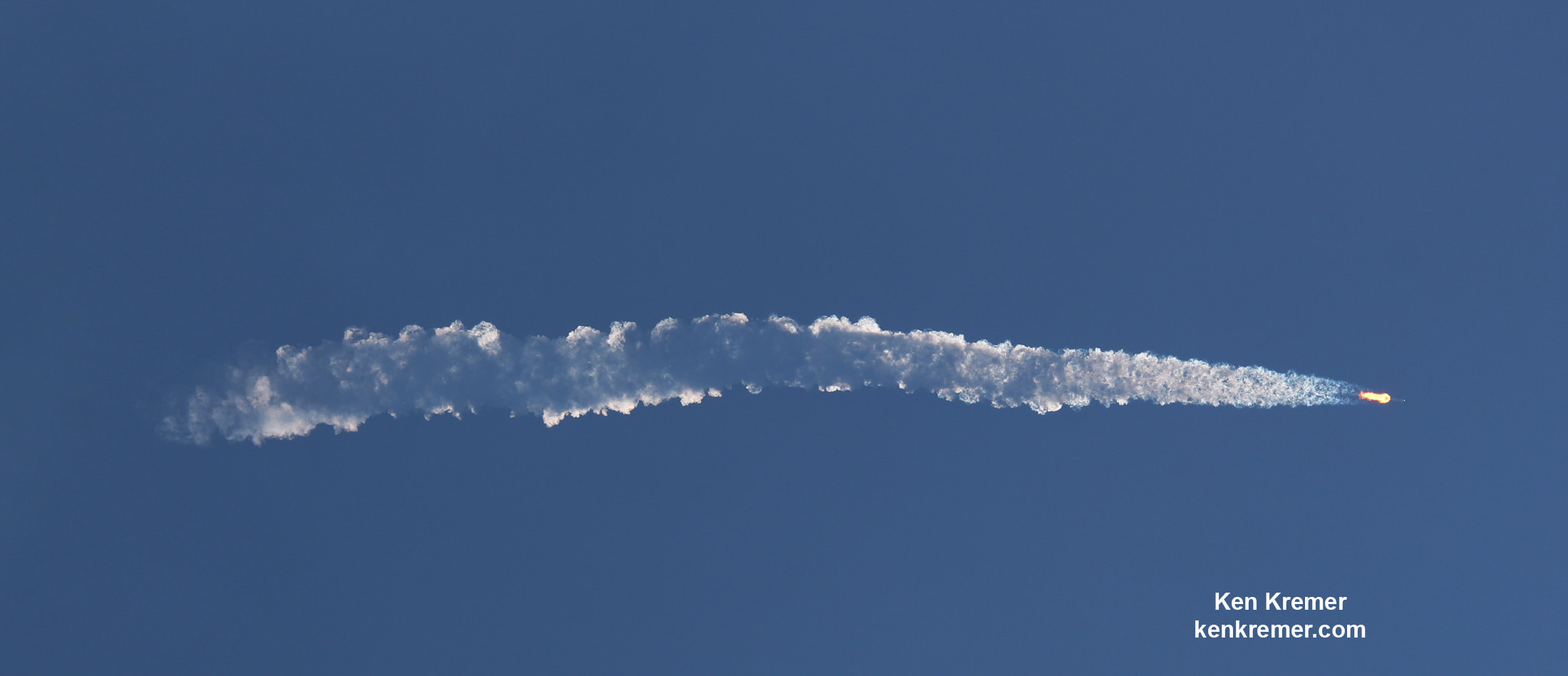
You could not have asked for better weather as the recycled Falcon 9 roared to life for the second time with a paying customer and put on a long and exciting space spectacle for those lucky and fortunate enough to witness history with their own eyeballs first hand and follow along for several minutes as the rocket accelerated magnificently to orbit and arched over to the African continent in the nearly cloudless sky.
Falcon 9’s first stage for the BulgariaSat-1 mission previously supported the Iridium-1 mission from Vandenberg Air Force Base in January of this year.
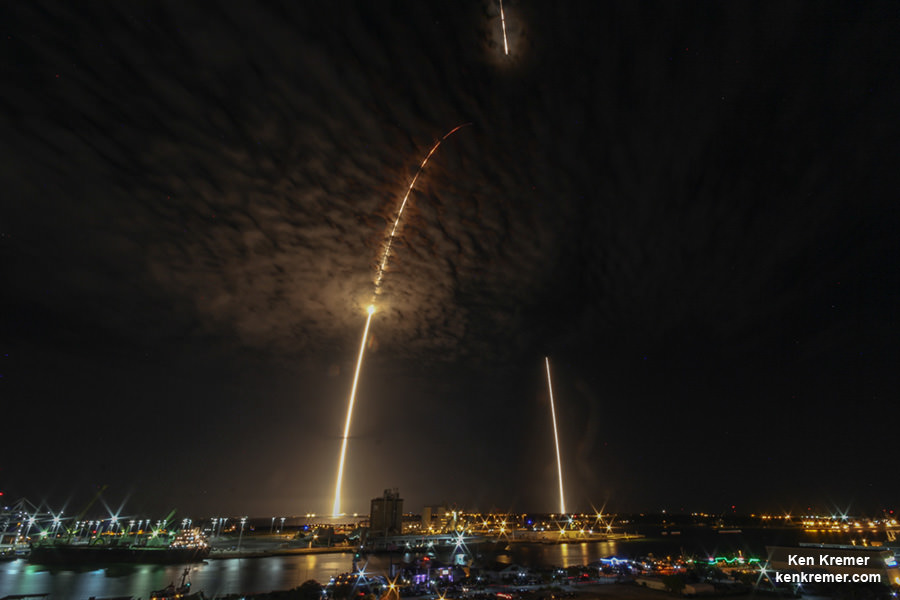
Some two minutes and 40 seconds after liftoff the first and second stages separated.
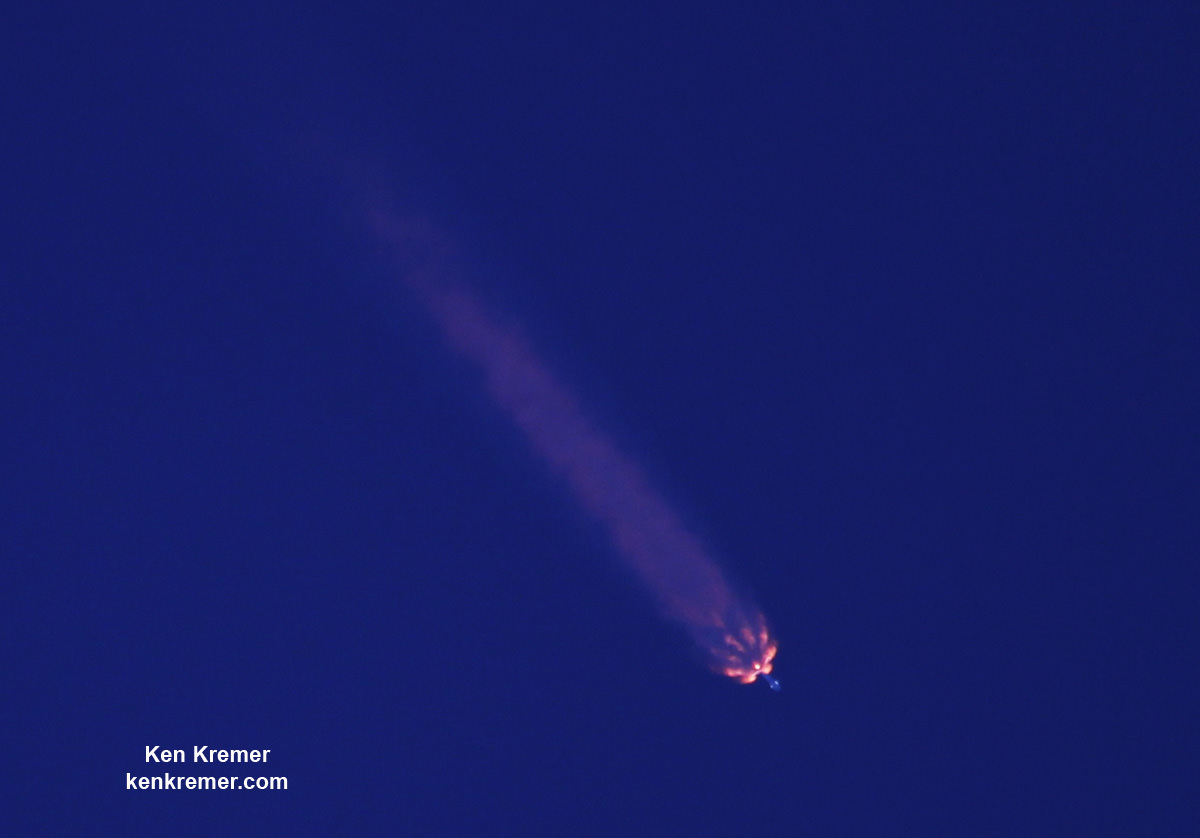
As the second stage continued to orbit, the recycled first stage began the daunting trip back to Earth on a very high energy trajectory that tested the limits of the boosters landing capability.
“Falcon 9 will experience its highest ever reentry force and heat in today’s launch. Good chance rocket booster doesn’t make it back,” SpaceX founder and CEO Elon Musk wrote in a prelaunch tweet.
Following stage separation, Falcon 9’s first stage carried out two burns, the entry burn and the landing burn using a trio of the Merlin 1D engines.
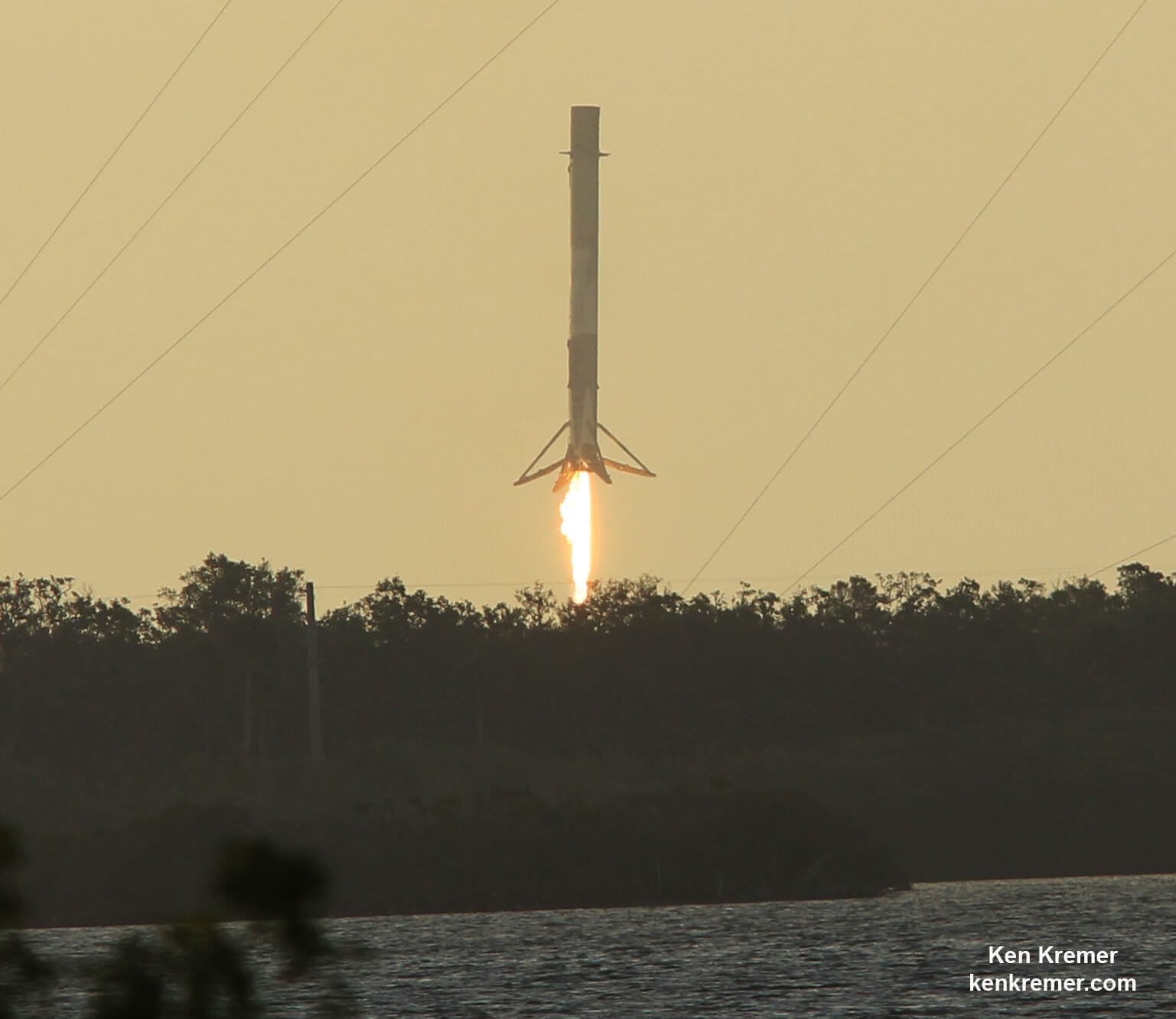
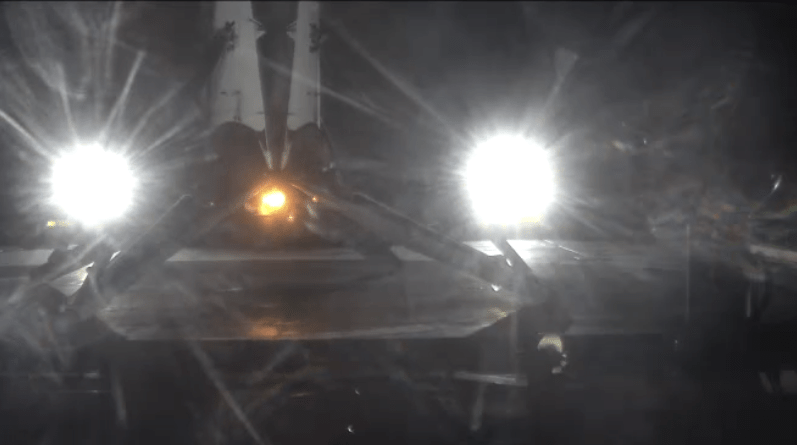
Ultimately the 15 story tall booster successfully landed on the “Of Course I Still Love You” or OCISLY droneship, stationed in the Atlantic Ocean about 400 miles (600 km) offshore and east of Cape Canaveral.
“Rocket is extra toasty and hit the deck hard (used almost all of the emergency crush core), but otherwise good,” Musk tweeted shortly after the recycled booster successfully launched and landed for its second time.
The 156 foot tall first stage may have touched down with a slight tilt.
The OCISLY droneship is expected back into Port Canaveral in a few days.
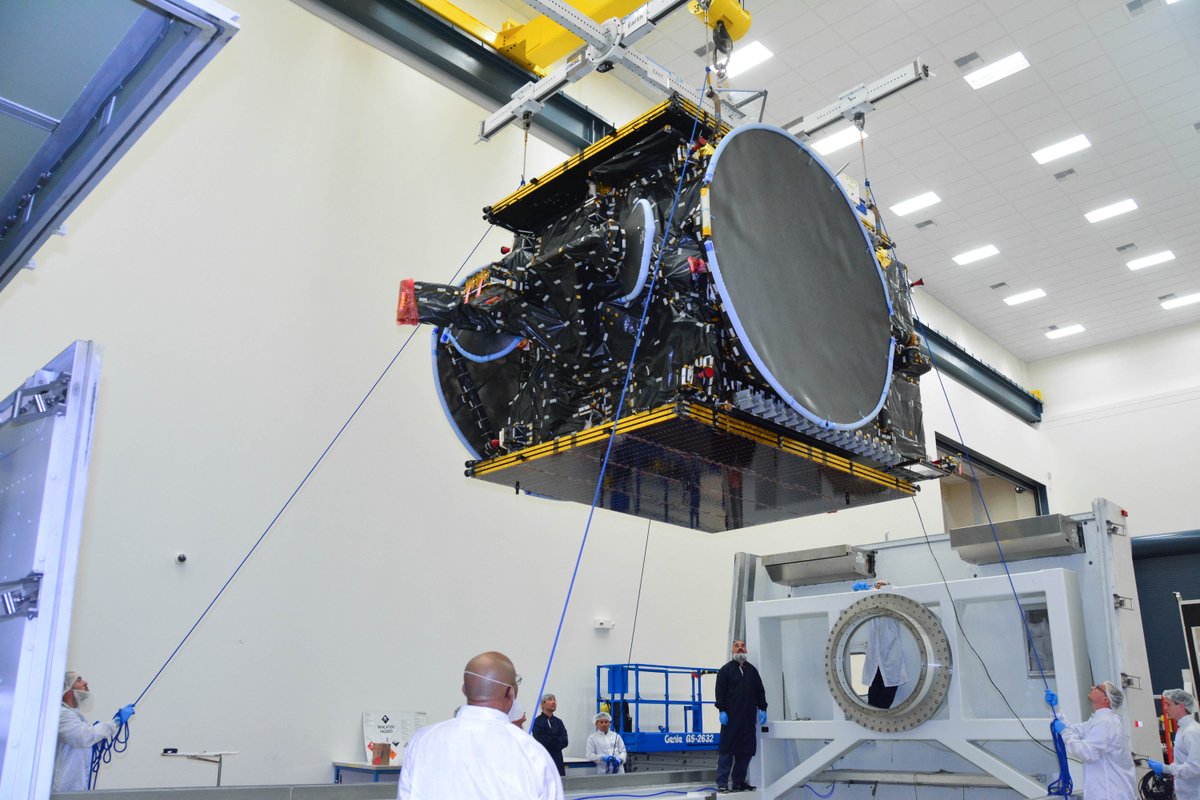
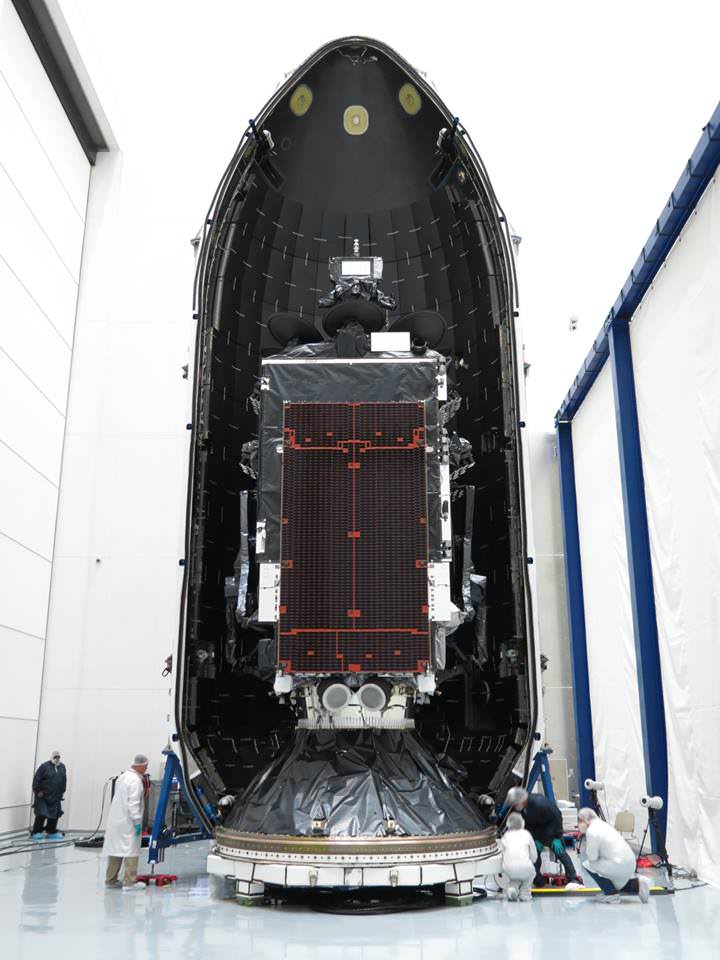
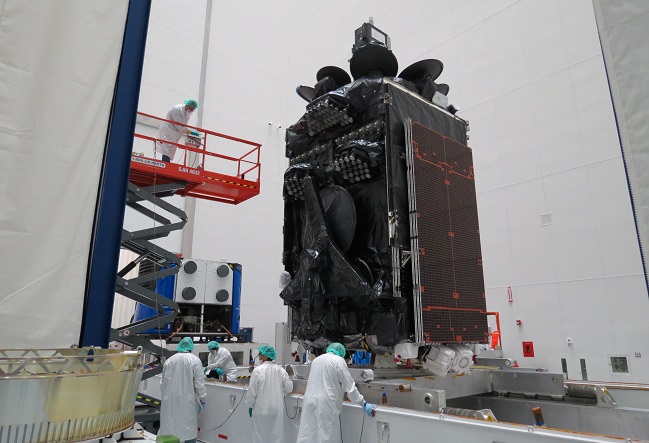
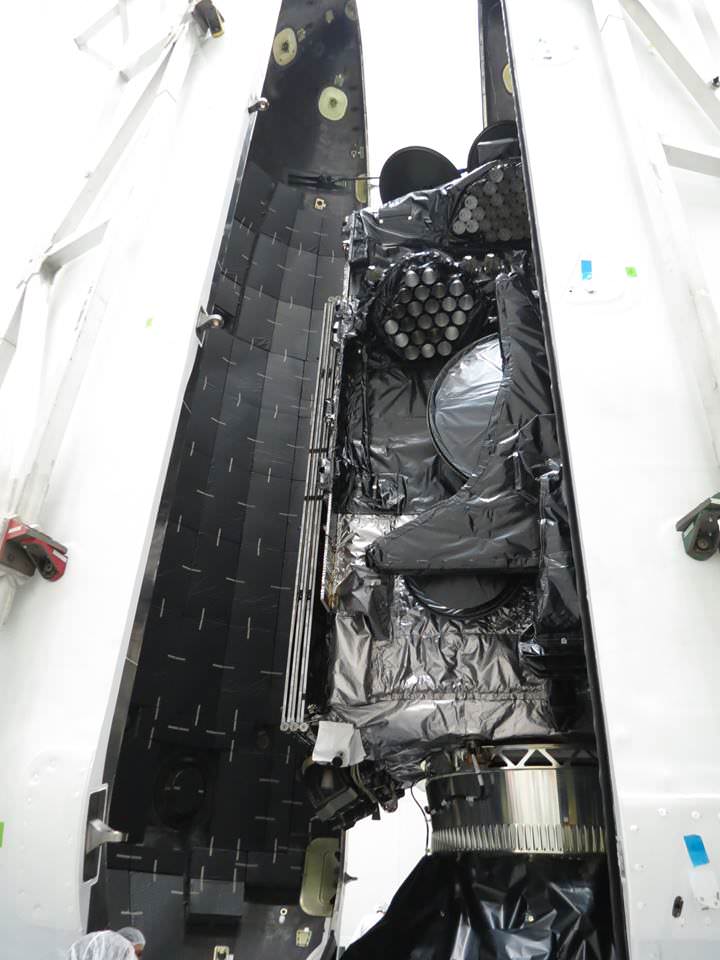
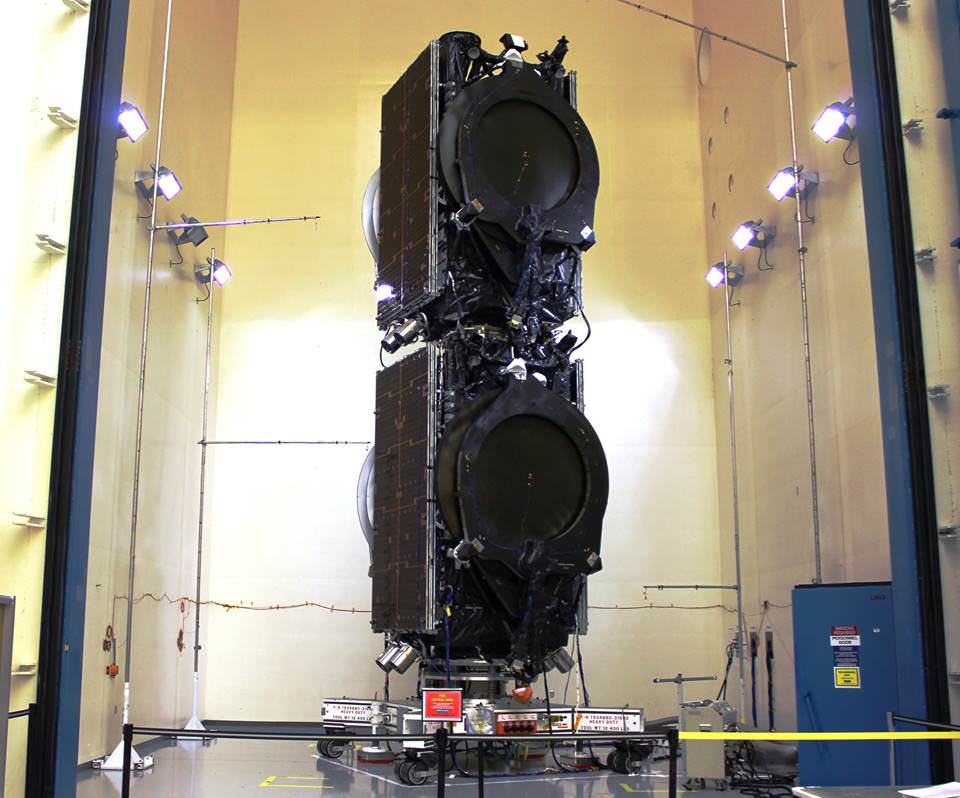
The 8,100 pounds (3,700 kilograms) BulgariaSat-1 satellite was built by SSL in Palo Alto, Calif. It has a design lifetime for a 15-year mission.
BulgariaSat-1 is equipped with 2 Ku-band FSS transponders and 30 Ku-band BSS transponders for fixed satellite services and advanced television services such as high definition television.
With BulgariaSat-1 now safely in orbit, a period of critical testing and checkout is on tap next.
“It takes about ten days to arrive and stabilize at the final orbital slot,” Zayakov stated. “Then after those 10 days it takes about another 20 to 30 days to actually do all the orbital checkouts and orbital tests required to make sure that the satellite is performing fine and that we can start using it for broadcasts.”
“So in about one and a half months we will be ready to start using BulgariaSat-1.”
“We will start using it as soon as we can!”

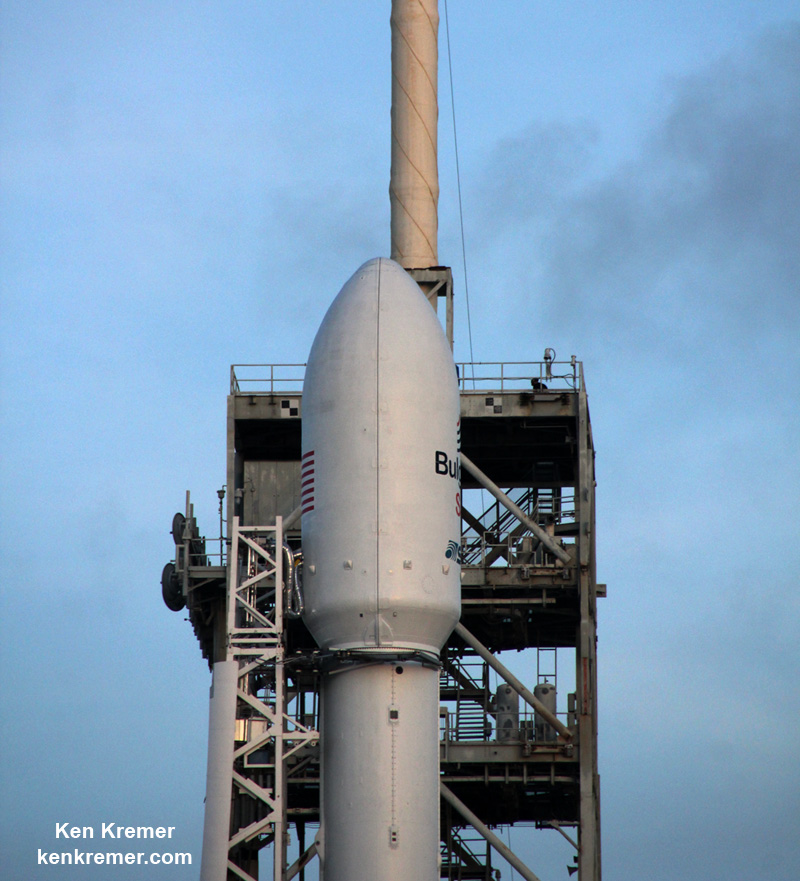
The BulgariaSat-1 launch had originally been slated for this past Monday, June 19 but was delayed four days to fix a valve in the payload fairing.
“Postponing launch to replace fairing pneumatic valve,” Musk tweeted last Sunday. “It is dual redundant, but not worth taking a chance.”
And everything went off without a hitch!
BulgariaSat-1 counts as the eighth SpaceX launch of 2017.

Watch for Ken’s onsite BulgariaSat-1 mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.