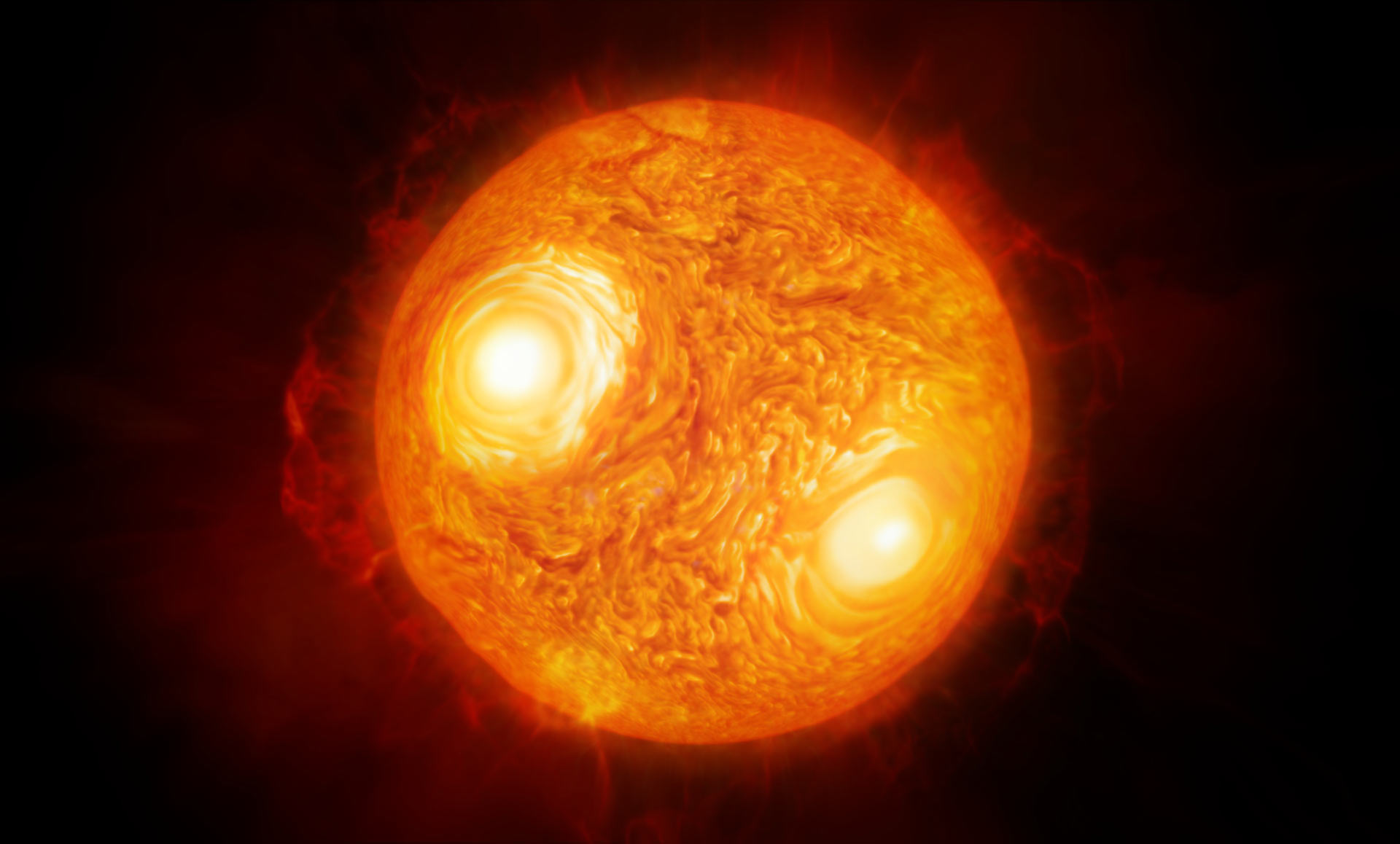
Of all the stars in the sky, betelgeuse must be among the most enigmatic. One of its many mysteries surrounds the speed of its rotation which is surprisingly fast for a supergiant star. If it were placed where the Sun was, then its photosphere (visible layer) would be out around the orbit of Jupiter and it would be moving at 5 km/s. A new study now hints that instead of high rotation, it may be that the surface is boiling so furiously that it has been mistakingly identified as fast rotation.
Continue reading “Betelgeuse’s Surface is Boiling Furiously”A Giant Star is Fading Away. But First, it Had an Enormous Eruption
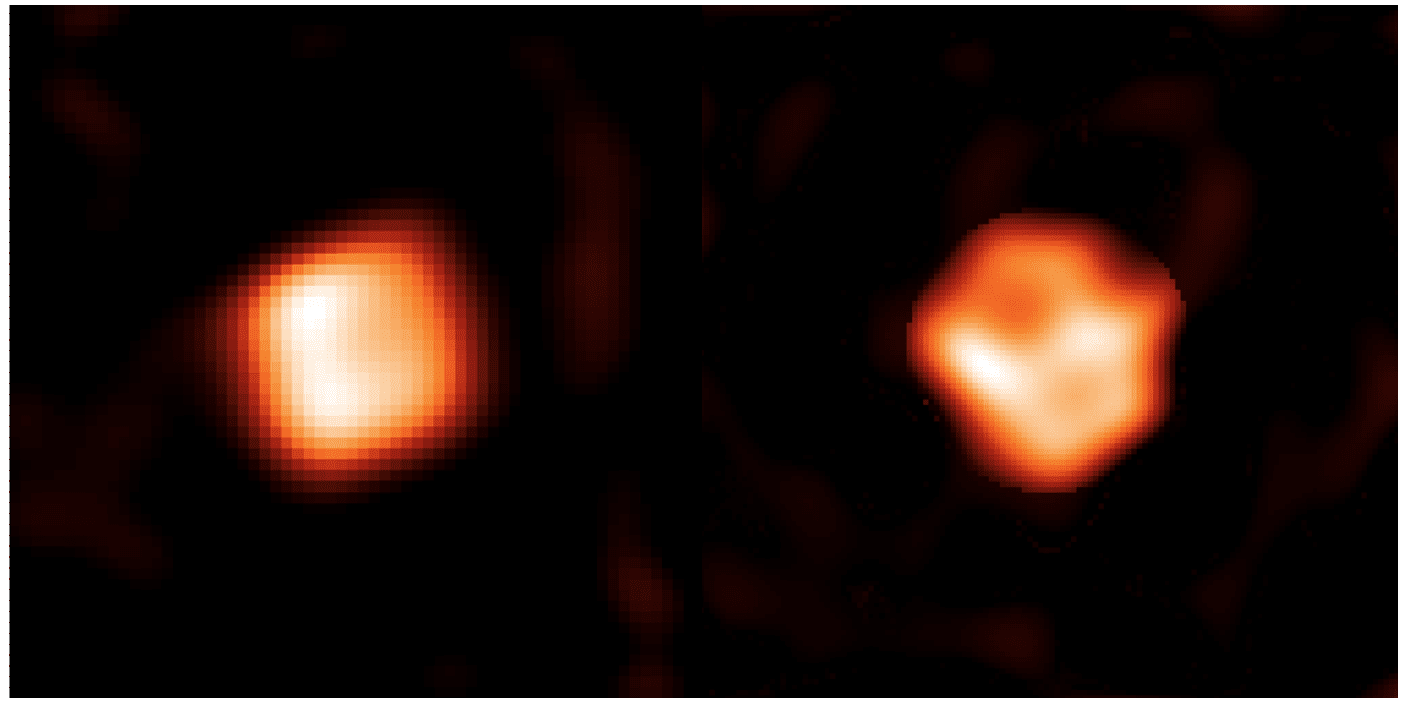
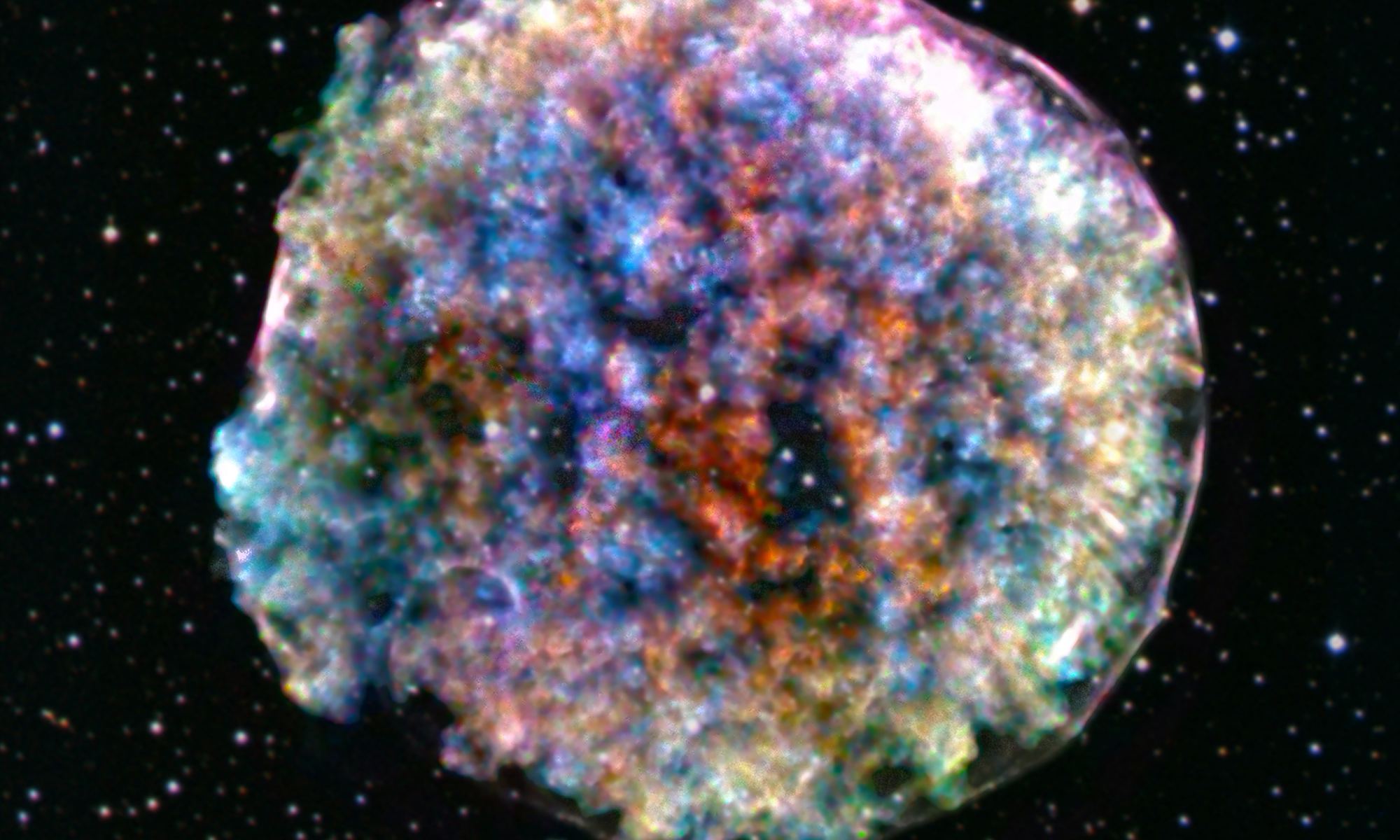
About 16,000 light-years away, a massive star experienced an unusual dimming event. This can happen in binary stars when one star passes in front of the other. It can also be due to intrinsic reasons like innate variability. But this star dimmed by as much as one-third, a huge amount.
What happened?
Continue reading “A Giant Star is Fading Away. But First, it Had an Enormous Eruption”Does Betelgeuse Even Rotate? Maybe Not

Betelgeuse is the well known red giant star in the corner of Orion the hunter. The name translated in some languages means ‘armpit of the giant’ which I think of all the star names, is simply the best! Betelgeuse has been fascinating observers of late not only because it unexpectedly faded a few years ago but more recently a study shows it’s super fast rotational speed which is, when compared to other supergiants, is like nothing seen before.
Continue reading “Does Betelgeuse Even Rotate? Maybe Not”Can Astronomers Predict Which Stars Are About to Explode as Supernovae?
In a recent study submitted to High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena, a team of researchers from Japan discuss strategies to observe, and possibly predict precursor signatures for an explosion from Local Type II and Galactic supernovae (SNe). This study has the potential to help us better understand both how and when supernovae could occur throughout the universe, with supernovae being the plural form of supernova (SN). But just how important is it to detect supernovae before they actually happen?
Continue reading “Can Astronomers Predict Which Stars Are About to Explode as Supernovae?”Betelgeuse and Antares Have Been Observed for Over 2,000 Years. Astronomers can use This to Figure out how old They are
Stars don’t usually evolve fast enough for humans to notice them change within one lifetime. Even a hundred lifetimes won’t do – astronomical processes are just too slow. But not always. There are some phases of stellar evolution that happen quickly, and when they do, they can be tracked. A new paper posted to ArXiv last week uses astronomical observations found in ancient Roman texts, medieval astronomical logs, and manuscripts from China’s Han Dynasty to trace the recent evolution of several bright stars, including red supergiant Antares, and Betelgeuse: one of the most dynamic stars in our sky. With observations from across the historical record, the paper suggests that Betelgeuse may have just recently passed through the ‘Hertzsprung gap,’ the transitional phase between a main sequence star and its current classification as a red supergiant.
Continue reading “Betelgeuse and Antares Have Been Observed for Over 2,000 Years. Astronomers can use This to Figure out how old They are”Astronomers Caught Betelgeuse Just Before it Started Dimming and Might Have Seen a Pressure Wave Rippling Through its Atmosphere

A couple of years ago, Betelgeuse generated much interest when it started dimming. That caught the attention of astronomers worldwide, who tried to understand what was happening. Was it about to go supernova?
Evidence showed that dust was the most likely culprit for the red supergiant’s dimming, though there are still questions. A new study shows that the star was behaving strangely just before the dimming.
Continue reading “Astronomers Caught Betelgeuse Just Before it Started Dimming and Might Have Seen a Pressure Wave Rippling Through its Atmosphere”VY Canis Majoris is “Like Betelgeuse on Steroids”
The disappearance of a star can take many forms. It could go supernova. It could turn into a black hole. Or it could just fade away quietly. Sometimes, the last of these is actually the most interesting to observe. That is the case for one of the largest stars ever found – VY Canis Majoris, a red supergiant approximately 3840 light years away in the Canis Major constellation.
Continue reading “VY Canis Majoris is “Like Betelgeuse on Steroids””Astronomers Hoped to see Evidence of Dark Matter Particles Inside Betelgeuse. No Luck

Axions are a hypothetical particle that might explain the existence of dark matter. But it might occasionally interact with normal matter, especially in the cores of stars. A team of physicists have searched for evidence of axions in Betelgeuse and come up with nothing. It doesn’t mean that the axion doesn’t exist, but it does mean that it will be harder to find.
Continue reading “Astronomers Hoped to see Evidence of Dark Matter Particles Inside Betelgeuse. No Luck”Wow, Betelgeuse Might Be 25% Closer than Previously Believed

In the last year, Betelgeuse has experienced two episodes of dimming. Normally, it’s one of the ten brightest stars in the sky, and astrophysicists and astronomers got busy trying to understand what was happening with the red supergiant. Different research came up with some possible answers: Enormous starspots, a build-up of dust, pre-supernova convulsions.
Now a new study is introducing another wrinkle into our understanding of Betelgeuse. The authors say that Betelgeuse is both smaller and closer than previously thought.
Continue reading “Wow, Betelgeuse Might Be 25% Closer than Previously Believed”What’s Happening with Betelgeuse? Astronomers Propose a Specialized Telescope to Watch the Star Every Night
Starting in late 2019, Betelgeuse began drawing a lot of attention after it mysteriously started dimming, only to brighten again a few months later. For a variable star like Betelgeuse, periodic dimming and brightening are normal, but the extent of its fluctuation led to all sorts of theories as to what might be causing it. Similar to Tabby’s Star in 2015, astronomers offered up the usual suspects (minus the alien megastructure theory!)
Whereas some thought that the dimming was a prelude to the star becoming a Type II supernova, others suggested that dust clouds, enormous sunspots, or ejected clouds of gas were the culprit. In any case, the “Great Dimming of Betelgeuse” has motivated an international team of astronomers to propose that a “Betelgeuse Scope” be created that cant monitor the star constantly.
Continue reading “What’s Happening with Betelgeuse? Astronomers Propose a Specialized Telescope to Watch the Star Every Night”




