Electricity is a form of energy and it occurs in nature, so it was not “invented.” As to who discovered it, many misconceptions abound. Some give credit to Benjamin Franklin for discovering electricity, but his experiments only helped establish the connection between lightning and electricity, nothing more.
The truth about the discovery of electricity is a bit more complex than a man flying his kite. It actually goes back more than two thousand years.
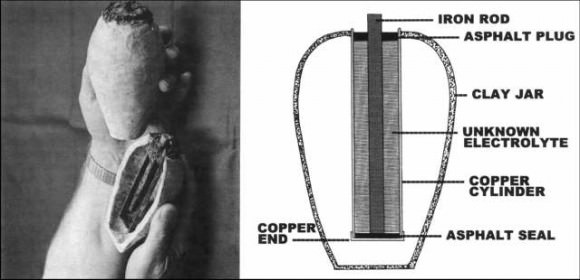
In about 600 BC, the Ancient Greeks discovered that rubbing fur on amber (fossilized tree resin) caused an attraction between the two – and so what the Greeks discovered was actually static electricity. Additionally, researchers and archeologists in the 1930’s discovered pots with sheets of copper inside that they believe may have been ancient batteries meant to produce light at ancient Roman sites. Similar devices were found in archeological digs near Baghdad meaning ancient Persians may have also used an early form of batteries.
But by the 17th century, many electricity-related discoveries had been made, such as the invention of an early electrostatic generator, the differentiation between positive and negative currents, and the classification of materials as conductors or insulators.
In the year 1600, English physician William Gilbert used the Latin word “electricus” to describe the force that certain substances exert when rubbed against each other. A few years later another English scientist, Thomas Browne, wrote several books and he used the word “electricity” to describe his investigations based on Gilbert’s work.

In 1752, Ben Franklin conducted his experiment with a kite, a key, and a storm. This simply proved that lightning and tiny electric sparks were the same thing.
Italian physicist Alessandro Volta discovered that particular chemical reactions could produce electricity, and in 1800 he constructed the voltaic pile (an early electric battery) that produced a steady electric current, and so he was the first person to create a steady flow of electrical charge. Volta also created the first transmission of electricity by linking positively-charged and negatively-charged connectors and driving an electrical charge, or voltage, through them.
In 1831 electricity became viable for use in technology when Michael Faraday created the electric dynamo (a crude power generator), which solved the problem of generating electric current in an ongoing and practical way. Faraday’s rather crude invention used a magnet that was moved inside a coil of copper wire, creating a tiny electric current that flowed through the wire. This opened the door to American Thomas Edison and British scientist Joseph Swan who each invented the incandescent filament light bulb in their respective countries in about 1878. Previously, light bulbs had been invented by others, but the incandescent bulb was the first practical bulb that would light for hours on end.

Swan and Edison later set up a joint company to produce the first practical filament lamp, and Edison used his direct-current system (DC) to provide power to illuminate the first New York electric street lamps in September 1882.
Later in the 1800’s and early 1900’s Serbian American engineer, inventor, and all around electrical wizard Nikola Tesla became an important contributor to the birth of commercial electricity. He worked with Edison and later had many revolutionary developments in electromagnetism, and had competing patents with Marconi for the invention of radio. He is well known for his work with alternating current (AC), AC motors, and the polyphase distribution system.
Later, American inventor and industrialist George Westinghouse purchased and developed Tesla’s patented motor for generating alternating current, and the work of Westinghouse, Tesla and others gradually convinced American society that the future of electricity lay with AC rather than DC.
Others who worked to bring the use of electricity to where it is today include Scottish inventor James Watt, Andre Ampere, a French mathematician, and German mathematician and physicist George Ohm.
And so, it was not just one person who discovered electricity. While the concept of electricity was known for thousands of years, when it came time to develop it commercially and scientifically, there were several great minds working on the problem at the same time.
We have written many articles about electricity for Universe Today. Here’s a separate article about static electricity, and here’s an interesting story about how astronomy was part of how electricity was brought to the World’s Fair in Chicago in 1933.
For more detailed information about the discovery of electricity, see our sources, below.
We’ve also recorded an entire episode of Astronomy Cast all about Electromagnetism. Listen here, Episode 103: Electromagnetism.
Sources:
Wikipedia: Electricity
Electricity Forum
A Short History of Ancient Electricity
Wise Geek
Wikipedia: Alessandro Volta
Wikipedia: Michael Faraday
Wikipedia: Thomas Edison
Wikipedia: Nikola Tesla
Wikipedia: Guglielmo Marconi






