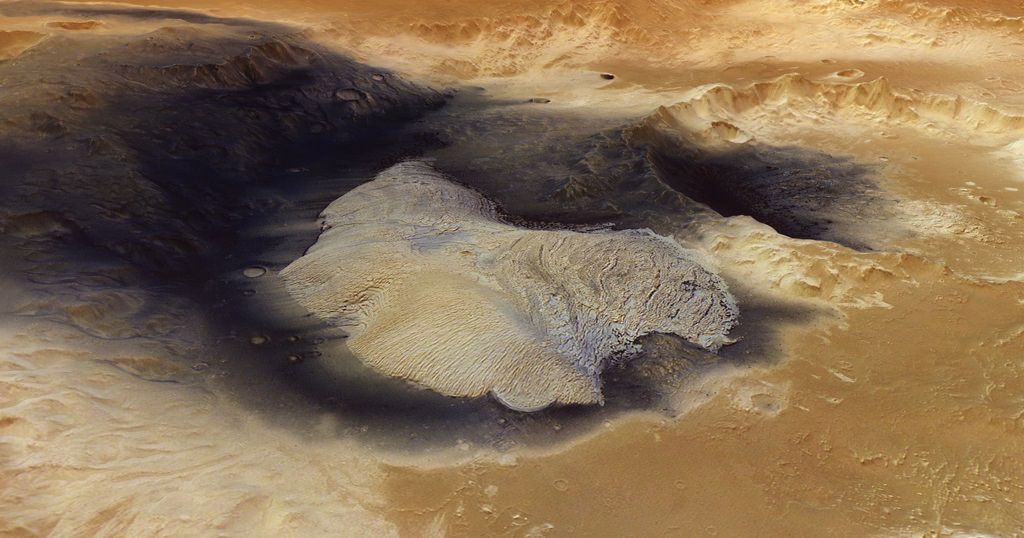
At first glance, it looks like somebody dropped a huge paint can on Mars, spilling black stuff all over Becquerel crater. That dark material, however, is likely blown from another location on the Red Planet. It could even be volcanic eruption remnants, the European Space Agency says.
A set of stunning new images of the spot in the Arabia Terra region — which straddles the so-called “transition zone” between the north and south regions of the planet — reveal a combination of probable effects from wind, water and perhaps even the tilt of the axis of Mars. These pictures came courtesy of ESA’s Mars Express, which is orbiting the planet.
The crater — named after French physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel, a co-discoverer of radioactivity — is 103 miles (167 kilometers) in diameter and sinks 2.2 miles (3.5 km) below the rest of the area. This depression might have held water at some point.
“The mound rises about 1 km [0.62 miles] above the crater floor and comprises hundreds of layers of light-toned sediments, each just a few metres thick, made of sulphate-bearing rocks,” ESA stated. “On Earth, sulphates are most often formed via the evaporation of water, so the presence of these minerals in Becquerel crater suggests that water may once have pooled here in a vast crater lake, before evaporating away.”

The mystery of Mars’ missing water is one that is still puzzling scientists — NASA’s Spirit, Curiosity and Opportunity rovers all found rocks that likely formed in the presence of water, and several spacecraft have spotted features that appear to be similar to riverbeds or perhaps even oceans.
“One popular theory is that large changes in the tilt of the rotational axis of Mars leads to significant changes in its climate, reflected in the thickness and repeating patterns found in the layers of sediment,” ESA added. “A change in the environmental conditions would affect the way in which the sediments were initially deposited, as well as their subsequent resistance to erosion.”
Speaking of sediments, the image above shows the dark material extending far beyond the crater walls, a sign of powerful winds on the Red Planet. Now who’s tempted to go down there with a shovel to see what’s underneath?
As a point of trivia, another spot in Arabia Terra (Vernal Crater) was once considered a possible landing site for Mars Curiosity because scientists found evidence of ancient hot springs on the Red Planet. On Earth, these locations are usually filled with bacterial life.