Black holes are created when stars die catastrophically in a supernova. So what in the universe is a white hole?
It’s imagination day, and we’re going to talk about fantasy creatures. Like unicorns, but even rarer. Like leprechauns, but even more fantastical!
Today, we’re going to talk about white holes. Before we talk about white holes, let’s talk about black holes. And before we talk about Black Holes, what’s is this thing you have with holes exactly?
Black holes are places in the Universe where matter and energy are compacted so densely together that their escape velocity is greater than the speed of light. We’ve done at least a million videos on them, but if you still want more info, you can start here with our Black Hole playlist.
Fully describing a black hole requires a lot of fancy math, but these are real objects in our Universe. They were predicted by Einstein’s theory of relativity, and actually discovered over the last few decades.
Black holes are created when stars, much more massive than our Sun, die catastrophically in a supernova.
So then what’s a white hole?
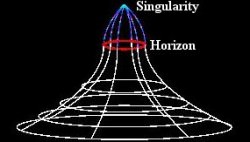
White holes are created when astrophysicists mathematically explore the environment around black holes, but pretend there’s no mass within the event horizon. What happens when you have a black hole singularity with no mass?
White holes are completely theoretical mathematical concepts. In fact, if you do black hole mathematics for a living, I’m told, ignoring the mass of the singularity makes your life so much easier.
They’re not things that actually exist. It’s not like astronomers detected an unusual outburst of radiation and then developed hypothetical white hole models to explain them.
As my good friend and sometimes Guide to Space contributor, Dr. Brian Koberlein says, “If you start with five cupcakes and start giving them away, you eventually run out. At that point you can’t give away any more. In this case you can’t count down past zero. Sure, you can hand out slips of paper with “I O U ONE cupcake.” written on them, but it would be ridiculous to use the existence of negative numbers to claim that “negative cupcakes” exist and can be handed out to people.”
Now if white holes did exist, which they probably don’t, they would behave like reverse black holes – just like the math predicts. Instead of pulling material inward, a white hole would blast material out into space like some kind of white chocolate fountain. So generous, these white holes and their chocolate.
One of the other implications of white hole math, is that they only theoretically exist as long as there isn’t a single speck of matter within the event horizon. As soon as single atom of hydrogen drifted into the region, the whole thing would collapse. Even if white holes were created back at the beginning of the Universe, they would have collapsed long ago, since our Universe is already filled with stray matter.
That said, there are a few physicists out there who think white holes might be more than theoretical. Hal Haggard and Carlo Rovelli of Aix-Marseille University in France are working to explain what happens within black holes using a branch of theoretical physics called loop quantum gravity.

In theory, a black hole singularity would compress down until the smallest possible size predicted by physics. Then it would rebound as a white hole. But because of the severe time dilation effect around a black hole, this event would take billions of years for even the lowest mass ones to finally get around to popping.
If there were microscopic black holes created after the Big Bang, they might get around to decaying and exploding as white holes any day now. Except, according to Stephen Hawking, they would have already evaporated.
Another interesting idea put forth by physicists, is that a white hole might explain the Big Bang, since this is another situation where a tremendous amount of matter and energy spontaneously appeared.
In all likelihood, white holes are just fancy math. And since fancy math rarely survives contact with reality, white holes are probably just imaginary.
What other highly theoretical theories in space and physics would you like us to investigate? Tell us in the comments below.