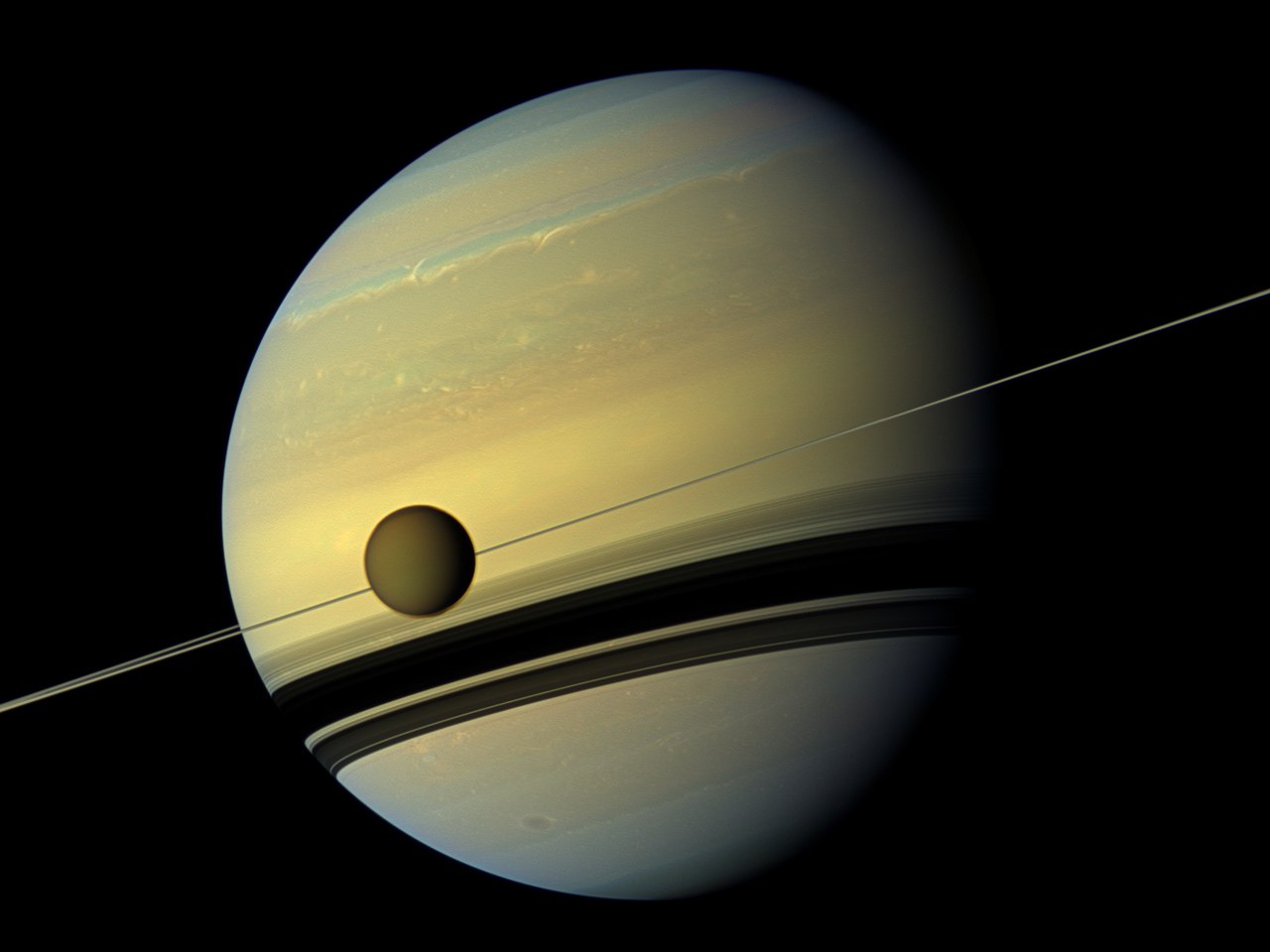
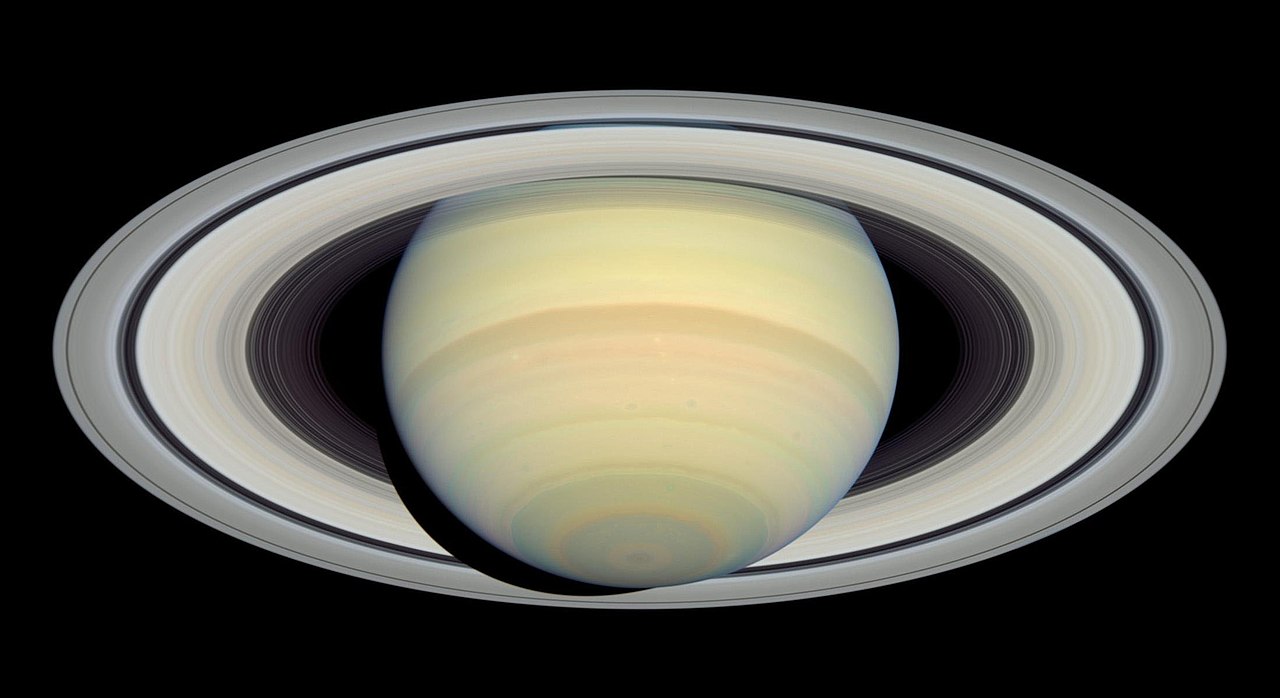
Six years ago the Cassini spacecraft, which had spent nearly two decades in orbit around Saturn, finished its mission with a grand finale, plunging itself into the depths of Saturn’s atmosphere. Those last few orbits and the final plunge revealed a wealth of information about Saturn’s interior. A team of astronomers have collected all of the available data and are now painting a portrait of the interior of the solar system’s second largest planet.
Continue reading “What Cassini’s “Grand Finale” Taught Us About Saturn’s Interior”62 New Moons Found for Saturn
Jupiter is the King, Earth is teeming with life, Venus is a weird, spacecraft-crushing hellhole, and now Saturn has the most moons. Again.
Jupiter sat atop the podium as the planet with the most moons for a while. But with the discovery of 62 more moons, Saturn has surpassed Jupiter as the planet with the most natural satellites and reclaimed the top spot.
Continue reading “62 New Moons Found for Saturn”Saturn’s Rings Warm Up its Atmosphere

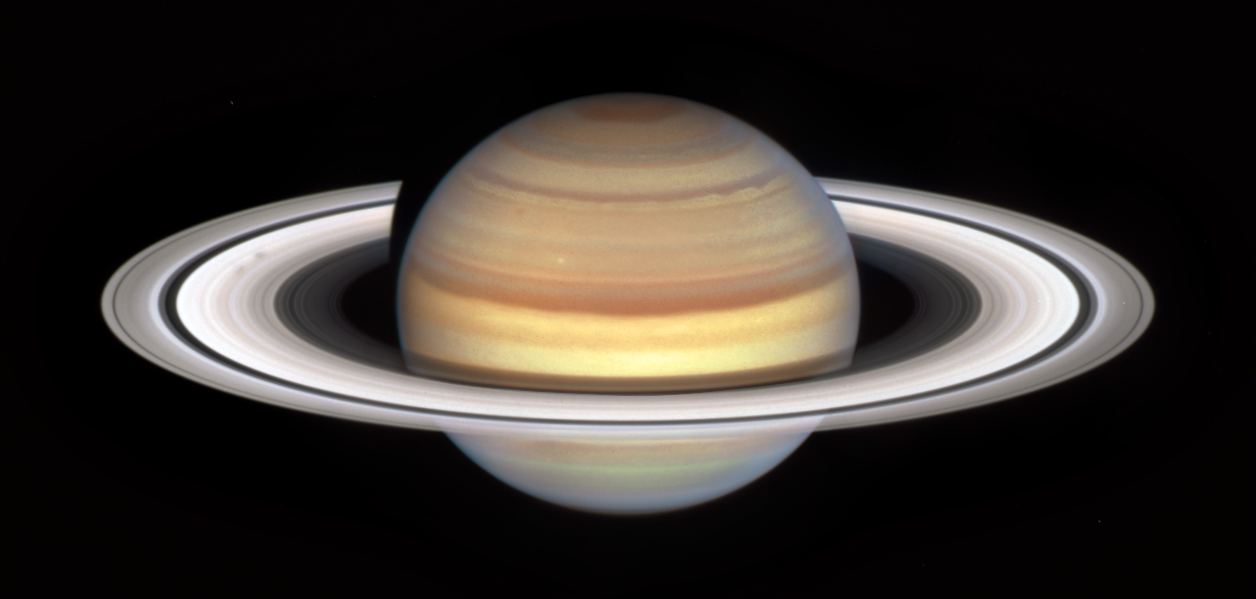
Saturn’s rings are one of the most well-known features throughout astronomy. While much is known about them, they still make headlines from time to time. This includes a recent study involving an international team of researchers that could help paint a clearer picture of the interaction between the gas giant and the massive ring system that encircles it.
Continue reading “Saturn’s Rings Warm Up its Atmosphere”If Titan Has the Chemistry For Life, Dragonfly Could Find it
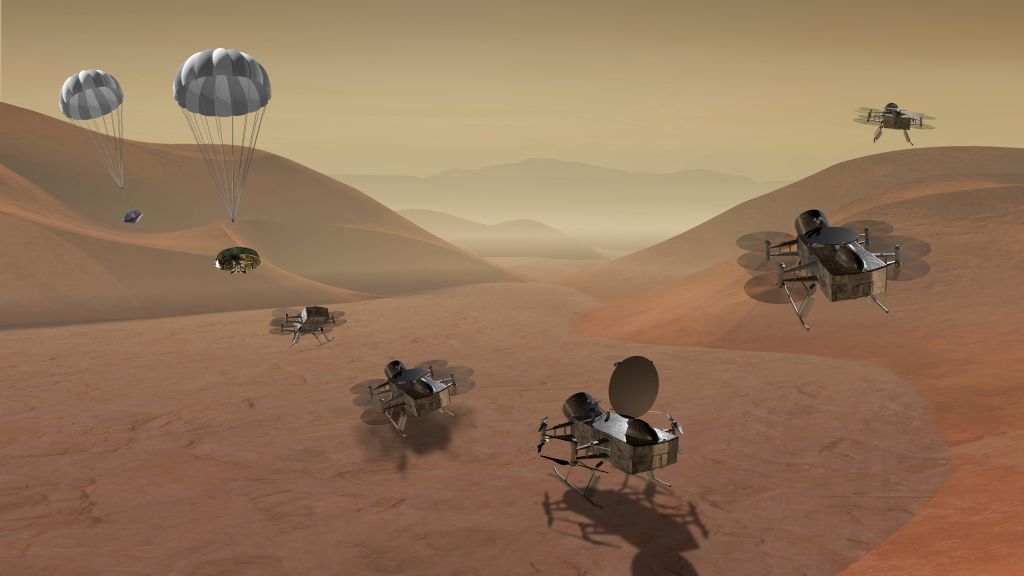

The highly-anticipated Dragonfly robotic rotocraft mission to Saturn’s moon Titan is scheduled to launch in 2027. When it arrives in the mid-2030s, it will hover and zoom around in the thick atmosphere of Titan, sampling the air and imaging the landscape. What could be more exciting than that!?
Well, actually … there’s more: Dragonfly will also be equipped with a mass spectrometer that will help it search for the chemistry of life in this alien world. Astrobiologists want to know if Titan has the same type of chemistry on its surface that Earth did in its early history, which could have helped give rise to life on our planet.
Continue reading “If Titan Has the Chemistry For Life, Dragonfly Could Find it”Saturn Might Have Torn a Moon Apart to Make its Rings

Saturn is a world of surprises. The Voyager 1 and 2 flybys and later on, the Cassini mission, opened our collective eyes to intricate details in its rings and atmosphere. They also gave us up-close and personal looks at those amazing moons. But, one thing they didn’t show us was Saturn’s proposed moon Chrysalis. That’s because it doesn’t exist. Well, actually, it is there, but in the form of those dazzling rings.
Continue reading “Saturn Might Have Torn a Moon Apart to Make its Rings”Jupiter's Giant Moons Prevent it From Having Rings Like Saturn
When the name Saturn is uttered, what comes to mind? For most people, the answer would probably be, “its fabulous system of rings.” There’s no doubt they are iconic, but what is perhaps lesser-known is that Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune all have ring systems of their own. However, whereas Saturn’s rings are composed mainly of ice particles (making them highly reflective), Jupiter’s rings are composed mainly of dust grains. Meanwhile, Uranus and Neptune have rings of extremely dark particles known as tholins that are very hard to see. For this reason, none of the other gas giants get much recognition for their rings.
However, the question of why Jupiter doesn’t have larger, more spectacular rings than Saturn has been bothering astronomers for quite some time. As the larger and more massive of the two bodies, Jupiter should have rings that would dwarf Saturn’s by comparison. This mystery may have finally been resolved thanks to new research by a team from UC Riverside. According to their study, Jupiter’s massive moons (aka. Jupiter’s Galilean Moons) prevented it from developing a big, bright, beautiful ring system that would put Saturn’s to shame.
Continue reading “Jupiter's Giant Moons Prevent it From Having Rings Like Saturn”A Spacecraft Orbiting the Moon Just Captured an Image of Saturn
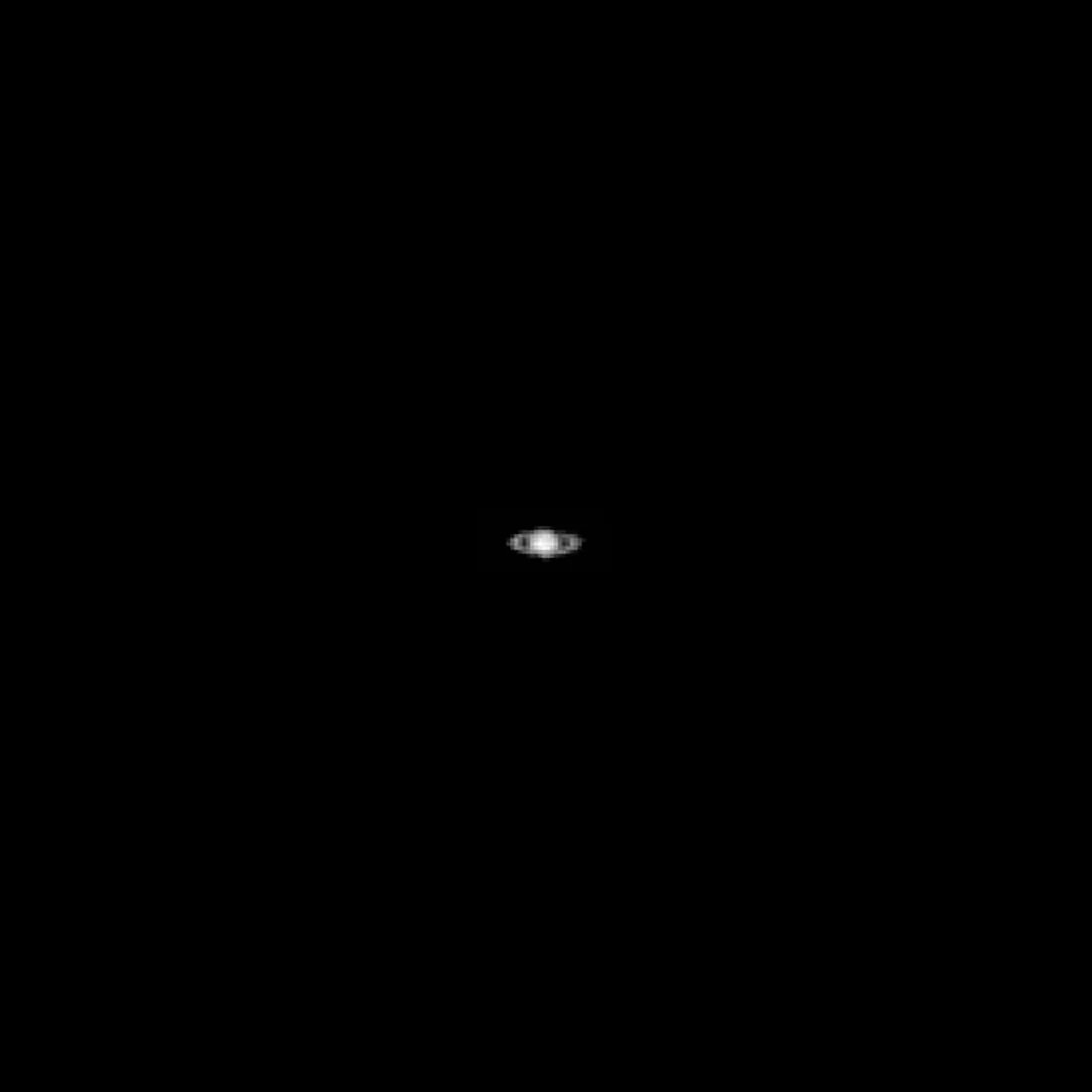
Cameras can be finicky – especially ones primarily used for astronomy. When used for a purpose other than their intended one, sometimes they result in horribly muddled or blurry images. However, sometimes an image works out just right and provides a whole new perspective on a familiar scene. That’s what happened recently when the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) turned one of its cameras toward one of astronomy’s favorite places – Saturn.
Continue reading “A Spacecraft Orbiting the Moon Just Captured an Image of Saturn”The Biggest Comet Ever Seen Will get as Close as Saturn in 2031

A mega-comet – potentially the largest ever discovered – is heading from the Oort Cloud towards our direction. Estimated to be 100–200 kilometers across, the unusual celestial wanderer will make its closest approach to the Sun in 2031. However, the closest it will come to Earth is to the orbit of Saturn.
Continue reading “The Biggest Comet Ever Seen Will get as Close as Saturn in 2031”Using Saturn’s Rings to Figure out What’s Inside the Planet
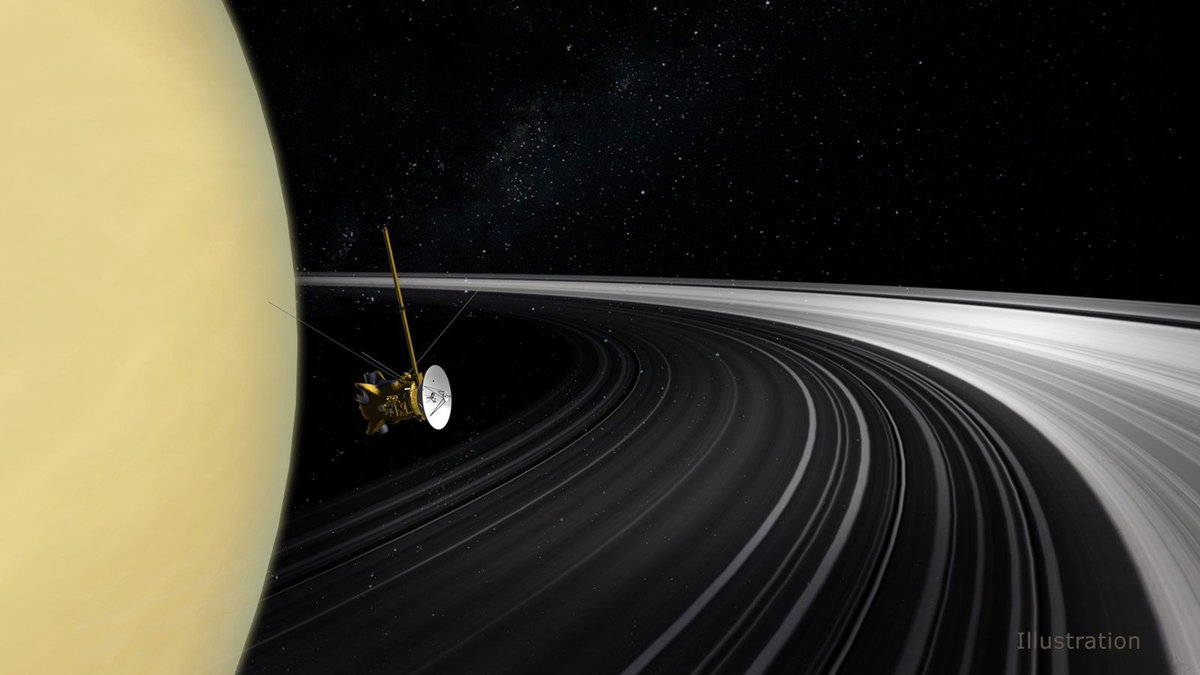

It’s tough to see inside of Saturn, because the atmosphere is opaque to all wavelengths of radiation. We have to rely on computer simulations and physics-based guesswork to try to understand the interior of that giant world. But researchers are becoming more adept at a different technique: looking for the slightest motions in the rings of Saturn.
Continue reading “Using Saturn’s Rings to Figure out What’s Inside the Planet”Cassini Saw Methane in Enceladus’ Plumes. Scientists Don’t Know How it Could be There Without Life
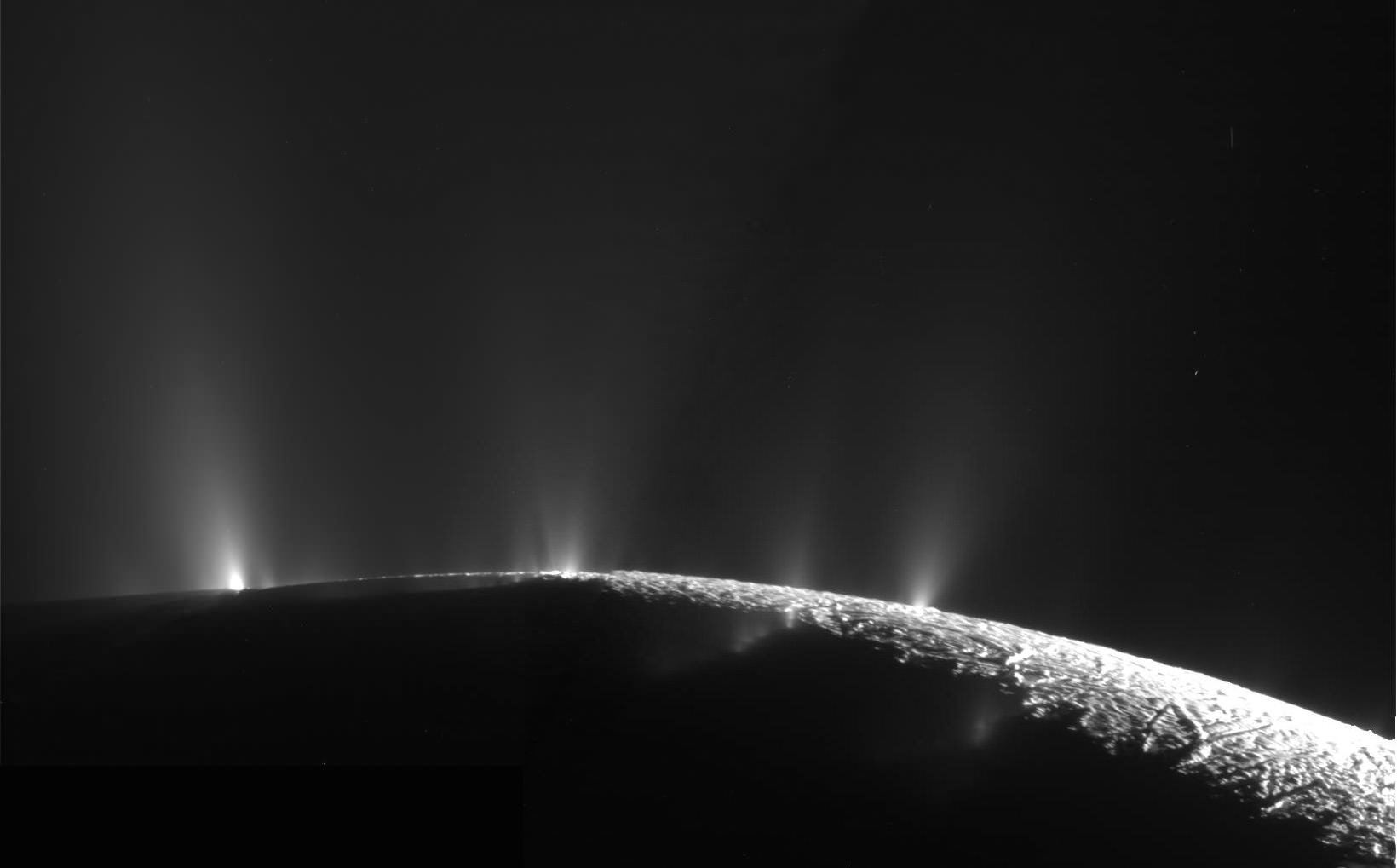
Even though the Cassini mission at Saturn ended nearly four years ago, data from the spacecraft still keeps scientists busy. And the latest research using Cassini’s wealth of data might be the most enticing yet.
Researchers say they’ve detected methane in the plumes of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus. The process for how the methane is produced is not known at this time, but the study suggests that the surprisingly large amount of methane found are likely coming from activity at hydrothermal vents present on Enceladus’s interior seafloor. These vents could be very similar those found in Earth’s oceans, where microorganisms live, feed on the energy from the vents and produce methane in a process called methanogenesis.
Continue reading “Cassini Saw Methane in Enceladus’ Plumes. Scientists Don’t Know How it Could be There Without Life”