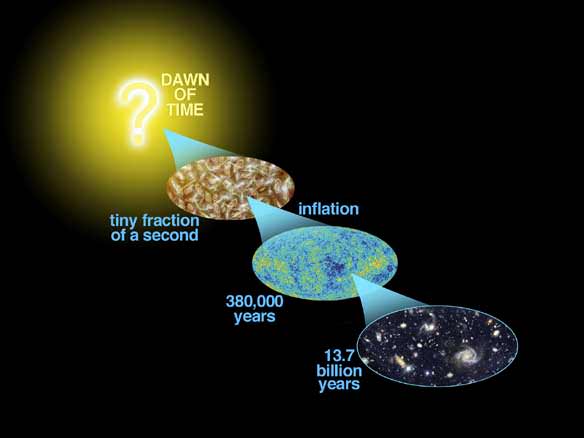
Astronomers routinely explore the universe using different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum from the familiar visible light to radio waves and infra-red to gamma rays. There is a problem with studying the Universe through the electromagnetic spectrum, we can only see light from a time when the Universe was only 380,000 years old. An alternate approach is to use gravitational waves which are thought to have been present in the early Universe and may allow us to probe back even further.
Continue reading “Gravitational Waves Could Show us the First Minute of the Universe”The Echoes From Inflation Could Still Be Shaking the Cosmos Today
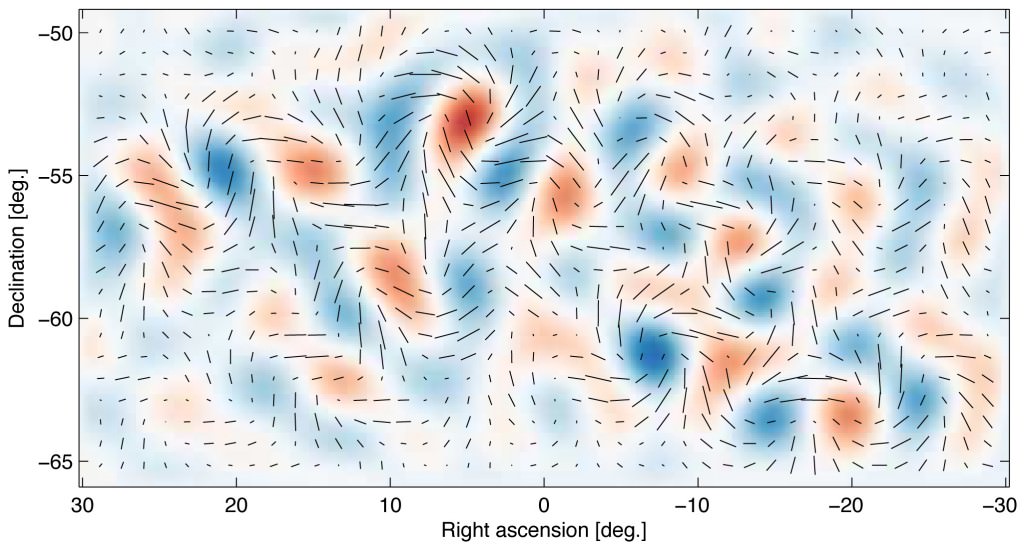
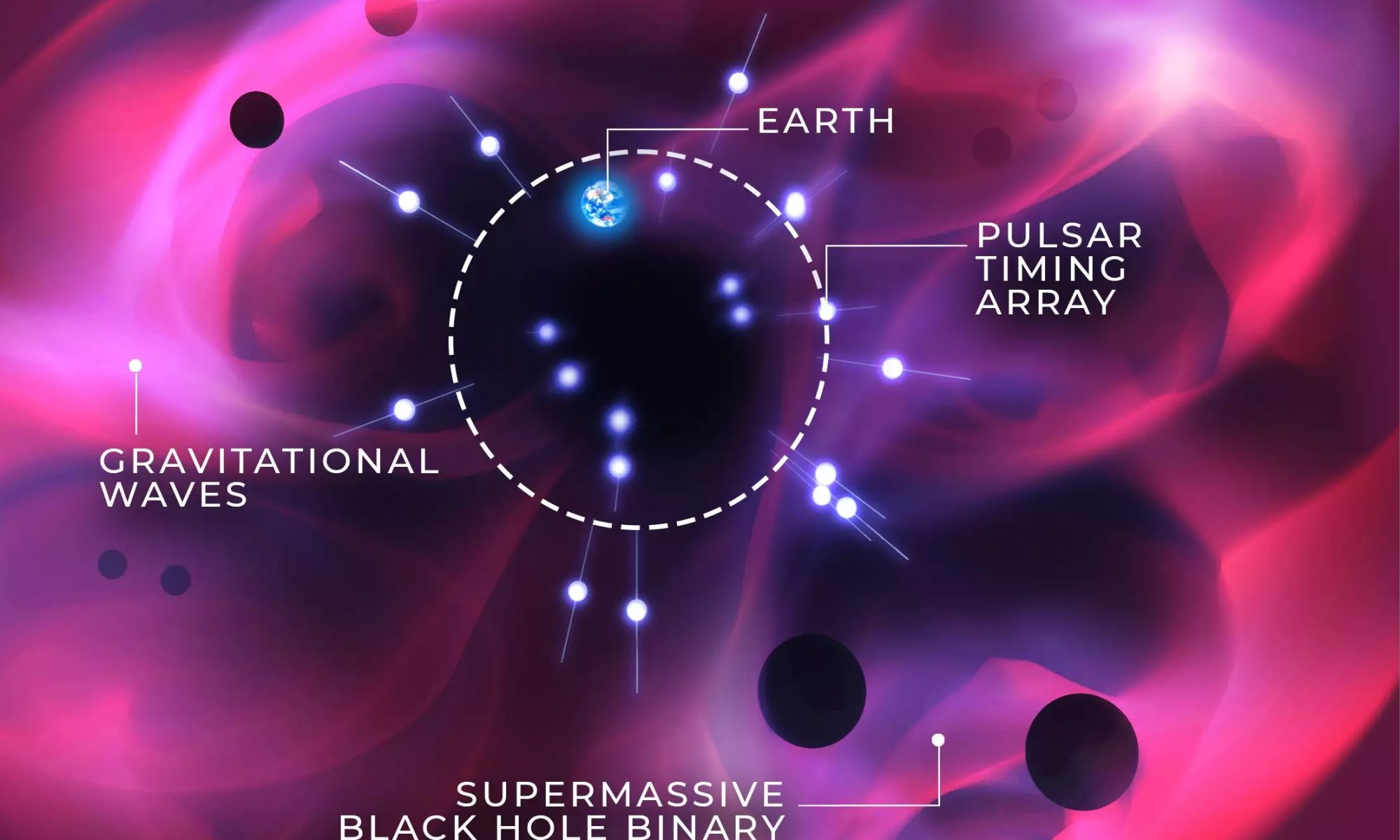
In the very early universe, physics was weird. A process known as “inflation,” where best we understand the universe went from a single infinitesimal point to everything we see today, was one such instance of that weird physics. Now, scientists from the Chinese Academy of Science have sifted through 15 years of pulsar timing data in order to put some constraints on what that physics looks like.
Continue reading “The Echoes From Inflation Could Still Be Shaking the Cosmos Today”Astronomers are Hoping to Detect Gravitational Waves Coming from Supernova 1987A
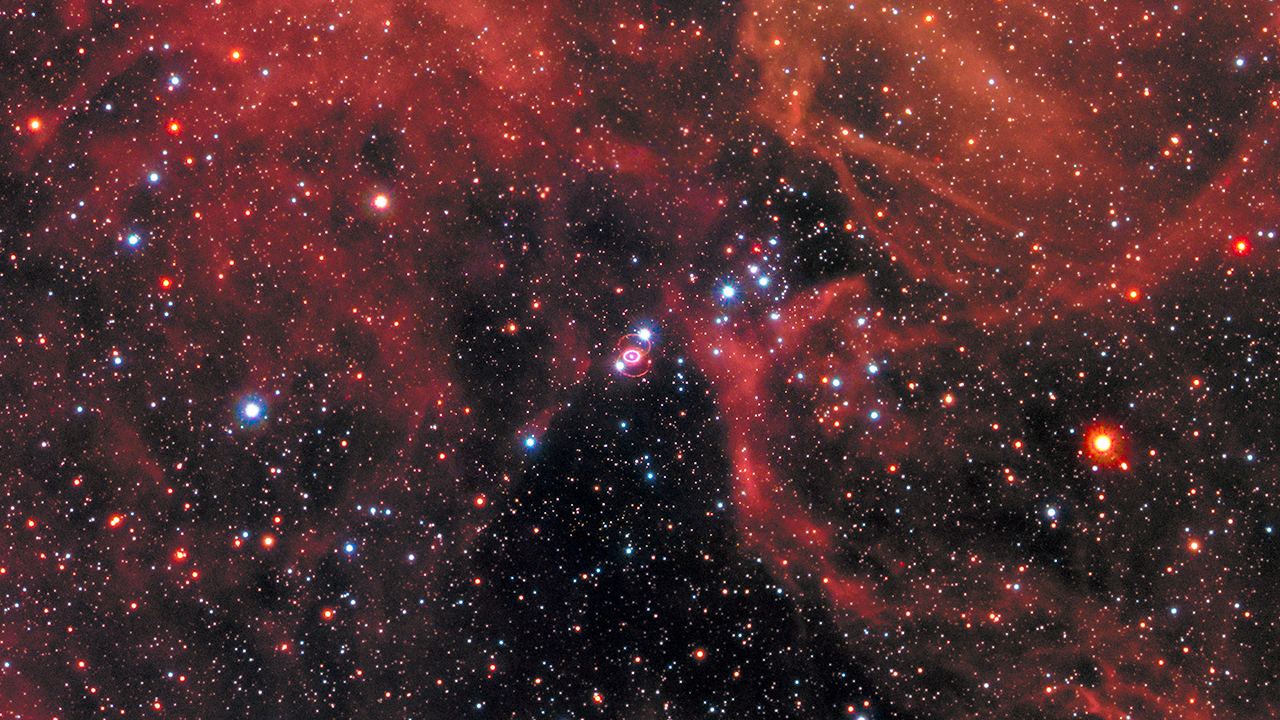
A supernova explosion is a cataclysmic explosion that marks the violent end of a massive star’s life. During the event, the star releases immense amounts of energy, often outshining the combined light from all the stars in the host galaxy for a very brief period of time. The explosion produces heavy elements and spreads them out among the stars to contribute to the formation of new stars and planets. The closest supernova in recent years occurred in the Large Magellanic Cloud in 1987 (SN1987A) and now, a team of astronomers have searched through mountains of data to see if they can detect gravitational waves from the remnant.
Continue reading “Astronomers are Hoping to Detect Gravitational Waves Coming from Supernova 1987A”Next Generation Gravitational Wave Observatories Could Detect 100-600 Solar Mass Black Hole Mergers
Humans are born wonderers. We’re always wondering about the next valley over, the next horizon, what we’ll understand next about this vast Universe that we’re all wrapped up in.
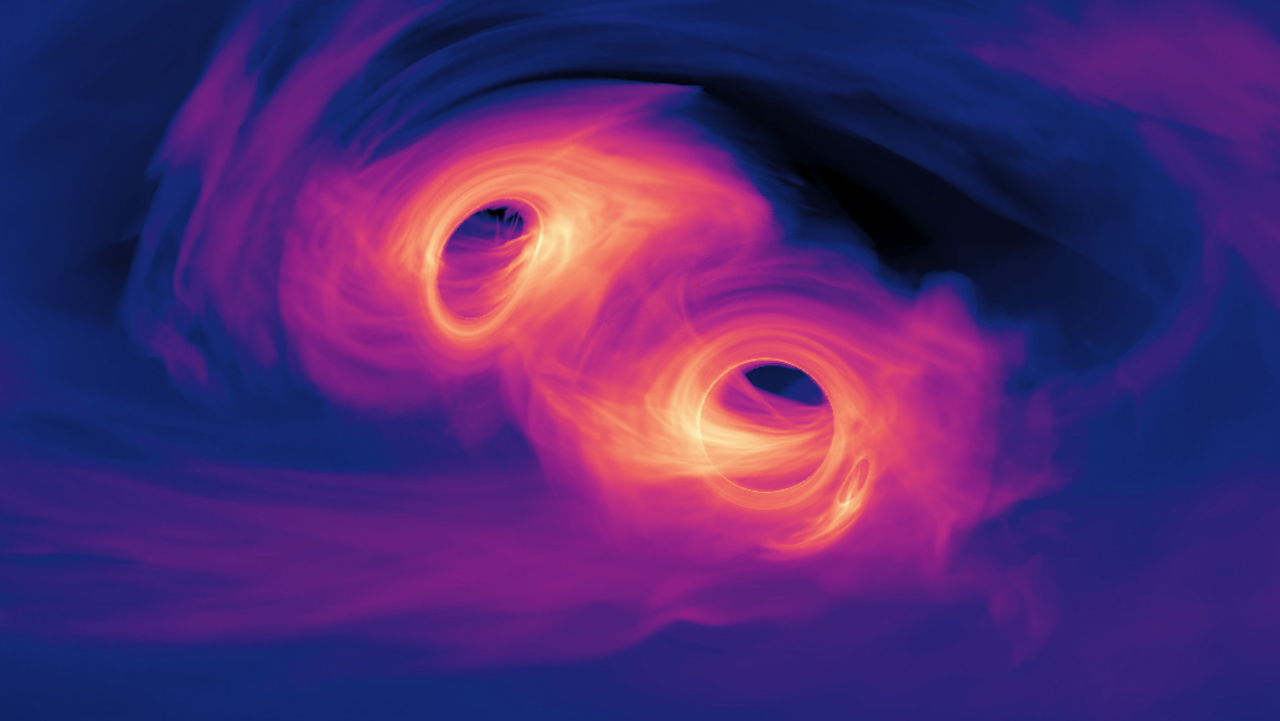
In 2015, we finally detected our first long-awaited and long-theorized gravitational wave from the distant merger of two stellar mass black holes. But now we want to know more, and only better detectors can feed our appetite.
Continue reading “Next Generation Gravitational Wave Observatories Could Detect 100-600 Solar Mass Black Hole Mergers”A Kilonova Simulated in 3D
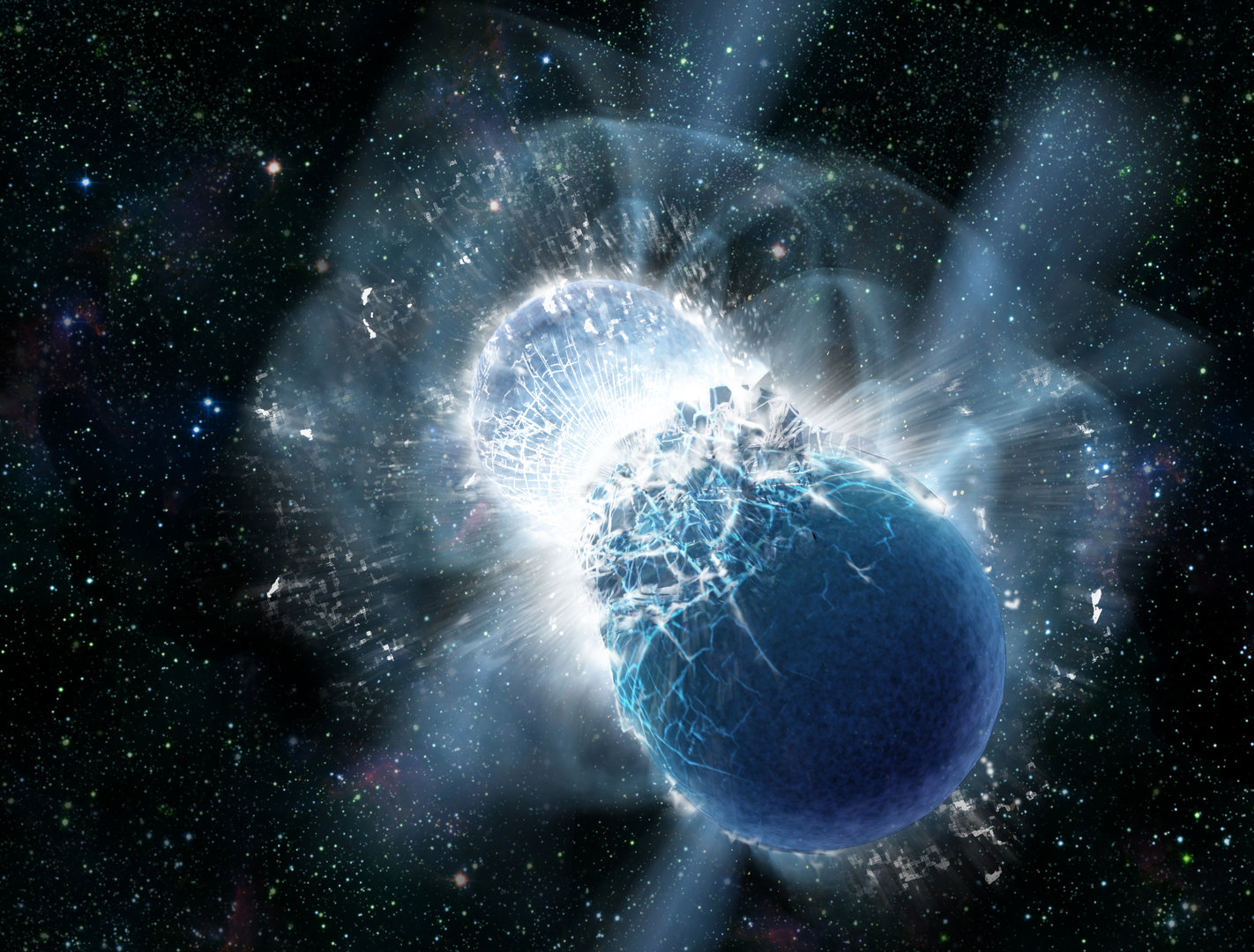

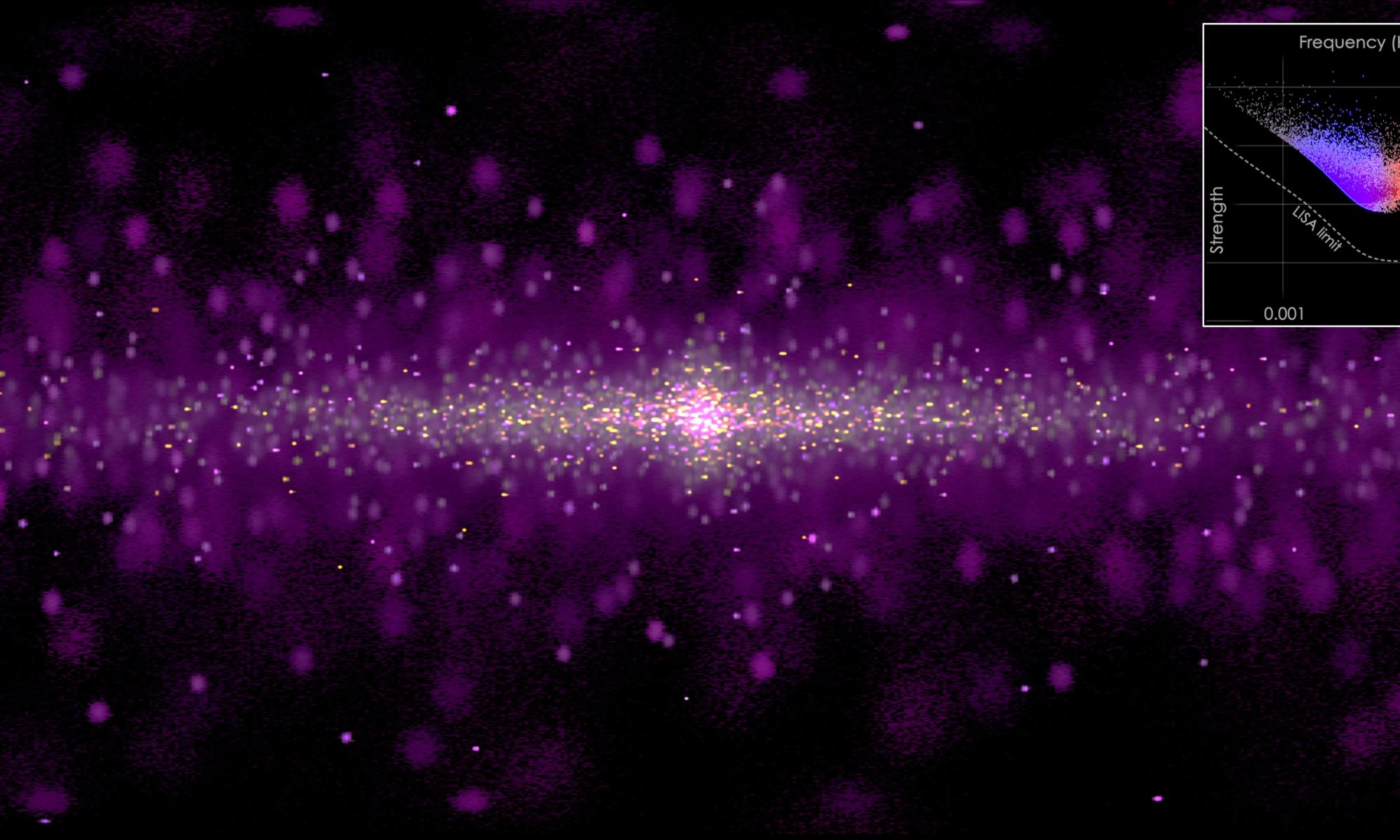
In 2017, astronomers detected gravitational waves from colliding neutron stars for the first time: a kilonova. Enormous amounts of heavy metals were detected in the light from the explosion, and astronomers continued to watch the expanding debris cloud.
Researchers have continued to study this event. Now, using a three-dimensional computer simulation, they have created a new recreation of this merger — second by second, as it happened — giving insights into all the high-energy mayhem and heavy elements formation in this catastrophic event.
Continue reading “A Kilonova Simulated in 3D”If You Could See Gravitational Waves, the Universe Would Look Like This
Imagine if you could see gravitational waves.
Of course, humans are too small to sense all but the strongest gravitational waves, so imagine you were a great creature of deep space, with tendrils that could extend a million kilometers. As gravitational waves rippled across your vast body, you would sense them squeezing and tugging ever so slightly upon you. And your brilliant mind could use these sensations to create an image in your mind. The ripples of distant supernovae, merging black holes, the undercurrent of the gravitational background. Creation, and destruction, all seen in your mind’s eye.
Continue reading “If You Could See Gravitational Waves, the Universe Would Look Like This”It's Time for a Gravitational Wave Observatory in the Southern Hemisphere
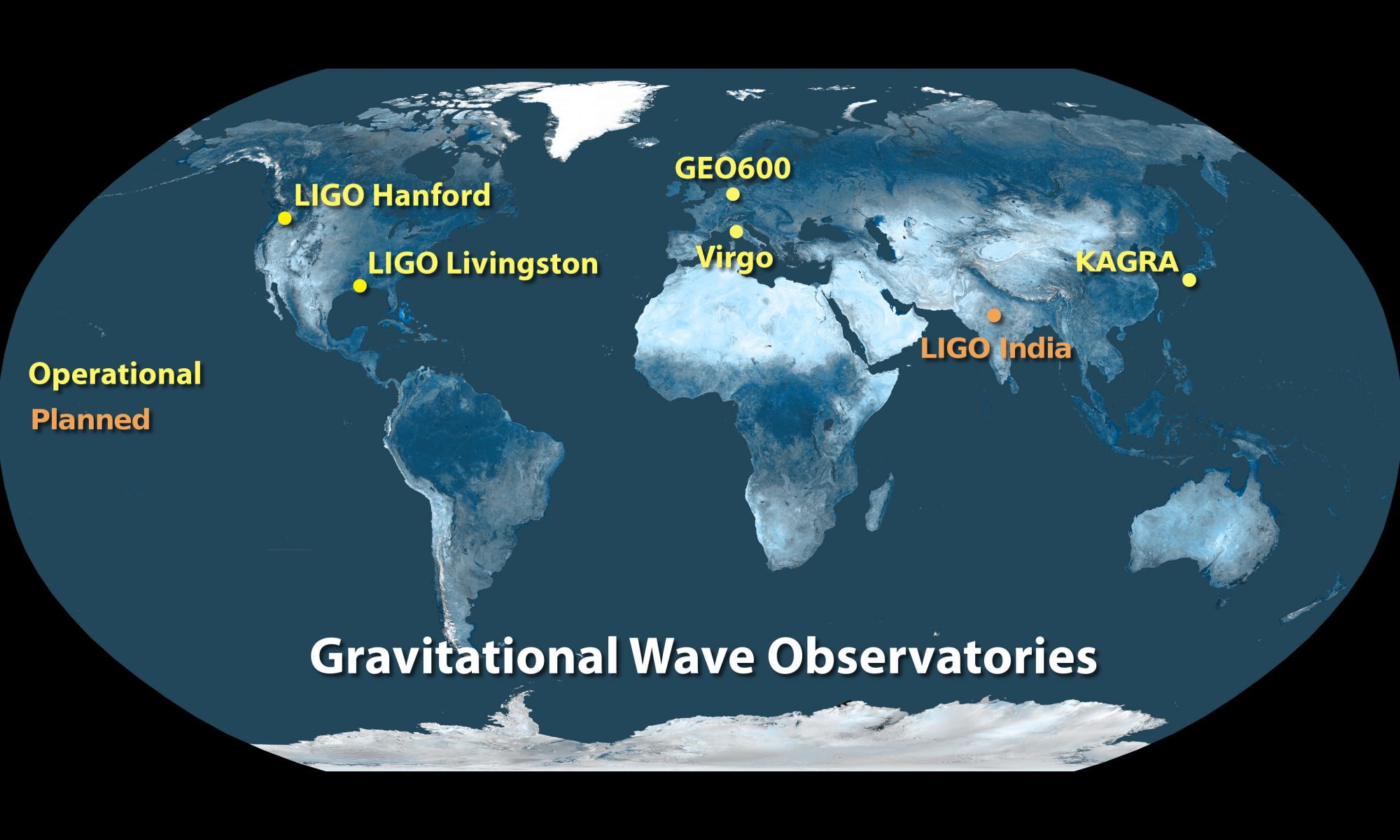
What’s true for optical astronomy is also true for gravitational wave astronomy: the more observatories you have, the better your view of the sky. This is why the list of active gravitational wave observatories is growing. But so far they are all in the Northern Hemisphere. As a recent article on the arXiv points out, that means we are missing out on a good number of gravitational events.
Continue reading “It's Time for a Gravitational Wave Observatory in the Southern Hemisphere”Pulsars Detected the Background Gravitational Hum of the Universe. Now Can They Detect Single Mergers?
Current gravitational wave observatories have two significant limitations. The first is that they can only observe powerful gravitational bursts such as the mergers of black holes and neutron stars. The second is that they can only observe these mergers for wavelengths on the order of hundreds to thousands of kilometers. This means we can only observe stellar mass mergers. Of course, there’s a lot of interesting gravitational astronomy going on at other wavelengths and noise levels, which has motivated astronomers to get clever. One of these clever ideas is to use pulsars as a telescope.
Continue reading “Pulsars Detected the Background Gravitational Hum of the Universe. Now Can They Detect Single Mergers?”Want to Find Colliding Black Holes? Check the Disks Around Quasars

The universe is awash in gravitational waves. The collisions of massive objects such as black holes and neutron stars generate many of them. Now astronomers are wondering about the environments where these catastrophic events occur. It turns out they might need to look at quasars.
Continue reading “Want to Find Colliding Black Holes? Check the Disks Around Quasars”Did the Pulsar Timing Array Actually Detect Colliding Primordial Black Holes?

The universe is filled with gravitational waves. We know this thanks to the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav), which recently announced the first observations of long wavelength gravitational waves rippling through the Milky Way. The waves are likely caused by the mergers of supermassive black holes, but can we prove it?
Continue reading “Did the Pulsar Timing Array Actually Detect Colliding Primordial Black Holes?”