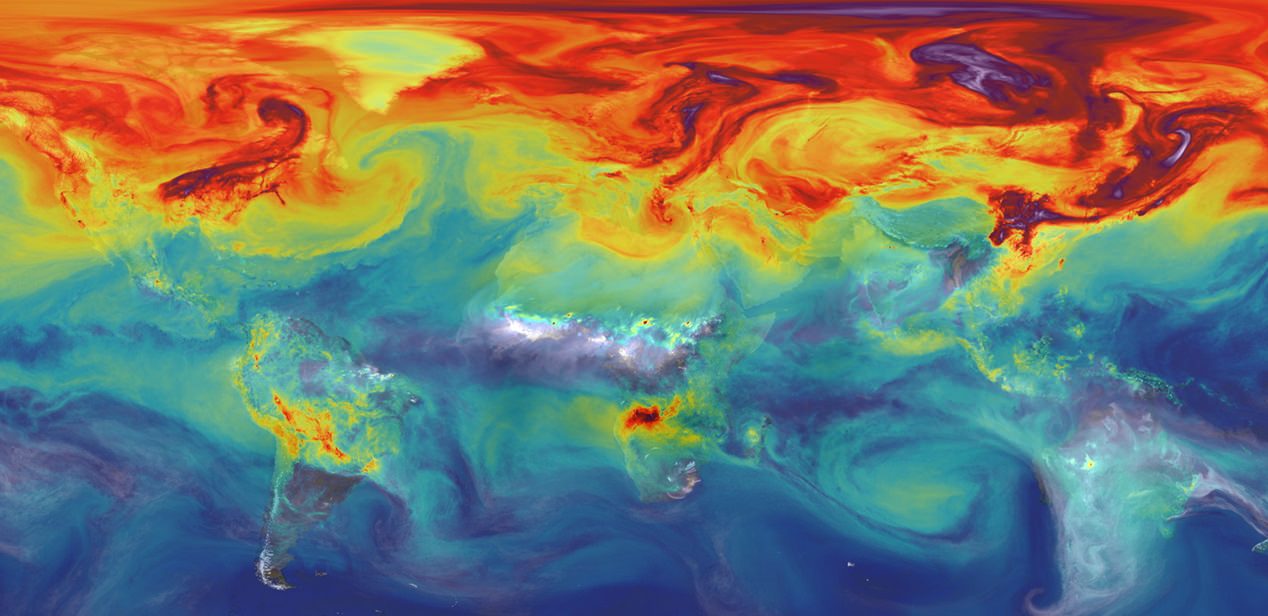
In 2013, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reported that atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO2) had reached four-hundred parts per million (ppm) for the first time since the Pliocene Era (ca. three million years ago). According to the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), “excess carbon dioxide” in our atmosphere will result in a global average temperature increase of between 1.5 and 2 °C (2.7 and 3.6 °F) by 2030. This will significantly affect ecological systems worldwide, including species extinction, droughts, wildfires, extreme weather, and crop failures.
Aside from curbing emissions, these changes call for mitigation and adaptation strategies and climate monitoring. This is the purpose of NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO) 2 and 3 missions, twin satellites that make space-based observations of CO2 in Earth’s atmosphere to understand the characteristics of climate change better. Using the world’s fifth-largest coal-fired power plant as a test case, a team of researchers used data from OCO 2 and 3 to detect and track changes in CO2 and quantify the emissions produced below.
Continue reading “NASA Satellites can Pinpoint the Exact Locations of Excessive CO2 Emissions”