No matter where we go in the universe, we’re going to need water. Thus far, human missions to Earth orbit and the Moon have taken water with them. But while that works for short missions, it isn’t practical in the long term. Water is heavy, and it would take far too much fuel to bring sufficient water to sustain long-term bases on the Moon or Mars. So we’ll have to use the water we can extract locally.
Continue reading “Thirsty on the Moon? Just Throw Some Regolith in the Microwave”Maybe We Don’t See Aliens Because Nobody Wants to Come Here
The Fermi Paradox won’t go away. It’s one of our most compelling thought experiments, and generations of scientists keep wrestling with it. The paradox pits high estimates for the number of civilizations in the galaxy against the fact that we don’t see any of those civs. It says that if rapidly expanding civilizations exist in the Milky Way, one should have arrived here in our Solar System. The fact that none have implies that none exist.
Many thinkers and scientists have addressed the Fermi Paradox and tried to come up with a reason why we don’t see any evidence of an expanding technological civilization. Life may be extraordinarily rare, and the obstacles to interstellar travel may be too challenging. It could be that simple.
But a new paper has a new answer: maybe our Solar System doesn’t offer what long-lived, rapidly expanding civilizations desire: the correct type of star.
Continue reading “Maybe We Don’t See Aliens Because Nobody Wants to Come Here”Socks, The Final Frontier

What is the greatest challenge facing humans as we prepare for the first crewed missions to Mars? Solar and cosmic radiation? Atrophying bone and muscle? Growing food? How about laundry? It’s strange but true, right now we don’t have a way to clean laundry in space.
Continue reading “Socks, The Final Frontier”Avoiding the Great Filter. How Long Until We’re Living Across the Solar System?
If you’re a fan of the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) and the Fermi Paradox, then it’s likely you’ve heard of a concept known as the Great Filter. In brief, it states that life in the Universe may be doomed to extinction, either as a result of cataclysmic events or due to circumstances of its own making (i.e., nuclear war, climate change, etc.) In recent years, it has been the subject of a lot of talk and speculation, and not just in academic circles.
Stephen Hawking and Elon Musk have also weighed in on the issue, claiming that humanity’s only chance at long-term survival is to become “interplanetary.” Addressing this very possibility, a research team led by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) recently created a timeline for potential human expansion beyond Earth. According to their findings, we have the potential of going interplanetary by the end of the century and intragalactic by the end of the 24th!
Continue reading “Avoiding the Great Filter. How Long Until We’re Living Across the Solar System?”A Habitat at Ceres Could be the Gateway to the Outer Solar System
In the near future, humanity stands a good chance of expanding its presence beyond Earth. This includes establishing infrastructure in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), on the surface of (and in orbit around) the Moon, and on Mars. This presents numerous challenges, as living in space and on other celestial bodies entails all kinds of potential risks and health hazards – not the least of which are radiation and long-term exposure to low gravity.
These issues demand innovative solutions; and over the years, several have been proposed! A good example is Dr. Pekka Janhunen‘s concept for a megasatellite settlement in orbit around the dwarf planet Ceres, the largest object in the Main Asteroid Belt. This settlement would provide artificial gravity for its residents while the local resources would allow for a closed-loop ecosystem to created inside – effectively bringing “terraforming” to a space settlement.
Continue reading “A Habitat at Ceres Could be the Gateway to the Outer Solar System”Gateway Foundation Gives a Detailed Update on its Voyager Station Concept
In 2012, the Gateway Foundation was founded with the purpose of building the world’s first rotating space station in orbit – known as The Gateway. This is no easy task and must be preceded by establishing the necessary infrastructure in orbit and the creation of a series of smaller structures to test the concept. This includes the Voyager Class station, a rotating structure designed to produce varying levels of artificial gravity.
In recent months, the Orbital Assembly Corporation (OAC) – founed in 2018 by the Gateway team – began working on a crucial component, known as the DSTAR. These and other updates about their Voyager Class station were the subjects of a recent video featuring Foundation and OAC CEO John Blincow. According to Blincow, he and his colleagues will be performing a demonstration and making a big announcement in the coming weeks!
Continue reading “Gateway Foundation Gives a Detailed Update on its Voyager Station Concept”What Martian Settlers Need to Know About Soil Can Teach us How to Grow Better on Earth
When human beings start living in space for extended periods of time they will need to be as self-sufficient as possible. The same holds true for settlements built on the Moon, on Mars, and other bodies in the Solar System. To avoid being entirely dependent on resupply missions from Earth (which is costly and time-consuming) the inhabitants will need to harvest resources locally – aka. In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU).
This means they’ll have to procure their own sources of water, building materials, and grow their own food. While the ISS has allowed for all kinds of experiments involving hydroponics in space, little has been done to see how soil fares in microgravity (or lower gravity). To address this, Morgan Irons – Chief Science Officer of the Virginia-based startup Deep Space Ecology (DSE) – recently sent her Soil Health in Space experiment to the ISS.
Continue reading “What Martian Settlers Need to Know About Soil Can Teach us How to Grow Better on Earth”The Bare Minimum Number of Martian Settlers? 110
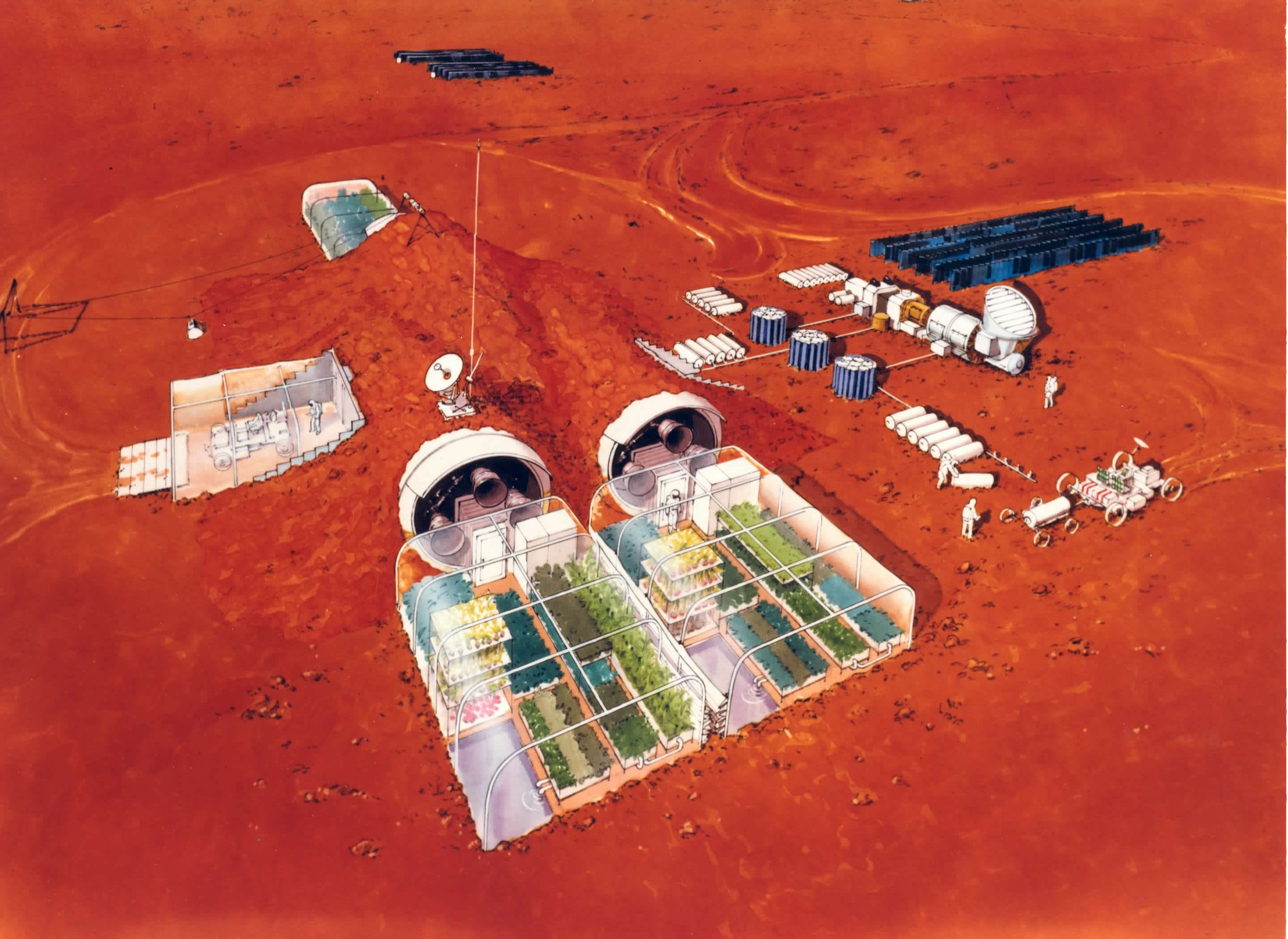

So you want to colonize Mars, huh? Well Mars is a long ways away, and in order for a colony to function that far from Earthly support, things have to be thought out very carefully. Including how many people are needed to make it work.
A new study pegs the minimum number of settlers at 110.
Continue reading “The Bare Minimum Number of Martian Settlers? 110”Learning to Live Sustainably on the Red Planet: Habitat Mars
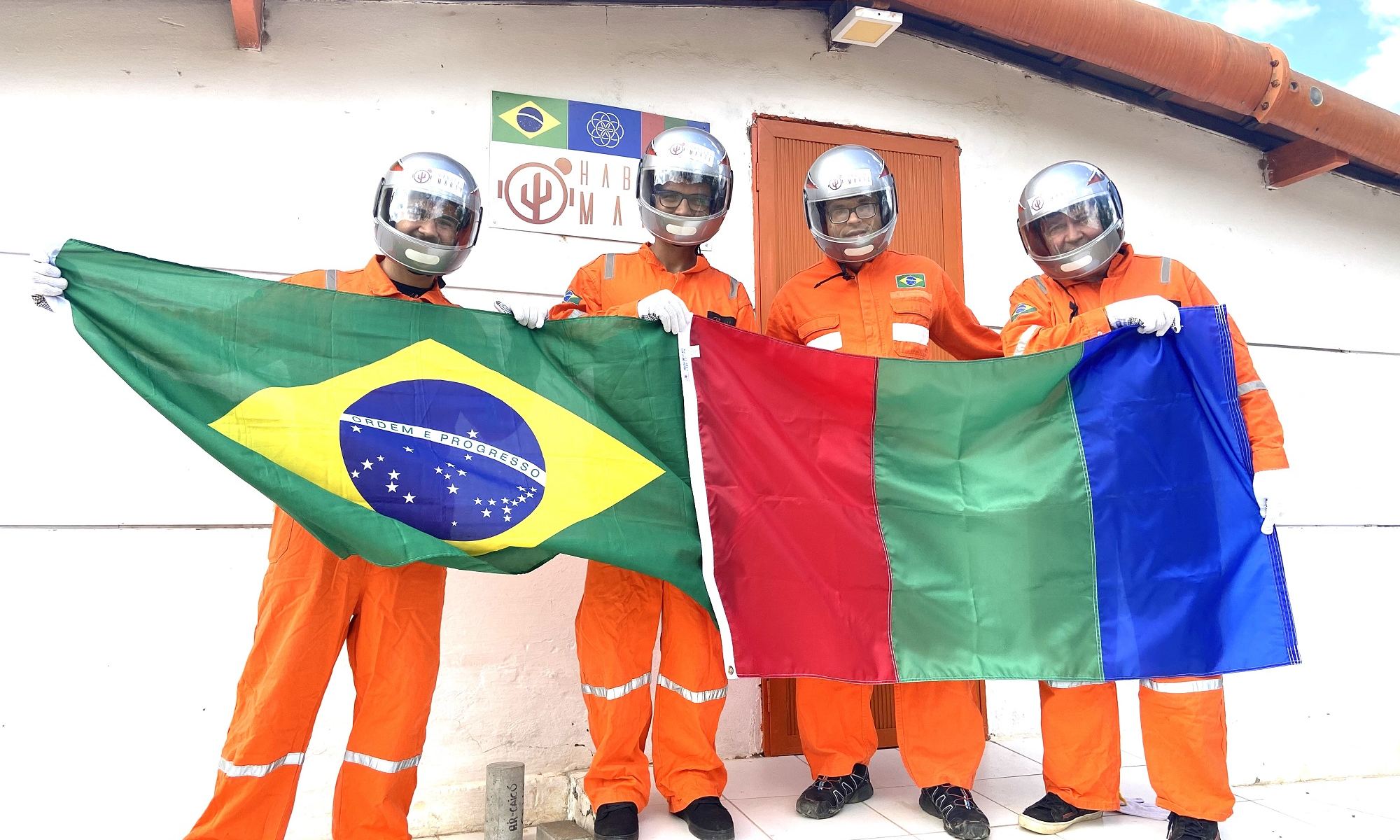
There’s quite a bit of buzz these days about how humanity could become a “multiplanetary” species. This is understandable considering that space agencies and aerospace companies from around the world are planning on conducting missions to Low Earth Orbit (LEO), the Moon, and Mars in the coming years, not to mention establishing a permanent human presence there and beyond.
To do this, humanity needs to develop the necessary strategies for sustainable living in hostile environments and enclosed spaces. To prepare humans for this kind of experience, groups like Habitat Marte (Mars Habitat) and others are dedicated to conducting simulated missions in analog environments. The lessons learned will not only prepare people to live and work in space but foster ideas for sustainable living here on Earth.
Continue reading “Learning to Live Sustainably on the Red Planet: Habitat Mars”Ideas for Sustainable Cities and Urban Farming… on Mars?
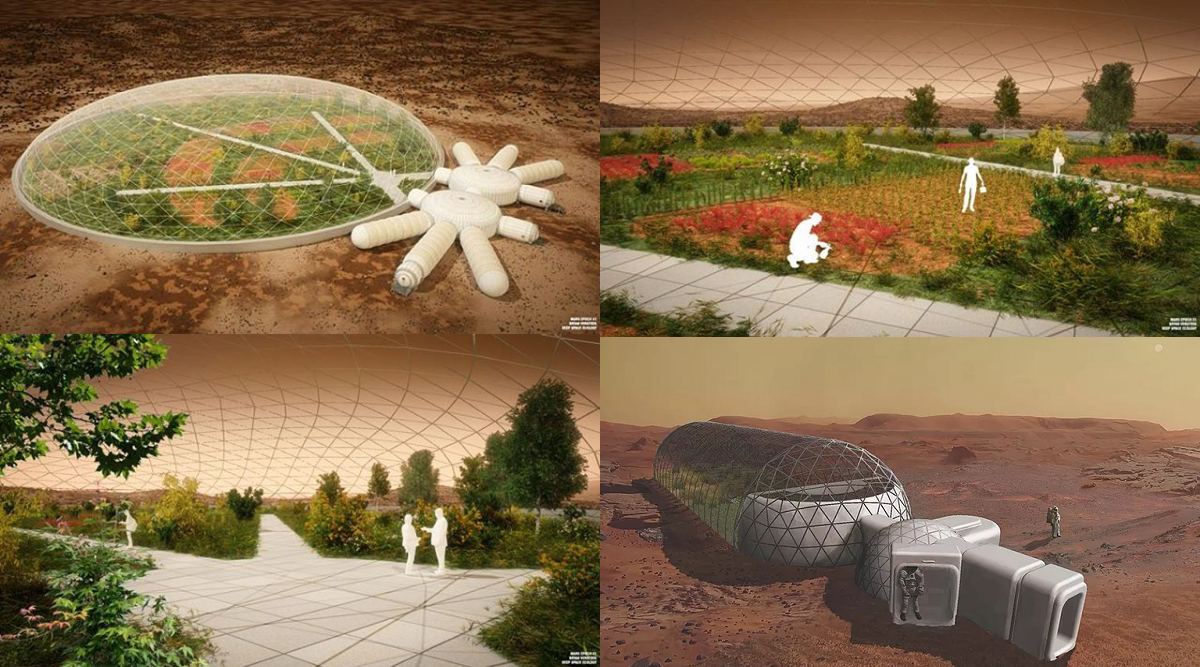
“The core essence of Mars City Design is —not to repeat the same mistakes that we did to our planet. The hope to start a new design for living on Mars, every single thing needs to have a sustainable answer within the big picture, of the regenerative circle of life and of the product itself. All things need an exit plan that allows them to be reusable or repurposed. That can hopefully inspire change on Earth.”
-Vera Mulyani (Vera Mars), Founder/CEO Mars City Design
Once the stuff of science fiction, the possibility that humans could establish a permanent settlement on Mars now appears to be a genuine possibility. While doing so represents a major challenge and there are many hurdles that still need to be overcome, the challenge itself is inspiring some truly creative solutions. But what is especially interesting is how these same solutions can also address problems here on Earth.
This is especially clear where the Mars City Design Challenges are concerned. This annual competition was founded with the purpose of inspiring innovative ideas that could lead to sustainable living on Mars. For this year’s challenge, “Urban Farming for Extreme Environment,” Mars City Design and its founder (Vera Mulyani) are looking for designs that incorporate urban farming to support a colony of 100 people.
Continue reading “Ideas for Sustainable Cities and Urban Farming… on Mars?”