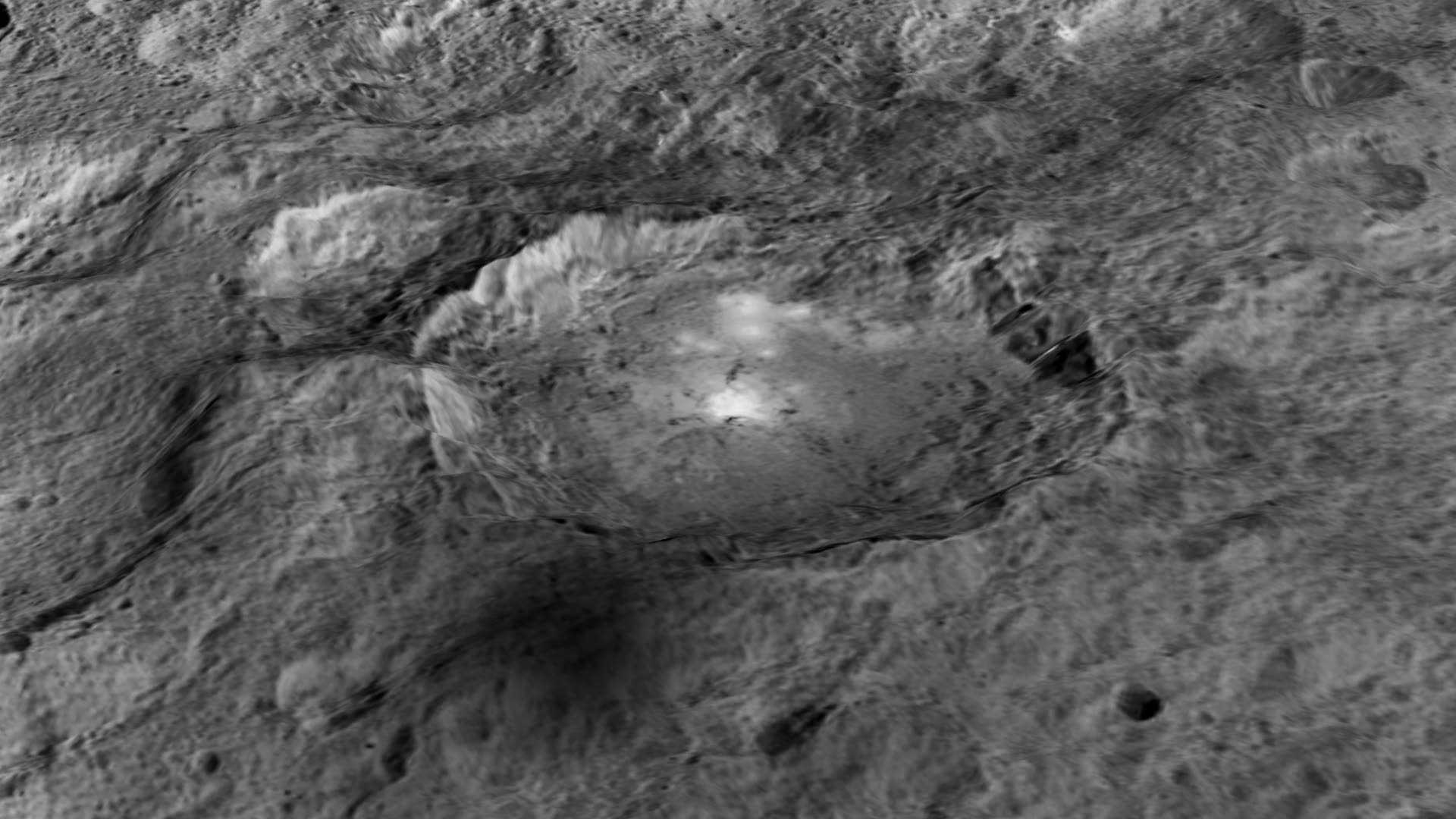
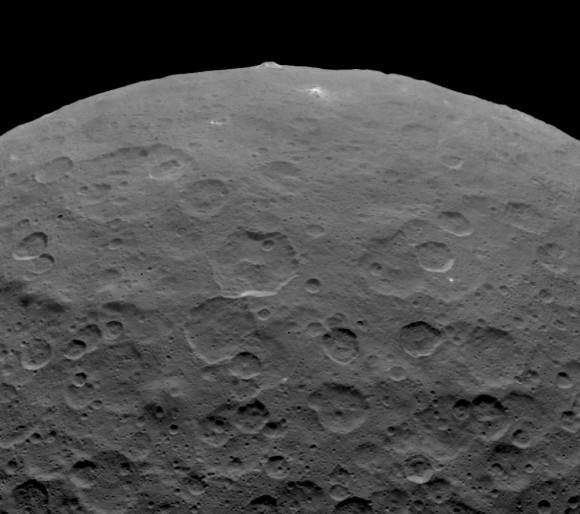
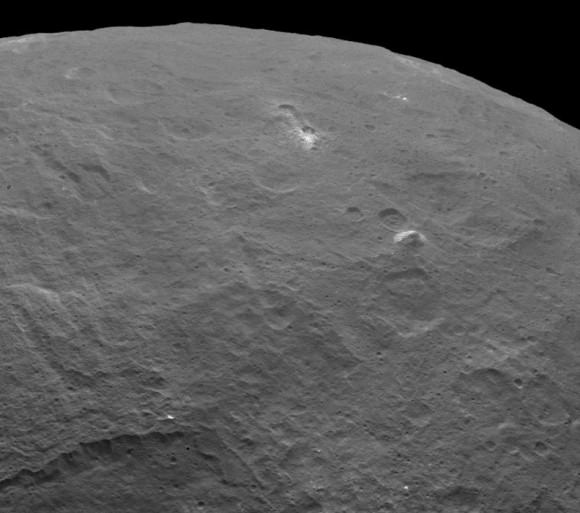
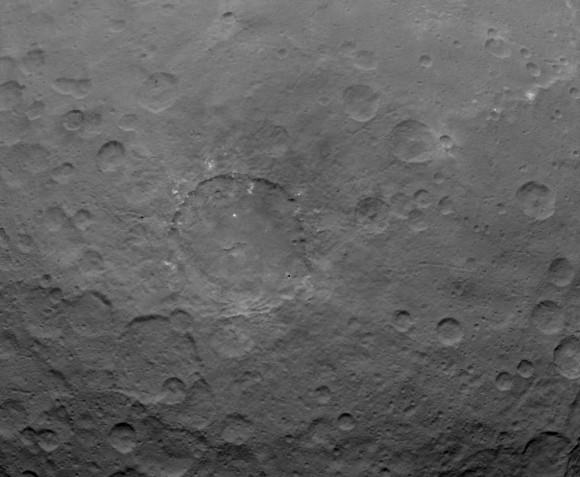
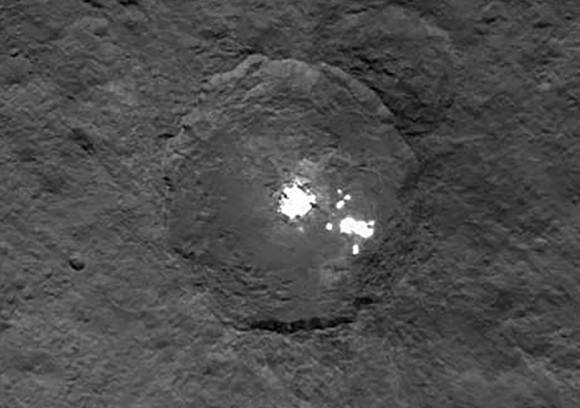
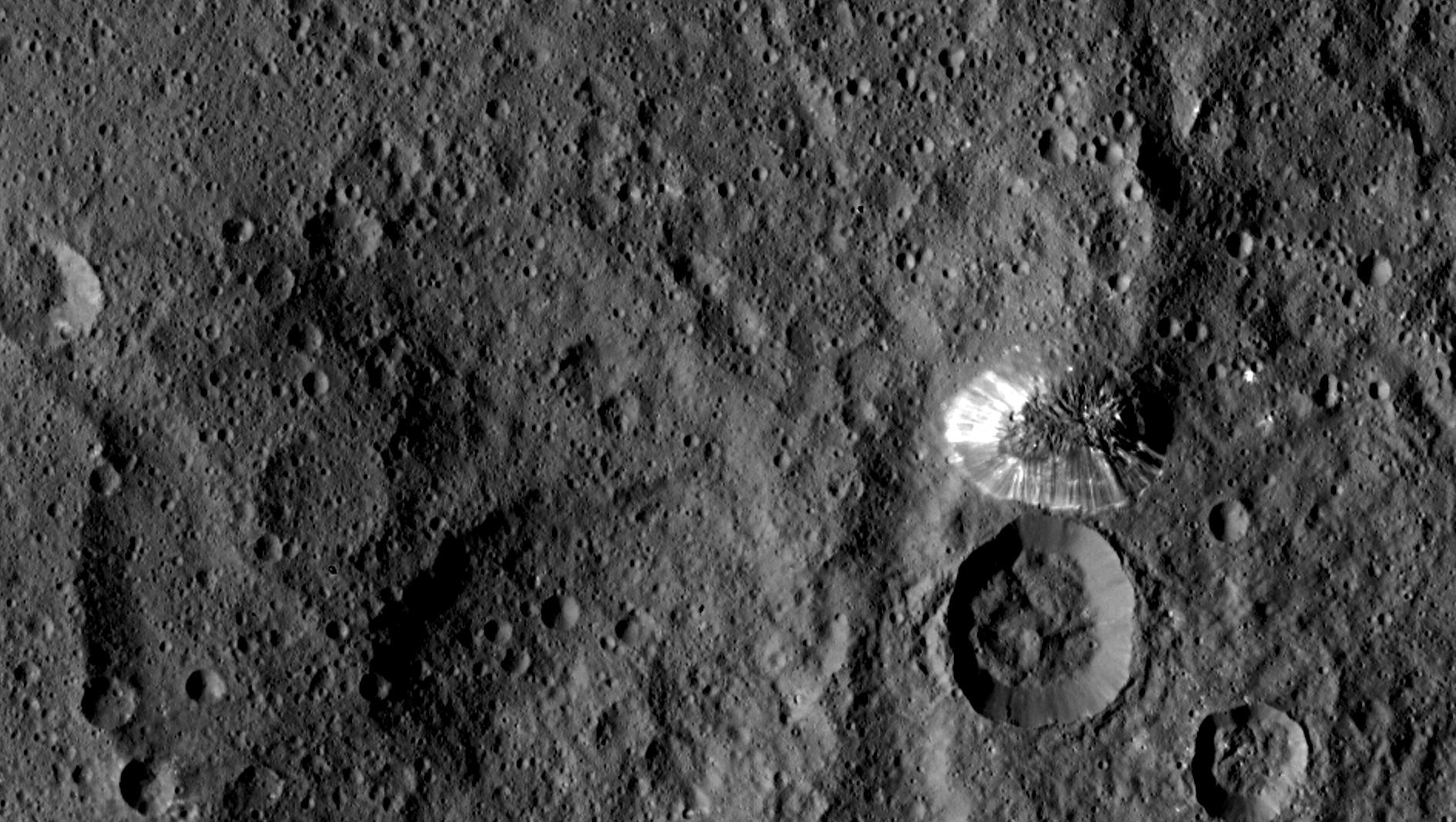
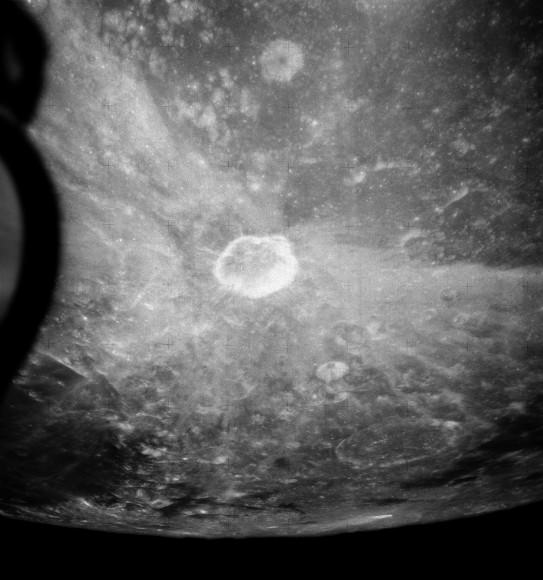
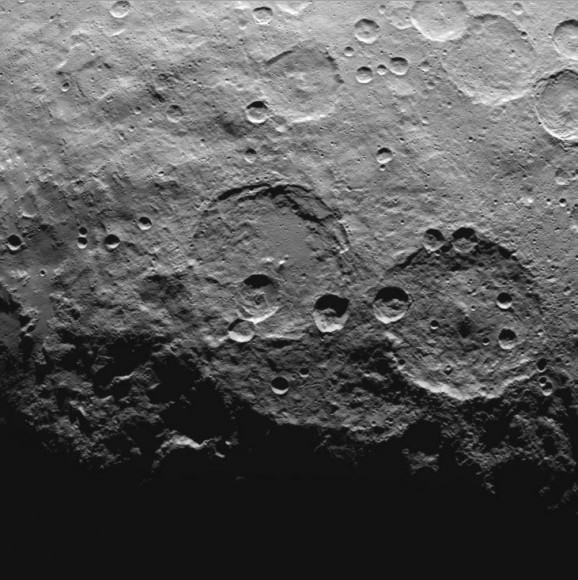
The Dawn spacecraft is now orbiting just 1,470 kilometers (915 miles) above Ceres’ surface, and the science team released these latest images. Above is a closest view yet of the so-called ‘pyramid’ on Ceres, although the closer Dawn gets, the less this feature looks like a pyramid. It’s actually more like a conical mountain with a flat top, almost like a butte.
And if you’re like me and you see a crater instead of a mountain, just turn the picture over (or stand on your head). Below, we’ve turned the image upside down for you:
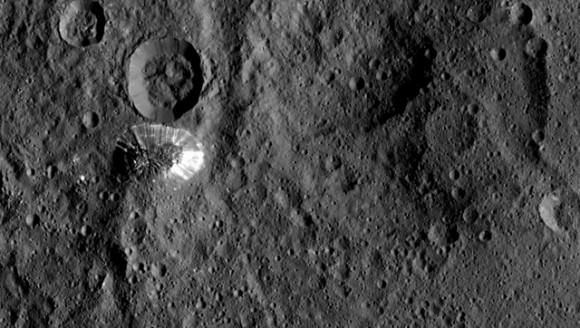
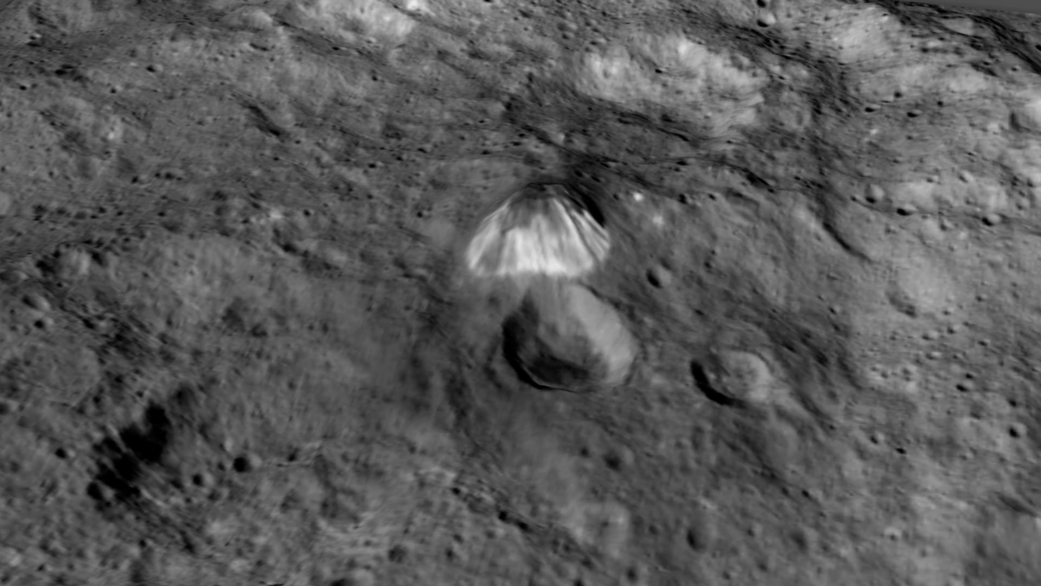
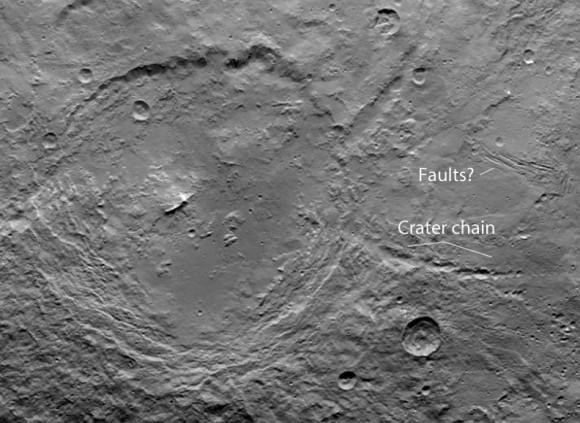
The mountain is located in the southern hemisphere, and stands 6 kilometers (4 miles) high. Visible on the sides of the mountain are narrow braided fractures and an intriguing bright area. Only time will tell if this bright region is similar to the mysterious bright spots seen in previous Dawn images of Ceres. The team released additional images as well.

As Dawn slowly moves ever-closer to Ceres surface, the team says the spacecraft is performing well.
“Dawn is performing flawlessly in this new orbit as it conducts its ambitious exploration. The spacecraft’s view is now three times as sharp as in its previous mapping orbit, revealing exciting new details of this intriguing dwarf planet,” said Marc Rayman, Dawn’s chief engineer and mission director, based at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena,
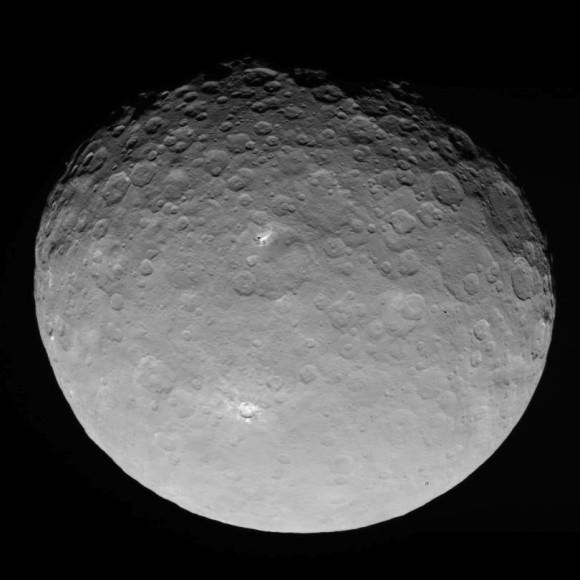
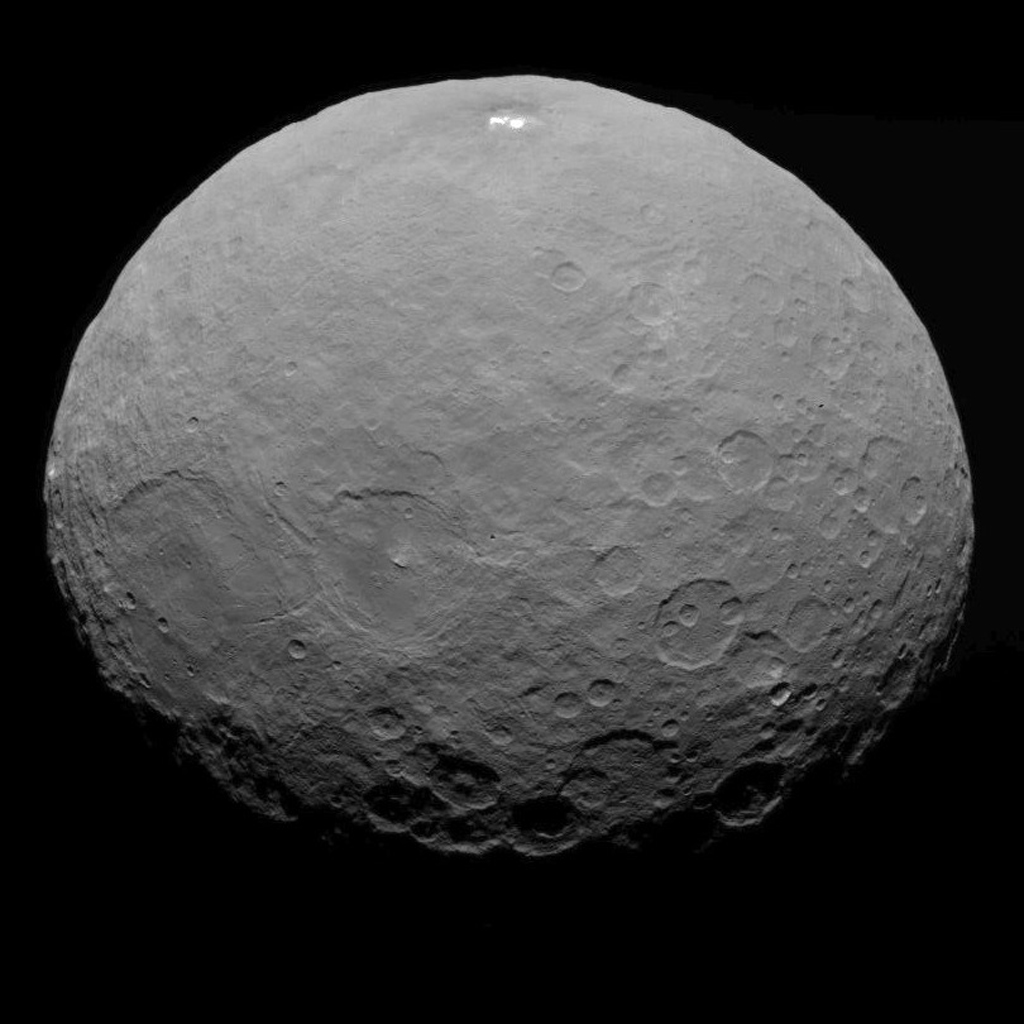
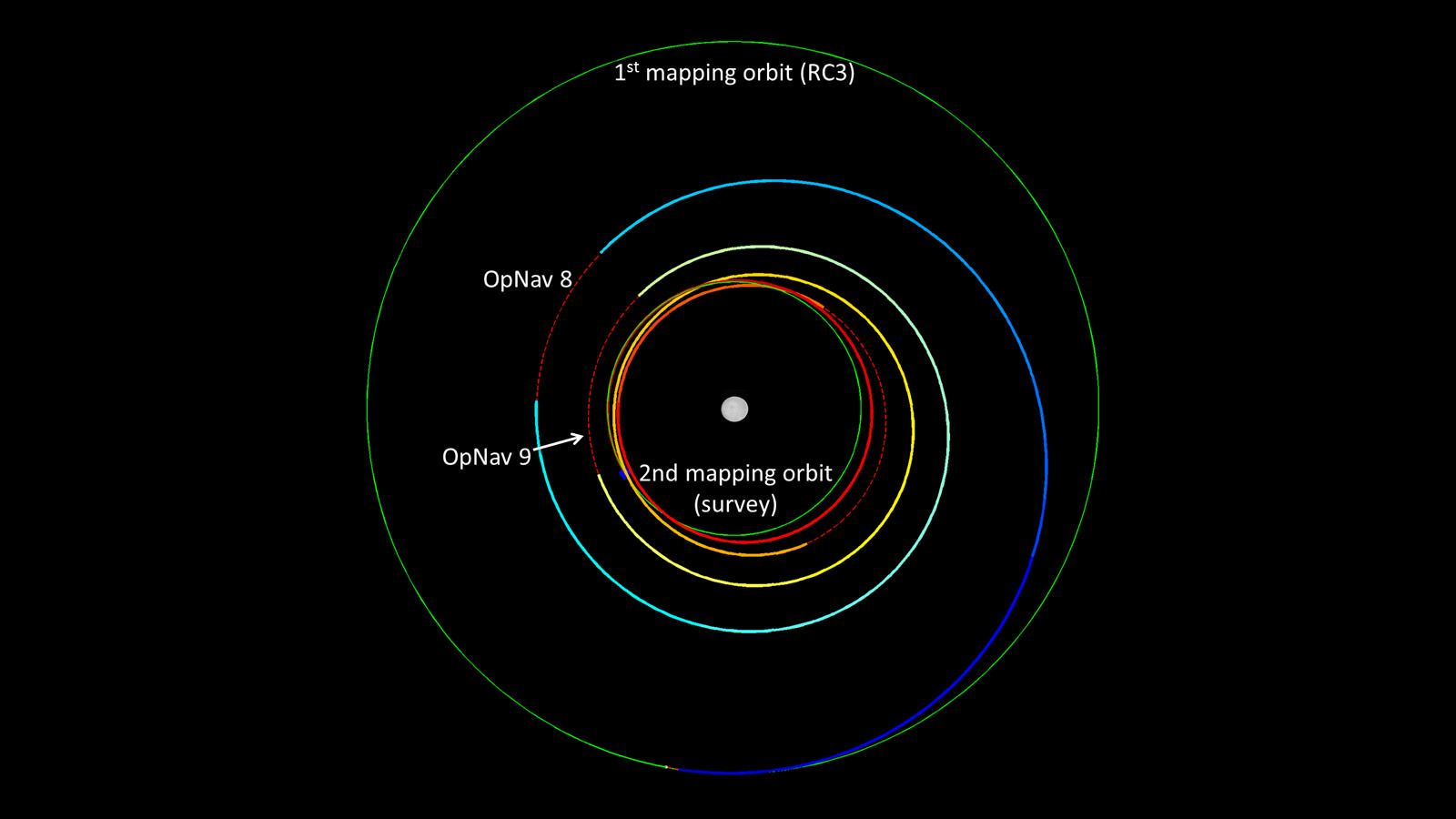
Dawn is currently taking images to try and map the entire surface. This will 11 days at this altitude and each 11-day cycle consists of 14 orbits. Over the next two months, the spacecraft will map the entirety of Ceres six times.

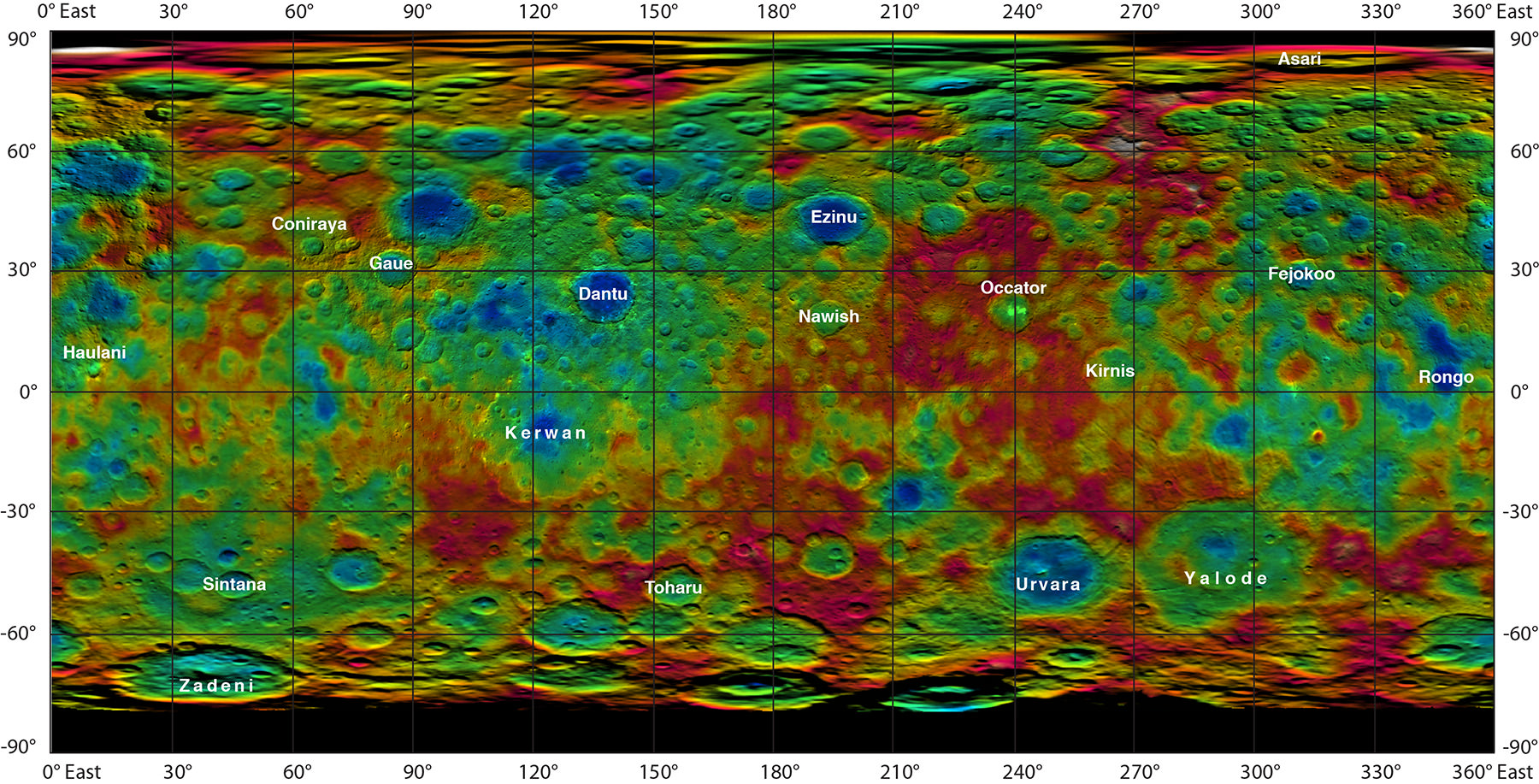
Using Dawn’s framing camera to map the surface in detail, scientists hope to create a 3-D modeling of Ceres’ surface. Every image from this orbit has a resolution of 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel, and covers less than 1 percent of the surface of Ceres.
At the same time, Dawn’s visible and infrared mapping spectrometer is collecting data that will give scientists a better understanding of the minerals found on Ceres’ surface.
The science and engineering teams are also taking a look at the data coming in from radio signals to help with measurements of Ceres’ gravity field. This will help determine the distribution of mass on Ceres interior and might provide clues if the asteroid has any liquid water beneath its surface.
Additionally, the radio data data will help mission planners design the maneuvers for lowering Dawn’s orbit even more. In late October, Dawn will begin spiraling toward this final orbit, which will be at an altitude of 375 kilometers (230 miles.)
In the latest entry on the Dawn Journal, Rayman said despite the loss of the reaction wheels (in 2010 and 2012) that help maneuver the spacecraft and keep it stable, engineers have learned how to be very efficient with the precious hydrazine the fuels the small jets of the reaction control system and they now have some to spare. They now expect to exceed the original mission parameters!
“Therefore, mission planners have recently decided to spend a few more in this mapping orbit,” Rayman said. “They have added extra turns to allow the robot to communicate with Earth during more of the transits over the nightside than they had previously budgeted. This means Dawn can send the contents of its computer memory to Earth more often and therefore have space to collect and store even more data than originally planned. An 11-day mapping cycle is going to be marvelously productive.”
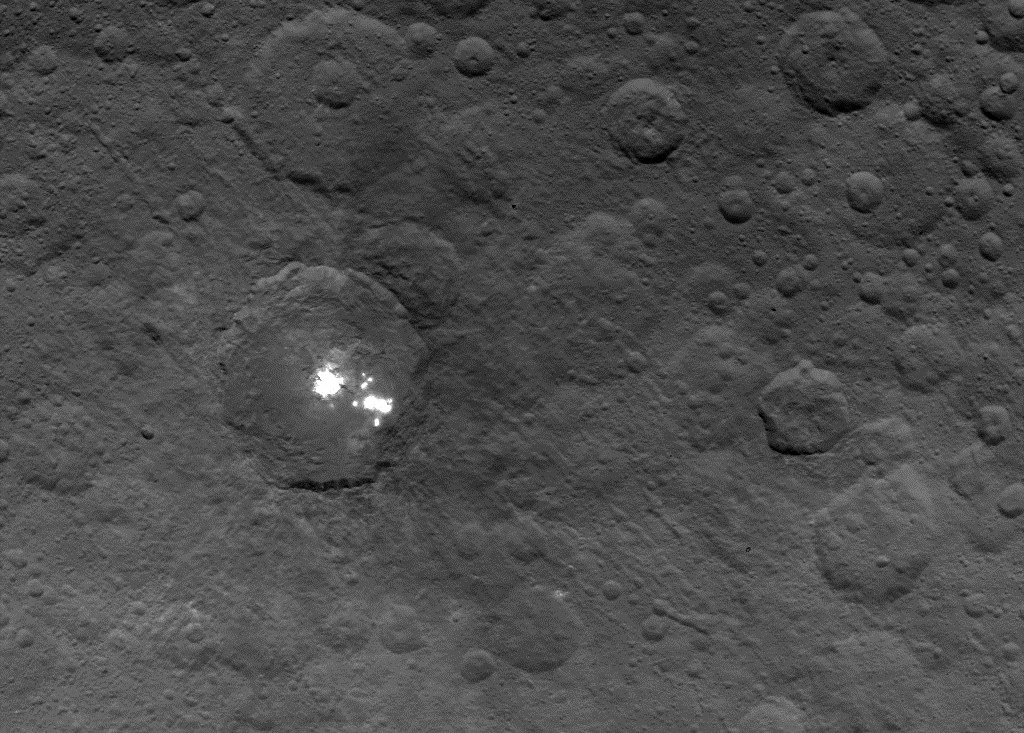
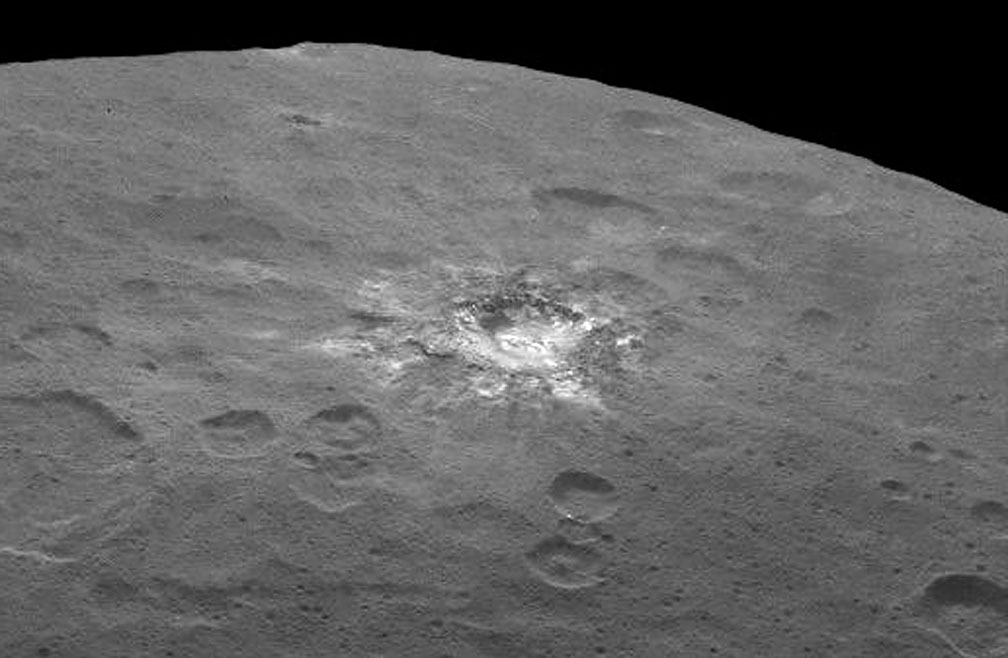
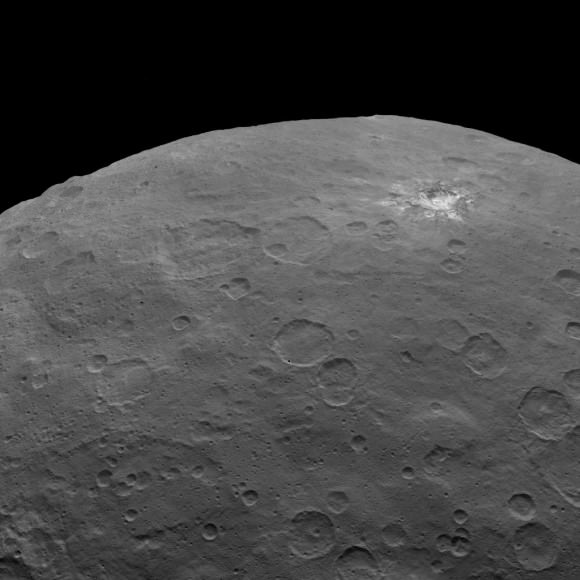
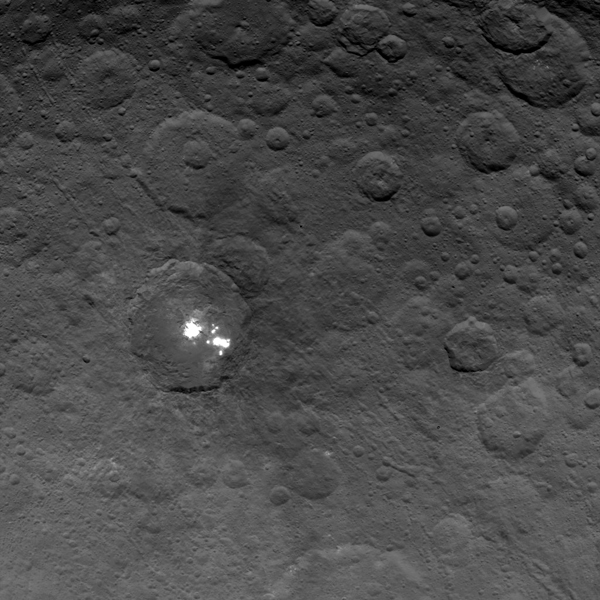
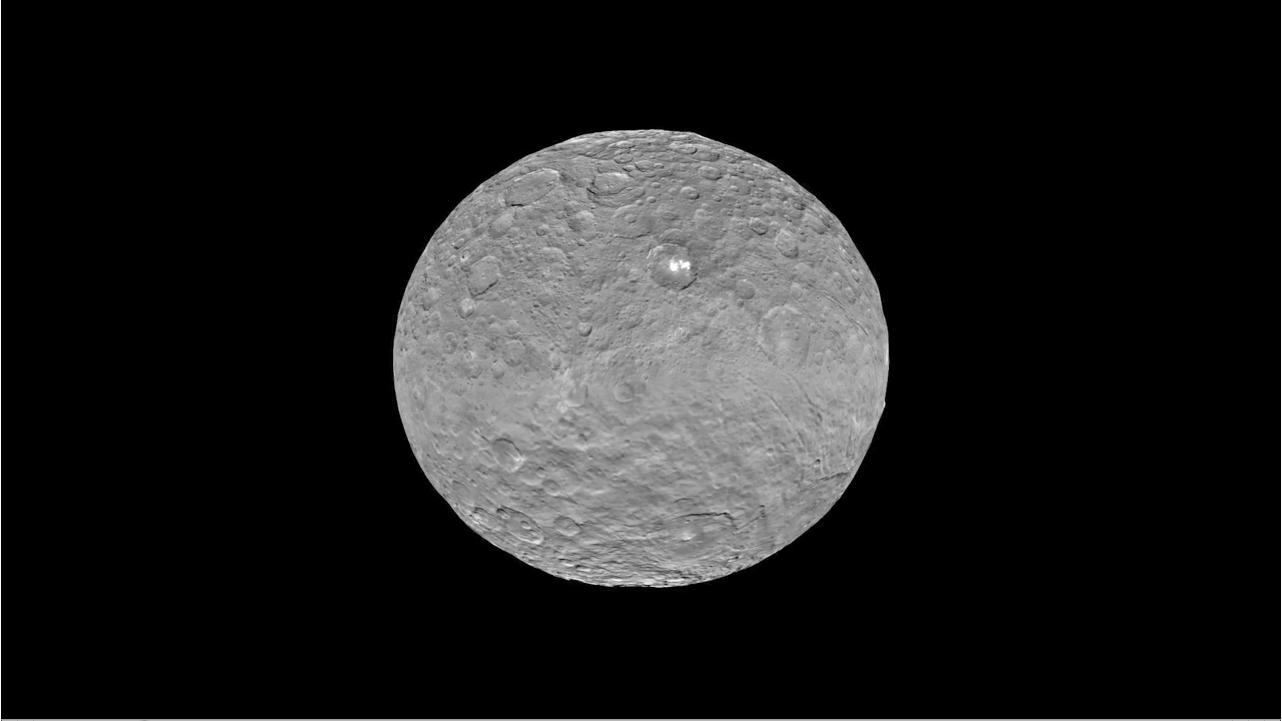
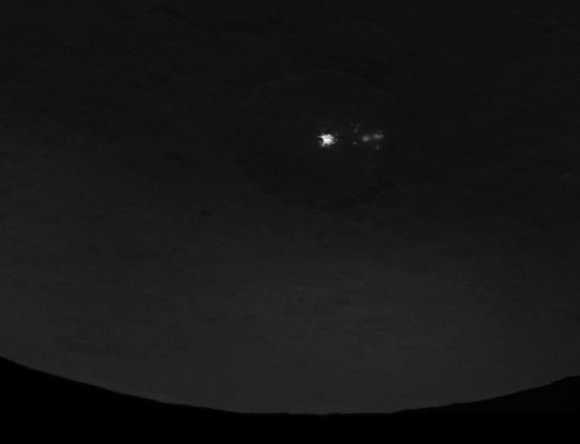
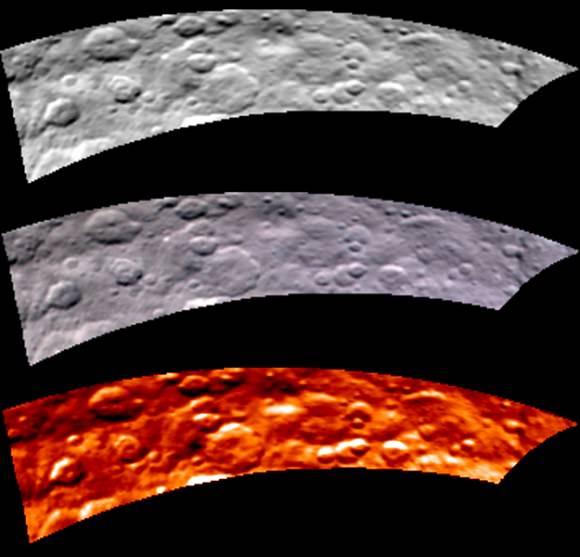
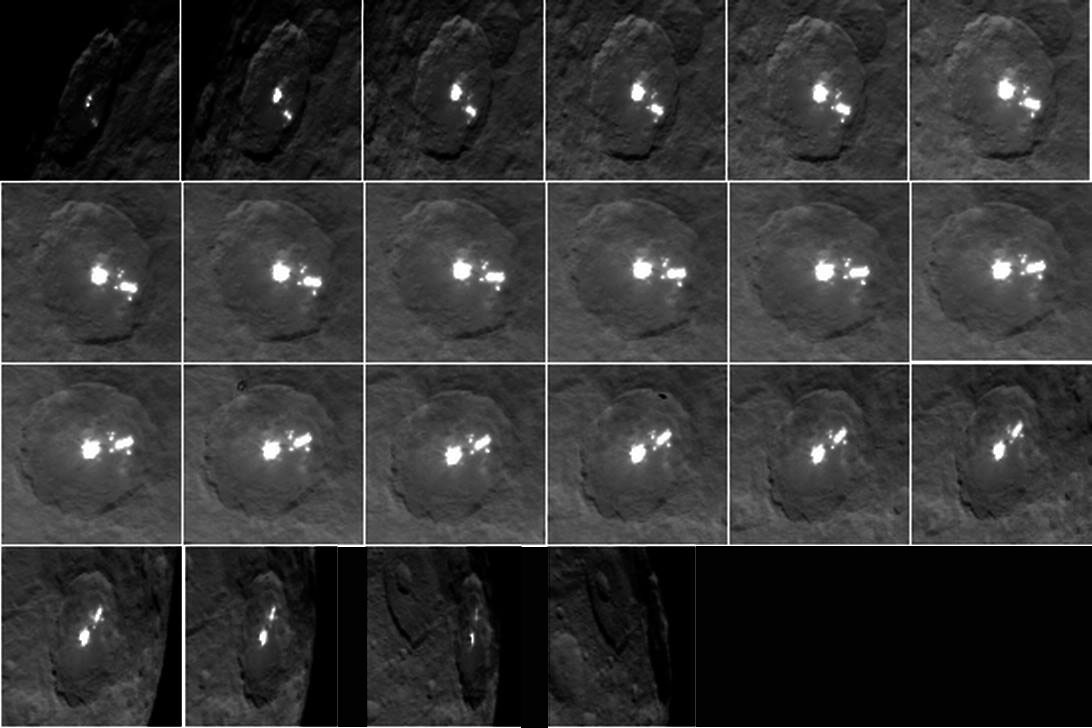
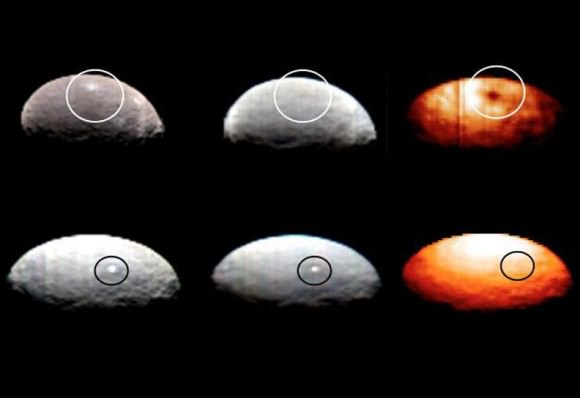
There’s still a debate about the unusually bright spots in some of Ceres craters that appear when the asteroid/dwarf planet turns into the sunlight. The team has speculated that they could be frozen pools of water ice, or patches of light-colored, salt-rich material.
The brightest spots are known collectively as Spot 5, and sit inside Occator Crater on Ceres, and hopefully new images of this area will be released soon. In a previous article on Universe Today, Dawn’s principal investigator, Chris Russell of the University of California at Los Angeles told us that the debate is continuing among the science team, but he wouldn’t harbor a guess as to which way the debate might end or which “side” was in the lead among the scientists.
“I originally was an advocate of ice, because of how bright the spots seemed to be,” Russell told writer Alan Boyle, but newer observations revealed the bright material’s albedo, or reflectivity factor, is about 50 percent – which is less than Russell originally thought. “This could be salt and is unlikely to be ice. I think the team opinion is now more in line with salt,” he said.
You can cast your vote as to what you think the bright spots are at this NASA page.
See all the latest images from Dawn at JPL’s Photojournal page.