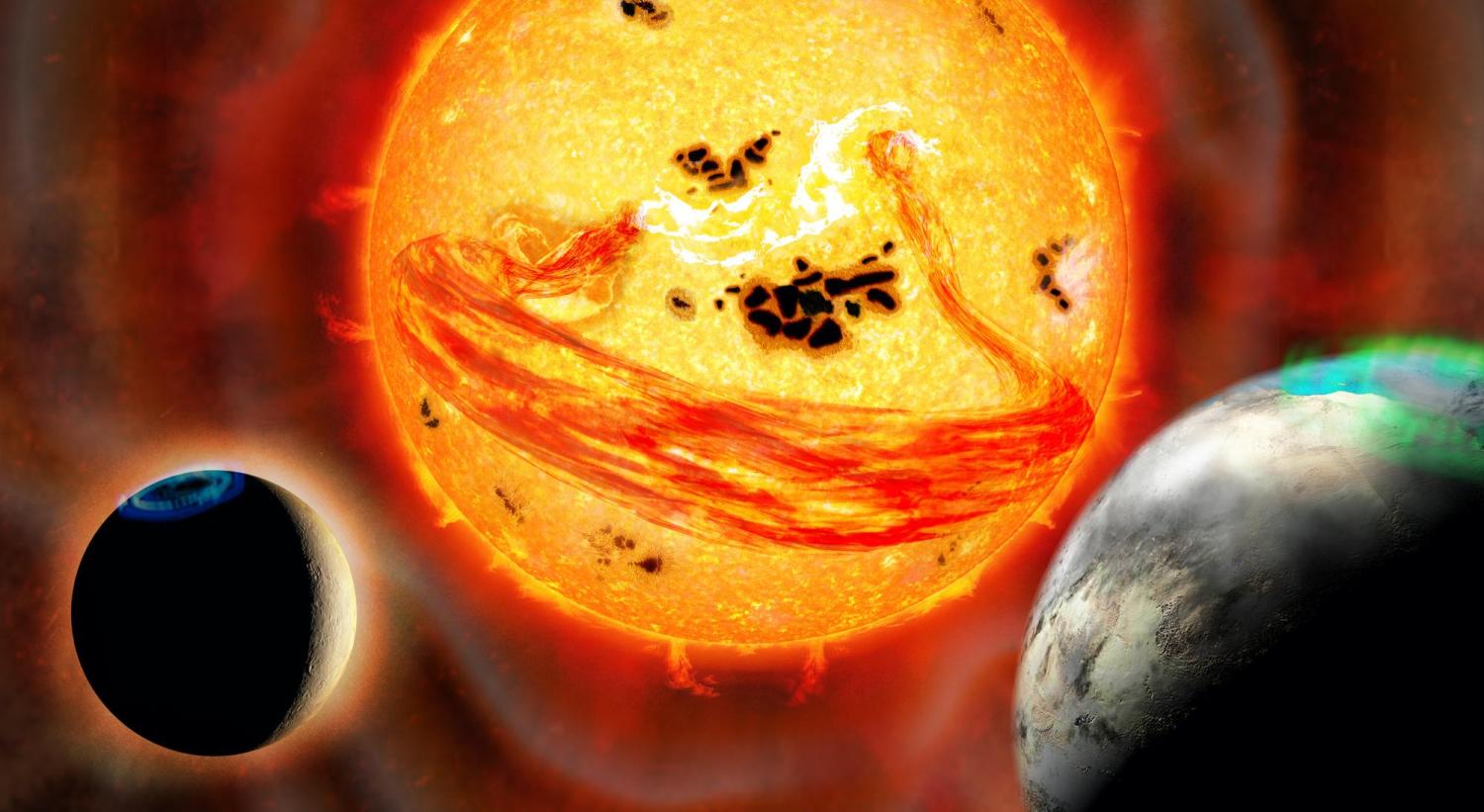
In the search for “potentially-habitable” extrasolar planets, one of the main things scientists look at is stellar activity. Whereas stars like our own, a G-type (G2V) yellow dwarf, are considered stable over time, other classes are variable and prone to flare-ups – particularly M-type red dwarf stars. Even if a star has multiple planets orbiting within its habitable zone (HZ), the tendency to periodically flare could render these planets completely uninhabitable.
According to a new study, stars like our own may not be as stable as previously thought. While observing EK Draconis, a G1.5V yellow dwarf located 110.71 light-years away, an international team of astronomers witnessed a massive coronal mass ejection that dwarfed anything we’ve ever seen in our Solar System. These observations suggest that these ejections can worsen over time, which could be a dire warning for life here on Earth.
Continue reading “A Sun-Like Star Just Blasted out a Flare That Would be Devastating if it Happened Here”