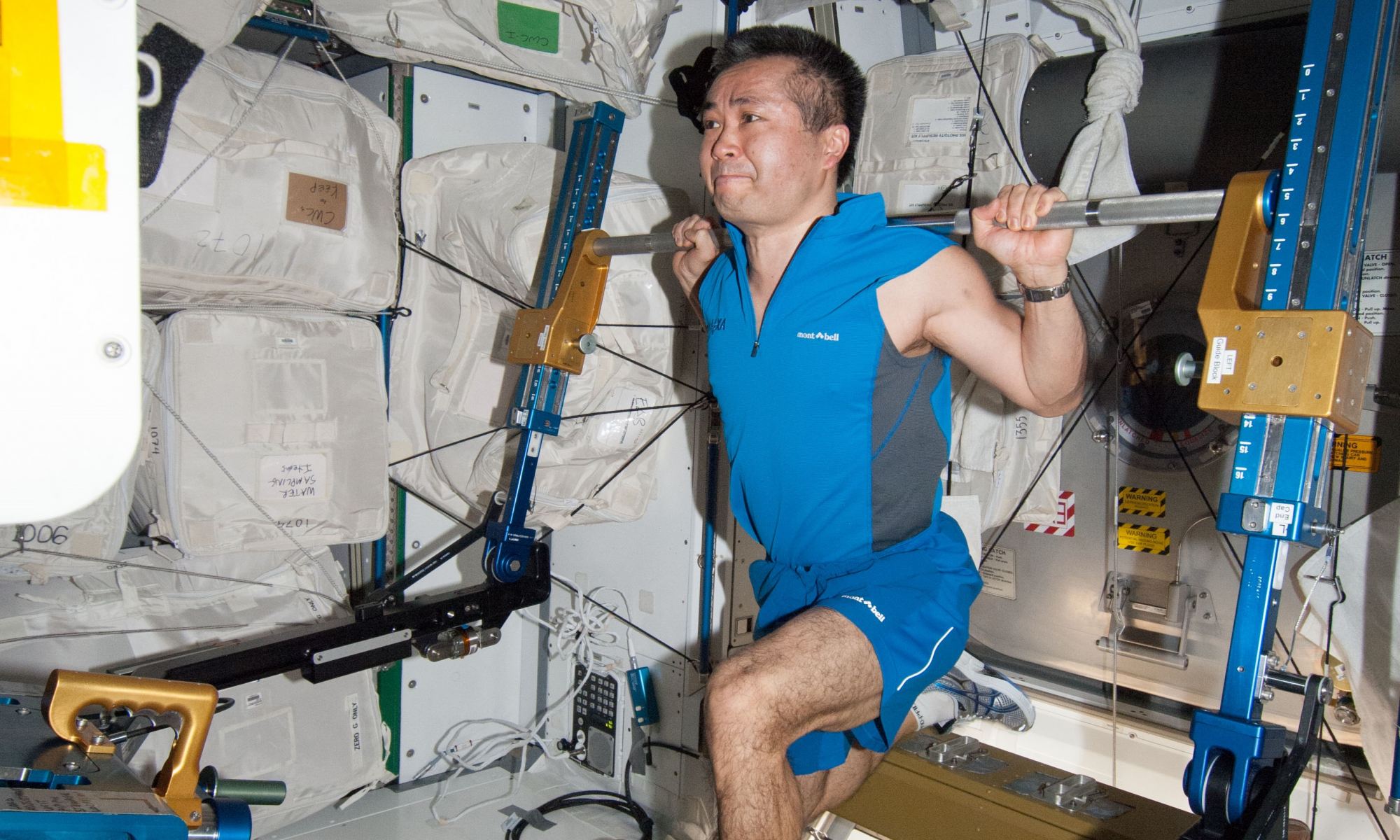
In his book, Endurance, astronaut Scott Kelly described the arduous task of readjusting to life on Earth after spending a year in space. As part of NASA’s Twins Study, Kelly lived and worked aboard the International Space Station (ISS) while his identical twin (astronaut Mark Kelly) remained on Earth. While the results of this study revealed how prolonged exposure to microgravity could lead to all manner of physiological changes, the long and painful recovery Kelly described in his book painted a much more personal and candid picture.
As it turns out, astronauts who spend extended periods in space may never fully recover. At least, that is the conclusion reached by an international team led by the University of Calgary after they assessed the bone strength of multiple astronauts before and after they went to space. They found that after twelve months of recovery, the astronaut’s bones had not regenerated completely. These findings could have significant implications for proposed future missions, many of which involve long-duration stays in space, on the Moon, and Mars.
Continue reading “Many Astronauts Never Recover all of their Bone Density after Returning to Earth”