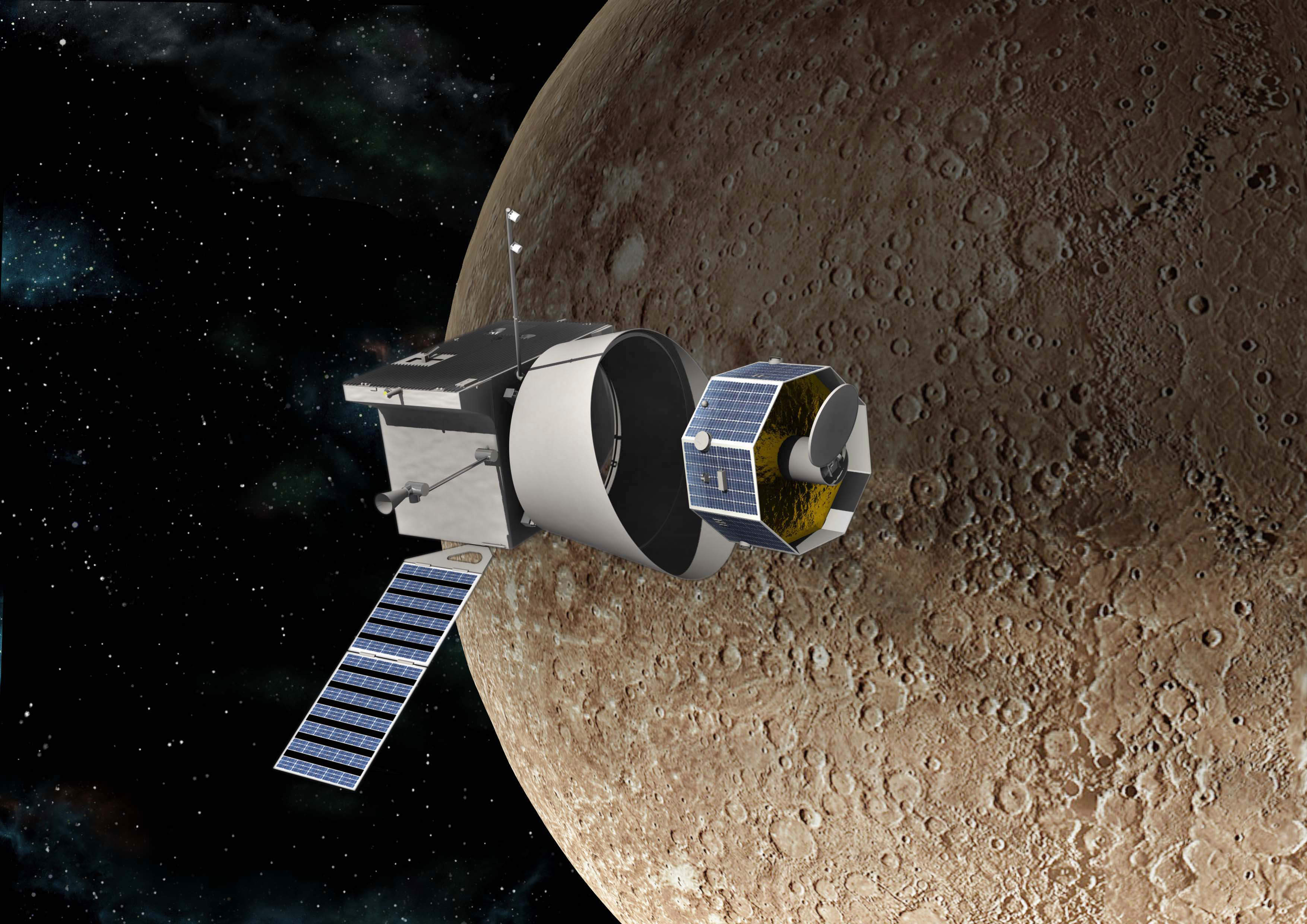
The BepiColombo mission, a joint effort between JAXA and the ESA, was only the second (and most advanced) mission to visit Mercury, the least explored planet in the Solar System. With two probes and an advanced suite of scientific instruments, the mission addressed several unresolved questions about Mercury, including the origin of its magnetic field, the depressions with bright material around them (“hollows”), and water ice around its poles. As it turns out, BepiColombo revealed some interesting things about Venus during its brief flyby.
Specifically, the two probes studied a previously unexplored region of Venus’ magnetic environment when they made their second pass on August 10th, 2021. In a recent study, an international team of scientists analyzed the data and found traces of carbon and oxygen being stripped from the upper layers of Venus’ atmosphere and accelerated to speeds where they can escape the planet’s gravitational pull. This data could provide new clues about atmospheric loss and how interactions between solar wind and planetary atmospheres influence planetary evolution.
Continue reading “The Solar Wind is Stripping Oxygen and Carbon Away From Venus”